概念
注解 (Annotation)是以“@注解名称”的形式存在于代码中的,相信用过spring的小伙伴们都会使用大量的注解。注解是JDK1.5之后引入的,它可以写在类、方法、属性上面,用于说明或标记某些含义,这些说明或标记可用于生成文档、程序编译时被读取、程序运行时被读取。
定义注解
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface TestAnnotation {
String value() default "hello";
String name();
}@interface:表示是一个注解
@ Target:注解的作用对象
TYPE:类、接口、枚举
FIELD:属性
METHOD:方法
@Retention:注解的被保留的阶段
SOURCE:保留在源文件中,编译时被丢弃
CLASS:由编译器记录在类文件中,但在运行时VM不必保留注解。这是默认行为。
RUNTIME:保留到class字节文件中,运行时可被jvm读取到,一般自定义注解指定这个
String value() default "hello":注解中一个叫value的属性,默认值是“hello”
MyField :注解名称
使用注解
@Data
public class Test {
@TestAnnotation(value = "aaaa", name = "bbbb")
private String name;
}读取注解
通过反射机制读取注解
public class Testaa {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
Field field = Test.class.getDeclaredField("name");
TestAnnotation annotation = field.getAnnotation(TestAnnotation.class);
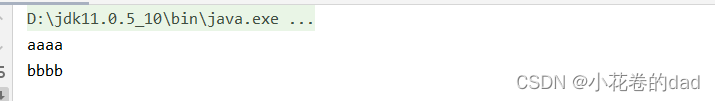
System.out.println(annotation.value());
System.out.println(annotation.name());
} catch (NoSuchFieldException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}