作业
实现一个图形类(Shape),包含受保护成员属性:周长、面积,
公共成员函数:特殊成员函数书写
定义一个圆形类(Circle),继承自图形类,包含私有属性:半径
公共成员函数:特殊成员函数、以及获取周长、获取面积函数
定义一个矩形类(Rect),继承自图形类,包含私有属性:长度、宽度
公共成员函数:特殊成员函数、以及获取周长、获取面积函数
在主函数中,分别实例化圆形类对象以及矩形类对象,并测试相关的成员函数。
03hmwk.h:
#ifndef __03HMWK_H__
#define __03HMWK_H__
#include <iostream>
#define PI 3.14
using namespace std;
class Shape{
protected:
double circumference;
double size;
public:
//无参构造
Shape();
//有参构造
Shape(double c,double s);
//析构
~Shape();
//拷贝构造
Shape(const Shape &other);
//移动构造
Shape(Shape && other);
//拷贝赋值
Shape & operator=(const Shape &other);
//移动赋值
Shape & operator=(Shape && other);
};
class Circle:public Shape{
private:
double radius;
public:
//无参构造
Circle();
//有参构造
Circle(double r);
//析构
~Circle();
//拷贝构造
Circle(const Circle &other);
//移动构造
Circle(Circle && other);
//拷贝赋值
Circle & operator=(const Circle &other);
//移动赋值
Circle & operator=(Circle && other);
//获取周长
double get_C();
//获取面积
double get_S();
};
class Rectangle:public Shape{
private:
double length;
double width;
public:
//无参构造
Rectangle();
//有参构造
Rectangle(double l,double w);
//析构
~Rectangle();
//拷贝构造
Rectangle(const Rectangle &other);
//移动构造
Rectangle(Rectangle && other);
//拷贝赋值
Rectangle & operator=(const Rectangle &other);
//移动赋值
Rectangle & operator=(Rectangle && other);
//获取周长
double get_C();
//获取面积
double get_S();
};
#endif // 03HMWK_H
03hmwk.cpp:
#include <03hmwk.h>
//无参构造
Shape::Shape():circumference(0),size(0){
cout<<"Shape::无参构造"<<endl;
}
//有参构造
Shape::Shape(double c,double s):circumference(c),size(s){
cout<<"Shape::有参构造"<<endl;
}
//析构
Shape::~Shape(){
cout<<"Shape::析构"<<endl;
}
//拷贝构造
Shape::Shape(const Shape &other):circumference(other.circumference),size(other.size){
cout<<"Shape::拷贝构造"<<endl;
}
//移动构造
