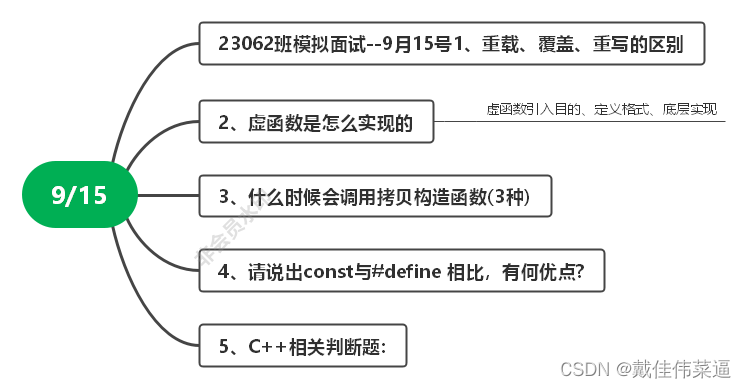
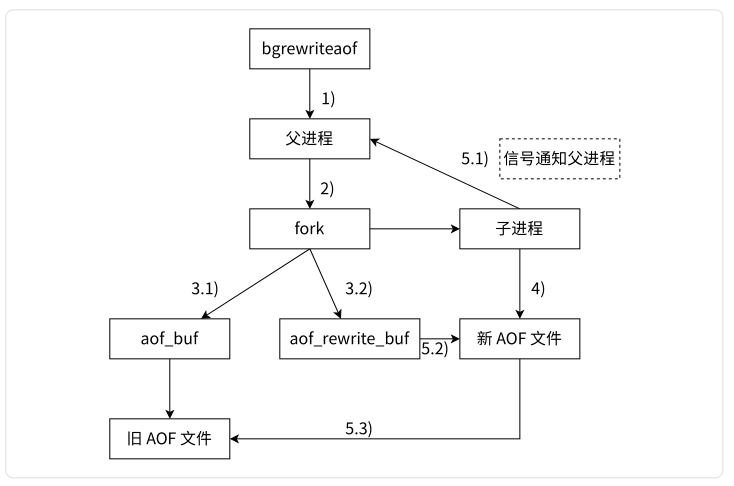
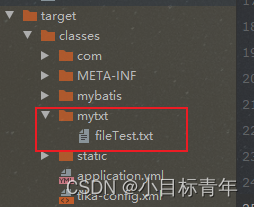
目标文件放在项目的resources文件夹下 的 mytxt文件里面,文件名叫 file Test.txt:
其实可以看到,项目运行后,这个文件被丢到了target文件夹下:
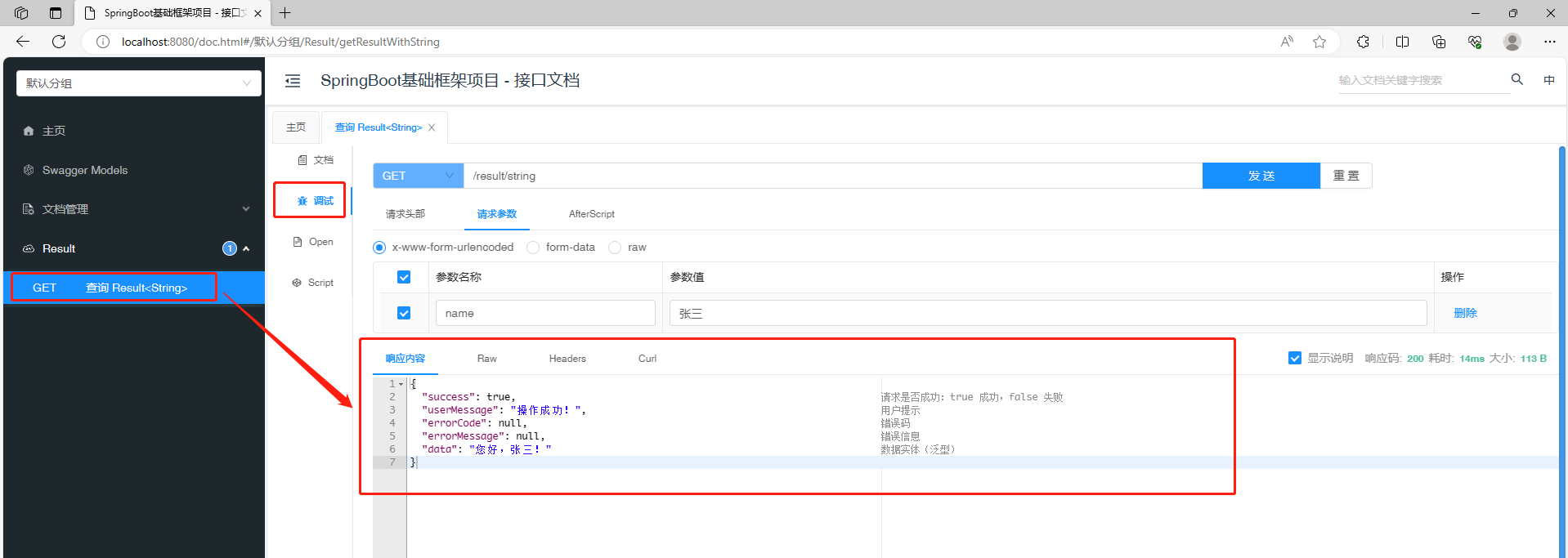
拿到这个文件的 InputStream :
比如我们在FileUtil里面写个获取文件流的方法,
public class FileUtil {
}
① getResourceAsStream
String filePath = "/mytxt/fileTest.txt";
InputStream inputStream = FileUtil.class.getResourceAsStream(filePath);
② getResource + getPath
String filePath = "/mytxt/fileTest.txt";
String path = FileUtil.class.getResource(filePath).getPath();
InputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(path);
③ getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream (注意了,这种方式文件路径path初始不带 / 杠)
String filePath = "mytxt/fileTest.txt";
InputStream inputStream = FileUtil.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream(filePath);
④ Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader().getResource (注意了,这种方式文件路径path初始不带 / 杠)
String filePath = "mytxt/fileTest.txt";
String path = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader().getResource(filePath ).getPath();
InputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(path);
⑤ System.getProperty 先拿项目根路径,再拼接target/classes 以及 文件路径
String filePath = "/mytxt/fileTest.txt";
String relativelyPath = System.getProperty("user.dir");InputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(relativelyPath + "/target/classes/" + filePath);
⑥ Paths.get("").toAbsolutePath() 先拿项目根路径,再拼接target/classes 以及 文件路径
String filePath = "/mytxt/fileTest.txt";
Path path = Paths.get("").toAbsolutePath();
InputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(path + "/target/classes/" + filePath);
拿到InputStream ,该干嘛干嘛,好了,该篇就到这。