文章目录
- 一、简介
- 二、安装与配置Elasticsearch
- 三、集成Spring Boot与Elasticsearch
- 1. 添加依赖与配置文件
- 2. 创建Elasticsearch数据模型
- 3. 定义Elasticsearch仓库接口
- 4. 实现Elasticsearch数据操作
- 四、基本查询与索引操作
- 1. 插入与更新数据
- 2. 删除数据与索引
- 3. 条件查询与分页查询
- 在Elasticsearch仓库定义一个分页查询的方法
- 在业务封装的类中调用该方法
- 4. 排序与聚合查询
- 排序
- 聚合查询
- 应用场景
- 五、高级查询与全文检索
- 1. 多字段匹配与模糊查询
- 2. 范围查询与正则表达式查询
- 3. 全文检索与高亮显示
- 六、总结
一、简介
最近项目中要使用Elasticsearch所以就去简单的学习了一下怎么使用,具体的一些在高级的功能暂时展示不了,能力目前有点限,不过一些基本的需求还是可以满足的。所以就写了一篇整理一下也希望能够指出不足之处
二、安装与配置Elasticsearch
docker部署
正常部署
三、集成Spring Boot与Elasticsearch
1. 添加依赖与配置文件
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-elasticsearch</artifactId>
</dependency>
spring:
elasticsearch:
rest:
uris: 127.0.0.1:9200 #可配置多个,以逗号间隔举例: ip,ip
connection-timeout: 1
read-timeout: 30
2. 创建Elasticsearch数据模型
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonFormat;
import lombok.Data;
import org.springframework.data.annotation.Id;
import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.annotations.DateFormat;
import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.annotations.Document;
import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.annotations.Field;
import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.annotations.FieldType;
import java.util.Date;
/**
* @BelongsProject: spring-elas
* @BelongsPackage: com.example.springelas.elas.entity
* @Author: gepengjun
* @CreateTime: 2023-09-07 09:16
