欢迎关注我的CSDN:https://spike.blog.csdn.net/
本文地址:https://spike.blog.csdn.net/article/details/132888139
蛋白质语言模型 ESM (Evolutionary Scale Modeling) 是一种利用深度学习技术来预测蛋白质结构和功能的方法。ESM 通过在大规模的蛋白质序列数据库上,训练一个自回归的神经网络,学习蛋白质的进化规律和序列-结构-功能的关系。ESM 可以根据给定的蛋白质序列,生成其对应的隐向量,表示其结构和功能的特征,还可以利用隐向量进行多种下游任务,如结构预测、功能注释、相互作用分析等。ESM 是一种强大而通用的蛋白质语言模型,为蛋白质科学提供了新的视角和工具。
ESM (Evolutionary Scale Modeling),即进化尺度模型,包括 ESM-2、ESMFold、ESM-MSA-1b、ESM-1v、ESM-IF1(反向折叠),即
ESM-2,2022.8,SOTA 通用目的蛋白质语言模型 v2 版,其中ESM-1v是 v1 版本。ESMFold,2022.11,端到端的单序列 3D 结构预测ESM-MSA-1b,2021.6,MSA Transformer 语言模型ESM-IF1,2022.4,反向折叠模型
具体参考:ESM GitHub
1. 配置 Docker 环境
配置 TORCH_HOME 与 BOS 环境,即:
vim ~/.bashrc
export TORCH_HOME=[your folder]/torch_home/
alias bos='bcecmd/bcecmd --conf-path bcecmd/bceconf/ bos'
建议配置 TORCH_HOME,固定 PyTorch 模型缓存地址,即
torch_home/hub/checkpoints中。
在 Docker Image 中,导入 ESM 环境:
conda create -n esmfold --clone miniconda3/envs/esmfold
需要安装的 Torch 相关包:
pip install -q torch-scatter -f https://data.pyg.org/whl/torch-1.12.1+cu113.html
pip install -q torch-sparse -f https://data.pyg.org/whl/torch-1.12.1+cu113.html
pip install -q torch-cluster -f https://data.pyg.org/whl/torch-1.12.1+cu113.html
pip install -q torch-spline-conv -f https://data.pyg.org/whl/torch-1.12.1+cu113.html
pip install -q torch-geometric
导出 Docker 环境:
# 提交 Tag
docker ps -a
docker commit [container id] esmfold:v1.0
# 准备远程 Tag
docker tag esmfold:v1.0 [your ip]/esmfold:v1.0
# 推送至远程
docker push [your ip]/esmfold:v1.0
# 从远程拉取
# docker pull [your ip]/esmfold:v1.0
2. 批量推理 ESM2 模型
配置 ESM 推理脚本:
set -xe
PROJECT_DIR="$(cd "$(dirname $0)" && pwd)/.."
source activate esmfold
export PATH="/usr/local/cuda-11.6/bin:$PATH"
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH="/usr/local/cuda-11.6/lib64:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH"
export TORCH_HOME=[your folder]/torch_home/
echo "${PROJECT_DIR}"
python "${PROJECT_DIR}/scripts/extract.py" esm2_t36_3B_UR50D \
"${PROJECT_DIR}/mydata/all-1.fasta" \
[your folder]/esm2_3B_feat/ \
--toks_per_batch 1536 \
--repr_layers -1 \
--include per_tok contacts \
--truncation_seq_length 1536 \
--num_workers 8
测试 A100 显卡 80G,最大支持 1536 序列长度。
优化 scripts/extract.py 脚本,输出结果是序列 MD5 编码的特征,避免序列过长或名字重复:
- 增加
num_workers,提升推理速度。 - 替换
label为蛋白质序列。 - 增加断点处理,避免重复搜索
即
# ...
data_loader = DataLoader(
dataset, collate_fn=alphabet.get_batch_converter(args.truncation_seq_length),
batch_sampler=batches, num_workers=args.num_workers,
)
# ...
# result = {"label": label}
result = {"label": strs[i]} # label 修改成序列
# ...
for i, label in enumerate(labels):
args.output_file = args.output_dir / f"{label}.pt"
if os.path.isfile(args.output_file):
warnings.warn(f"The feat has processed. {args.output_file}")
