1、结构体的定义和使用
#include <iostream> using namespace std; #include <string> struct Student { string name; int age; int score; }s3; int main() { //1、 struct Student s1; s1.name = "张三"; s1.age = 18; s1.score = 100; cout << "姓名:" << s1.name << " 年龄:" << s1.age << " 分数:" << s1.score << endl; //2、 struct Student s2 = { "李四",19,80 }; cout << "姓名:" << s2.name << " 年龄:" << s2.age << " 分数:" << s2.score << endl; //3、 s3.name = "王五"; s3.age = 20; s3.score = 60; cout << "姓名:" << s3.name << " 年龄:" << s3.age << " 分数:" << s3.score << endl; system("pause"); return 0; }
结构体变量创建的时候 struct可以省略
2、结构体数组
#include <iostream> using namespace std; #include <string> struct Student { string name; int age; int score; }s3; int main() { struct Student stuArray[3] = { {"张三",18,100}, {"李四",28,99}, {"王五",38,66} }; stuArray[2].name = "赵六"; stuArray[2].age = 80; stuArray[2].score = 60; for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) { cout << stuArray[i].name <<" "<< stuArray[i].age <<" "<< stuArray[i].score << " "<<endl; } system("pause"); return 0; }
3、结构体指针
#include <iostream> using namespace std; #include <string> struct Student { string name; int age; int score; }; int main() { struct Student s = { "张三",18,100 }; struct Student* p = &s; cout << "姓名:" << p->name << " 年龄:" << p->age << " 成绩:" << p->score << endl; system("pause"); return 0; }
4、结构体嵌套结构体
#include <iostream> using namespace std; #include <string> struct student { string name; int age; int score; }; struct teacher { int id; string name; int age; struct student stu; }; int main() { teacher t; t.id = 10000; t.name = "老王"; t.age = 50; t.stu.name = "小王"; t.stu.age = 20; t.stu.score = 60; cout << "老师姓名:" << t.name << " 老师编号:" << t.id << " 老师年龄:" << t.age << " 老师辅导的学生姓名:" << t.stu.name << " 学生年龄:" << t.stu.age << " 学生成绩:" << t.stu.score << endl; system("pause"); return 0; }
5、结构体做函数参数
#include <iostream> using namespace std; #include <string> struct student { string name; int age; int score; }; void printfStudent1(struct student s) { cout << "在子函数中打印 姓名:" << s.name << " 年龄:" << s.age << " 分数:" << s.score << endl; } void printfStudent2(struct student* p) { cout << "子函数2中 姓名:" << p->name << " 年龄:" << p->age << " 分数:" << p->score << endl; } int main() { struct student s; s.name = "张三"; s.age = 20; s.score = 85; //cout << "main函数中打印 姓名:" << s.name << " 年龄:" << s.age << " 分数:" << s.score << endl; //printfStudent1(s); printfStudent2(&s); system("pause"); return 0; }
6、结构体中const的使用
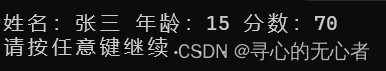
#include <iostream> using namespace std; #include <string> struct student { string name; int age; int score; }; void printfStudent(const student *s) { //s->age = 150;加入const之后,一旦有修改的操作就会报错,可以防止误操作 cout << "姓名:" << s->name << " 年龄:" << s->age << " 分数:" << s->score << endl; } int main() { struct student s; s.name = "张三"; s.age = 15; s.score = 70; printfStudent(&s); system("pause"); return 0; }
