本文是上一篇关于“在低分辨率图像上实现洪水损害检测”的博客的延申。
代码来源:https://github.com/weining20000/Flooding-Damage-Detection-from-Post-Hurricane-Satellite-Imagery-Based-on-CNN/tree/master
数据储存地址:https://github.com/JeffereyWu/FloodDamageDetection/tree/main
目标:利用迁移学习训练两个预训练的CNN模型(VGG和Resnet),自动化识别一个区域是否存在洪水损害。
运行环境:Google Colab
1. 导入库
# Pytoch
import torch
from torchvision import datasets, models
from torch.utils.data import Dataset, DataLoader
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
import torch.nn as nn
from torch_lr_finder import LRFinder
# Data science tools
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import os
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
from PIL import Image
# Visualizations
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
2. 迁移学习知识点
- 对于卷积神经网络(CNN)等模型,通常包括一些卷积层和池化层,这些层的权重用于提取图像的特征。当这些层的参数被冻结时,这些权重将保持不变,不会在训练过程中进行更新。这意味着模型会继续使用预训练模型的特征提取能力。
- 如果模型还包含其他的预训练层,例如预训练的全连接层,这些层的权重也将被冻结,不会更新。
- 通常,当使用预训练模型进行微调时,会替换模型的最后一层或几层,以适应新的任务。新添加的自定义分类器层的权重将被训练和更新,以适应特定的分类任务。
3. 加载和配置预训练的深度学习模型
#Load pre-trained model
def get_pretrained_model(model_name):
"""
获取预训练模型的函数。
参数:
model_name: 要加载的预训练模型的名称(例如,'vgg16' 或 'resnet50')
返回:
MODEL: 加载并配置好的预训练模型
"""
if model_name == 'vgg16':
model = models.vgg16(pretrained=True)
# 将模型的参数(权重)冻结,不进行微调。这意味着这些参数在训练过程中不会更新
for param in model.parameters():
param.requires_grad = False
n_inputs = model.classifier[6].in_features # 获取模型分类器最后一层的输入特征数
n_classes = 2
# 替换模型的分类器部分,添加自定义的分类器
model.classifier[6] = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(n_inputs, 256), nn.ReLU(), nn.Dropout(0.2),
nn.Linear(256, n_classes))
elif model_name == 'resnet50':
model = models.resnet50(pretrained=True)
for param in model.parameters():
param.requires_grad = False
# 获取模型最后一层全连接层的输入特征数
n_inputs = model.fc.in_features
n_classes = 2
model.fc = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(n_inputs, 256), nn.ReLU(), nn.Dropout(0.2),
nn.Linear(256, n_classes))
# Move to GPU
MODEL = model.to(device)
return MODEL # 返回加载和配置好的预训练模型
注意,这里vgg16的classifier结构原本为:
Sequential(
(0): Linear(in_features=25088, out_features=4096, bias=True)
(1): ReLU(inplace=True)
(2): Dropout(p=0.5, inplace=False)
(3): Linear(in_features=4096, out_features=4096, bias=True)
(4): ReLU(inplace=True)
(5): Dropout(p=0.5, inplace=False)
(6): Linear(in_features=4096, out_features=1000, bias=True)
)
以上代码替换了最后一层的classifier,改为:
Sequential(
(0): Linear(in_features=25088, out_features=4096, bias=True)
(1): ReLU(inplace=True)
(2): Dropout(p=0.5, inplace=False)
(3): Linear(in_features=4096, out_features=4096, bias=True)
(4): ReLU(inplace=True)
(5): Dropout(p=0.5, inplace=False)
(6): Sequential(
(0): Linear(in_features=4096, out_features=256, bias=True)
