"觇其平生,岂能容物?"
- 0. 简单认识
- 1. 公式对比解读
- 2. 应用举例
- 3. 解决方案(公式---代码对应)
- 3.1 初始化
- 3.2 EKF
- 3.2.1 预测---状态方程
- 3.2.2 系统协方差矩阵
- 3.2.3 预测---系统协方差矩阵
- 3.2.4 设置测量矩阵
- 3.2.5 更新---状态变量,卡尔曼增益,状态协方差矩阵
- 4. 源码
- 4.1 Extended_kalman_filter.hpp
- 4.2 main.cpp
- 4.3 CMakeLists.txt
前置事项: 7.2节将KF进行简单介绍和实现,本节介绍EKF扩展卡尔曼滤波
- 下边统一将卡尔曼滤波器记作KF,扩展卡尔曼滤波器记作EKF
0. 简单认识
- KF 假设当前状态只由上一时刻状态决定,但是只使用线性方程对系统进行了建模;
- 为了能够应用到非线性系统,EKF 利用泰勒展开,并只保留一次项,抛弃高次项,将非线性关系近似为线性关系。
1. 公式对比解读
为了易于理解,这里以噪声为加性噪声为例展开:
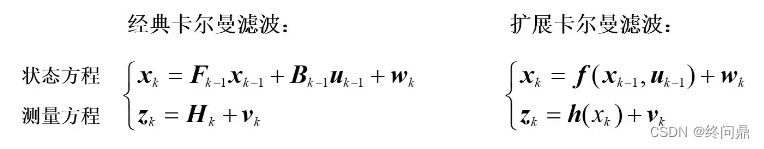
- EKF主要解决非线性问题。如上是线性和非线性系统的运动方程和观测方程。其中EKF的 f f f 和 z z z 都是非线性的。
- 上节对KF(线性系统已经做了阐述),而EKF将此时状态
x
^
k
\hat x_{k}
x^k 非线性的表达式
f
f
f 在上一时刻的后验估计
x
^
k
−
1
\hat x_{k-1}
x^k−1 利用泰勒公式进行一阶展开,做了线性化,具体推导略,比较简单,直接看KF 和 EKF 的结论对比(大体不变):
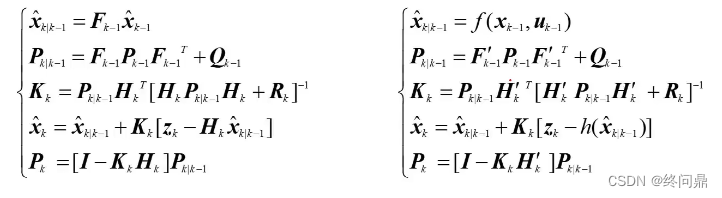
其中:
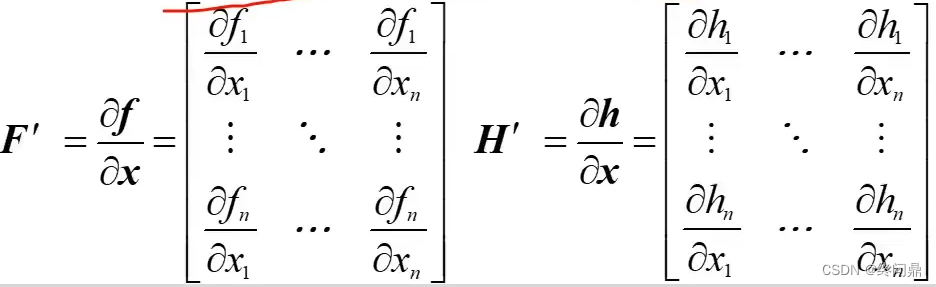
对比KF的线性系统:
- 状态量 x x x 的先验估计(预测),由线性方程表述,变为非线性表述;
- 系统的状态协方差矩阵中的 F F F,在KF中就是状态转移矩阵,而在EKF中求法如上,是 f f f 对各状态量的偏导;
- 测量矩阵在EKF中的求法,是 非线性观测函数 h h h 对 各状态量求偏导数;
2. 应用举例
假设场景:
小车从原点出发,做匀速运动;
- 信息1:车载传感器能每隔 Δ t \Delta t Δt 输出车此时的速度 v t v_t vt 和 w t w_t wt ;
- 信息2:在原点有一激光雷达,每隔 Δ t \Delta t Δt 检测得到车辆距离 d t d_t dt ;
要求:
- 充分利用以上信息,求出小车每一时刻对应的 x 和 y 坐标 a t a_t at 和 b t b_t bt;
3. 解决方案(公式—代码对应)
首先写出系统的观测量,根据题设,可以观测到的量设置如下:
z
=
[
d
t
2
v
t
w
t
]
z = \begin{bmatrix}d_t^2 \\ v_t \\ w_t \end{bmatrix}
z=
dt2vtwt
写出系统的观测量,为了更好利用所有以上信息,设状态量如下:
x
=
[
x
y
v
x
v
y
]
x = \begin{bmatrix}x \\y \\v_x \\v_y \end{bmatrix}
x=
xyvxvy
3.1 初始化
这一部分是,在卡尔曼滤波中保持不变只需要初始化操作一次的矩阵,设置P,Q,R的初始值,:
Eigen::VectorXd x_in(x_noise[0]) ;
EKF.Initialization(x_in) ;
Eigen::MatrixXd P_in(5, 5) ;
P_in << 10, 10, 1, 0, 0,
10, 10, 1, 0, 0,
1, 1, 0.1, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, pow(10,-8), 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, pow(10,-8) ;
EKF.Set_P(P_in) ;
Eigen::MatrixXd Q_in(5, 5) ;
Q_in << 0.01, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0,
0.0, 0.01, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0,
0.0, 0.0, 0.0001, 0.0, 0.0,
0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.01, 0.0,
0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.01 ;
EKF.SetQ(Q_in) ;
//R is provided by Sensor producer, in their datasheet
Eigen::MatrixXd R_in(3, 3) ;
R_in << 0.0001, 0, 0,
0, 0.0001, 0,
0, 0, 0.0001 ;
EKF.SetR(R_in) ;
3.2 EKF
3.2.1 预测—状态方程
这里是非线性的方程,对应公式:
x
k
+
1
=
f
(
x
k
)
x_{k+1} = f(x_k)
xk+1=f(xk)
代码如下:
void PredictX(double delta_time){
// x_t prediction
x_(0) = x_(0) + x_(3) * cos(x_(2)) * delta_time;
x_(1) = x_(1) + x_(3) * sin(x_(2)) * delta_time;
x_(2) = x_(2) + x_(4) * delta_time;
//其余的值理论上不变
}
3.2.2 系统协方差矩阵
这里是手动状态方程对状态变量求偏导数,对应EKF第二个公式中手动求得的:
F
′
F'
F′,代码中为了对应将F设置为了A,一样的,是手动求得公式输入的:
void Set_A(double delta_time){
double theta = x_(2) ;
double tmp_v = x_(3) ;
double sv = -sin(theta)*tmp_v*delta_time ;
double cv = cos(theta)*tmp_v*delta_time ;
double st = sin(theta)*delta_time ;
double ct = cos(theta)*delta_time ;