7、案例一
案例描述:
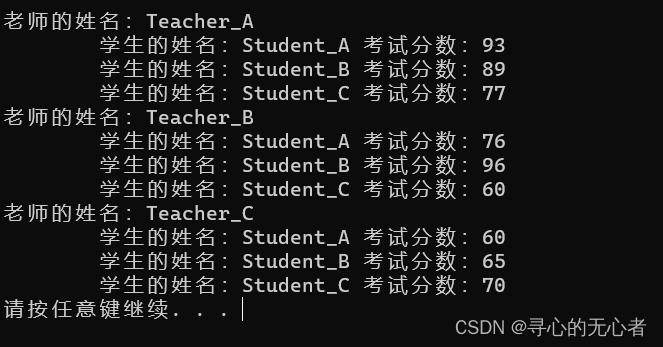
学校正在做毕设项目,每名老师带领5个学生,总共有3名老师,需求如下设计学生和老师的结构体,其中在老师的结构体中,有老师姓名和一个存放5名学生的数组作为成员。学生的成员有姓名、考试分数,创建数组存放3名老师,通过函数给每个老师及所带的学生赋值,最终打印出老师数据以及老师所带的学生数据。
#include <iostream> using namespace std; #include <string> #include <ctime> struct student { string sName; int score; }; struct Teacher { string tName; struct student sArray[5]; }; void allocatSpace(struct Teacher tArray[],int len) { string nameSeed = "ABCDE"; for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) { tArray[i].tName = "Teacher_"; tArray[i].tName += nameSeed[i]; for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++) { tArray[i].sArray[j].sName = "Student_"; tArray[i].sArray[j].sName += nameSeed[j]; int random = rand() % 61+40;//40`100 tArray[i].sArray[j].score = random; } } } void printfInfo(struct Teacher tArray[], int len) { for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) { cout << "老师的姓名:" << tArray[i].tName << endl; for (int j = 0; j < len; j++) { cout << "\t学生的姓名:" << tArray[i].sArray[j].sName << " 考试分数:" << tArray[i].sArray[j].score << endl; } } } int main() { srand((unsigned int)time(NULL)); Teacher tArray[3]; int len = sizeof(tArray) / sizeof(tArray[0]); allocatSpace(tArray, len); printfInfo(tArray,len); system("pause"); return 0; }
8、案例二
案例描述:
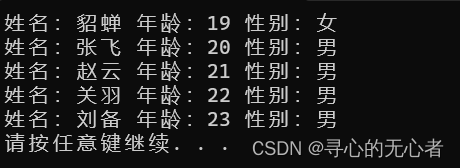
设计一个英雄的结构体,包括成员姓名,年龄,性别;创建结构体数组,数组中存放5名英雄。
通过冒泡排序的算法,将数组中的英雄按照年龄进行升序排序,最终打印排序后的结果。#include <iostream> using namespace std; #include <string> struct Hero { string name; int age; string sex; }; void bubbleSort(struct Hero heroArray[], int len) { for (int i = 0; i < len - 1; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < len - i - 1; j++) { if (heroArray[j].age > heroArray[j + 1].age) { struct Hero temp = heroArray[j]; heroArray[j] = heroArray[j + 1]; heroArray[j + 1] = temp; } } } } void printfHero(struct Hero heroArray[], int len) { for (int i= 0; i < len; i++) { cout << "姓名:" << heroArray[i].name << " 年龄:" << heroArray[i].age << " 性别:" << heroArray[i].sex << endl; } } int main() { struct Hero heroArray[5] = { {"刘备",23,"男"}, {"关羽",22,"男"}, {"张飞",20,"男"}, {"赵云",21,"男"}, {"貂蝉",19,"女"}, }; int len = sizeof(heroArray) / sizeof(heroArray[0]); bubbleSort(heroArray, len); printfHero(heroArray, len); system("pause"); return 0; }
结构体(个人学习笔记黑马学习)
news2026/2/11 5:57:55
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。如若转载,请注明出处:http://www.coloradmin.cn/o/951783.html
如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系多彩编程网进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!相关文章
【记录】手机QQ和电脑QQ里的emoji种类有什么差异?