Shape::Shape(Shape && other):circumference(other.circumference),size(other.size){
cout<<"Shape::移动构造"<<endl;
}
//拷贝赋值
Shape & Shape::operator=(const Shape &other){
circumference = other.circumference;
size = other.size;
cout<<"Shape::拷贝赋值"<<endl;
return *this;
}
//移动赋值
Shape & Shape::operator=(Shape && other){
circumference = other.circumference;
size = other.size;
cout<<"Shape::移动赋值"<<endl;
return *this;
}
/**********************************圆*************************************************/
//无参构造
Circle::Circle():Shape(0,0),radius(0){
cout<<"Circle::无参构造"<<endl;
}
//有参构造
Circle::Circle(double r):Shape(2*PI*r,PI*r*r),radius(r){
cout<<"Circle::有参构造"<<endl;
}
//析构
Circle::~Circle(){
cout<<"Circle::析构"<<endl;
}
//拷贝构造
Circle::Circle(const Circle &other):Shape(other.circumference,other.size),radius(other.radius){
cout<<"Circle::拷贝构造"<<endl;
}
//移动构造
Circle::Circle(Circle && other):Shape(other.circumference,other.size),radius(other.radius){
cout<<"Circle::移动构造"<<endl;
}
//拷贝赋值
Circle & Circle::operator=(const Circle &other){
circumference = other.circumference;
size = other.size;
radius = other.radius;
cout<<"Circle::拷贝赋值"<<endl;
return *this;
}
//移动赋值
Circle & Circle::operator=(Circle && other){
circumference = other.circumference;
size = other.size;
radius = other.radius;
cout<<"Circle::移动赋值"<<endl;
return *this;
}
//获取周长
double Circle::get_C(){
return circumference;
}
//获取面积
double Circle::get_S(){
return size;
}
/***********************************矩形************************************************/
//无参构造
Rectangle::Rectangle():Shape(0,0),length(0),width(0){
cout<<"Rectangle::无参构造"<<endl;
}
//有参构造
Rectangle::Rectangle(double l,double w):Shape(2*(l+w),l*w),length(l),width(w){
cout<<"Rectangle::有参构造"<<endl;
}
//析构
Rectangle::~Rectangle(){
