🎈个人主页:🎈 :✨✨✨初阶牛✨✨✨
🐻推荐专栏1: 🍔🍟🌯C语言初阶
🐻推荐专栏2: 🍔🍟🌯C语言进阶
🔑个人信条: 🌵知行合一
🍉本篇简介:>:介绍vector的使用
vector官网链接:传送门
目录
- 一、构造函数
- (1)无参构造
- (2)初始化为n个值
- (3) 迭代器区间初始化
- (4)拷贝构造
- 二、容量操作
- (1) 一览表
- (2) 代码演示
- 三、修改与访问
- (1) push_back && pop_back
- assign()
- (2) insert()
- (3) erase()函数
- (4) swap()
- (5) `[]`运算符重载
一、构造函数

| 构造函数 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| vector (const allocator_type& alloc = allocator_type()); | 无参构造 |
| vector(size_type n, const value_type& val = value_type()) | 初始化为n个val |
| vector (InputIterator first, InputIterator last,const allocator_type& alloc = allocator_type()) | 迭代器区间初始化 |
| vector (const vector& x); | 拷贝构造 |
(1)无参构造
默认什么元素也没有.
有效元素个数:size=0
容量:capacity=0;
//无参构造
vector<int> v1;
//auto it1 = v1.begin();//可以使用auto自动推导类型
vector<int>::iterator it1 = v1.begin();
while (it1 != v1.end())
{
cout << *it1 << " ";
it1 ++ ;
}
cout << "v1.size=" << v1.size() << endl;
cout << "v1.capacity=" << v1.capacity() << endl;
cout << endl;
运行结果:
v1.size=0
v1.capacity=0
(2)初始化为n个值
用n个val去初始化vector;
//初始化为n个值
vector<int> v2(4,0);
//auto it2 = v2.begin();
vector<int>::iterator it2 = v2.begin();
while (it2 != v2.end())
{
cout << *it2 << " ";
it2++;
}
cout << endl;
运行结果:
0 0 0 0
(3) 迭代器区间初始化
用一个迭代器区间进行初始化,这里采用数组的头和尾作为迭代器区间.
//迭代器区间初始化
int a3[10] = { 1,3,4,5,6,7,8,98,100,11 };
vector<int> v3(a3, a3 + 10);//注意这里给的是+10,因为迭代器的end是指向最后一个有效元素的下一个位置,左闭右开