版本 手机 QQ:V 8.9.76.12115 电脑 QQ:QQ9.7.15(29157) 偶然发现,有一种emoji手机上怎么找都找不到,一开始以为自己失忆了,后来发现这种emoji只在电脑上有。
接下来简单说一下找emoji差异的方式…
解决博客不能解析PHP直接下载源码问题
背景:
在网站设置反向代理后,网站突然不能正常访问,而是会直接下载访问文件的PHP源码
解决办法: 由于在搞完反向代理之后,PHP版本变成了纯静态,所以网站不能正常解析;只需要把PHP版本恢复正常…
Python的os.walk()函数使用案例
在Python中,os模块是一个非常实用的工具,它可以让我们与操作系统进行交互,操作文件和目录。在本文中,我们将详细介绍os模块中的遍历文件功能,并通过具体案例和使用场景来解释。
首先,导入os模块。在Pytho…
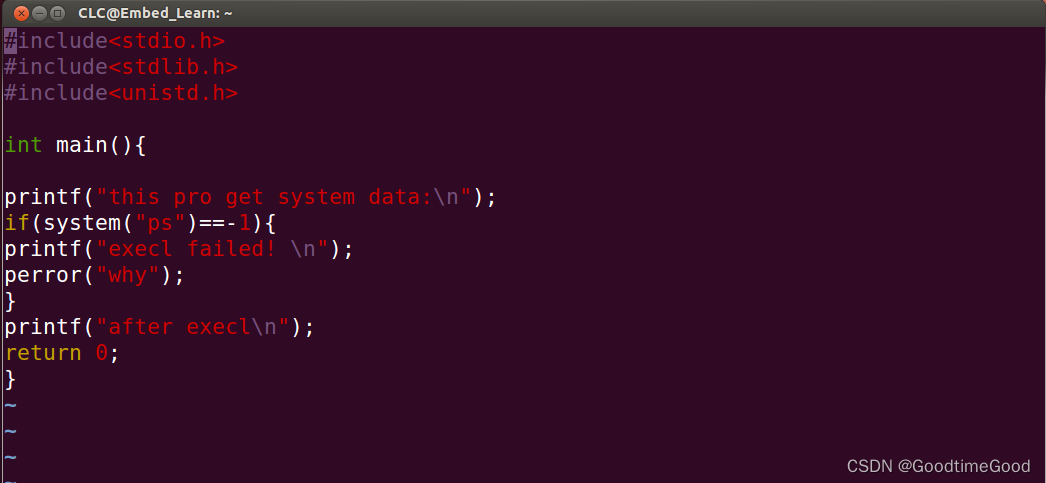
嵌入式学习之exec族函数
今天,主要学习的内容是exec族函数和system函数,以及system函数和fork函数的配合使用。今日写的代码如下:
《Kubernetes部署篇:Ubuntu20.04基于containerd部署kubernetes1.24.17集群(多主多从)》
一、架构图 如下图所示: 二、环境信息 1、部署规划主机名K8S版本系统版本内核版本IP地址备注k8s-master-631.24.17Ubuntu 20.04.5 LTS5.15.0-69-generic192.168.1.63master节点 + etcd节点k8s-master-641.24.17Ubuntu 20.04.5 LTS5.15.0-69-generic192.168.1.64master节点 + …
