fscanf()函数的功能是从文件中按格式读取一个或多个数据;
例如文件中有一行数据,
22 3.34 hello
则使用 fscanf(fp, "%d%f%s", &a, &f, str) 可一次读取整型、浮点、字符串三个数据;
此函数位于C标准库头文件<stdio.h>中;
示例;
测试文件如下;

代码;
void CFiletest1View::OnDraw(CDC* pDC)
{
CFiletest1Doc* pDoc = GetDocument();
ASSERT_VALID(pDoc);
// TODO: add draw code for native data here
int a = 0;
float f = 0;
char str[100] = "";
CString str1;
int d=0;
float f2=0;
FILE* fp = fopen("test1.txt", "r");
for(int i=0; i<3; i++)
{
fscanf(fp, "%d%f%s", &a, &f, str);
str1.Format("%d,%f,%s", a, f, str);
pDC->TextOut(50, 50 + i*20, str1);
d += a;
f2 += f;
}
str1.Format("整数和:%d", d);
pDC->TextOut(50, 115, str1);
str1.Format("浮点数和:%f", f2);
pDC->TextOut(50, 135, str1);
fclose(fp);
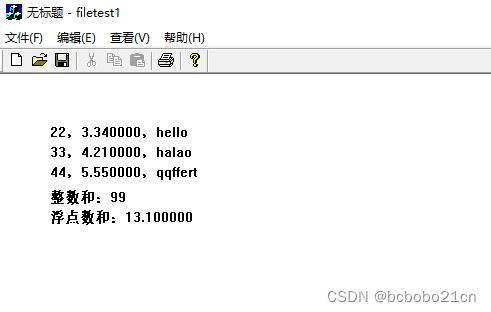
}运行如下;
在MFC中常常使用的是CStdioFile类;能否仍然可以使用fscanf()函数呢?
首先看一下,使用CStdioFile类打开文件后,返回的是BOOL类型,而fscanf需要一个FILE*类型;如果用C标准库函数fopen打开文件,返回的就是FILE*类型;
查一下MFC文档;
CStdioFile类有一个成员m_pStream,
CStdioFile::m_pStream
m_pStream数据成员是指向一个打开文件的指针,该文件是由C运行时函数fopen返回的。如果文件从来没有被打开过或者已经被关闭了,则它是NULL。
从文档说明这个m_pStream就是C标准库函数fopen打开文件后的返回值;
那么改为如下的代码看一下;
void CFiletest1View::OnDraw(CDC* pDC)
{
CFiletest1Doc* pDoc = GetDocument();
ASSERT_VALID(pDoc);
// TODO: add draw code for native data here
int a = 0;
float f = 0;
char str[100] = "";
CString str1;
int d=0;
float f2=0;
CStdioFile file;
file.Open("test1.txt", CFile::modeRead);
for(int i=0; i<3; i++)
{
//根据字符类型读取txt文件中的数据
fscanf(file.m_pStream, "%d%f%s", &a, &f, str);
str1.Format("%d,%f,%s", a, f, str);
pDC->TextOut(50, 50 + i*20, str1);
d += a;
f2 += f;
}
str1.Format("整数和:%d", d);
pDC->TextOut(50, 115, str1);
str1.Format("浮点数和:%f", f2);
pDC->TextOut(50, 135, str1);
file.Close();
}运行一下;没有问题,一样的;