auto it3 = v3.begin();
while (it3 != v3.end())
{
cout << *it3 << " ";
it3++;
}
cout << endl;
运行结果:
1 3 4 5 6 7 8 98 100 11
(4)拷贝构造
//拷贝构造
vector<int> v4(v3);//v3就是上面的迭代器区间初始化好的v3
auto it4 = v4.begin();
while (it4 != v4.end())
{
cout << *it4 << " ";
it4++;
}
cout << endl;
运行结果:
1 3 4 5 6 7 8 98 100 11
二、容量操作
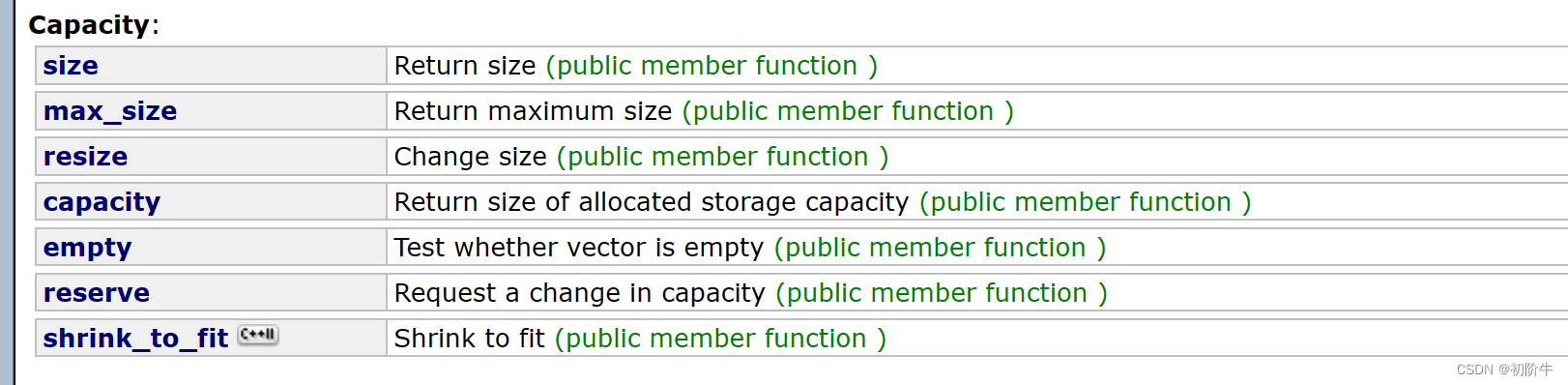
(1) 一览表
| 接口 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| size() | 有效数据的个数 |
| resize() | 改变有效数据的个数 |
| capacity() | 容量大小 |
| empty() | 判空 |
| reserve() | 改变容量大小 |
(2) 代码演示
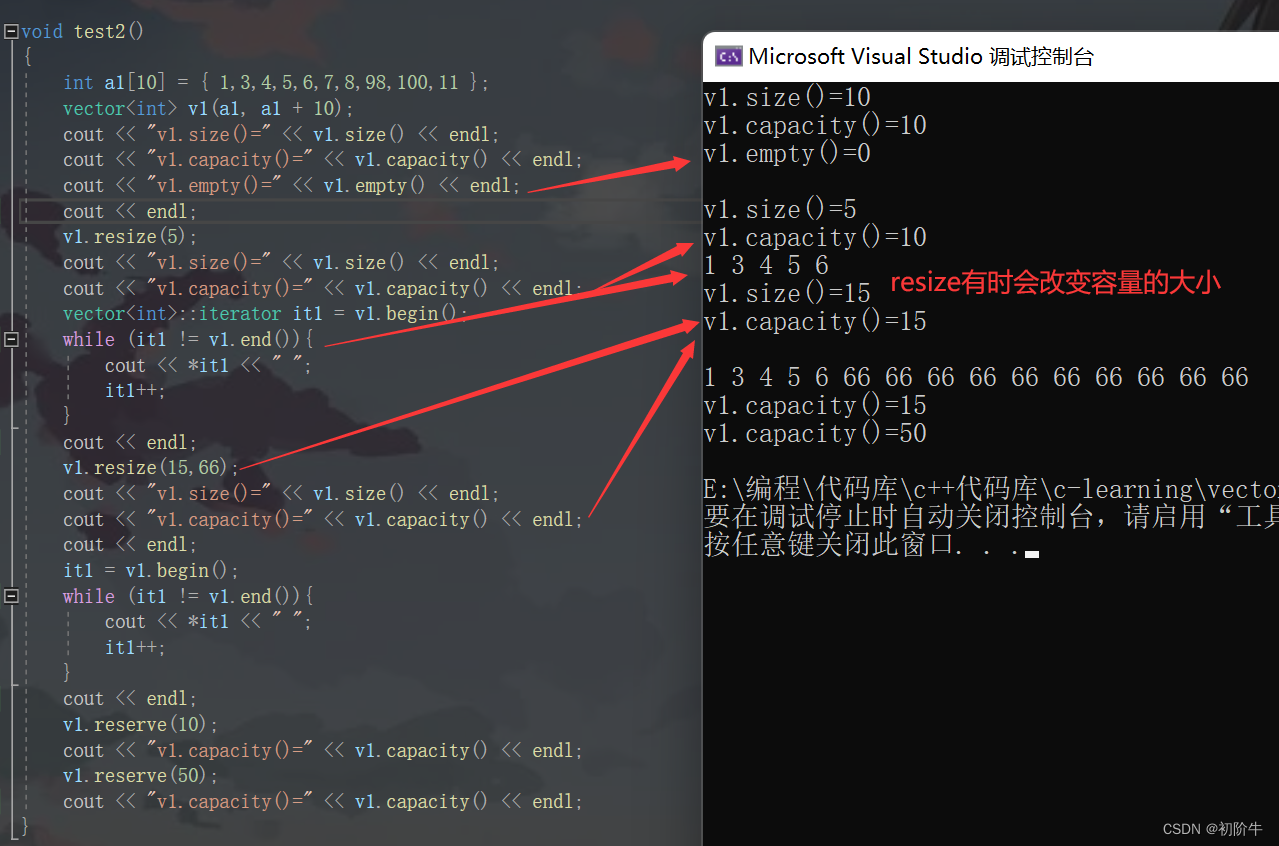
void test2()
{
int a1[10] = { 1,3,4,5,6,7,8,98,100,11 };
vector<int> v1(a1, a1 + 10);
cout << "v1.size()=" << v1.size() << endl;//显示有效数据的个数
cout << "v1.capacity()=" << v1.capacity() << endl;//显示容量的大小
cout << "v1.empty()=" << v1.empty() << endl;//判断容器是否为NULL
cout << endl;
v1.resize(5);//改变有效数据的个数
cout << "v1.size()=" << v1.size() << endl;
cout << "v1.capacity()=" << v1.capacity() << endl;
vector<int>::iterator it1 = v1.begin();
while (it1 != v1.end())
{
cout << *it1 << " ";
it1++;
}
cout << endl;
v1.resize(15,66);
cout << "v1.size()=" << v1.size() << endl;
cout << "v1.capacity()=" << v1.capacity() << endl;
cout << endl;
it1 = v1.begin();
while (it1 != v1.end())
{
cout << *it1 << " ";
it1++;
}
cout << endl;
v1.reserve(10);//改变容量的大小.