* @Description: TODO
* @Version: 1.0
*/
@Data
@Document(indexName = "book",createIndex = true)
public class Book {
@Id
@Field(type = FieldType.Text)
private String id;
@Field(analyzer="ik_max_word")
private String title;
@Field(analyzer="ik_max_word")
private String author;
@Field(type = FieldType.Double)
private Double price;
@JsonFormat(pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ss")
@Field(type = FieldType.Date,format = DateFormat.custom, pattern = "8uuuu-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ss")
private Date createTime;
@Field(type = FieldType.Date,format = DateFormat.time)
private Date updateTime;
/**
* 1. Jackson日期时间序列化问题:
* Cannot deserialize value of type `java.time.LocalDateTime` from String "2020-06-04 15:07:54": Failed to deserialize java.time.LocalDateTime: (java.time.format.DateTimeParseException) Text '2020-06-04 15:07:54' could not be parsed at index 10
* 解决:@JsonFormat(pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss")
* 2. 日期在ES存为long类型
* 解决:需要加format = DateFormat.custom
* 3. java.time.DateTimeException: Unable to obtain LocalDate from TemporalAccessor: {DayOfMonth=5, YearOfEra=2020, MonthOfYear=6},ISO of type java.time.format.Parsed
* 解决:pattern = "uuuu-MM-dd HH:mm:ss" 即将yyyy改为uuuu,或8uuuu: pattern = "8uuuu-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"