cout<<"Rectangle::析构"<<endl;
}
//拷贝构造
Rectangle::Rectangle(const Rectangle &other):Shape(other.circumference,other.size),length(other.length),width(other.width){
cout<<"Rectangle::拷贝构造"<<endl;
}
//移动构造
Rectangle::Rectangle(Rectangle && other):Shape(other.circumference,other.size),length(other.length),width(other.width){
cout<<"Rectangle::移动构造"<<endl;
}
//拷贝赋值
Rectangle & Rectangle::operator=(const Rectangle &other){
circumference = other.circumference;
size = other.size;
length = other.length;
width = other.width;
cout<<"Rectangle::拷贝赋值"<<endl;
return *this;
}
//移动赋值
Rectangle & Rectangle::operator=(Rectangle && other){
circumference = other.circumference;
size = other.size;
length = other.length;
width = other.width;
cout<<"Rectangle::移动赋值"<<endl;
return *this;
}
//获取周长
double Rectangle::get_C(){
return circumference;
}
//获取面积
double Rectangle::get_S(){
return size;
}
main.cpp:
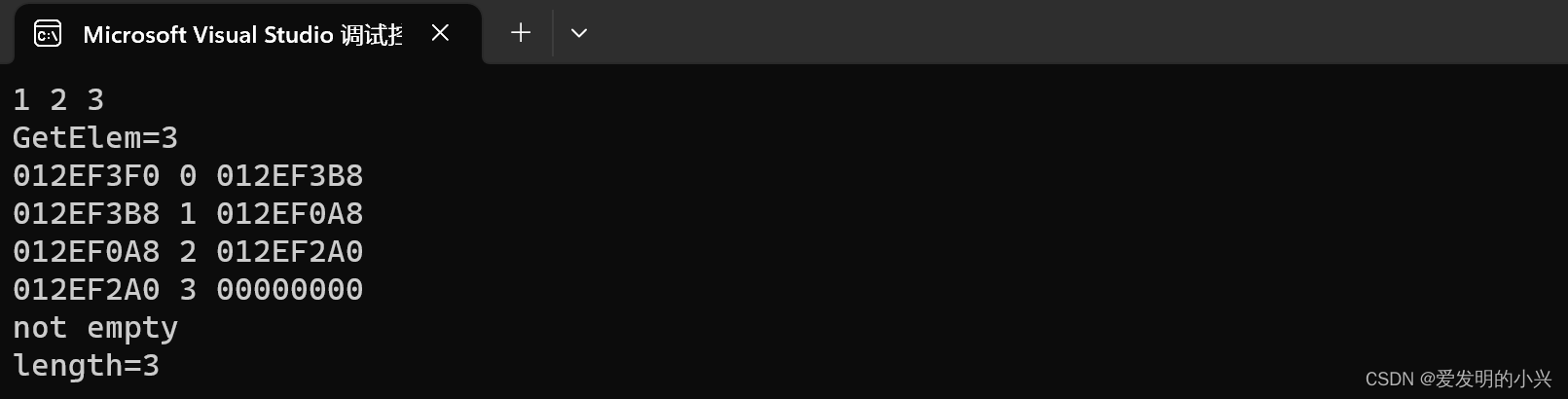
#include <03hmwk.h>
int main()
{
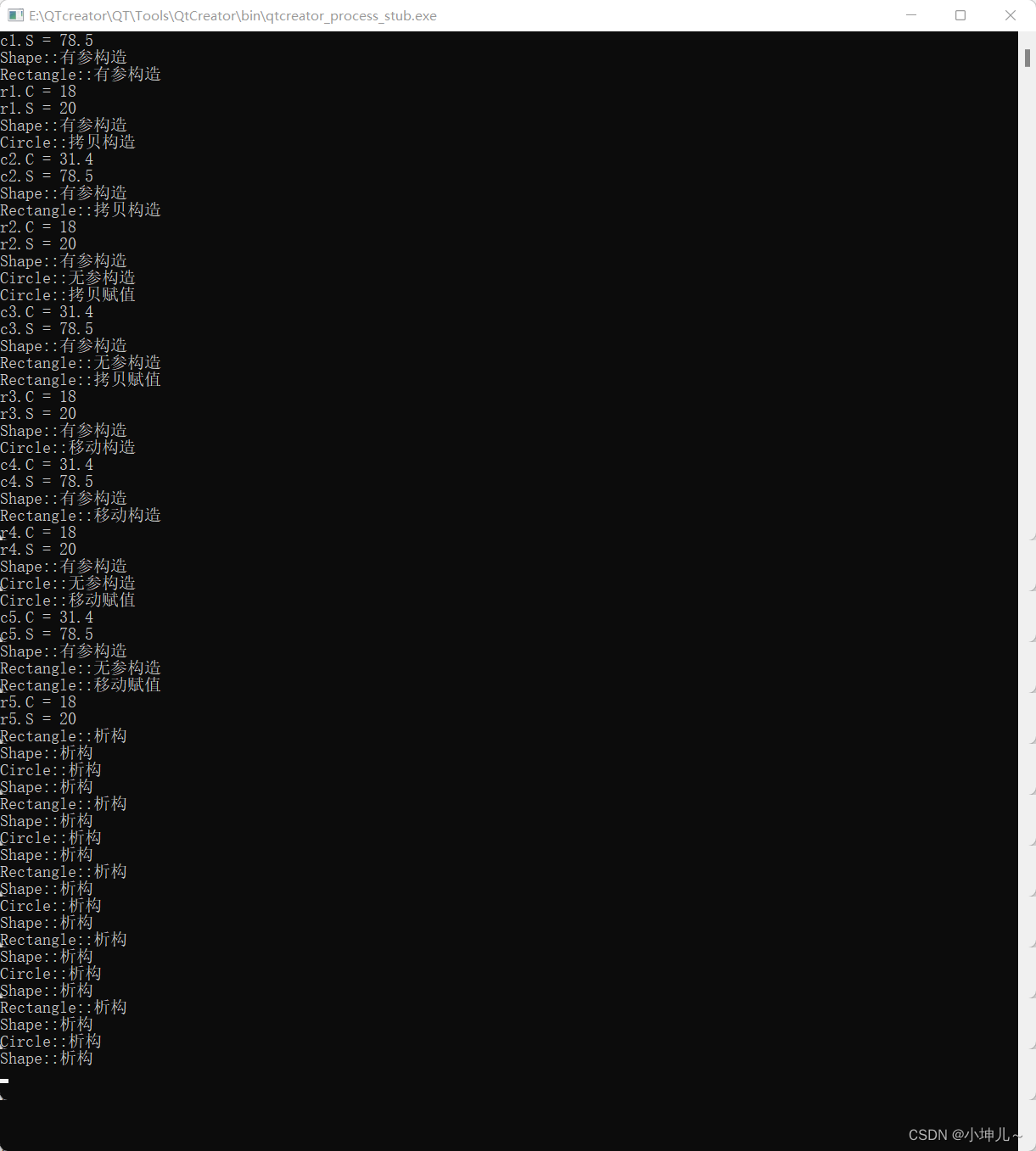
Circle c1(5);
cout<<"c1.C = "<<c1.get_C()<<endl;
cout<<"c1.S = "<<c1.get_S()<<endl;
Rectangle r1(5,4);
cout<<"r1.C = "<<r1.get_C()<<endl;
cout<<"r1.S = "<<r1.get_S()<<endl;
Circle c2 = c1;
cout<<"c2.C = "<<c2.get_C()<<endl;
cout<<"c2.S = "<<c2.get_S()<<endl;
Rectangle r2 = r1;
cout<<"r2.C = "<<r2.get_C()<<endl;
cout<<"r2.S = "<<r2.get_S()<<endl;
Circle c3;
c3 = c2;
cout<<"c3.C = "<<c3.get_C()<<endl;
cout<<"c3.S = "<<c3.get_S()<<endl;
Rectangle r3;
r3 = r2;
cout<<"r3.C = "<<r3.get_C()<<endl;
cout<<"r3.S = "<<r3.get_S()<<endl;
Circle c4 = move(c3);
cout<<"c4.C = "<<c4.get_C()<<endl;
cout<<"c4.S = "<<c4.get_S()<<endl;
Rectangle r4 = move(r3);
cout<<"r4.C = "<<r4.get_C()<<endl;
cout<<"r4.S = "<<r4.get_S()<<endl;
Circle c5;