(1): ReLU()
(2): Dropout(p=0.2, inplace=False)
(3): Linear(in_features=256, out_features=2, bias=True)
)
)
注意,这里resnet50的fc结构原本为:
Linear(in_features=2048, out_features=1000, bias=True)
以上代码替换了最后一层fc,改为:
Sequential(
(0): Linear(in_features=2048, out_features=256, bias=True)
(1): ReLU()
(2): Dropout(p=0.2, inplace=False)
(3): Linear(in_features=256, out_features=2, bias=True)
)
4. 建立模型
# VGG 16
model_vgg = get_pretrained_model('vgg16') # 包含加载和配置好的 VGG16 模型
criterion_vgg = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer_vgg = torch.optim.Adam(model_vgg.parameters(), lr=0.00002)
# ResNet 50
model_resnet50 = get_pretrained_model('resnet50') # 包含加载和配置好的 ResNet50 模型
criterion_resnet50 = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer_resnet50 = torch.optim.Adam(model_resnet50.parameters(), lr=0.001)
5. 定义计算准确率的函数
def acc_vgg(x, y, return_labels=False):
with torch.no_grad(): # 禁止梯度计算,因为在准确率计算中不需要梯度信息
logits = model_vgg(x)
pred_labels = np.argmax(logits.cpu().numpy(), axis=1)
if return_labels:
return pred_labels
else:
return 100*accuracy_score(y.cpu().numpy(), pred_labels)
def acc_resnet50(x, y, return_labels=False):
with torch.no_grad():
logits = model_resnet50(x)
pred_labels = np.argmax(logits.cpu().numpy(), axis=1)
if return_labels:
return pred_labels
else:
return 100*accuracy_score(y.cpu().numpy(), pred_labels)
6. 定义一个用于训练深度学习模型的函数
def train(model, criterion, optimizer, acc, xtrain, ytrain, xval, yval, save_file_name, n_epochs, BATCH_SIZE):
"""
训练深度学习模型的函数。
参数:
model: 要训练的深度学习模型
criterion: 损失函数
optimizer: 优化器
acc: 准确率计算函数
xtrain: 训练数据
ytrain: 训练标签
xval: 验证数据
yval: 验证标签
save_file_name: 保存训练后模型权重的文件名
n_epochs: 训练的总轮数(epochs)
BATCH_SIZE: 每个批次的样本数量
返回:
训练完成的模型和训练历史记录
"""
history1 = []
# Number of epochs already trained (if using loaded in model weights)
try:
print(f'Model has been trained for: {model.epochs} epochs.\n')
except:
model.epochs = 0
print(f'Starting Training from Scratch.\n')
# Main loop
for epoch in range(n_epochs):
# keep track of training and validation loss each epoch
train_loss = 0.0
val_loss = 0.0
train_acc = 0
val_acc = 0
# Set to training
model.train()
#Training loop
for batch in range(len(xtrain)//BATCH_SIZE):
idx = slice(batch * BATCH_SIZE, (batch+1)*BATCH_SIZE)
# Clear gradients
optimizer.zero_grad()
# Predicted outputs
output = model(xtrain[idx])
# Loss and BP of gradients
loss = criterion(output, ytrain[idx])
loss.backward()
# Update the parameters
optimizer.step()
# Track train loss
train_loss += loss.item()
train_acc = acc(xtrain, ytrain)
# After training loops ends, start validation
# set to evaluation mode
model.eval()
# Don't need to keep track of gradients
with torch.no_grad():