A_ = Eigen::MatrixXd(5,5) ;
//状态方程对状态向量求雅克比矩阵
A_ << 1.0, 0.0, sv, ct, 0.0,
0.0, 1.0, cv, st, 0.0,
0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, delta_time,
0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0,
0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0;
}
3.2.3 预测—系统协方差矩阵
对应公式:
P
k
=
F
k
−
1
P
k
−
1
F
k
−
1
T
+
Q
k
−
1
P_{k} = F_{k-1}P_{k-1}F_{k-1}^T + Q_{k-1}
Pk=Fk−1Pk−1Fk−1T+Qk−1
更新P,代码如下:
// state covariance matrix for predict x
void PredictP(){
P_ = A_ * P_ * A_.transpose() + Q_ ;
}
3.2.4 设置测量矩阵
这里是观测方程对状态变量求偏导数,对应EKF第二个公式中手动求得的:
H
′
H'
H′手动输入代码如下:
void SetH(){
H_ = Eigen::MatrixXd(3,5) ;
//观测方程对状态向量求雅可比矩阵
H_ << 2*x_(0), 2*x_(1), 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 1, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 1;
}
3.2.5 更新—状态变量,卡尔曼增益,状态协方差矩阵
对应所有更新公式,代码如下:其中的入口参数是测量值,z_pre是预测值
void MeasurementUpdate(Eigen::MatrixXd z){
Eigen::Vector3d z_pre (pow(x_(0),2) + pow(x_(1), 2), x_(3), x_(4)) ;
Eigen::MatrixXd S = H_ * P_ * H_.transpose() + R_ ;
Eigen::MatrixXd K = P_ * H_.transpose() * S.inverse() ;
x_ = x_ + (K * (z - z_pre)) ; //观测-预测
P_ = P_ - K*H_*P_ ;
}
4. 源码
4.1 Extended_kalman_filter.hpp
#ifndef EXTENDED_KALMAN_FILTER_H
#define EXTENDED_KALMAN_FILTER_H
#include "Eigen/Dense"
#include "matplotlibcpp.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
#include <random>
class ExtendedKalmanFilter
{
public:
ExtendedKalmanFilter(){
is_initialized_ = false ;
};
~ExtendedKalmanFilter();
void Initialization(Eigen::VectorXd x_in){
x_ = x_in ;
is_initialized_ = true ;
}
bool IsInitialized(){
return this->is_initialized_ ;
}
/**********calculate / predict x'************/
// state transistion matrix for predict x'
void PredictX(double delta_time){
// x_t prediction
x_(0) = x_(0) + x_(3) * cos(x_(2)) * delta_time;
x_(1) = x_(1) + x_(3) * sin(x_(2)) * delta_time;
x_(2) = x_(2) + x_(4) * delta_time;
//其余的值理论上不变
}
void Set_A(double delta_time){
double theta = x_(2) ;
double tmp_v = x_(3) ;
double sv = -sin(theta)*tmp_v*delta_time ;
double cv = cos(theta)*tmp_v*delta_time ;
double st = sin(theta)*delta_time ;
double ct = cos(theta)*delta_time ;
A_ = Eigen::MatrixXd(5,5) ;
//状态方程对状态向量求雅克比矩阵
A_ << 1.0, 0.0, sv, ct, 0.0,
0.0, 1.0, cv, st, 0.0,
0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, delta_time,
0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0,
0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0;
}
void Set_P(Eigen::MatrixXd P_in){
P_ = P_in ;
}
// state covariance matrix for predict x
void PredictP(){
P_ = A_ * P_ * A_.transpose() + Q_ ;
}
// process covariance matrix for predict x'
void SetQ(Eigen::MatrixXd Q_in){
Q_ = Q_in ;
}
void SetH(){
H_ = Eigen::MatrixXd(3,5) ;
//观测方程对状态向量求雅可比矩阵
H_ << 2*x_(0), 2*x_(1), 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 1, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 1;
}
void SetR(Eigen::MatrixXd R_in){
R_ = R_in ;
}
void MeasurementUpdate(Eigen::MatrixXd z){