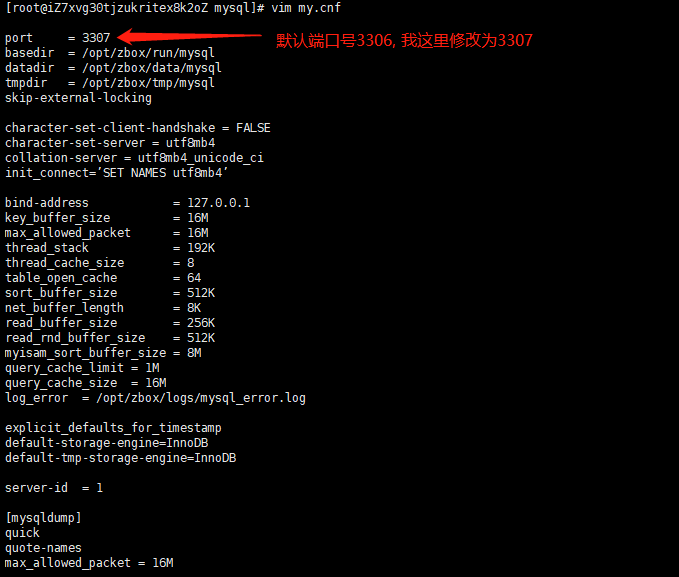
Linux禅道上修改Apache 和 MySQL 默认端口号
1. 修改Apache默认端口号 80 cd /opt/zbox/etc/apachevim httpd.conf :wq 保存 2. 修改MySQL默认端口号 3306 cd /opt/zbox/etc/mysql vim my.cnf :wq 保存 3. 重启服务
./zbox restart
计算机网络-笔记-第六章-应用层
目录
六、第六章——应用层
1、应用层概述
2、(C/S)客户-服务器方式 & (P2P)对等方式
(1)客户-服务器方式【C/S】
(2)对等方式【P2P】
3、DHCP——动态主机配置协议
(1)诞…
面试结束后:如何写一封有效的感谢信
🌷🍁 博主猫头虎 带您 Go to New World.✨🍁 🦄 博客首页——猫头虎的博客🎐 🐳《面试题大全专栏》 文章图文并茂🦕生动形象🦖简单易学!欢迎大家来踩踩~🌺 &a…
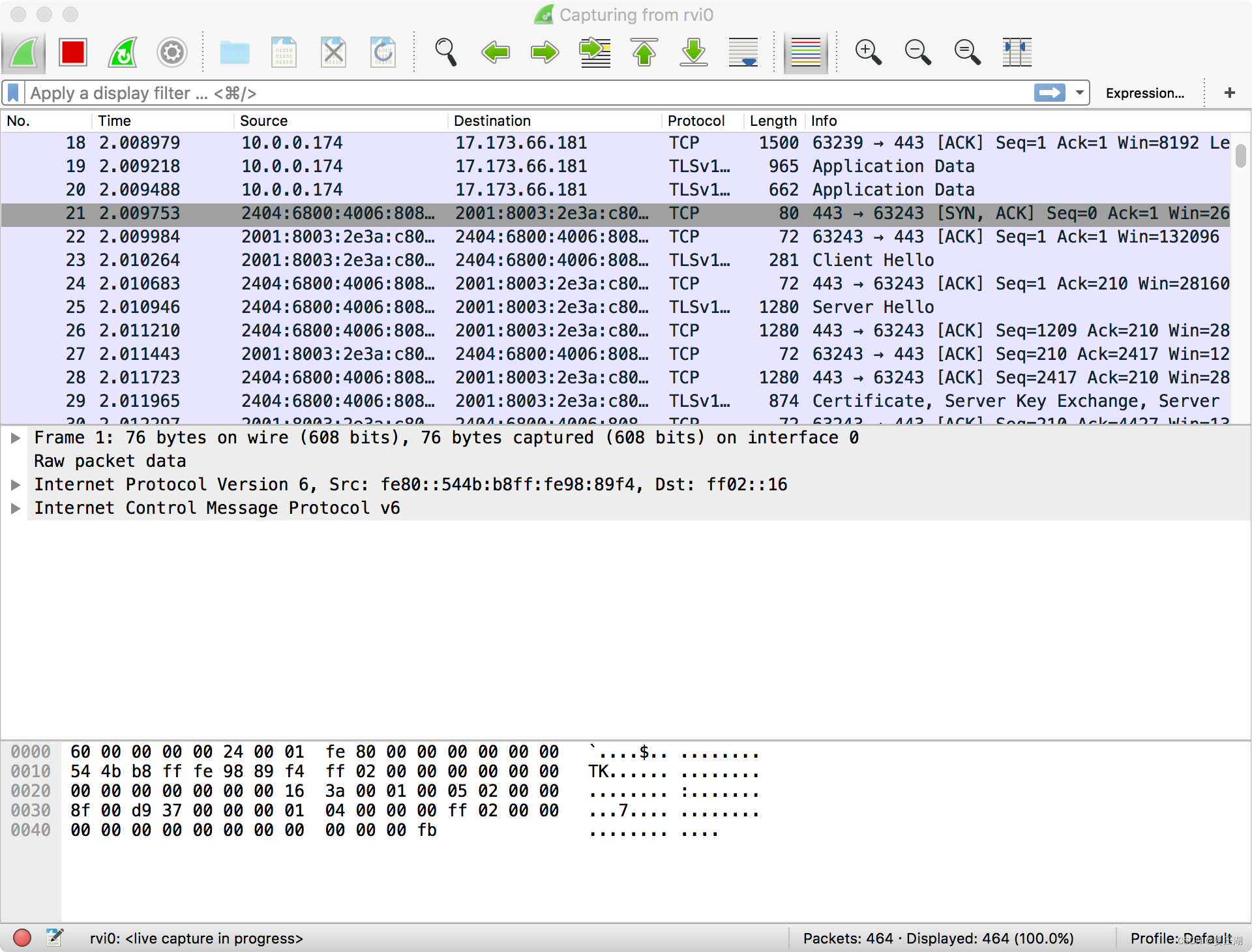
开源且强大的网络嗅探分析工具——Wireshark
Wireshark是一款强大的开源网络协议分析工具,旨在帮助用户深入了解网络通信的细节。通过捕获、解析和展示网络数据包,Wireshark能够帮助工程师诊断问题、优化性能,以及解决各种网络难题。无论是深入分析还是快速调试,Wireshark都是…
