一、JDK体系
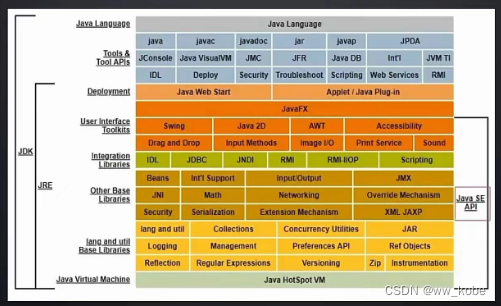
二、JVM体系

三、JVM内存模型
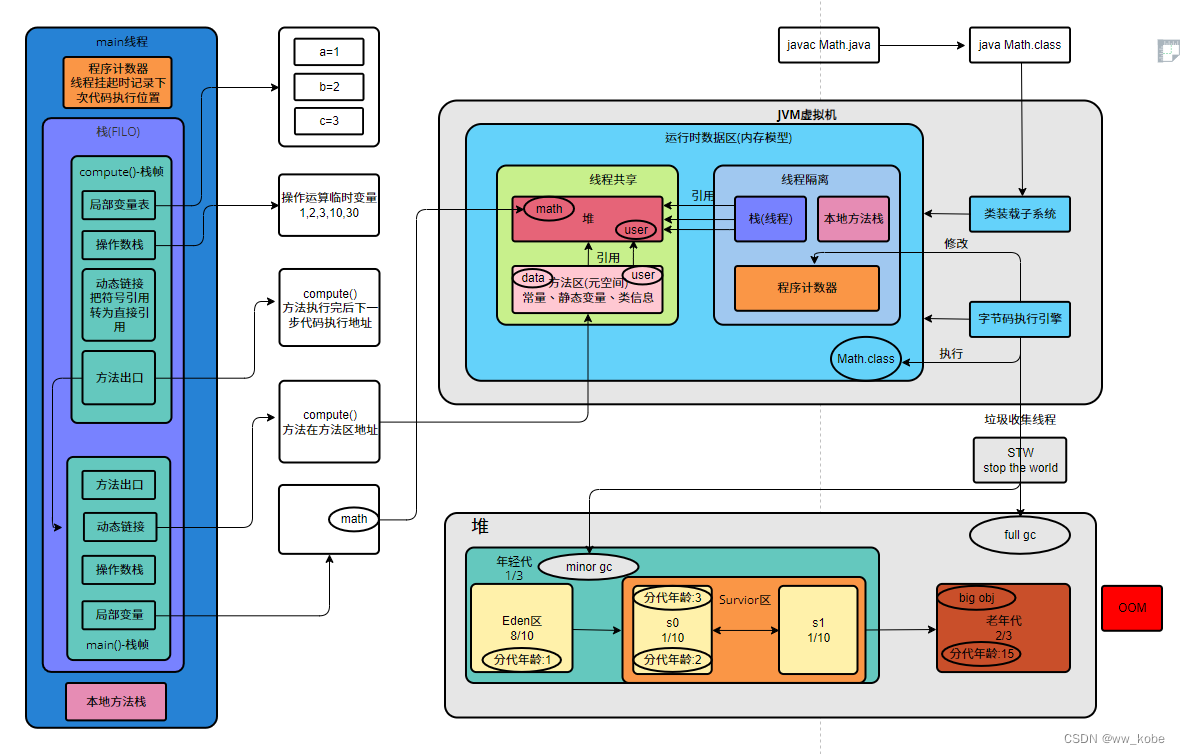
public class Math {
public static final int data = 666;
public static UserEntity user = new UserEntity();
public int compute() { // 一个方法对应一块栈帧内存区域
int a = 1;
int b = 2;
int c = (a+b)*10;
return c;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Math math = new Math();
math.compute();
// 底层会调用start0(),是一个本地方法(C++实现的private native void start0())
new Thread().start();
System.out.println("--------end--------");
}
}对代码进行反汇编:javap -c Math.class > math.txt
Compiled from "Math.java"
public class com.ww.sso.controller.Math {
public static final int data;
public static com.ww.sso.entity.UserEntity user;
public com.ww.sso.controller.Math();
Code:
0: aload_0
1: invokespecial #1 // Method java/lang/Object."<init>":()V
4: return
public int compute();
Code:
0: iconst_1 // JVM指令码
1: istore_1
2: iconst_2
3: istore_2
4: iload_1
5: iload_2
6: iadd
7: bipush 10
9: imul
10: istore_3
11: iload_3
12: ireturn
public static void main(java.lang.String[]);
Code:
0: new #2 // class com/ww/sso/controller/Math
3: dup
4: invokespecial #3 // Method "<init>":()V
7: astore_1
8: aload_1
9: invokevirtual #4 // Method compute:()I
12: pop
13: getstatic #5 // Field java/lang/System.out:Ljava/io/PrintStream;
16: ldc #6 // String --------end--------
