目录
- ChatGpt问答
- 原生代码
- 简单工厂模式代码
- 简单工厂模式(Simple Factory Pattern)
- 新增boat 对比两种方法
- 原生代码
- 为什么使用强制转换?
- 简单工厂模式
- 简单工厂方法总结
- 与原生代码的区别:
- 优点:
- 缺点:
- 参考
本文将介绍什么事简单工厂模式,为什么要使用这个模式?比起原生代码它是如何降低代码的耦合度的,以及详细的代码对比,结合ChatGPT的问答进行讲解,也是自己学习的记录,有不对的地方请指正。
ChatGpt问答
Q:Give an example to illustrate the benefits of reducing the coupling
of the simple factory model in java, which is best reflected in code
举个例子来说明java中简单工厂模式减少耦合的好处,在代码中最能体现
Certainly! Let’s illustrate the benefits of reducing coupling by using a simple factory model in Java. We’ll start with a coupled implementation and then refactor it to reduce coupling.
当然! 让我们说明一下在 Java 中使用简单工厂模型来减少耦合的好处。 我们将从耦合实现开始,然后重构它以减少耦合。
Coupled Implementation (High Coupling):
Consider a simple factory that produces different types of vehicles (e.g., cars and bicycles) based on a provided type. In this coupled example, the factory method has a high level of coupling with the concrete vehicle classes.
考虑一个简单的工厂,它根据提供的类型生产不同类型的车辆(例如汽车和自行车)。 在这个耦合示例中,工厂方法与具体车辆类具有高度耦合。
原生代码
class VehicleFactory {
public Vehicle createVehicle(String type) {
if ("car".equalsIgnoreCase(type)) {
return new Car();
} else if ("bicycle".equalsIgnoreCase(type)) {
return new Bicycle();
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid vehicle type");
}
}
}
class Car {
void start() {
System.out.println("Car started.");
}
}
class Bicycle {
void start() {
System.out.println("Bicycle started.");
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
VehicleFactory factory = new VehicleFactory();
Vehicle vehicle1 = factory.createVehicle("car");
vehicle1.start(); // Output: Car started.
Vehicle vehicle2 = factory.createVehicle("bicycle");
vehicle2.start(); // Output: Bicycle started.
}
}
In this example, the VehicleFactory class has high coupling because it directly creates instances of Car and Bicycle. If we need to add more types of vehicles in the future, we would need to modify the factory method, resulting in increased coupling and reduced flexibility.
在这个例子中,VehicleFactory类具有高耦合性,因为它直接创建Car和Bicycle的实例。 如果以后需要增加更多类型的车辆,就需要修改工厂方法,导致耦合性增加,灵活性降低。
简单工厂模式代码
Reduced Coupling Implementation (Low Coupling):
To reduce coupling, we can use interfaces and abstract classes to define a common contract for all vehicles. This way, the factory method doesn’t need to know the concrete classes of vehicles.
interface Vehicle {
void start();
}
class Car implements Vehicle {
public void start() {
System.out.println("Car started.");
}
}
class Bicycle implements Vehicle {
public void start() {
System.out.println("Bicycle started.");
}
}
class VehicleFactory {
public Vehicle createVehicle(String type) {
if ("car".equalsIgnoreCase(type)) {
return new Car();
} else if ("bicycle".equalsIgnoreCase(type)) {
return new Bicycle();
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid vehicle type");
}
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
VehicleFactory factory = new VehicleFactory();
Vehicle vehicle1 = factory.createVehicle("car");
vehicle1.start(); // Output: Car started.
Vehicle vehicle2 = factory.createVehicle("bicycle");
vehicle2.start(); // Output: Bicycle started.
}
}
In this refactored example, we’ve introduced an interface Vehicle, which both Car and Bicycle implement. The VehicleFactory now returns instances of the Vehicle interface instead of concrete classes. This reduces coupling because the factory method doesn’t depend on specific implementations, making it easier to extend the system with new types of vehicles without modifying existing code.