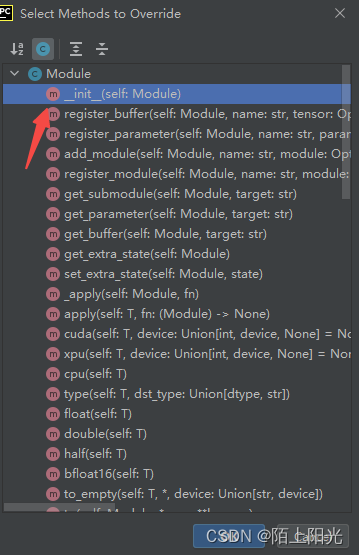
学习pytorch7 神经网络的基本骨架--nn,module的使用
神经网络的基本骨架--nn,module的使用 官网Module介绍Python父类子类继承关系前向神经网络pycharm快捷键重写类方法codedebug B站小土堆视频学习笔记
官网Module介绍 https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.nn.Module.html#torch.nn.Module Python父类子类继承关系…
4.4 对幻灯片进行动画制作
动画是演示文稿的重要构成要素,WPS演示为用户提供了多种动画类型,通过学习设置页面切换、动画效果等相关功能,可使演示文稿更加生动,富于表现力。
4.4.1 设置页面的切换方式 页面的切换是指从一张幻灯片切换到另一张幻灯片时的页…
【ES6】JavaScript中的Symbol
Symbol是JavaScript中的一种特殊的、不可变的、不可枚举的数据类型。它通常用于表示一个唯一的标识符,可以作为对象的属性键,确保对象的属性键的唯一性和不可变性。
Symbol.for()是Symbol的一个方法,它用于创建一个已经注册的Symbol对象。当…
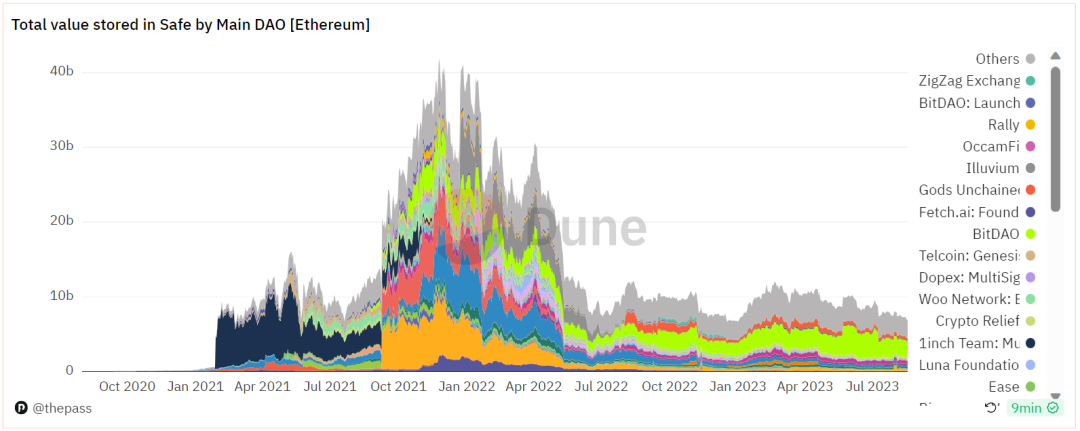
ThePASS研究院|以Safe为例,解码DAO国库管理