# Evaluation loop
# F.P.
y_val_pred = model(xval)
# Validation loss
loss = criterion(y_val_pred, yval)
val_loss = loss.item()
val_acc = acc(xval, yval)
history1.append([train_loss / BATCH_SIZE, val_loss, train_acc, val_acc])
torch.save(model.state_dict(), save_file_name) # 保存模型权重
torch.cuda.empty_cache()
# Print training and validation results
print("Epoch {} | Train Loss: {:.5f} | Train Acc: {:.2f} | Valid Loss: {:.5f} | Valid Acc: {:.2f} |".format(
epoch, train_loss / BATCH_SIZE, acc(xtrain, ytrain), val_loss, acc(xval, yval)))
# Format history
history = pd.DataFrame(history1, columns=['train_loss', 'val_loss', 'train_acc', 'val_acc'])
return model, history
7. 开始训练
N_EPOCHS = 30
model_vgg, history_vgg = train(model_vgg,
criterion_vgg,
optimizer_vgg,
acc_vgg,
x_train,
y_train,
x_val,
y_val,
save_file_name = 'model_vgg.pt',
n_epochs = N_EPOCHS,
BATCH_SIZE = 3)
model_resnet50, history_resnet50 = train(model_resnet50,
criterion_resnet50,
optimizer_resnet50,
acc_resnet50,
x_train,
y_train,
x_val,
y_val,
save_file_name = 'model_resnet50.pt',
n_epochs = N_EPOCHS,
BATCH_SIZE = 4)
8. 绘画VGG训练和验证准确率的曲线图
plt.figure() # 创建一个新的绘图窗口
vgg_train_acc = history_vgg['train_acc']
vgg_val_acc = history_vgg['val_acc']
vgg_epoch = range(0, len(vgg_train_acc), 1) # 创建一个包含训练轮次(epochs)的范围对象
plot1, = plt.plot(vgg_epoch, vgg_train_acc, linestyle = "solid", color = "skyblue")
plot2, = plt.plot(vgg_epoch, vgg_val_acc, linestyle = "dashed", color = "orange")
plt.legend([plot1, plot2], ['training acc', 'validation acc']) # 添加图例,以标识图中的两条曲线
plt.xlabel('Epoch')
plt.ylabel('Average Accuracy per Batch')
plt.title('Model VGG-16: Training and Validation Accuracy', pad = 20)
plt.savefig('VGG16-Acc-Plot.png')

9. 绘画VGG训练和验证损失的曲线图
plt.figure()
vgg_train_loss = history_vgg['train_loss']
vgg_val_loss = history_vgg['val_loss']
vgg_epoch = range(0, len(vgg_train_loss), 1)
plot3, = plt.plot(vgg_epoch, vgg_train_loss, linestyle = "solid", color = "skyblue")
plot4, = plt.plot(vgg_epoch, vgg_val_loss, linestyle = "dashed", color = "orange")
plt.legend([plot3, plot4], ['training loss', 'validation loss'])
plt.xlabel('Epoch')
plt.ylabel('Average Loss per Batch')
plt.title('Model VGG-16: Training and Validation Loss', pad = 20)
plt.savefig('VGG16-Loss-Plot.png')

10. 绘画Resnet训练和验证准确率的曲线图
# Training Reseults: Resnet50
plt.figure()
resnet50_train_acc = history_resnet50['train_acc']
resnet50_val_acc = history_resnet50['val_acc']
resnet50_epoch = range(0, len(resnet50_train_acc), 1)
plot5, = plt.plot(resnet50_epoch, resnet50_train_acc, linestyle = "solid", color = "skyblue")
plot6, = plt.plot(resnet50_epoch, resnet50_val_acc, linestyle = "dashed", color = "orange")
plt.legend([plot5, plot6], ['training acc', 'validation acc'])
plt.xlabel('Epoch')
plt.ylabel('Average Accuracy per Batch')
plt.title('Model Resnet50: Training and Validation Accuracy', pad = 20)
plt.savefig('Resnet50-Acc-Plot.png')

11. 绘画Resnet训练和验证损失的曲线图
plt.figure()