cout << "v1.capacity()=" << v1.capacity() << endl;
v1.reserve(50);
cout << "v1.capacity()=" << v1.capacity() << endl;
}
运行结果:
三、修改与访问

| 接口 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| assign() | 将新内容覆盖给容器,替换其当前内容,并相应地修改其大小。 |
| push_back() | 尾插 |
| pop_back() | 尾删 |
| insert() | 指定位置pos之前插入 |
| erase() | 删除指定位置pos的值 |
| swap() | 交换两个容器 |
operator[ ]() | 下标访问运算符重载 |
(1) push_back && pop_back
尾插和尾删相信大家已经比较熟悉了.
assign()
assign函数需要注意.
void assign (size_type n, const value_type& val);
如果n<size,则是将n个val将原有数据覆盖,令size=n,而不修改容量.
如果n>size,则先扩容,再将n个val值存入.
//push_back &&pop_back
int a1[5] = { 1,2,3,4,5 };
vector<int> v1(a1, a1 + 5);
for (auto itt : v1){ //1 2 3 4 5
cout << itt << " ";
}
cout << endl;
//尾插
v1.push_back(6);
v1.push_back(7);
for (auto itt : v1){ //1 2 3 4 5 6 7
cout << itt << " ";
}
cout << endl;
//尾删
v1.pop_back();
for (auto itt : v1){ //1 2 3 4 5 6
cout << itt<<" ";
}
cout << endl;
//将新内容覆盖给容器,替换其当前内容,并相应地修改其大小
v1.assign(5, 2);
for (auto itt : v1){ //2 2 2 2 2
cout << itt << " ";
}
cout << endl << v1.size() << " " << v1.capacity() << endl;//5 7
cout << endl;
运行结果:
1 2 3 4 5
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
1 2 3 4 5 6
2 2 2 2 2
5 7