本研究文章由ThePASS团队呈现。ThePASS是一家开创性的DAO聚合器和搜索引擎,在为DAO提供洞察力和分析方面发挥着关键作用。
Intro
随着去中心化自治组织(DAOs)的发展,它们被赋予了越来越多的角色和期望。在这种巨幅增长的背景下&…
大数据平台与数据仓库的五大区别
随着大数据的快速发展,很多人难以区分大数据平台与数据仓库的区别,两者傻傻分不清楚。今天我们小编就给大家汇总了大数据平台与数据仓库的五大区别,希望有用哦!仅供参考! 大数据平台与数据仓库的五大区别
一、概念不同…
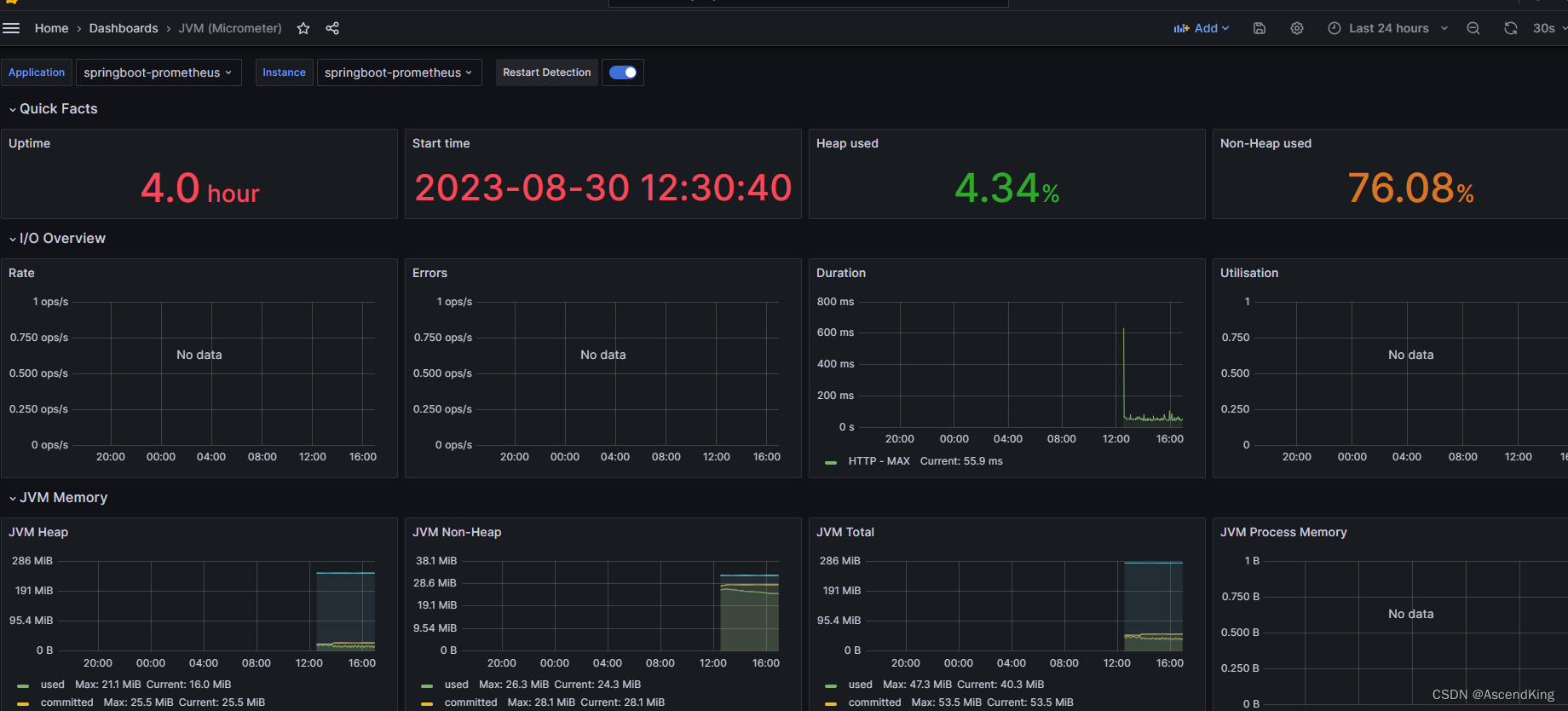
docker安装grafana,prometheus,exporter以及springboot整合详细教程(GPE)
springboot项目ip:192.168.168.1
测试服务器ip:192.168.168.81
文章来自互联网,自己略微整理下,更容易上手,方便自己,方便大家
最终效果:
node springboot 1.下载镜像
docker pull prom/node-exporter docker pull prom/mysqld-exporter docker pull google/cadvisor dock…
微前端-monorepo-无界
文章目录 前言一、微前端二 、monorepo三 、pnpm硬链接软链接(符号链接)幽灵依赖依赖安装耗时长monorepo项目搭建子模块复用 四、无界接入无界无界预加载无界传参 总结 前言
本文主要记录微前端框架 无界 的使用与理解以及monorepo代码管理方式。 一、微…