在这个重构的示例中,我们引入了一个“Vehicle”接口,“Car”和“Bicycle”都实现了该接口。 “VehicleFactory”现在返回“Vehicle”接口的实例,而不是具体类。 这减少了耦合,因为工厂方法不依赖于特定的实现,从而可以更轻松地使用新型车辆扩展系统,而无需修改现有代码。
简单工厂模式(Simple Factory Pattern)
是一种创建型设计模式,它提供了一种简单的方法来创建对象,而不需要直接暴露对象的创建逻辑给客户端。
简单工厂模式又称静态工厂方法模式。它存在的目的很简单:定义一个用于创建对象的接口。
组成结构:
-
工厂类角色(Creator):这是本模式的核心,含有一定的商业逻辑和判断逻辑。在java中它往往由一个具体类实现。
-
抽象产品角色(Product):它一般是具体产品继承的父类或者实现的接口。在java中由接口或者抽象类来实现。
-
具体产品角色(ConcreteProduct):工厂类所创建的对象就是此角色的实例。在java中由一个具体类实现。
用类图表示它们之间的关系
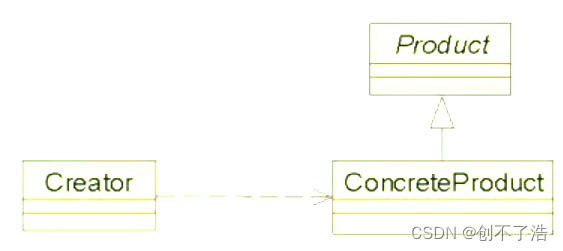
抽象产品角色–Vehicle 交通工具
具体产品角色 – Car、Bicycle
工厂类角色–VehicleFactory
新增boat 对比两种方法
原生代码
Certainly! In a high coupling approach, you would directly create instances of vehicle classes within the factory method, which can lead to tight dependencies between the factory and the concrete vehicle classes. Here’s an example of a high coupling approach:
当然! 在高耦合方法中,您将直接在工厂方法中创建车辆类的实例,这可能导致工厂和具体车辆类之间的紧密依赖关系。 这是一个高耦合方法的示例:
class Car {
void start() {
System.out.println("Car started.");
}
}
class Bicycle {
void start() {
System.out.println("Bicycle started.");
}
}
class Boat {
void start() {
System.out.println("Boat started.");
}
}
class VehicleFactory {
public Object createVehicle(String type) {
if ("car".equalsIgnoreCase(type)) {
return new Car();
} else if ("bicycle".equalsIgnoreCase(type)) {
return new Bicycle();
} else if ("boat".equalsIgnoreCase(type)) {
return new Boat();
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid vehicle type");
}
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
VehicleFactory factory = new VehicleFactory();
Car car = (Car) factory.createVehicle("car");
car.start(); // Output: Car started.
Bicycle bicycle = (Bicycle) factory.createVehicle("bicycle");
bicycle.start(); // Output: Bicycle started.
Boat boat = (Boat) factory.createVehicle("boat");
boat.start(); // Output: Boat started.
}
}
In this high coupling approach:
- Each vehicle class (
Car,Bicycle,Boat) is directly instantiated within thecreateVehiclemethod of theVehicleFactory. - To use a specific vehicle, you need to cast the object returned by the factory to the corresponding vehicle class (
Car,Bicycle,Boat). - Adding a new type of vehicle would require modifying the
VehicleFactoryto create that vehicle type directly.
在这种高耦合方法中:
- 每个车辆类(“Car”、“Bicycle”、“Boat”)都直接在“VehicleFactory”的“createVehicle”方法中实例化。
- 要使用特定的车辆,需要将工厂返回的对象转换为相应的车辆类(
Car、Bicycle、Boat)。 - 添加新类型的车辆需要修改
VehicleFactory以直接创建该车辆类型。
High coupling can make the code less flexible and harder to maintain because any changes to the factory method or the concrete vehicle classes may affect other parts of the code that rely on them. It’s generally a best practice to reduce coupling and use interfaces or abstract classes to achieve better flexibility and maintainability.
高耦合会使代码不太灵活且难以维护,因为对工厂方法或具体车辆类的任何更改都可能会影响依赖它们的代码的其他部分。 通常,最佳实践是减少耦合并使用接口或抽象类来实现更好的灵活性和可维护性。
为什么使用强制转换?
Car car = (Car) factory.createVehicle(“car”)
In the high coupling approach I provided earlier, you are correct that type casting is required when you retrieve the created objects from the factory. This is a limitation of high coupling because you’re directly creating instances of specific classes within the factory method. Let me explain this in more detail:
In the createVehicle method of the VehicleFactory, the factory creates instances of Car, Bicycle, or Boat based on the type parameter.
Since the createVehicle method is declared to return an Object, when you retrieve the created object, it’s treated as an Object reference.
To use the specific functionality of a Car, for example, you need to cast the Object reference back to Car to access Car-specific methods like start.
This type casting introduces potential issues because if you provide the wrong type for the type parameter or if you introduce a new vehicle type in the future, you might get runtime errors (ClassCastException) if the casting doesn’t match the actual type.
In contrast, a low coupling approach, as demonstrated in the previous example, uses interfaces or abstract classes to create a common contract for all vehicles. This way, you can avoid type casting and handle all vehicles uniformly by relying on the common interface. It provides better flexibility, maintainability, and type safety, as you don’t need to cast objects to specific types when using them.