continue
# ...
注意不能使用
num_workers否则程序无法运行。
日志:
python workspace/esm-by-chenlong/run/../scripts/extract.py esm2_t36_3B_UR50D workspace/esm-by-chenlong/mydata/all-1.fasta pdb_dataset/esm2_6b_feat/ --toks_per_batch 1536 --repr_layers -1 --include per_tok contacts --truncation_seq_length 1536 --num_workers 32
Transferred model to GPU
Read /nfs_beijing_ai/chenlong/workspace/esm-by-chenlong/run/../mydata/all-1.fasta with 27115 sequences
Processing 1 of 6668 batches (66 sequences)
Processing 2 of 6668 batches (61 sequences)
Processing 3 of 6668 batches (56 sequences)
Processing 4 of 6668 batches (52 sequences)
Processing 5 of 6668 batches (51 sequences)
注意序列尺寸 2048 导致显存溢出。
3. 准备 ESM2 输入 FASTA 数据
将 FASTA 文件夹中的全部 FASTA 文件组成1个文件,并且序列描述,转换成 Hash 编码,避免相同序列的特征重复生成特征,即:
seq_encoder:Hash 编码函数,同时也用于查找。load_feat:读取 feature 特征,支持显示数据和绘制图像。merge_fasta_folder:合并 FASTA 文件夹。
即:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -- coding: utf-8 --
"""
Copyright (c) 2022. All rights reserved.
Created by C. L. Wang on 2023/9/13
"""
import argparse
import os
import sys
import warnings
from pathlib import Path
from tqdm import tqdm
p = os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__)))
if p not in sys.path:
sys.path.append(p)
from myutils.project_utils import traverse_dir_files_for_large, read_file, write_list_to_file
class Esm2FastaGenerator(object):
"""
ESM2 工具类
"""
def __init__(self):
pass
@staticmethod
def seq_encoder(sequence):
"""
将 seq 使用 hash 编码,避免重复生成
"""
import hashlib
return hashlib.md5(sequence.encode(encoding="utf-8")).hexdigest()
@staticmethod
def load_feat(path, is_print=False):
"""
加载 ESM 特征文件,以及打印特征
"""
import torch
from torch import Tensor
rep = torch.load(path)
if is_print:
print(f"[Info] rep: {rep.keys()}")
for key in rep.keys():
val = rep[key]
if isinstance(val, str):
print(f"[Info] {key}: {val}")
elif isinstance(val, dict):
for sub_key in val.keys():
print(f"[Info] {key}: {sub_key}: {val[sub_key].shape}")
elif isinstance(val, Tensor):
print(f"[Info] {key}: {val.shape}")
else:
print(f"[Info] {key}: {val}")
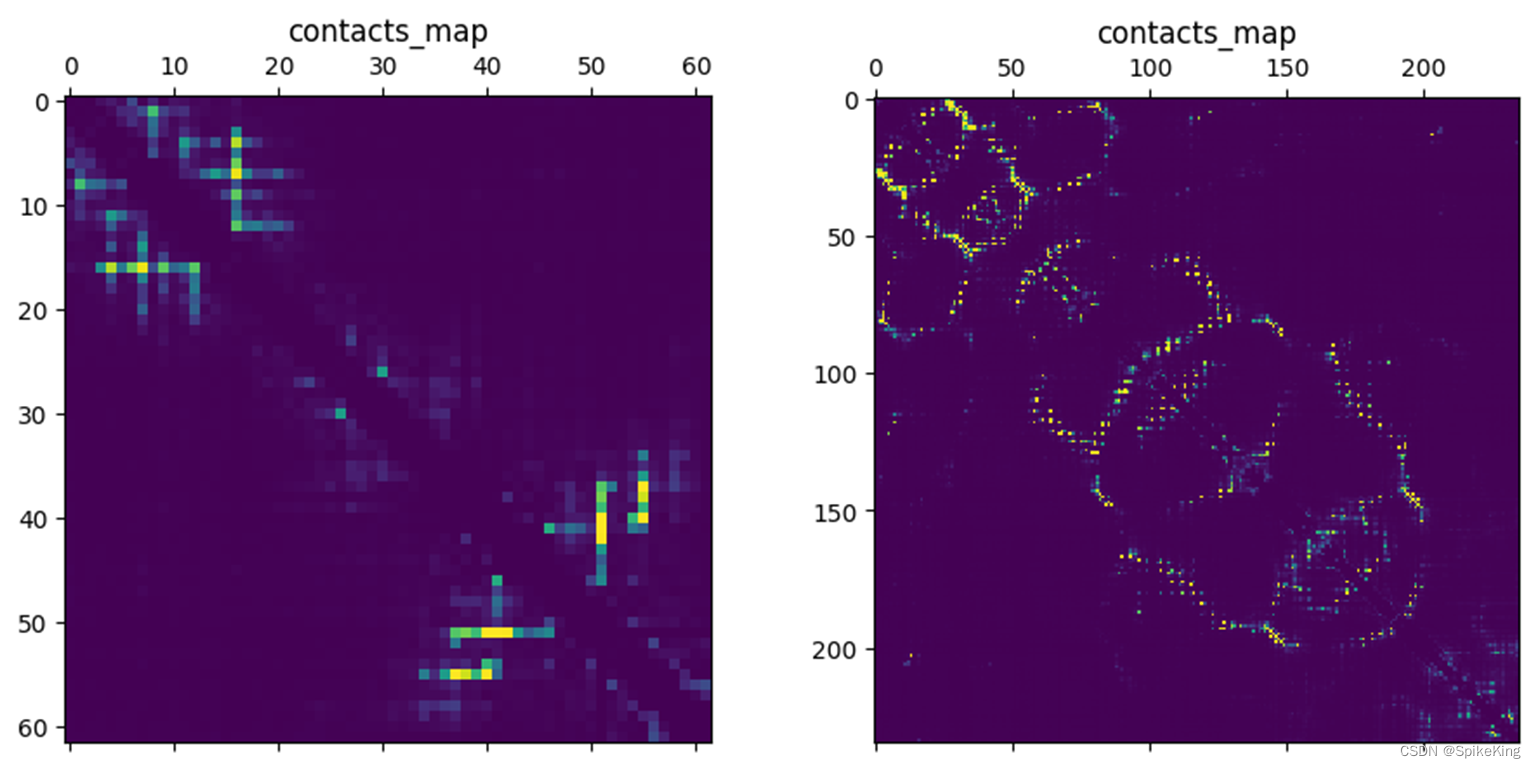
# 绘制接触矩阵
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
contacts_map = rep["contacts"]
plt.matshow(contacts_map)
plt.title("contacts_map")
save_name = "contacts_map.png"
plt.savefig(save_name, bbox_inches='tight', format='png')
plt.show()
return rep
@classmethod