18: invokevirtual #7 // Method java/io/PrintStream.println:(Ljava/lang/String;)V
21: return
static {};
Code:
0: new #8 // class com/ww/sso/entity/UserEntity
3: dup
4: invokespecial #9 // Method com/ww/sso/entity/UserEntity."<init>":()V
7: putstatic #10 // Field user:Lcom/ww/sso/entity/UserEntity;
10: return
}
public class HeapTest {
byte[] a = new byte[1024*100]; // 100KB
public static void main(String args) throws InterruptedException {
List<HeapTest> heapTestList = new ArrayList<>();
while (true) {
heapTestList.add(new HeapTest());
Thread.sleep(5);
}
}
}阿里巴巴Arthas![]() https://alibaba.github.io/arthas
https://alibaba.github.io/arthas
public class ArthasTest {
private static HashSet hashSet = new HashSet();
private static void main(String args) {
// 模拟CPU过高
cpuHigh();
// 模拟线程死锁
deadThread();
// 不断的想hashSet集合添加数据
addHashSetThread();
}
private static void addHashSetThread() {
new Thread(() -> {
// 初始化常量
int cnt = 0;
while (true) {
try {
hashSet.add("cnt"+cnt);
Thread.sleep(10000);
cnt++;
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}).start();
}
private static void deadThread() {
new Thread(() -> {
while (true) {
}
}).start();
}
private static void cpuHigh() {
Object objA = new Object();
Object objB = new Object();
Thread threadA = new Thread(() -> {
synchronized (objA) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + "get objA");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + "waiting get objB");