c5 = move(c4);
cout<<"c5.C = "<<c5.get_C()<<endl;
cout<<"c5.S = "<<c5.get_S()<<endl;
Rectangle r5;
r5 = move(r4);
cout<<"r5.C = "<<r5.get_C()<<endl;
cout<<"r5.S = "<<r5.get_S()<<endl;
return 0;
}
效果图:
一、静态成员(static)
程序员有时在实例化对象时,想让某个成员或某几个成员独立于类对象而存在,但是又属于类对象的属性,不占用类对象的空间,那么此时我们可以将这些成员设置成静态成员,相当于在类体内定义一个全局的成员。静态成员分为静态成员变量和静态成员函数。
1.1 静态成员变量
- 定义格式:在定义成员变量时,在前面加关键字static,那么该变量就是静态成员变量
- 静态成员变量一般声明成public权限,并且需要在类内声明,类外定义,定义时如果不初始化,默认为0,
- 静态成员变量,不依附于类对象而存在,不占用类对象的空间,在编译时,系统在静态区为其分配空间
- 静态成员变量也是每个类对象拥有的属性,一个对象对其更改,所有对象的该属性都会更改
- 使用方式:每个类对象都可以使用成员运算符进行调用,也可以通过类名加作用域限定符直接调用
- 静态成员变量,从功能上来说相当于全局变量,但是相比于全局变量更能体现类的封装性
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Stu
{
private:
int age;
public:
static int score; //在类内声明
Stu() {}
};
//在类外定义一下静态成员变量
int Stu::score = 100;
int main()
{
Stu::score = 50; //通过 类名直接访问类中的静态成员变量
Stu s;
cout<<"score = "<<s.score<<endl;
cout<<"sizeof s = "<<sizeof (s)<<endl; //4字节,静态成员变量不占用类对象的空间
Stu s1;
cout<<"score = "<<s1.score<<endl; //100
Stu s2;
s2.score = 90; //一个对象的该值进行改变,所有对象的该值都跟着改变
cout<<"score = "<<s.score<<endl;
cout<<"score = "<<s1.score<<endl;
return 0;
}1.2 静态成员函数
- 定义格式:在定义成员函数前加关键static,那么该函数就是静态成员函数
- 静态成员函数相当于在类体中定义一个全局函数,但是,只能是该类对象或者该类进行调用
- 静态成员函数的调用:可以使用类对象通过成员运算符进行调用也可以使用类名直接进行调用
- 静态成员函数中,没有this指针
- 静态成员函数,不依赖于类对象而存在,所以也可以不实例化对象,直接使用类名进行调用
- 在静态成员函数中,只能使用静态成员变量不能使用非静态成员变量
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Stu
{
private:
int age;
public:
static int score; //在类内声明
Stu() {}
Stu(int a):age(a) {}
//该函数是静态成员函数
static void show()
{
//cout<<"age = "<<age<<endl; //在静态成员函数中不能使用非静态成员变量
cout<<"score = "<<score<<endl; //可以使用静态成员变量
}
//静态成员函数和同名的非静态成员函数不构成重载关系,原因是作用域不同
// void show()
// {
// cout<<"age = "<<age<<endl; //在静态成员函数中不能使用非静态成员变量
// cout<<"score = "<<score<<endl; //可以使用静态成员变量
