GRACE的全球重力场产品以球谐系数(SHCs)的形式表现出明显的南北条带噪声问题,这种噪声被认为来源于它的极轨道、缺乏横向敏感性以及采样频率引起的混叠效应。
空间滤波器的例子包括各向同性高斯滤波器(Wahr et al.,1998)及其非各向同性变体(Han et al.,2005;Zhang et al.,2009),维纳滤波器(Klees et al.,2008;Sasgen et al.,2006),DDK滤波器(Kusche,2007;Kusche et al.,2009),以及正则化滤波器(Devaraju and Sneeuw,2017)。这些滤波器在结构上有所不同(例如,它们是均匀的还是不均匀的,各向同性还是非各向同性,更多细节请参阅(Devaraju and Sneeuw,2017)),是否利用信号和噪声协方差矩阵,以及如何推导先验协方差信息。
时域滤波器包括EOF滤波器(Schrama et al.,2007;Wouters and Schrama,2007),随机滤波器(Wang et al.,2016),SSA滤波器(Prevost et al.,2019)和最小二乘滤波器(Crowley and Huang,2020)。
一、一个基于SSA的去除南北条带误差的matlab空间滤波函数
下载路径:https://github. com/shuang-yi/SSAS-GRACE-filter
假设SHCs的每个元素包含三个成分:信号、南北条带噪声(也称为相关噪声)和随机噪声。GRACE数据处理的基本思想是保留信号部分并抑制其他噪声部分。通常有两种策略来实现这一目标:(i) 直接将滤波器应用于系数本身,以及 (ii) 提出一种模式来分解南北条带噪声成分,并施加额外的滤波器以抑制剩余噪声。卫星任务“重力恢复与气候实验”(GRACE)的球谐系数产品中普遍存在的南北条纹(NSS)噪声极大地阻碍了信号的解释。过多的NSS噪声总是导致数据过度平滑,如果能事先减轻这种特定的NSS噪声,空间分辨率将有很大提升空间。因此,此文提出了一种新的空间滤波器,可以有效地去除NSS噪声同时保持与物理信号正交。这种新方法克服了之前由Swenson和Wahr(2006)提出的方法的局限性,该方法导致信号失真严重,高阶系数无法纠正。该滤波器基于经度方向上的自相关和纬度方向上的互相关。此方法识别出的NSS类型噪声主要位于球谐阶数大约为20以上,纬度在±60°之间的系数中。在用我们的方法去除主要的NSS噪声后,再加上较弱的滤波器来处理残留噪声。因此,可以增加空间分辨率并降低幅度衰减。此方法可以巧妙地减少时间序列中的异常值而不引入显著的趋势偏差,这支撑了其有效性和可靠性。
主要的代码:
clear;
%% envirionment setting
addpath functions
%% read in data
% SH0 = load_SH('csr06','trange',[2004,12,2005,2]);
% SH0.save('csr06_gsm_2004-12_2005-02.mat');
a = load('data/csr06_gsm_2004-12_2005-02.mat'); % SH
SH0 = cSH(a.SH); % convert to the data format used here.
SH0 = SH0(3); % only use the first month
%% main parameters
% do not search coefficients with the degree <= Njump for NS stripe noise
Njump = 20;
% window width for SSA
M = 40;
% only the leading K modes are searched. Since the noise may also exist in
% higher modes, the whole process will iteratively remove the paired modes
% and search for new paired ones, until 1) a maximum Nstep is reached,
% or 2) no more paired modes are found
K = 20;
% -- other parameters
% the signals in greenland and antarctic are reduced to 10%,
% set to 1 if no extra weight is needed
ipolar_weight = 0.1;
% 1: create a gap region in sumatra
igap_sumatra = 1;
%% main program
% SH0: monthly input of SH
% SH_filter: filtered SH
% LLZ_noise: identified NS-stripe noise by SSAS
[SH_filter, LLZ_noise]=fun_ssa_spatial_filter( SH0, ...