def merge_fasta_folder(cls, folder_path, output_path):
"""
合并 fasta 文件,用于 esm 推理
"""
print(f"[Info] folder_path: {folder_path}")
print(f"[Info] output_path: {output_path}")
assert os.path.isdir(folder_path)
path_list = traverse_dir_files_for_large(folder_path, ext="fasta")
print(f"[Info] fasta: {len(path_list)}")
seq_set = set()
for path in tqdm(path_list, "[Info] fasta"):
data_lines = read_file(path)
n = len(data_lines)
for i in range(1, n, 2):
seq = data_lines[i]
if seq:
seq_set.add(seq)
seq_list = list(seq_set)
print(f"[Info] seq unique: {len(seq_list)}")
# create_empty_file(output_path)
seq_lines = []
header_set = set()
for seq in tqdm(seq_list, "[Info] seq"):
header = cls.seq_encoder(seq)
header_set.add(header)
seq_lines.append(f">{header}")
seq_lines.append(seq)
assert len(seq_lines) // 2 == len(header_set)
write_list_to_file(output_path, seq_lines)
print(f"[Info] over! {output_path}")
def main():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument(
"-f",
"--folder-path",
type=Path,
required=True,
)
parser.add_argument(
"-o",
"--output-path",
type=Path,
required=True
)
args = parser.parse_args()
folder_path = str(args.folder_path)
output_path = str(args.output_path)
if os.path.isfile(output_path):
warnings.warn(f"The output file exists, append lines to it! {output_path}")
# from root_dir import DATA_DIR
# folder_path = os.path.join(DATA_DIR, "fasta")
# output_path = os.path.join(DATA_DIR, "all.fasta")
Esm2FastaGenerator.merge_fasta_folder(folder_path, output_path)
def main2():
from root_dir import DATA_DIR
feat_path = os.path.join(DATA_DIR, "fffd26f4307d76eec938ac9c2c93a698.pt")
Esm2FastaGenerator.load_feat(feat_path, is_print=True)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
# main2()
输出的序列 ESM2 特征包括:
label序列描述representations序列表征 LxHmean_representations均值化表征 Hbos_representations起始 Token 表征 Hcontacts序列接触表征 LxL
例如 序列长度是 65,ESM2 650M 的 Embeddings 是 1280,ESM2 3B 是 2560,即:
[Info] rep: dict_keys(['label', 'representations', 'contacts'])
[Info] label: MAKDSKAPVVEIFDERDGCTSAGSTGKASDAGEKGLLVKVSMQKVGYNAIMAKSVAASYMNK
[Info] representations: 36: torch.Size([62, 2560])
[Info] contacts: torch.Size([62, 62])
其中 序列长度 235 的 ESM2 3B 特征,约是 2.6M,序列长度 65 的 ESM2 650M 特征,约是 361 KB。
4. 测试 ESM2 推理脚本
推理脚本:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -- coding: utf-8 --
"""
Copyright (c) 2022. All rights reserved.