(2) insert()
指定位置pos之前插入.

代码演示:
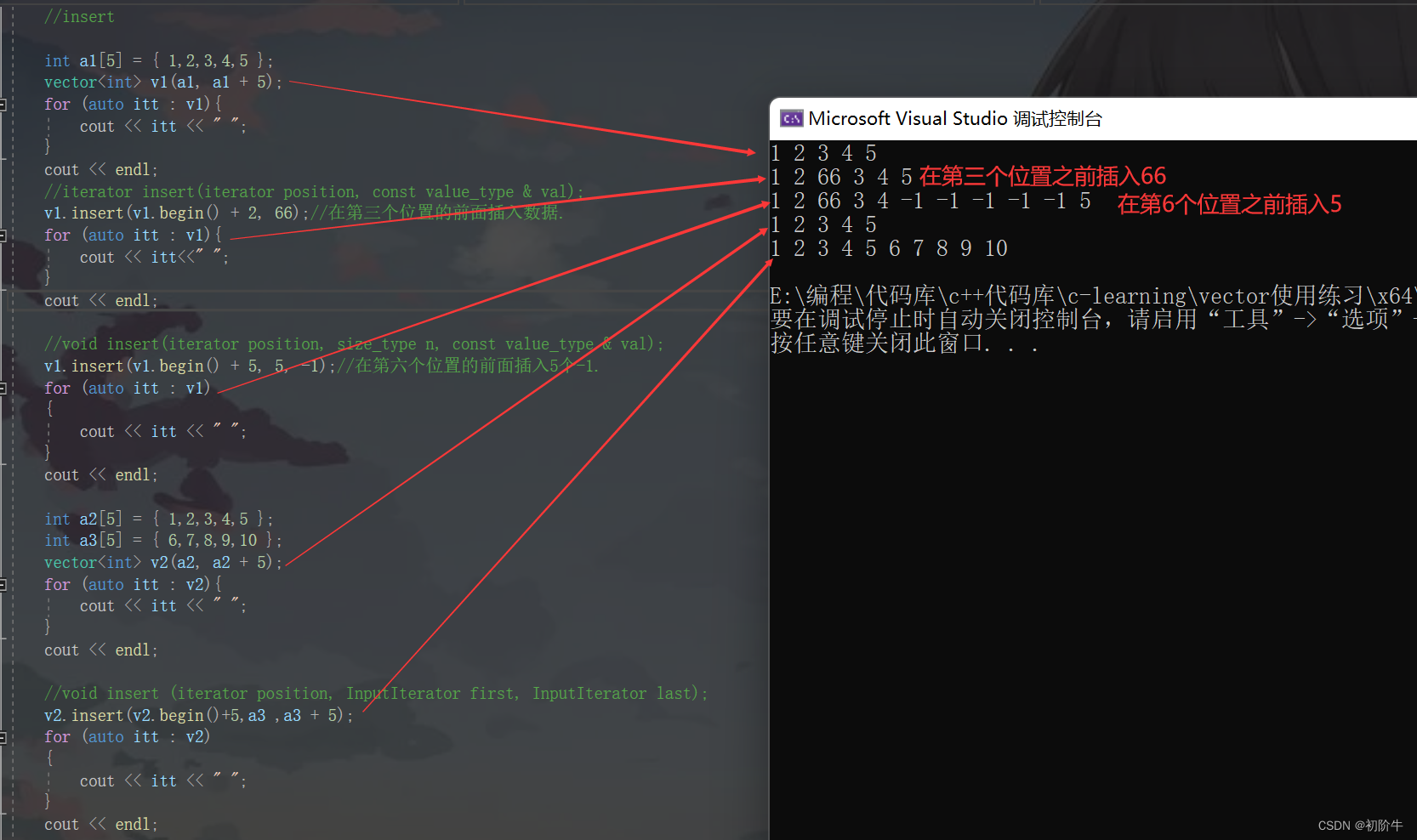
int a1[5] = { 1,2,3,4,5 };
vector<int> v1(a1, a1 + 5);
for (auto itt : v1){
cout << itt << " ";
}
cout << endl;
//iterator insert(iterator position, const value_type & val);
v1.insert(v1.begin() + 2, 66);//在第三个位置的前面插入数据.
for (auto itt : v1)
{
cout << itt<<" ";
}
cout << endl;
//void insert(iterator position, size_type n, const value_type & val);
v1.insert(v1.begin() + 5, 5, -1);//在第六个位置的前面插入5个-1.
for (auto itt : v1)
{
cout << itt << " ";
}
cout << endl;
int a2[5] = { 1,2,3,4,5 };
int a3[5] = { 6,7,8,9,10 };
vector<int> v2(a2, a2 + 5);
for (auto itt : v2)
{
cout << itt << " ";
}
cout << endl;
//void insert (iterator position, InputIterator first, InputIterator last);
v2.insert(v2.begin()+5,a3 ,a3 + 5);
for (auto itt : v2)
{
cout << itt << " ";
}
cout << endl;
运行结果:
(3) erase()函数
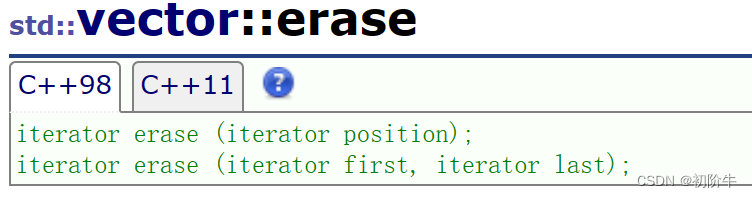
删除指定位置pos的值
//erase
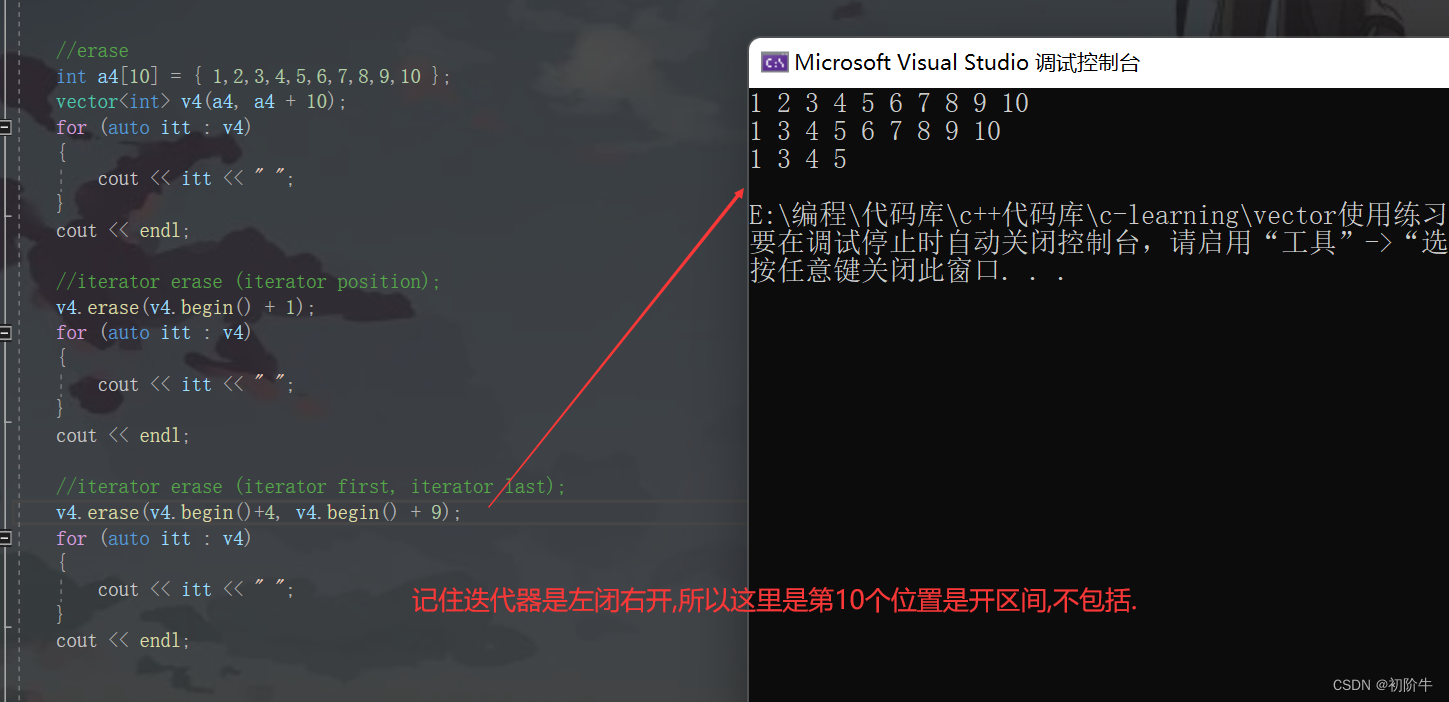
int a4[10] = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10 };
vector<int> v4(a4, a4 + 10);
for (auto itt : v4)
{
cout << itt << " ";
}
cout << endl;
//iterator erase (iterator position);
v4.erase(v4.begin() + 1);