'Njump',Njump, 'M',M, 'K',K, ...
'ipolar_weight',ipolar_weight, 'igap_sumatra',igap_sumatra);
%% check the results
% compare your figures with these in the check/ folder.
icheck = 1;
if icheck == 1 % map view
figure('position',[1,1,1000,600]);
imon = 1;
SH_t0 = SH0(imon);
SH_t1 = SH_filter(imon);
cran = [-10,10];
subplot(2,2,1)
[LLZ]=LLZ_forward_ns(SH_t0, 'to', 'gr','resolution',1);
mypcolor(LLZ.lon,LLZ.lat,LLZ.rg);
caxis(cran);
title('(a) Original map w/o filtering, in gravity disturbance (\mu Gal)')
subplot(2,2,2)
[LLZ]=LLZ_forward_ns(SH_t1, 'to', 'gr','resolution',1);
mypcolor(LLZ.lon,LLZ.lat,LLZ.rg);
caxis(cran);
title('(b) After SSAS')
subplot(2,2,3);
dSH = SH_t0 - SH_t1;
[LLZ]=LLZ_forward_ns(dSH, 'to', 'gr','resolution',1);
mypcolor(LLZ.lon,LLZ.lat,LLZ.rg);
caxis(cran);
title('(c) a - b')
elseif icheck == 2 % Kaula curve