* 参考:https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/migrate-to-java-time.html#java-time-migration-incompatible-date-formats
*/
}
3. 定义Elasticsearch仓库接口
public interface ESBookRepository extends ElasticsearchRepository<Book, String> {
List<Book> findByTitleOrAuthor(String title, String author);
@Highlight(fields = {
@HighlightField(name = "title"),
@HighlightField(name = "author")
})
@Query("{\"match\":{\"title\":\"?0\"}}")
SearchHits<Book> find(String keyword);
}
4. 实现Elasticsearch数据操作
@Service
public class ESBookImpl {
@Autowired
ESBookRepository esBookRepository;
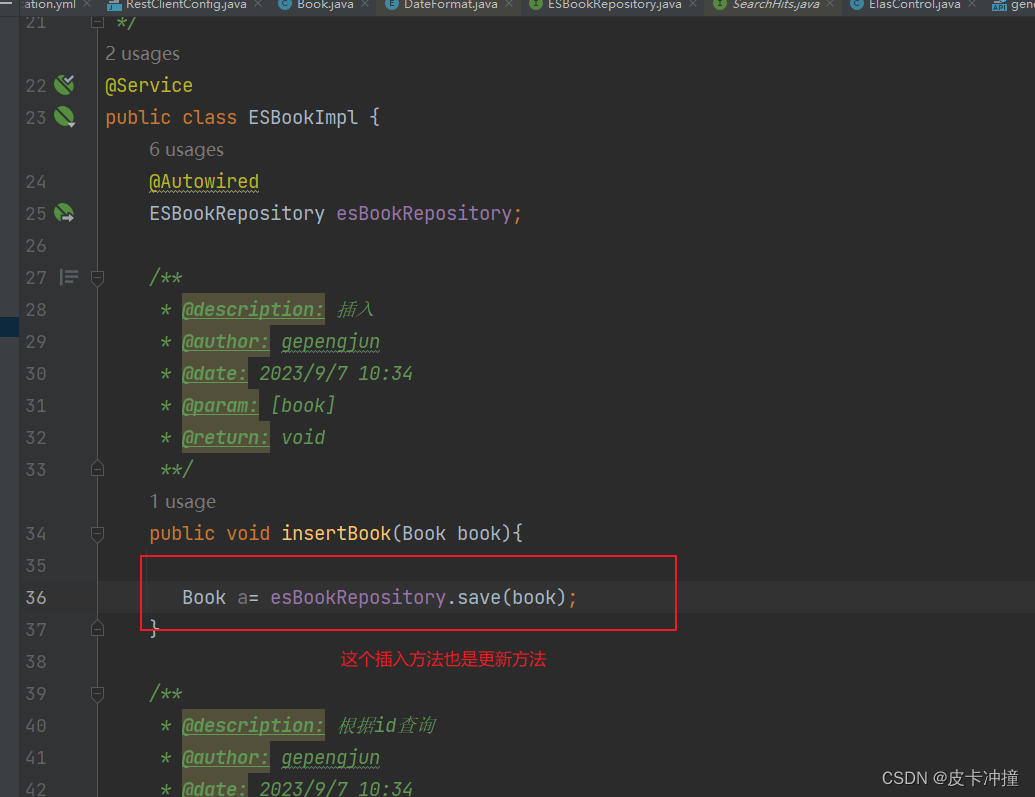
public void insertBook(Book book){
Book a= esBookRepository.save(book);
System.out.println(a);
}
public Book queryBook(String keyWord){
return esBookRepository.findById(keyWord).get();
}
}
四、基本查询与索引操作
1. 插入与更新数据
2. 删除数据与索引
/**
* @description: 根据id删除
* @author: gepengjun
* @date: 2023/9/7 10:35
* @param: [keyWord]
* @return: void
**/
public void deleteBook(String keyWord){
esBookRepository.deleteById(keyWord);
// esBookRepository.delete(book); //可通过实体删除
}
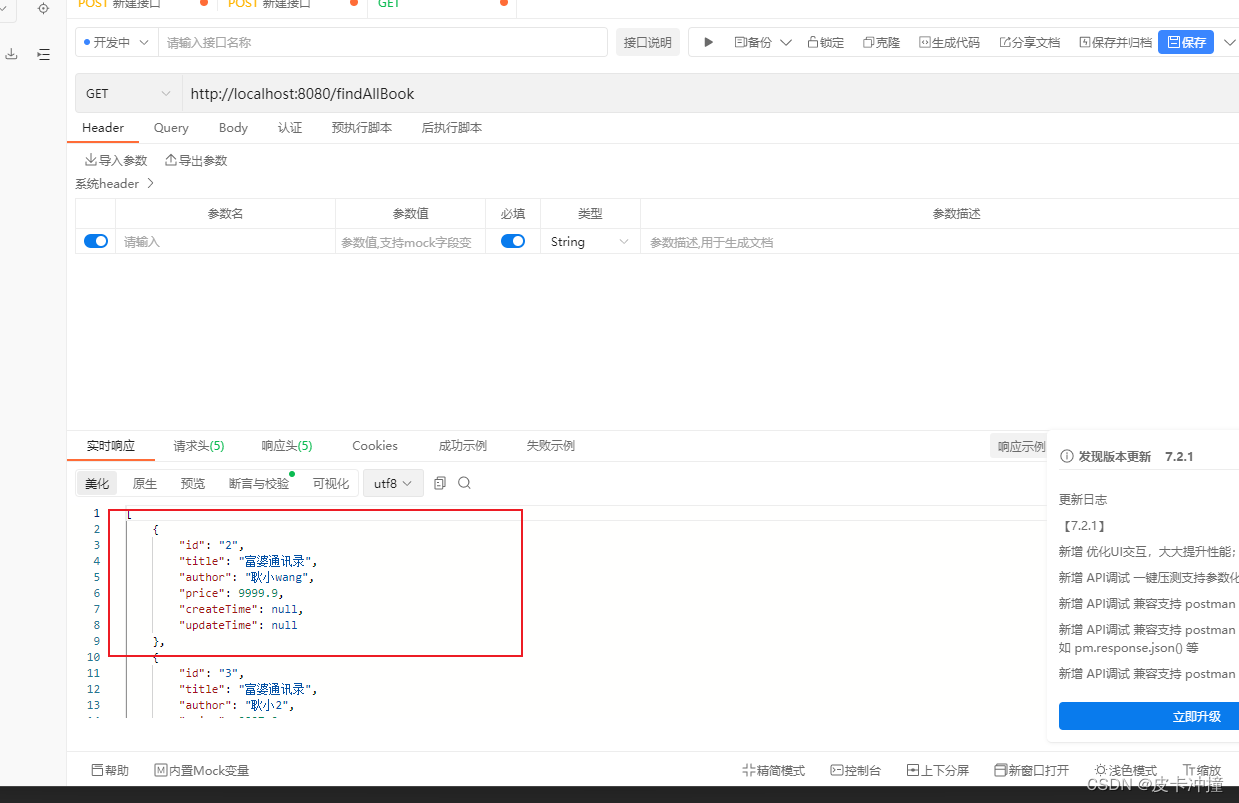
首先根据spring提供的findAll方法获取所有数据

然后调用删除方法,根据id删除
可以看到id为1的数据已经不在了
3. 条件查询与分页查询
在Elasticsearch仓库定义一个分页查询的方法
Page<Book> findByTitle(String title, Pageable pageable);
在业务封装的类中调用该方法
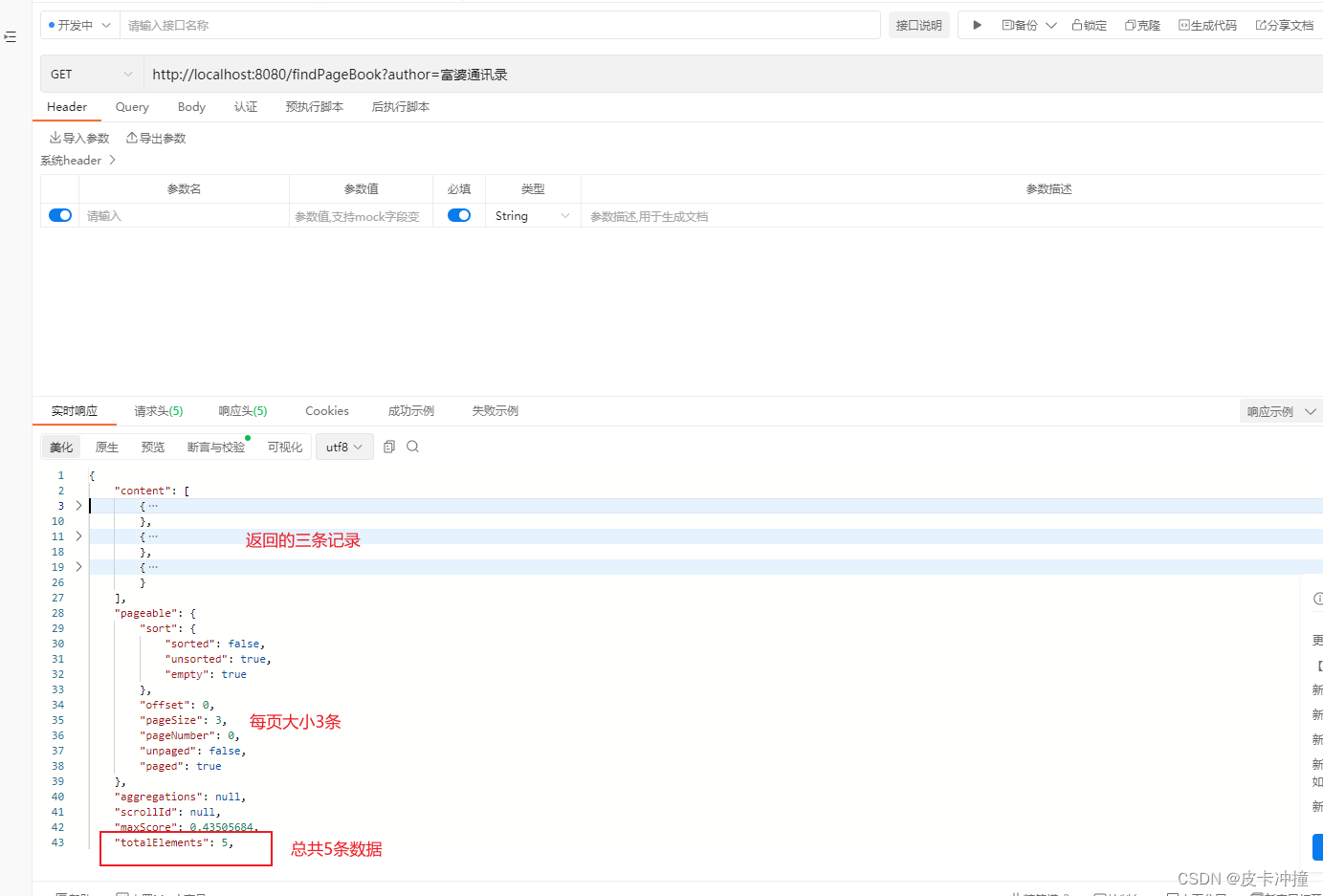
public Object pageBook(String author){
Pageable pageable= PageRequest.of(0, 3);
return esBookRepository.findByTitle(author,pageable);