// }
};
//在类外定义一下静态成员变量
int Stu::score = 100;
int main()
{
Stu::score = 50; //通过 类名直接访问类中的静态成员变量
Stu s;
cout<<"score = "<<s.score<<endl;
cout<<"sizeof s = "<<sizeof (s)<<endl; //4字节,静态成员变量不占用类对象的空间
Stu s1;
cout<<"score = "<<s1.score<<endl; //100
Stu s2;
s2.score = 90; //一个对象的该值进行改变,所有对象的该值都跟着改变
cout<<"score = "<<s.score<<endl;
cout<<"score = "<<s1.score<<endl;
cout<<"********************************************************"<<endl;
Stu s3(18);
s3.show(); //通过类对象调用静态成员函数
Stu::show(); //通过函数名直接调用静态成员函数
return 0;
}二、继承(inherit)
2.1 继承的概念
1> 所谓继承,就是在一个类的基础上去定义另一个新类的过程叫做继承
2> 作用:
- 继承能够提高代码的复用性
- 继承是实现多态的必要条件
2.2 继承格式
class 子类名:继承方式 父类名
{
//子类拓展的成员
}
继承方式有三种:public、protected、private
子类:也叫派生类
父类:也叫基类2.3 继承方式对类中成员的权限的影响
父类中 public|protected|private|不能访问 public|protected|private|不能访问 public|protected|private|不能访问
继承方式 public protected private
子类中 public|protected|不能访问|不能访问 protected|protected|不能访问|不能访问 private|private|不能访问|不能访问总结:
- 所谓继承方式,其实就是父类中的成员的访问权限在子类中的最高权限
- 如果继承过程中没有加访问权限,默认是私有继承
- 常用的继承方式是public
- 在所有继承方式中,都不能在子类中访问父类的私有成员以及父类不能访问的成员
2.4 子类会继承父类中的所有成员
1> 子类会继承父类中的所有成员,包括私有成员,只是私有成员不能访问而已
2> 父类和子类是不同的类
3> 为了对子类从父类中继承下来成员进行初始化工作,需要在子类的构造函数初始化列表中显性调用父类的有参构造完成,否则系统会自动调用父类的无参构造,此时,如果父类没有无参构造,则系统报错
4> 在这个过程中,虽然调用了父类的构造函数,但是,并没有实例化一个父类对象
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Person
{
public:
string name;
protected:
int value;
private:
double money; //私房钱
public:
Person() {cout<<"Person::无参构造"<<endl;}
Person(string n, int v, double m):name(n),value(v),money(m) {cout<<"Person::有参构造"<<endl;}
void show()
{
cout<<"Person::name = "<<name<<endl; //自己类中的公有成员,自己类内可以访问
cout<<"Person::value = "<<value<<endl; //自己类中的受保护成员,自己类内可以访问
cout<<"Person::money = "<<money<<endl; //自己类中的私有成员,自己类内可以访问
}