figure;
imon = 1;
[y1,~] = SH0(imon).kaula;
[y2,nn] = SH_filter(imon).kaula;
semilogy(nn(2:end),y1(2:end));
hold on;
semilogy(nn(2:end),y2(2:end));
hold off;
legend('Original','Filtered');
grid on
xlabel('Degree');
ylabel('Dimensionless')
end
二、一个基于二维傅里叶变换的去除南北条带误差的matlab空间滤波函数
Yang et al.(2022) 研究指出来自“重力恢复与气候实验”(GRACE)二级数据的全球月等效水位高度(异常(ΔEWH)有助于了解陆地水储量的变化。然而,ΔEWH数据包含条纹或噪声。已经研究了许多去噪方法,但存在以下问题:可能导致过度平滑的结果,两步法(去条纹和基于高斯平滑)引入额外的不确定性和误差传播,需要多时相数据或先验知识,以及可能的计算效率低下。因此,在分析ΔEWH数据的频谱后,提出了一种新颖的低通滤波算法来去除噪声并解决问题。此外,在没有全球原位测量数据的情况下,基于GRACE数据中信号和噪声的可加性特征研究了一种替代评估方法。该方法包括残差分析和去噪信号的均方根(RMS)值。然后,将所提出的算法应用于2002年至2015年之间的ΔEWH数据去噪。去噪结果在定性和定量上都是令人满意的。与众所周知的两步去噪方法相比,在所提出的算法后不会出现数据模糊。通过残差分析评估,该算法去除了最多的噪声,并通过较大的RMS值评估保留了最多的信号。
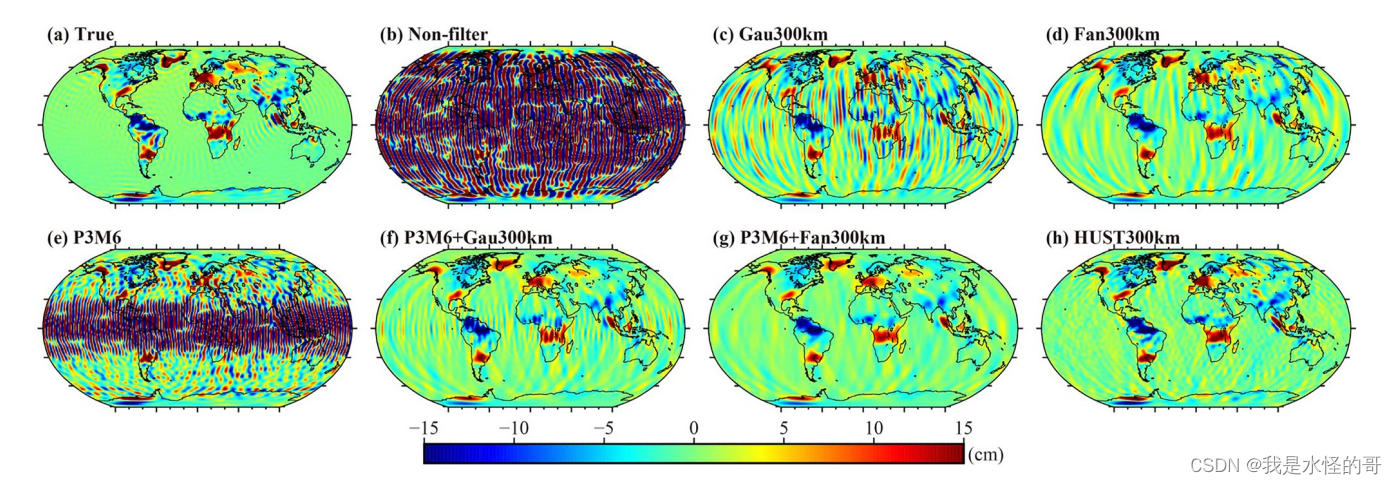
同样的,Zhou et al.(2023)开发了一种基于图像处理的新方法,用于滤除GRACE和GRACE-FO球谐解中的条纹误差。在这种方法中,重力场被视为受噪声污染的图像,预期通过将输入与适当的核卷积来抑制条纹误差。