}
最后在control中调用,可以看一下执行情况
4. 排序与聚合查询
排序
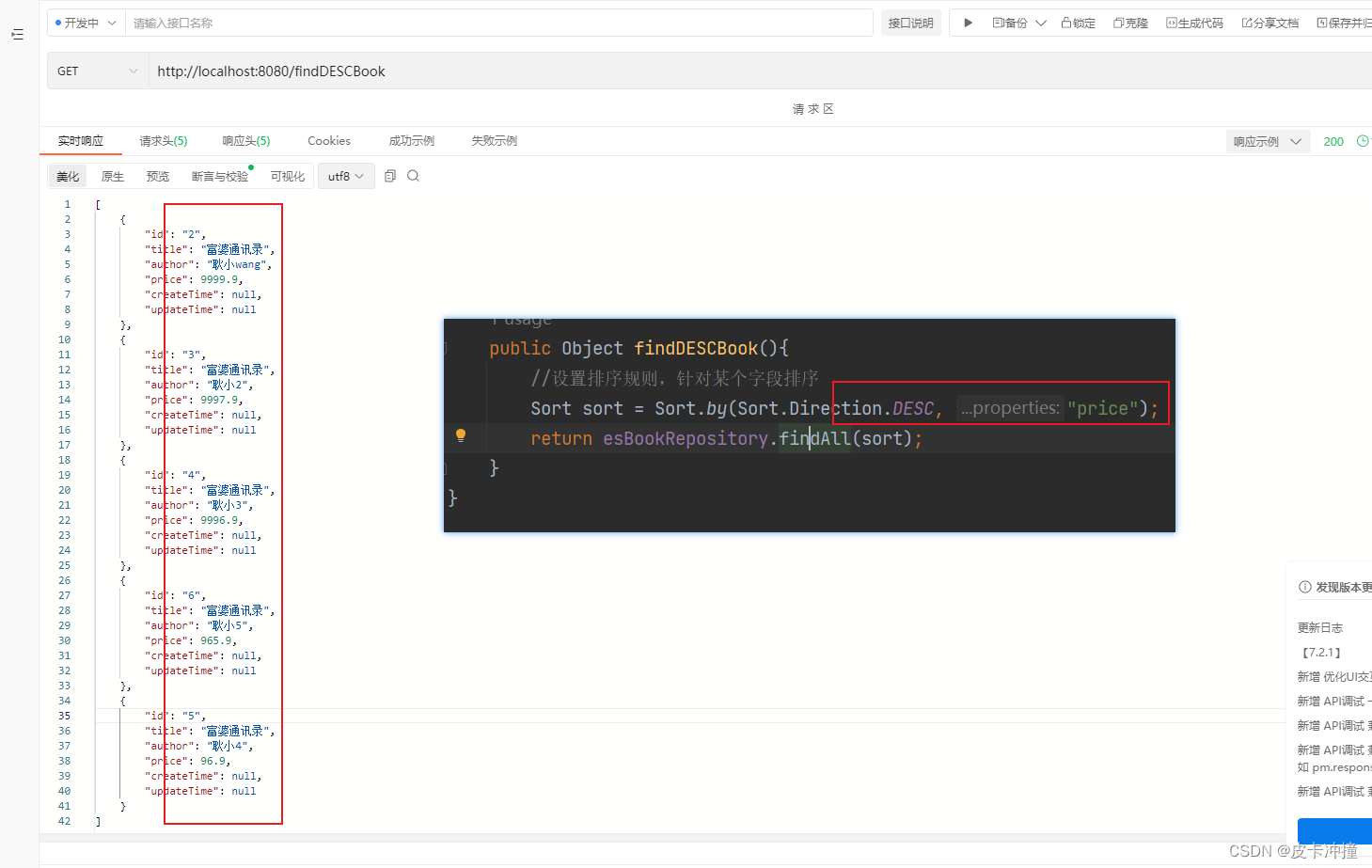
这是查询全部进行的排序,如果有需要根据条件查询进行排序,可以参考上面的分页自行设置。
public Object findDESCBook(){
//设置排序规则,针对某个字段排序
Sort sort = Sort.by(Sort.Direction.DESC, "price");
return esBookRepository.findAll(sort);
}
根据价格字段进行排序
聚合查询
这个聚合查询还有点小瑕疵。
@Autowired
private ElasticsearchOperations elasticsearchOperations;
/**
* @description: 聚合查询
* @author: gepengjun
* @date: 2023/9/7 11:37
* @param: []
* @return: java.lang.Object
**/
public Object findAggregationBOOK(String title){
Pageable pageable= PageRequest.of(0, 3);
TermsAggregationBuilder builder1 = AggregationBuilders.terms("taxonomy").field("title.keyword");
//构建查询
NativeSearchQuery build = new NativeSearchQueryBuilder()
.addAggregation(builder1)
.withPageable(pageable)
.build();
SearchHits<Book> search = elasticsearchOperations.search(build, Book.class);
for (SearchHit<Book> bookSearchHit : search) {
System.out.println(bookSearchHit.getContent());
}
Aggregations aggregations = search.getAggregations();
Map<String, Aggregation> asMap = aggregations.getAsMap();
return asMap;
}

应用场景
聚合查询是 Elasticsearch 中的一项重要功能,可用于从大量数据中提取有意义的汇总信息和统计结果。以下是聚合查询在 Elasticsearch 中的几个常见应用场景总结:
-
数据分析和统计:聚合查询可以对大量数据进行统计和分析,如计算平均值、求和、最大值、最小值等。它可以用于生成报表、绘图或执行复杂的数据分析任务。
-
分组统计:聚合查询使我们能够根据指定的字段对数据进行分组,并计算每个组的统计结果。例如,在电子商务中,可以根据商品类别对销售数据进行分组统计,以获得每个类别的销售额或销售量。
-