Eigen::Vector3d z_pre (pow(x_(0),2) + pow(x_(1), 2), x_(3), x_(4)) ;
Eigen::MatrixXd S = H_ * P_ * H_.transpose() + R_ ;
Eigen::MatrixXd K = P_ * H_.transpose() * S.inverse() ;
x_ = x_ + (K * (z - z_pre)) ; //观测-预测
P_ = P_ - K*H_*P_ ;
}
Eigen::VectorXd GetX(){
return x_ ;
}
private:
bool is_initialized_ ; // flag of initialized
Eigen::VectorXd x_ ; // state vector
Eigen::MatrixXd A_ ; // jacba matrix for P predict
Eigen::MatrixXd P_ ; // state covariance matrix
Eigen::MatrixXd Q_ ; // process covariance matrix
Eigen::MatrixXd H_ ; // mesurement matrix
Eigen::MatrixXd R_ ; // mesurement covariance matrix
};
ExtendedKalmanFilter::~ExtendedKalmanFilter()
{
}
#endif
4.2 main.cpp
#include "extended_kalman_filter.hpp"
namespace plt = matplotlibcpp;
// creat data
void create_data(std::vector<Eigen::VectorXd> &x_stand,
std::vector<Eigen::VectorXd> &x_noise,
std::vector<Eigen::VectorXd> &measure,
int all_data)
{
double car_speed = 0.1, delta_time = 0.1, car_omega = 0.01;
bool watch = false ;
double tmp_x = 0, tmp_y = 0, tmp_theta = 0, tmp_v = 0, tmp_w = 0; //初值0
std::random_device rd; // 用于生成种子
std::mt19937 random_w(rd()); // 以随机设备生成的种子初始化Mersenne Twister伪随机数生成器
std::uniform_real_distribution<> dis(0, 0.01); // 定义一个0-0.01之间的均匀分布
// inital value
// first value
Eigen::VectorXd a(5, 1), a_measure(3, 1) ;
a << tmp_x, tmp_y, tmp_theta, tmp_v, tmp_w;
x_stand.push_back(a);
x_noise = x_stand;
a_measure << 0.0, 0.0, 0.0 ;
measure.push_back(a_measure) ;
for (size_t i = 0; i < all_data; i++)
{ // standard state data
// x1 = x0 + v*cos(theta)*time ; v的x分量速度
tmp_x = x_stand[i](0) + car_speed * cos(x_stand[i](2)) * delta_time;
tmp_y = x_stand[i](1) + car_speed * sin(x_stand[i](2)) * delta_time;
tmp_theta = x_stand[i](2) + car_omega * delta_time;
a << tmp_x, tmp_y, tmp_theta, car_speed, car_omega;
x_stand.push_back(a);
// noise measure data
float speed_noise = car_speed + dis(random_w) * 10; // 原速度0.1 + 一个0-0.1的值
float omega_noise = car_omega + dis(random_w);
a_measure(0) = pow(tmp_x, 2) + pow(tmp_y, 2) + dis(random_w)/10 ;
a_measure(1) = speed_noise ;
a_measure(2) = omega_noise ;
measure.push_back(a_measure) ;
// noise state data
speed_noise = car_speed + dis(random_w) * 10; // 原速度0.1 + 一个0-0.1的值
omega_noise = car_omega + dis(random_w);
tmp_x = x_noise[i](0) + speed_noise * cos(x_noise[i](2)) * delta_time;
tmp_y = x_noise[i](1) + speed_noise * sin(x_noise[i](2)) * delta_time;
tmp_theta = x_stand[i](2) + omega_noise * delta_time;
a << tmp_x, tmp_y, tmp_theta, speed_noise, omega_noise;
x_noise.push_back(a);
}
if (watch)
{
std::cout << std::fixed; // 输出固定格式
std::cout.precision(4); // 保留4位小数
for (size_t i = 0; i < all_data; i++)
{
for (size_t j = 0; j < 5; j++)
{
std::cout << x_noise[i](j) << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl ;
}
}
}
int main(int argc, const char **argv)
{
int all_data_num = 1000;