resnet50_train_loss = history_resnet50['train_loss']
resnet50_val_loss = history_resnet50['val_loss']
resnet50_epoch = range(0, len(resnet50_train_loss), 1)
plot7, = plt.plot(resnet50_epoch, resnet50_train_loss, linestyle = "solid", color = "skyblue")
plot8, = plt.plot(resnet50_epoch, resnet50_val_loss, linestyle = "dashed", color = "orange")
plt.legend([plot7, plot8], ['training loss', 'validation loss'])
plt.xlabel('Epoch')
plt.ylabel('Average Loss per Batch')
plt.title('Model Resnet50: Training and Validation Loss', pad = 20)
plt.savefig('Resnet50-Loss-Plot.png')

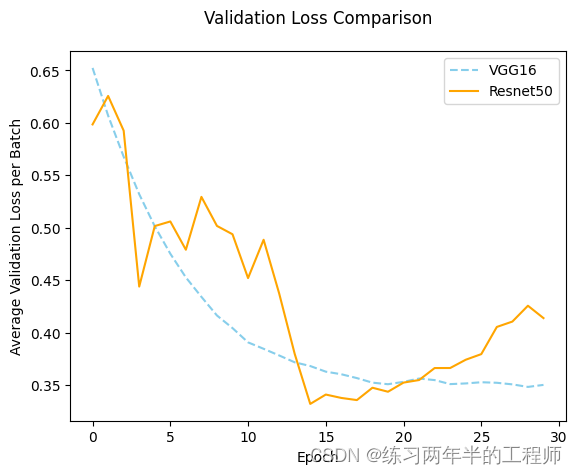
12. 绘画验证损失的比较图
plt.figure()
df_valid_loss = pd.DataFrame({'Epoch': range(0, N_EPOCHS, 1),
'valid_loss_vgg': history_vgg['val_loss'],
'valid_loss_resnet50':history_resnet50['val_loss']
})
plota, = plt.plot('Epoch', 'valid_loss_vgg', data=df_valid_loss, linestyle = '--', color = 'skyblue')
plotb, = plt.plot('Epoch', 'valid_loss_resnet50', data=df_valid_loss, color = 'orange')
plt.xlabel('Epoch')
plt.ylabel('Average Validation Loss per Batch')
plt.title('Validation Loss Comparison', pad = 20)
plt.legend([plota, plotb], ['VGG16', 'Resnet50'])
plt.savefig('Result_Comparison.png')
13. 定义并执行预测函数
def predict(mymodel, model_name_pt, loader):
model = mymodel
model.load_state_dict(torch.load(model_name_pt))
model.to(device)
model.eval()
y_actual_np = []
y_pred_np = []
for idx, data in enumerate(loader):
test_x, test_label = data[0], data[1]
test_x = test_x.to(device)
y_actual_np.extend(test_label.cpu().numpy().tolist())
with torch.no_grad():
y_pred_logits = model(test_x)
pred_labels = np.argmax(y_pred_logits.cpu().numpy(), axis=1)
print("Predicting ---->", pred_labels)
y_pred_np.extend(pred_labels.tolist())
return y_actual_np, y_pred_np
y_actual_vgg, y_predict_vgg = predict(model_vgg, "model_vgg.pt", test_loader)
y_actual_resnet50, y_predict_resnet50 = predict(model_resnet50, "model_resnet50.pt", test_loader)
14. 计算VGG的准确性和混淆矩阵
# VGG-16 Accuracy
print("=====================================================")
acc_rate_vgg = 100*accuracy_score(y_actual_vgg, y_predict_vgg)
print("The Accuracy rate for the VGG-16 model is: ", acc_rate_vgg)
# Confusion matrix for model-VGG-16
print("The Confusion Matrix for VGG-16 is as below:")
print(confusion_matrix(y_actual_vgg, y_predict_vgg))
输出为:
The Accuracy rate for the VGG-16 model is: 88.16666666666667
The Confusion Matrix for VGG-16 is as below:
[[7106 894]
[ 171 829]]
15. 计算Resnet的准确性和混淆矩阵
print("=====================================================")
acc_rate_resnet50 = 100*accuracy_score(y_actual_resnet50, y_predict_resnet50)
print("The Accuracy rate for the Resnet50 model is: ", acc_rate_resnet50)
# Confusion matrix for model Resnet50
print("The Confusion Matrix for Resnet50 is as below:")
print(confusion_matrix(y_actual_resnet50, y_predict_resnet50))
输出为:
The Accuracy rate for the Resnet50 model is: 85.35555555555555
The Confusion Matrix for Resnet50 is as below:
[[6843 1157]
[ 161 839]]