嵌套聚合:Elasticsearch 支持将多个聚合操作嵌套在一起,以实现更复杂的统计和分析需求。通过构建多级嵌套聚合,可以深入了解数据之间的关系,并获取更详细的洞察力。
-
时间分析:聚合查询在时间序列数据分析中非常有用。它可以按照指定的时间间隔对数据进行分桶,然后在每个时间段内执行统计分析操作。例如,可以按小时、天、周或月对访问日志数据进行时间分析。
-
桶(Bucket)分析:桶聚合是一种将数据分割为不同桶(bucket)或区间的聚合方式。可以通过范围、词条匹配或脚本等方式定义桶的条件,并对每个桶进行统计分析。
-
基数和去重计数:聚合查询还支持基数统计和去重计数。可以查找某个字段中的唯一值的数量,或者对其中的重复值进行计数。
-
多字段统计:Elasticsearch 允许在一个聚合操作中统计多个字段的信息。这对于同时分析多个指标或维度非常有用。
五、高级查询与全文检索
1. 多字段匹配与模糊查询
/**
* @description: 多字段匹配查询
* @author: gepengjun
* @date: 2023/9/7 15:40
* @param: [field1, field2]
* @return: java.util.List<com.example.springelas.elas.entity.Book>
**/
List<Book> findByAuthorOrPrice(String field1, String field2);
/**
* @description: 针对一个字段模糊查询
* @author: gepengjun
* @date: 2023/9/7 15:40
* @param: [pattern]
* @return: java.util.List<com.example.springelas.elas.entity.Book>
**/
List<Book> findByAuthorLike(String pattern);
2. 范围查询与正则表达式查询
/**
* @description: 查询某一个字段根据正则表达式
* @author: gepengjun
* @date: 2023/9/7 15:41
* @param: [regexPattern]
* @return: java.util.List<com.example.springelas.elas.entity.Book>
**/
List<Book> findByAuthorRegex(String regexPattern);
//具体使用即使直接传入一个正则表达式
List<Book> entityList = esBookRepository.findByAuthorRegex("^abc.*");
3. 全文检索与高亮显示
这个就是高亮
@Highlight(fields = {
@HighlightField(name = "title"),
@HighlightField(name = "author")
})
@Query("{\"match\":{\"title\":\"?0\"}}")
SearchHits<Book> find(String keyword);
六、总结
el的使用就和我们使用的一些orm框架一样,所以spring提供的这个和el交互的包放在了data下。