为验证所提出方法的有效性,设计了一个在5年的标称任务寿命内的闭环模拟环境。图像处理指标和地球物理信息评估结果表明,新方法在抑制条纹误差方面表现出卓越的性能。在实际GRACE数据处理的背景下,我们的新方法仍然取得了更好的结果,具体如下:(a) 在空间分布、幅度谱和系数谱的展示中,去条纹和保留细节的综合能力略微优于一些常用的滤波器。(b) 相当于流域尺度的等效水高时间序列与其他滤波器或Level-3产品的结果相当。(c) 2004年苏门答腊岛9.1级地震余震重力变化的估计信号幅度比高斯300公里滤波器得到的结果大52.7%,这更接近于根据错理论导出的理论值。


HUST滤波流程图(Zhou et al., 2023)

(1)二维傅里叶变换的一个例子
具体的关于二维傅里叶变换的物理含义可以参考这个博主的文章内容(kiyoxi,2020-12-30).可以理解为:对于一个二维图像,二维傅里叶变换本质上可以理解为在一组由sine和cosine函数构成的二维基底下,求取每个基底对应的相关值,这些相关值构成了这个二维图像在傅里叶变换基下的表达。下图是将本人的头像进行二维傅里叶变换的例子。
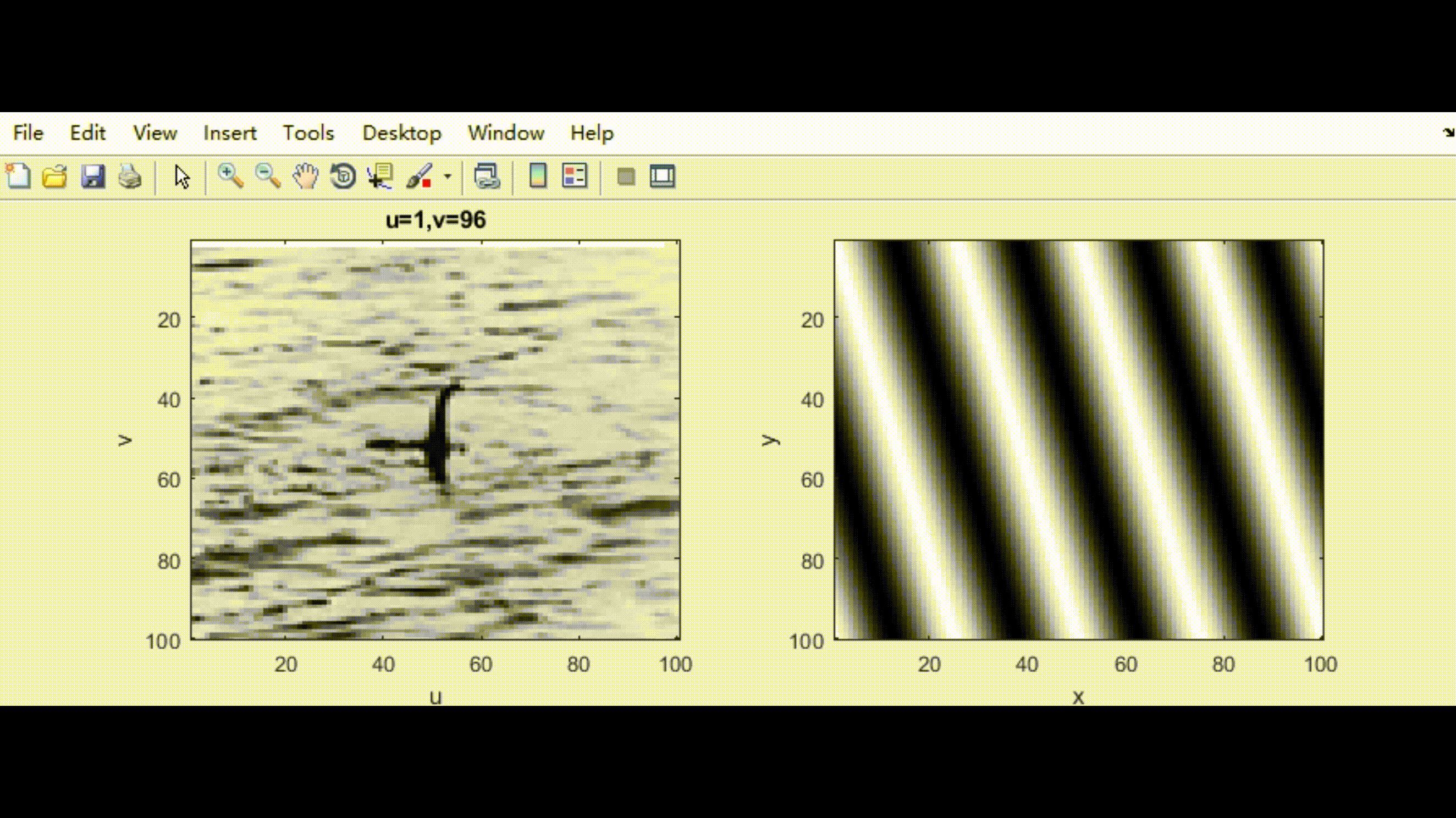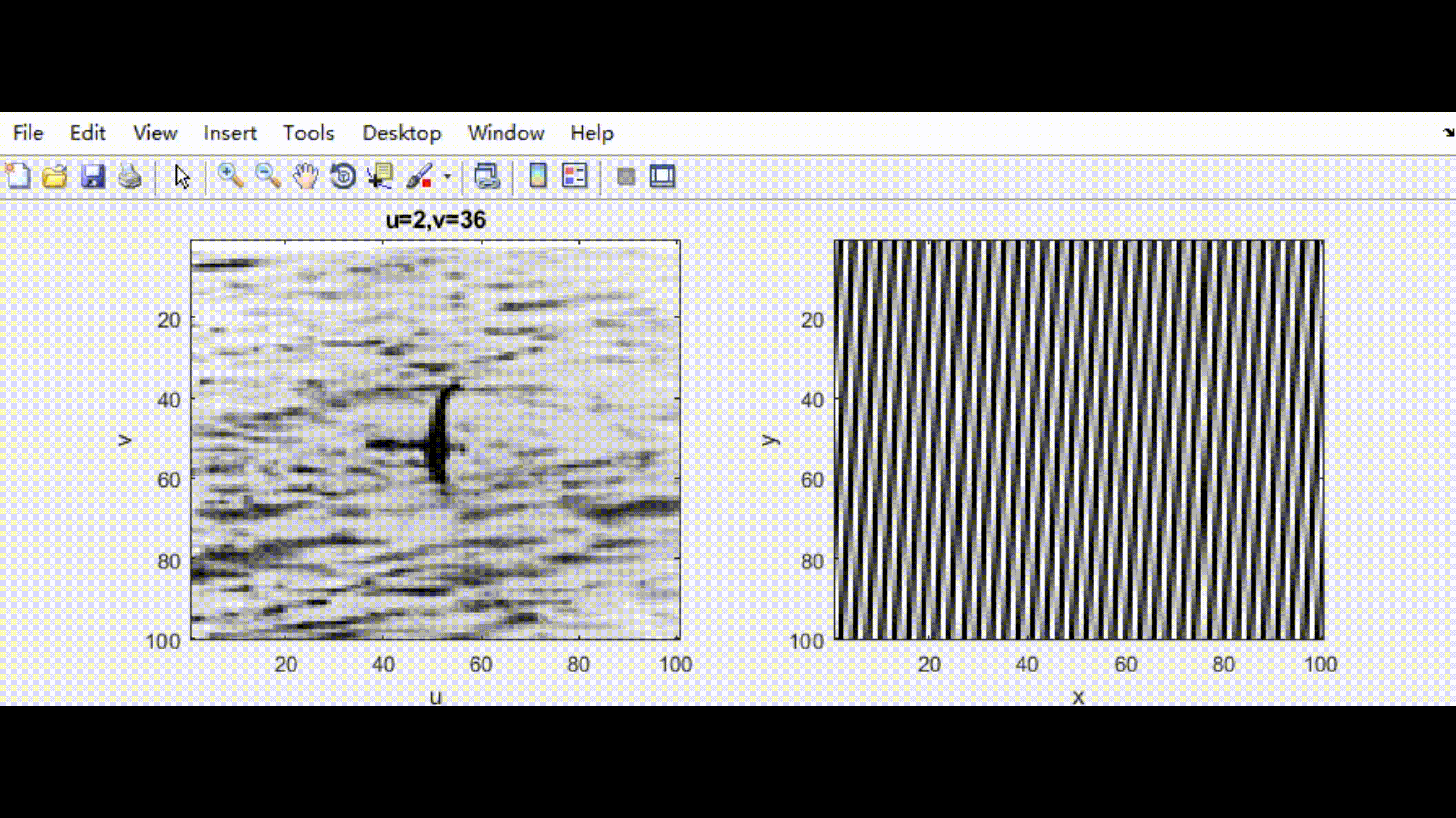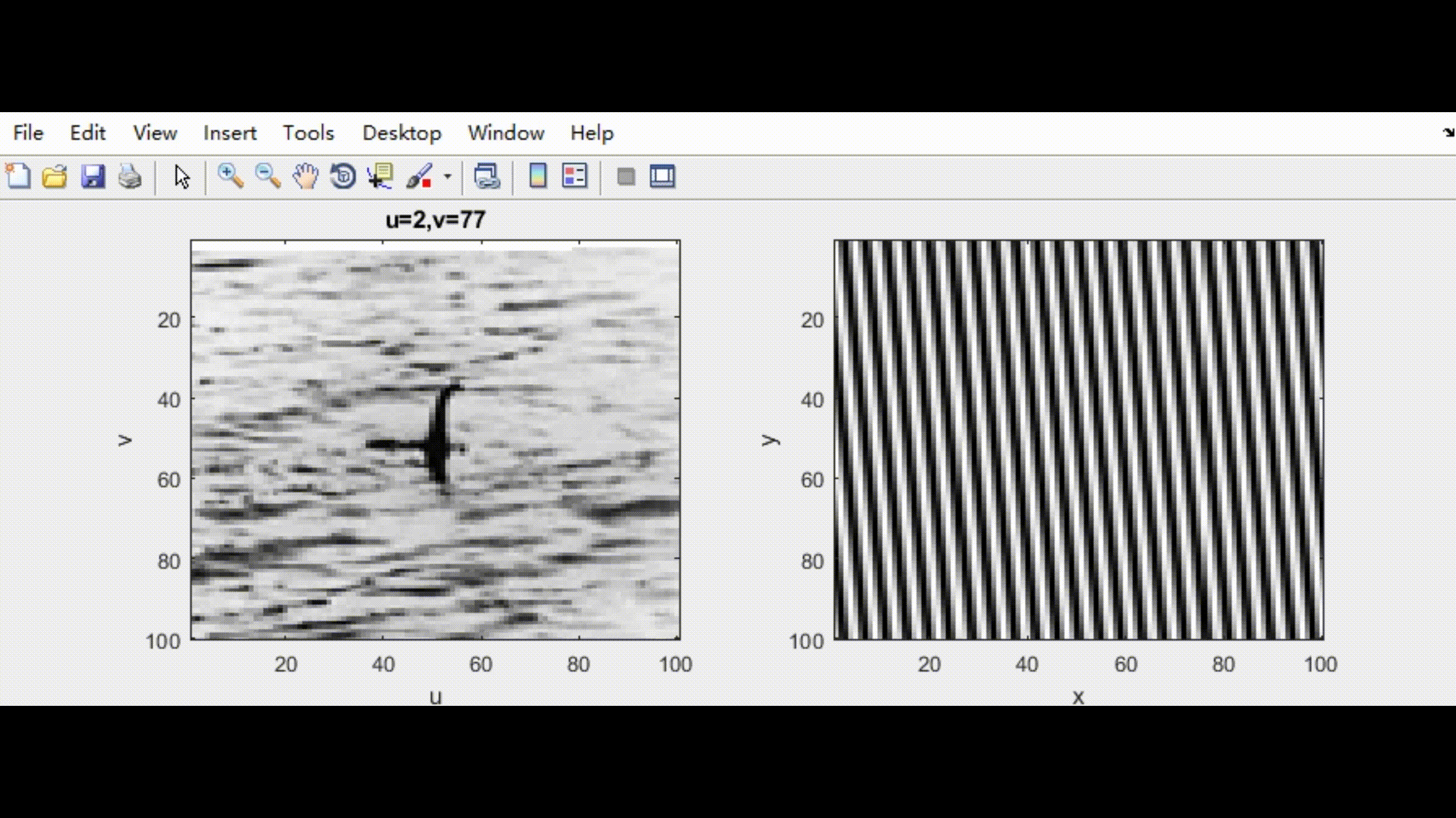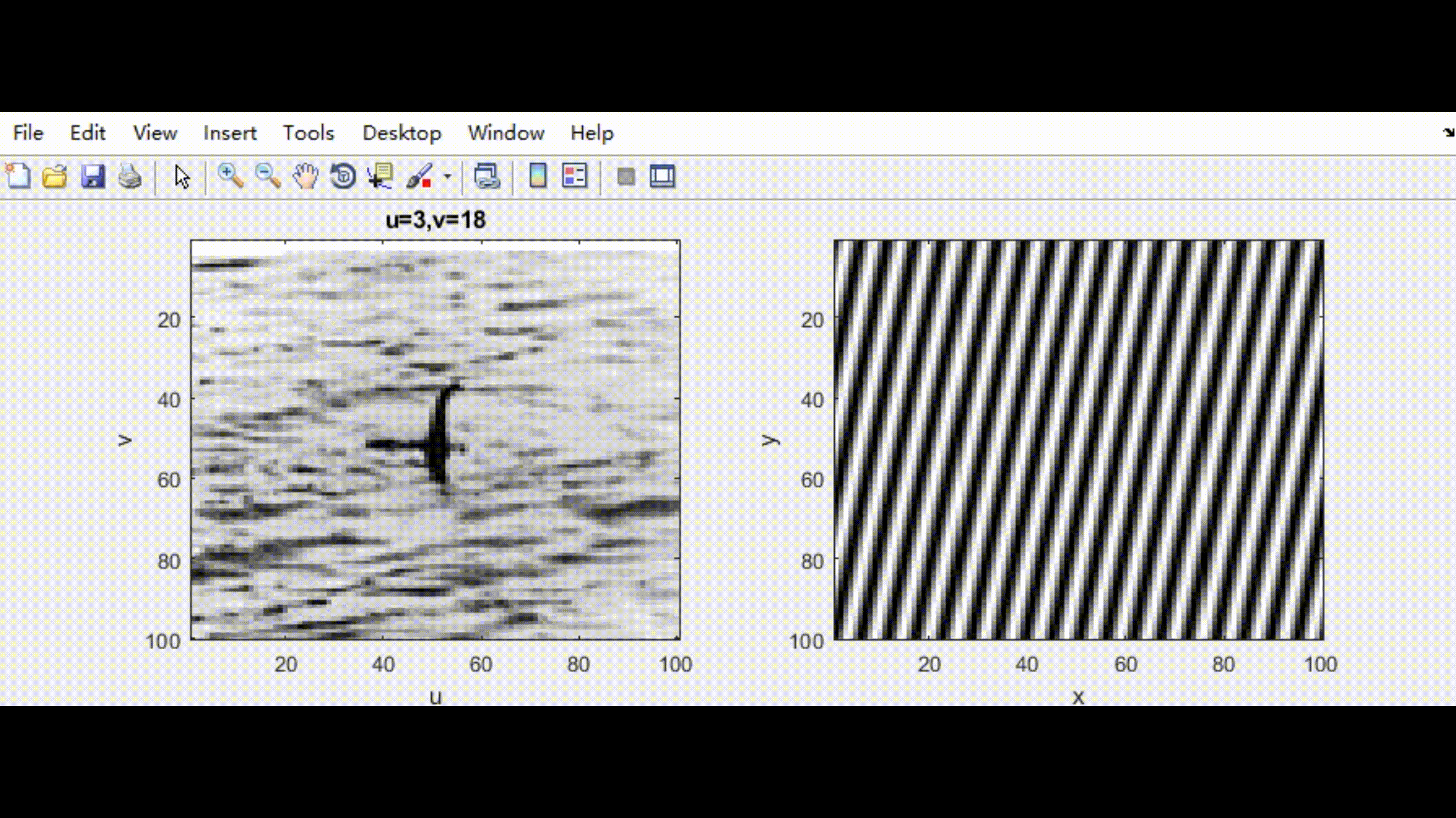
然后我在图片中添加高斯白噪声,并同时进行傅里叶变换。
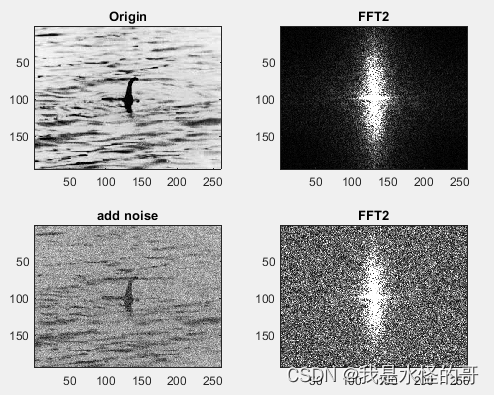

![]()
下面是一个某个月的GRACE数据的转换过程

下面展示了不同滤波器的滤波效果(Zhou et al., 2023)
进一步的滤波效果实现将在后续专栏贴出。欢迎交流学习!