};
//定义一个员工类,继承自人类
class Worker:public Person //公有继承
/*class Worker:protected Person*/ //受保护继承
//class Worker:private Person
{
private:
double salary; //工资
public:
Worker() {cout<<"Worker::无参构造"<<endl;}
//需要在子类的构造函数中显性调用父类的有参构造完成对子类从父类中继承下来的成员的初始化
Worker(string n, int v, double m, double s):Person(n,v,m), salary(s)
{
// name = n;
// value = v;
// money = m;
cout<<"Worker::有参构造"<<endl;
}
void display()
{
cout<<"Worker::name = "<<name<<endl; //继承下来的公有成员,子类中还是公有成员,子类内可以访问
cout<<"Worker::value = "<<value<<endl; //继承下来的受保护成员,子类中还是受保护成员,子类内可以访问
//cout<<"Worker::money = "<<money<<endl; //继承下来的父类私有成员,子类中不可访问
cout<<"Worker::salary = "<<salary<<endl; //自己的私有成员,类内可以访问
}
};
int main()
{
//cout << sizeof(Worker) << endl;
// Worker w;
// cout<<"w.name = "<<w.name<<endl; //继承下来的公有成员,子类中也是公有的,类外可以被访问
// cout<<"w.value = "<<w.value<<endl; //继承下来的受保护成员,子类中也是受保护的,子类外不能被访问
// cout<<"w.money = "<<w.money<<endl; //继承下来的私有成员,子类中不能被访问,类外不能被访问
// cout<<"w.salary = "<<w.salary<<endl; //子类的私有成员,子类外无法访问
Worker w1("zhangpp", 520, 1, 100);
w1.display();
w1.show();
return 0;
}2.5 类的关系模型
1> has - a模型
包含关系,一个类中包含另一个类的成员对象
2> use - a模型
友元关系,将某个类设置成友元,那么另一个类就可以使用自己的所有权限下的成员
3> is - a模型
继承关系,并且,is-a模型是特殊的has-a模型
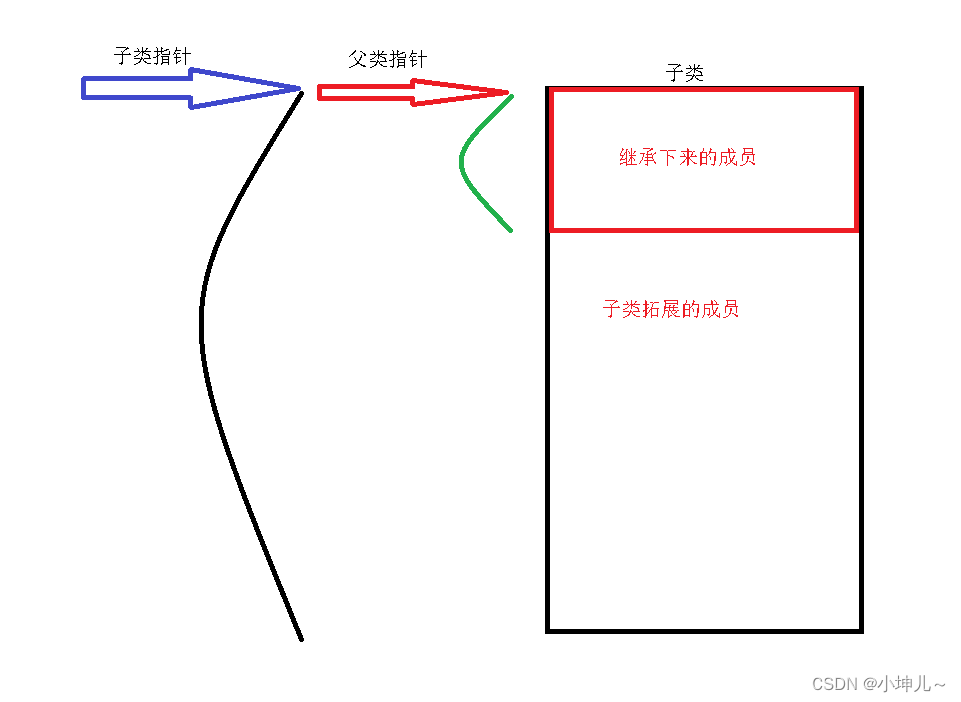
2.6 类的继承步骤
1> 全盘吸收父类
2> 改造父类:继承方式、通过using关键字改变
3> 拓展新成员
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Person
{
public:
string name;
protected:
int salary;
private:
int money;
public:
Person() {}
};
//定义学生类继承自Person
class Stu:public Person
{
protected:
using Person::name; //将继承的name的权限更改成受保护权限
public:
using Person::salary; //将继承的salary权限更改成公共权限
//using Person::money; //父类的私有成员不能进行改造
double score; //拓展新成员
public:
Stu() {}
};
int main()
{
Stu s;
//s.name = "hello";
//s.salary = 1000;
return 0;
}