double delta_time = 0.1 ; //two state vector(1, 5) and one measure vector(1,3)
std::vector<Eigen::VectorXd> x_stand, x_noise, measure_x;
static std::vector<double> vis_x_std, vis_y_std, vis_x_nse, vis_y_nse, vis_x_ekf, vis_y_ekf;
create_data(x_stand, x_noise, measure_x, all_data_num);
ExtendedKalmanFilter EKF;
while (x_noise.size())
{
// Initialize kalman filter
if (!EKF.IsInitialized())
{
Eigen::VectorXd x_in(x_noise[0]) ;
EKF.Initialization(x_in) ;
Eigen::MatrixXd P_in(5, 5) ;
P_in << 10, 10, 1, 0, 0,
10, 10, 1, 0, 0,
1, 1, 0.1, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, pow(10,-8), 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, pow(10,-8) ;
EKF.Set_P(P_in) ;
Eigen::MatrixXd Q_in(5, 5) ;
Q_in << 0.01, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0,
0.0, 0.01, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0,
0.0, 0.0, 0.0001, 0.0, 0.0,
0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.01, 0.0,
0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.01 ;
EKF.SetQ(Q_in) ;
//R is provided by Sensor producer, in their datasheet
Eigen::MatrixXd R_in(3, 3) ;
R_in << 0.0001, 0, 0,
0, 0.0001, 0,
0, 0, 0.0001 ;
EKF.SetR(R_in) ;
}
//state forward eqution
EKF.PredictX(delta_time) ;
EKF.Set_A(delta_time) ; //first update x, the calculate A
EKF.PredictP() ; // state convarince matrix
EKF.SetH() ; // measurement convarince matrix
// measurement value
Eigen::VectorXd z(measure_x[0]) ;
EKF.MeasurementUpdate(z) ;
//result
Eigen::VectorXd x_out = EKF.GetX() ;
// std::cout << "original output x : " << x_noise[0](0) <<
// " y: " << x_noise[0](1) << std::endl ;
// std::cout << "ideal output x : " << x_stand[0](0) <<
// " y: " << x_stand[0](1) << std::endl ;
// std::cout << "kalman output x : " << x_out(0) <<
// " y: " << x_out(1) << std::endl << std::endl;
//for painting//
vis_x_ekf.push_back(x_out(0)) ;
vis_y_ekf.push_back(x_out(1)) ;
vis_x_nse.push_back(x_noise[0](0)) ;
vis_y_nse.push_back(x_noise[0](1)) ;
vis_x_std.push_back(x_stand[0](0)) ;
vis_y_std.push_back(x_stand[0](1)) ;
x_noise.erase(x_noise.begin()) ;
x_stand.erase(x_stand.begin()) ;
measure_x.erase(measure_x.begin()) ;
}
plt::figure_size(1200, 780);
plt::plot(vis_x_ekf, vis_y_ekf,"r");
plt::plot(vis_x_nse, vis_y_nse,"g");
plt::plot(vis_x_std, vis_y_std,"b");
plt::title("ekf-red, noise-green, stand-blue");
plt::save("./basic.png");
// //for painting//
return 0;
}
4.3 CMakeLists.txt
# CMakeLists.txt
# 设置构建类型为 Release
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.10)
project(common_kf)
set(CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE "Debug")
set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 14) # 使用 C++14 标准
find_package(PythonLibs REQUIRED)
include_directories(
${PYTHON_INCLUDE_DIRS}
)
# 添加当前目录到 include 路径
include_directories(${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/include)
# 添加源文件到编译
add_executable(KalDemo main.cpp)
target_link_libraries(KalDemo
${PYTHON_LIBRARIES}
)