使用队列实现栈的下列操作:
- push(x) -- 元素 x 入栈
- pop() -- 移除栈顶元素
- top() -- 获取栈顶元素
- empty() -- 返回栈是否为空
(这里要强调是单向队列)
用两个队列que1和que2实现队列的功能,que2其实完全就是一个备份的作用
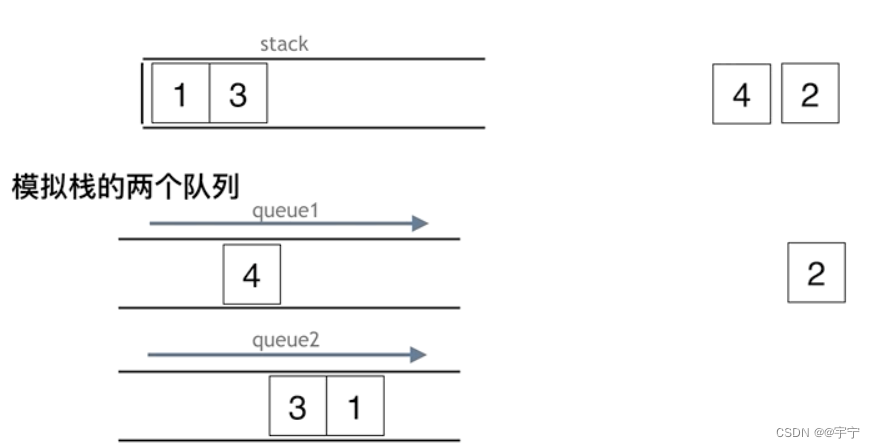
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class Stack {
Queue<Integer> queue1; // 和栈中保持一样元素的队列
Queue<Integer> queue2; // 辅助队列
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
public Stack() {
queue1 = new LinkedList<>();
queue2 = new LinkedList<>();
}
/** Push element x onto stack. */
public void push(int x) {
queue2.offer(x); // 先放在辅助队列中
while (!queue1.isEmpty()){
queue2.offer(queue1.poll());
}
Queue<Integer> queueTemp;
queueTemp = queue1;
queue1 = queue2;
queue2 = queueTemp; // 最后交换queue1和queue2,将元素都放到queue1中
}
/** Removes the element on top of the stack and returns that element. */
public int pop() {
return queue1.poll(); // 因为queue1中的元素和栈中的保持一致,所以这个和下面两个的操作只看queue1即可
}
/** Get the top element. */
public int top() {
return queue1.peek();
}
/** Returns whether the stack is empty. */
public boolean empty() {
return queue1.isEmpty();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack stack = new Stack();
stack.push(1);
stack.push(2);
System.out.println(stack.pop());
System.out.println(stack.top());
System.out.println(stack.empty());
}
}