参考资料:
二维Fourier变换及Matlab实现 - 知乎 (zhihu.com)
Yang, T., et al. (2022). "An efficient low-pass-filtering algorithm to de-noise global GRACE data." Remote Sensing of Environment 283.
Yi, S. and N. Sneeuw (2022). "A novel spatial filter to reduce north–south striping noise in GRACE spherical harmonic coefficients." Journal of Geodesy 96(4).
Wahr J, Molenaar M, Bryan F (1998) Time variability of the earth’s gravity field: hydrological and oceanic effects and their possible detection using GRACE. J Geophys Res-Solid Earth 103(B12):30205–30229. https://doi.org/10.1029/98jb02844
Han S-C, Shum CK, Jekeli C, Kuo C-Y, Wilson C, Seo K-W (2005) Non-isotropic filtering of GRACE temporal gravity for geophysical signal enhancement. Geophys J Int 163(1):18–25. https://doi. org/10.1111/j.1365-246X.2005.02756.x
Zhang Z-Z, Chao BF, Lu Y, Hsu H-T (2009) An effective filtering for GRACE time-variable gravity: fan filter. Geophys Res Lett 36(17):L17311. https://doi.org/10.1029/2009GL039459
Klees R, Revtova EA, Gunter BC, Ditmar P, Oudman E,WinsemiusHC, Savenije HHG (2008) The design of an optimal filter for monthly GRACE gravity models. Geophys J Int 175(2):417–432. https:// doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-246X.2008.03922.x
Sasgen I, Martinec Z, Fleming K (2006) Wiener optimal filtering of GRACE data. Stud Geophys Geod 50(4):499–508. https://doi.org/ 10.1007/s11200-006-0031-y
Kusche J (2007) Approximate decorrelation and non-isotropic smoothing of time-variable GRACE-type gravity field models. J Geodesy 81(11):733–749. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-007-0143-3
Kusche J, Schmidt R, Petrovic S, Rietbroek R (2009) Decorrelated GRACE time-variable gravity solutions by GFZ, and their validation using a hydrological model. J Geodesy 83(10):903–913
Devaraju B, Sneeuw N (2017) The polar form of the spherical harmonic spectrum: implications for filtering grace data. J Geodesy 91(12):1475–1489. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-017-1037-7
Schrama EJO,Wouters B, Lavallée DA (2007) Signal and noise in gravity recovery and climate experiment (GRACE) observed surface mass variations. J Geophys Res 112(B8):B08407. https://doi.org/ 10.1029/2006JB004882
Wouters B, Schrama EJO (2007) Improved accuracy ofGRACE gravity solutions through empirical orthogonal function filtering of spherical harmonics: EOF filtering of grace coefficients. Geophys Res Lett. https://doi.org/10.1029/2007GL032098
Wang L, Davis JL, Hill EM, Tamisiea ME (2016) Stochastic filtering for determining gravity variations for decade-long time series of GRACE gravity. J Geophys Res Solid Earth 121(4):2915–2931. https://doi.org/10.1002/2015JB012650
Prevost P, Chanard K, Fleitout L, Calais E, Walwer D, van Dam T, Ghil M (2019) Data-adaptive spatio-temporal filtering of GRACE data. Geophys J Int 219(3):2034–2055. https://doi.org/10.1093/ gji/ggz409
Crowley JW, Huang J (2020) A least-squares method for estimating the correlated error of GRACE models. Geophys J Int 221(3):1736–1749. https://doi.org/10.1093/gji/ggaa104
Zhou, H., Wang, P., Tang, L., & Luo, Z. (2023). A new GRACE filtering approach based on iterative image convolution. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 128, e2023JB026553. https://doi. org/10.1029/2023JB026553




![[移动通讯]【Carrier Aggregation-4】【LTE-4】](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/bfd45e55e3a24bf3a3d524c3def0cd3b.png)