在我之前提供的高耦合方法中,当您从工厂检索创建的对象时,需要进行类型转换,这是正确的。 这是高耦合的限制,因为您是在工厂方法中直接创建特定类的实例。 让我更详细地解释一下:
在 VehicleFactory 的 createVehicle 方法中,工厂根据类型参数创建 Car、Bicycle 或 Boat 的实例。
由于 createVehicle 方法被声明为返回一个对象,因此当您检索创建的对象时,它将被视为对象引用。
例如,要使用汽车的特定功能,您需要将对象引用强制转换回汽车以访问汽车特定的方法,例如启动。
这种类型转换会带来潜在的问题,因为如果您为类型参数提供了错误的类型,或者如果您将来引入新的车辆类型,并且转换与实际类型不匹配,则可能会出现运行时错误 (ClassCastException)。
相反,低耦合方法(如前面的示例所示)使用接口或抽象类为所有车辆创建通用契约。 这样,您可以避免类型转换并依靠通用接口统一处理所有车辆。 它提供了更好的灵活性、可维护性和类型安全性,因为您在使用对象时不需要将对象强制转换为特定类型。
简单工厂模式
Q:show me High Coupling method
Certainly! Let’s add a new Boat vehicle to the existing code. We’ll follow the same approach of using an interface for Boat and updating the factory method to create Boat instances without modifying the existing code.
当然! 让我们在现有代码中添加一个新的“Boat”车辆。 我们将遵循相同的方法,使用“Boat”接口并更新工厂方法来创建“Boat”实例,而无需修改现有代码。
Adding a Boat Vehicle (Low Coupling):
interface Vehicle {
void start();
}
class Car implements Vehicle {
public void start() {
System.out.println("Car started.");
}
}
class Bicycle implements Vehicle {
public void start() {
System.out.println("Bicycle started.");
}
}
class Boat implements Vehicle {
public void start() {
System.out.println("Boat started.");
}
}
class VehicleFactory {
public Vehicle createVehicle(String type) {
if ("car".equalsIgnoreCase(type)) {
return new Car();
} else if ("bicycle".equalsIgnoreCase(type)) {
return new Bicycle();
} else if ("boat".equalsIgnoreCase(type)) {
return new Boat();
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid vehicle type");
}
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
VehicleFactory factory = new VehicleFactory();
Vehicle vehicle1 = factory.createVehicle("car");
vehicle1.start(); // Output: Car started.
Vehicle vehicle2 = factory.createVehicle("bicycle");
vehicle2.start(); // Output: Bicycle started.
Vehicle vehicle3 = factory.createVehicle("boat");
vehicle3.start(); // Output: Boat started.
}
}
In this updated code, we’ve introduced a new Boat class that implements the Vehicle interface. The VehicleFactory has been updated to handle the creation of Boat instances when “boat” is passed as the type. This allows us to add a new type of vehicle (in this case, a boat) without modifying the existing code for the factory or the other vehicles. This demonstrates the flexibility and low coupling achieved by using interfaces and an abstract factory approach.
在此更新的代码中,我们引入了一个新的“Boat”类,它实现了“Vehicle”接口。 “VehicleFactory”已更新,可以在“boat”作为类型传递时处理“Boat”实例的创建。 这使我们能够添加一种新型车辆(在本例中为船),而无需修改工厂或其他车辆的现有代码。 这展示了通过使用接口和抽象工厂方法实现的灵活性和低耦合。
简单工厂方法总结
与原生代码的区别:
从三个维度来说明:
抽象产品角色–Vehicle 交通工具
具体产品角色 – Car、Bicycle
工厂类角色–VehicleFactory
1 简单工厂模式中抽象产品角色Vehicle 使用interface,原生代码是class
2 简单工厂模式中具体产品角色Car,需要实现接口,原生代码为单独类
3 简单工厂模式中具体工厂类角色–VehicleFactory 返回对象是Vehicle 接口,原生代码的返回对象是Object
优点:
- 将对象的创建逻辑集中在工厂类中,降低了客户端的复杂度。
- 隐藏了创建对象的细节,客户端只需要关心需要创建何种对象,无需关心对象是如何创建的。
可以通过修改工厂类来轻松添加新的产品类
缺点:
- 如果产品的类太多,会导致工厂类中的代码变得很复杂,难以维护。
- 添加新产品时,需要修改工厂类,也就是会在OperationFactory类中新增case语句,这违背了开闭原则。
总体而言,简单工厂模式适用于创建对象的逻辑相对简单,且产品类的数量较少的场景。对于更复杂的对象创建和对象之间的依赖关系,可以考虑使用其他创建型设计模式,如工厂方法模式或抽象工厂模式。
参考
1 设计模式-01.简单工厂方法https://juejin.cn/post/7267091509953855543
2 JAVA设计模式(三) – 工厂模式
https://juejin.cn/post/7257441765976162361?searchId=202309061335355A323BC0D43AD67B950D#heading-0