for (auto itt : v4)
{
cout << itt << " ";
}
cout << endl;
//iterator erase (iterator first, iterator last);
v4.erase(v4.begin()+4, v4.begin() + 9);
for (auto itt : v4)
{
cout << itt << " ";
}
cout << endl;
运行结果:
(4) swap()
用于交换两个容器,注意观察交换后容量的变化.
//swap
//void swap(vector & x);
int a5[10] = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10 };
vector<int> v5(a5, a5 + 10);
int a6[10] = { 2,4,6,8,10 };
vector<int> v6(a6, a6+5);
cout << "v5=";
for (auto itt : v5){
cout << itt << " ";
}
cout << endl;
cout << "v6=";
for (auto itt : v6){
cout << itt << " ";
}
cout << endl;
swap(v5, v6);
cout << endl;
cout << "v5=";
for (auto itt : v5){
cout << itt << " ";
}
cout << endl;
cout << "v6=";
for (auto itt : v6){
cout << itt << " ";
}
cout << endl;
cout << "v5.capacity()" << v5.capacity();
cout << endl;
cout << "v6.capacity()" << v6.capacity();
cout << endl;
运行结果:

(5) []运算符重载
可以像数组一样通过下标直接访问.
//[]
int a7[10] = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10 };
vector<int> v7(a5, a5 + 10);
cout << "v7=";
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
cout << v7[i] << " ";
}
v7=1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
vector的使用就分享到这里了.下一期vector模拟实现见.