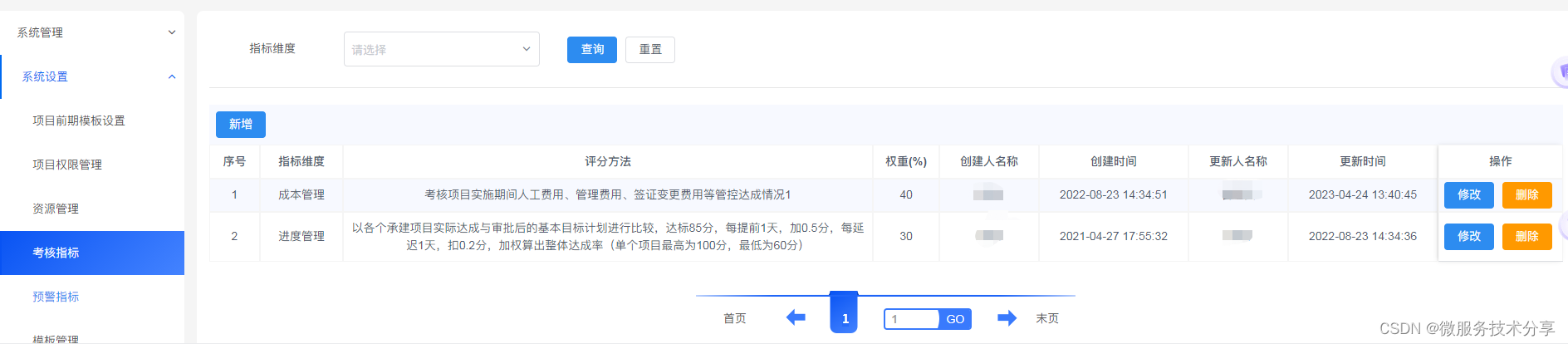
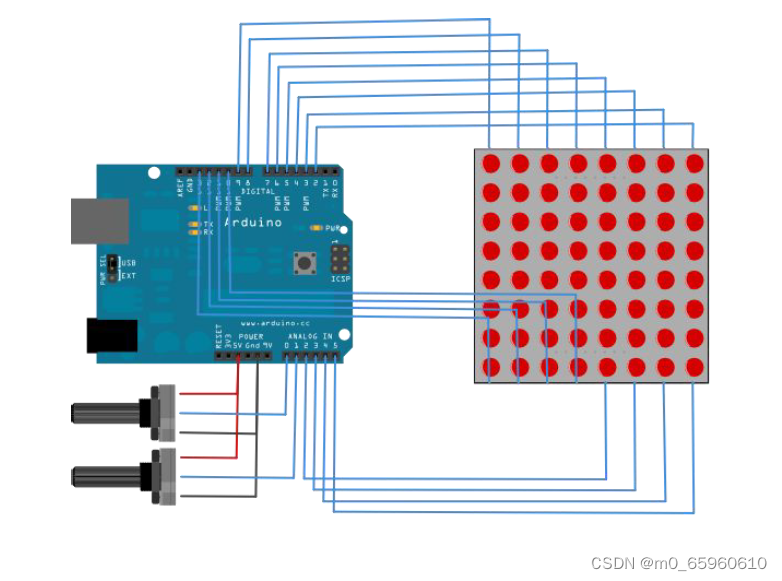
硬件准备
8*8点阵:1个
旋钮电位器:1个
面包板:1块
杜邦线:若干
硬件连线
软件程序
//定义引脚
#define xKnob_pin A0 //x轴旋钮的引脚
#define yKnob_pin A1 //y轴旋钮的引脚
const int row_pin[8] = { 6, 11, 10, 3, 17, 4, 8, 9 }; // 行引脚对应的数组
const int col_pin[8] = { 2, 7, 19, 5, 13, 18, 12, 16 }; // 列引脚对应的数组
int pixels[8][8]; // 点阵对应的数组
//定义变量
unsigned int x_val = -1;//x轴变量
unsigned int y_val = -1;
//函数声明
void Init();
void display();
void test();
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
for (int thisRow = 0; thisRow < 8; thisRow++) {
pinMode(row_pin[thisRow], OUTPUT); //设置行引脚为输出模式
digitalWrite(row_pin[thisRow], LOW); //行引脚输出低电平
}
for (int thisCol = 0; thisCol < 8; thisCol++) {
pinMode(col_pin[thisCol], OUTPUT); //设置列引脚为输出模式
digitalWrite(col_pin[thisCol], HIGH); //列引脚输出高电平
}
}
void loop() {
Init();
display();
//test();
}
void Init(){
for (int thisRow = 0; thisRow < 8; thisRow++) {
digitalWrite(row_pin[thisRow], LOW); //行引脚输出低电平
}
for (int thisCol = 0; thisCol < 8; thisCol++) {
digitalWrite(col_pin[thisCol], HIGH); //列引脚输出高电平
}
}
void display(){
//读取旋钮模拟值,映射为0~7
x_val = map(analogRead(xKnob_pin),0,1023,0,7);
y_val = map(analogRead(yKnob_pin),0,1023,0,7);
Serial.print("x ");
Serial.println(x_val);
Serial.print("y ");
Serial.println(y_val);
//根据模拟值决定哪行哪列亮
digitalWrite(col_pin[y_val], LOW);
digitalWrite(row_pin[x_val], HIGH);
}
void test() {
for (int thisCol = 0; thisCol < 8; thisCol++) {
digitalWrite(col_pin[thisCol], LOW); //列引脚输出低电平
for (int thisRow = 0; thisRow < 8; thisRow++) {
digitalWrite(row_pin[thisRow], HIGH);
delay(500);
digitalWrite(row_pin[thisRow], LOW);
}
digitalWrite(col_pin[thisCol], HIGH); //列引脚输出高电平
}
}产品展示视频
【Arduino24】88点阵
总结
通过本次实验,我学会了8*8点阵的使用,并复习了旋钮电位器的知识。