synchronized (objB) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + "get objB");
}
}
});
Thread threadB = new Thread(() -> {
synchronized (objB) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + "get objB");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + "waiting get objA");
synchronized (objA) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + "get objA");
}
}
});
threadA.start();
threadB.start();
}
}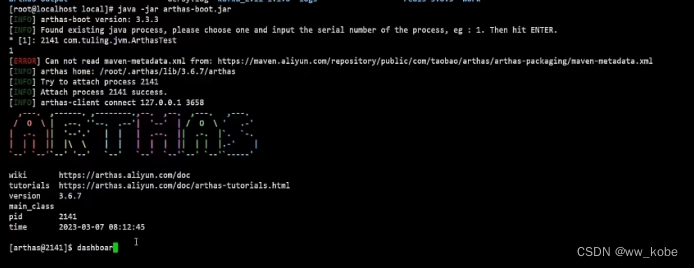
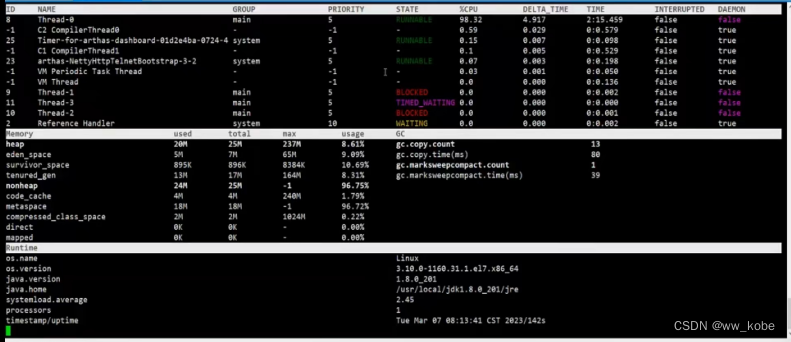
jad xxx.xxx.ArthasTest 命令反编译线上代码。
ognl 命令可以查看线上系统变量的值,甚至可以修改变量的值。
四、JVM优化
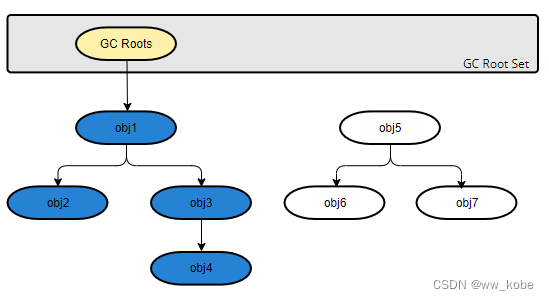
可达性分析算法
将“GC Roots”对象作为起点,从这些节点向下开始向下搜索引用对象,找到的对象都标记为非垃圾对象,其余未标记的对象都是垃圾对象。
GC Roots根节点:线程的本地变量、静态变量、本地方法栈的变量等等。
案例分析
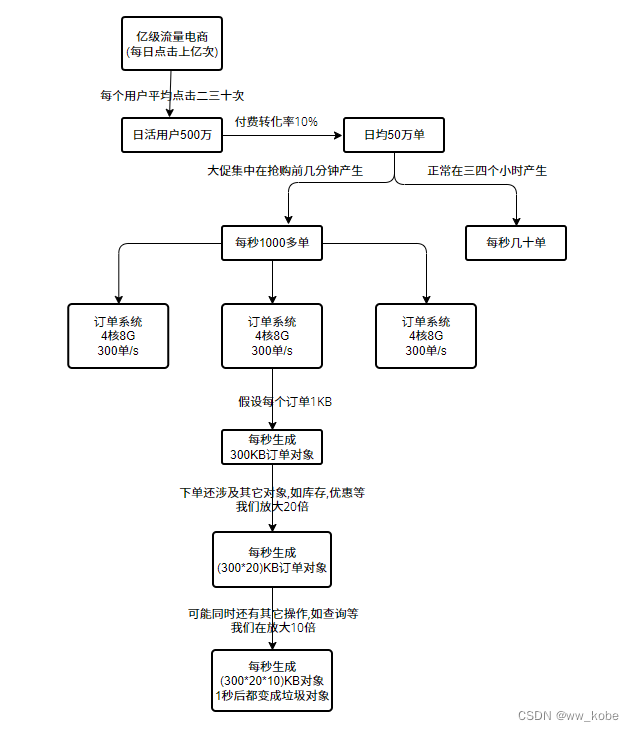
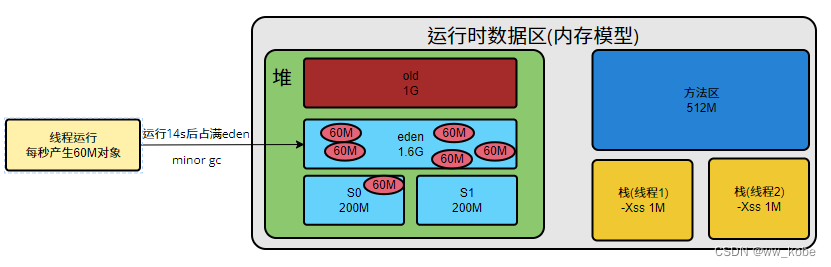
JVM参数设置:java -Xms3G -Xmx3G -Xss1M -XX:MetaspaceSize=512M
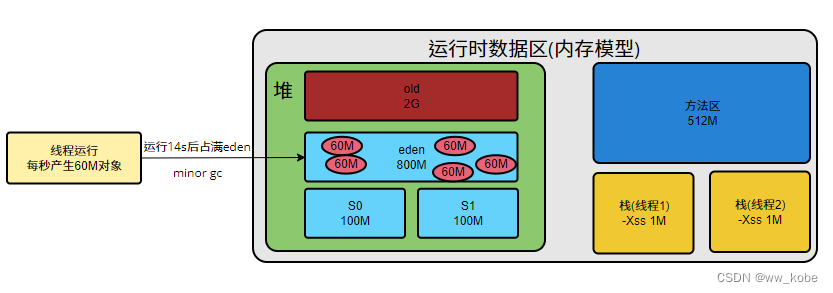
线程运行每秒产生60M对象,运行14s左右,eden区就满了,进行一次minor gc,触发对象动态年龄判断。
对象动态年龄判断
当前对象的survivor区域里(其中一块区域,放对象的那块s区),一批对象的总大小大于这块survivor区域内存大小的50%(-XX:TargetSurvivor可以指定),那么此时大于等于这批对象年龄最大值的对象,就可以直接进入老年代。例如survivor区域里现有一批对象,年龄1+年龄2+年龄n的多个对象总和超过survivor区域的50%,此时就把年龄n(含)以上的对象都放入老年代。这个规则希望那些可能是长期存活的对象尽早进入老年代。对象动态年龄判断机制一般在minor gc后出发。
问:能否对JVM调优,让其几乎不进行full gc ?
JVM参数设置:
java -Xms3G -Xmx3G -Xmn2G -Xss1M -XX:MetaspaceSize=512M -XX:MaxMetaspaceSize=512M