Created by C. L. Wang on 2023/9/11
"""
import math
import os
import sys
import time
import torch
import esm
p = os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__)))
if p not in sys.path:
sys.path.append(p)
from myutils.project_utils import time_elapsed
class Esm2Infer(object):
"""
推理 ESM2 特征
"""
def __init__(self):
print("[Info] 加载模型开始! ")
s_time = time.time()
self.model, self.alphabet = esm.pretrained.esm2_t33_650M_UR50D()
print(f"[Info] vocab: {self.alphabet.to_dict()}")
self.batch_converter = self.alphabet.get_batch_converter()
self.model.eval() # disables dropout for deterministic results
print(f"[Info] 加载模型完成! 耗时: {time_elapsed(s_time, time.time())}")
def predict(self, data_list):
"""
数据示例:
data_list = [
("protein1", "MKTVRQERLKSIVRILERSKEPVSGAQLAEELSVSRQVIVQDIAYLRSLGYNIVATPRGYVLAGG"),
("protein2", "KALTARQQEVFDLIRDHISQTGMPPTRAEIAQRLGFRSPNAAEEHLKALARKGVIEIVSGASRGIRLLQEE"),
("protein2 with mask", "KALTARQQEVFDLIRD<mask>ISQTGMPPTRAEIAQRLGFRSPNAAEEHLKALARKGVIEIVSGASRGIRLLQEE"),
("protein3", "K A <mask> I S Q"),
]
"""
print(f"[Info] data_list: {len(data_list)}")
batch_labels, batch_strs, batch_tokens = self.batch_converter(data_list)
print(f"[Info] batch_labels: {batch_labels}")
print(f"[Info] batch_tokens: {batch_tokens}")
batch_lens = (batch_tokens != self.alphabet.padding_idx).sum(1)
print(f"[Info] batch_lens: {batch_lens}") # 有效维数
# Extract per-residue representations (on CPU)
with torch.no_grad():
results = self.model(batch_tokens, repr_layers=[33], return_contacts=True)
token_representations = results["representations"][33]
# Generate per-sequence representations via averaging
# NOTE: token 0 is always a beginning-of-sequence token, so the first residue is token 1.
sequence_representations = []
for i, tokens_len in enumerate(batch_lens):
feat = token_representations[i, 1: tokens_len - 1]
# embeddings = feat.mean(0)
# print(f"[Info] idx: {i}, feat: {feat.shape}, embeddings: {embeddings.shape}")
# sequence_representations.append(embeddings)
sequence_representations.append(feat)
return sequence_representations
def main():
data_list = [
("protein1", "MKTVRQERLKSIVRILERSKEPVSGAQLAEELSVSRQVIVQDIAYLRSLGYNIVATPRGYVLAGG"),
("protein2", "KALTARQQEVFDLIRDHISQTGMPPTRAEIAQRLGFRSPNAAEEHLKALARKGVIEIVSGASRGIRLLQEE"),
("protein2 with mask", "KALTARQQEVFDLIRD<mask>ISQTGMPPTRAEIAQRLGFRSPNAAEEHLKALARKGVIEIVSGASRGIRLLQEE"),
("protein3", "K A <mask> I S Q"),
]
ei = Esm2Infer()
ei.predict(data_list)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()