前言
CMH检验(Cochran-Mantel-Haenszel Test),分层卡方检验,考虑中心效应,分析干预对结果的影响。如果存在中心效应,即干预结果与中心相关,那么简单的将中心数据合并做卡方分析并不合理。需要采用Breslow-test检验或Woolf -test检验中心效应的一致性,采用CMH检验来分析考虑了中心因素的影响后干预和结局的相关性(排除了影响因素后卡方检验的显著性)。分层因素还包括年龄、性别等其他混杂因素。
一、CMH检验
高维列联表的分析,控制了某一个或几个混杂因素(分层变量)之后,检验二维R*C表中行变量X与列变量Y之间是否存在统计学关联。
H0:任一层的行变量与列变量均不相关
H1:至少存在一层行变量与列变量均相关
当各层行变量与列变量相关的方向不一致时,CMH统计量的检验效能较低。
二、CMH检验统计量的分类
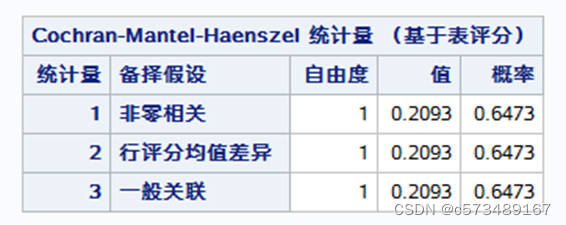
(1) 相关统计量(非零相关)
X、Y均为有序变量,自由度为1。
(2) 方差分析统计量(行平均得分统计量)
Y为有序变量,自由度为R-1。
H0:所有层的各行Y变量平均得分均相等
H1:至少有一层各行Y变量平均得分均不相等
一维RC列联表=各行Y变量平均得分的方差分析
秩和检验:Kruskal-Wallis检验。
(3)一般关联统计量
X、Y均为无序分类资料,目的是检验是否有关联性。
分层变量校正的Pearson χ2统计量。自由度(R-1)(C-1)。
SAS中的三种CMH统计量如下:
非零相关(nonzero correlation statistic):行变量(原因变量)与列变量(结果变量)均有序。
行评分均值差异(row mean scores (ANOVA) statistic):行变量无序,列变量有序
一般关联(general association statistic):行变量与列变量均无序。
当结果变量为二分类时,3种统计量的数值结果一致。
CMH χ2统计量计算方法(以四格表为例)
第h层的四格表
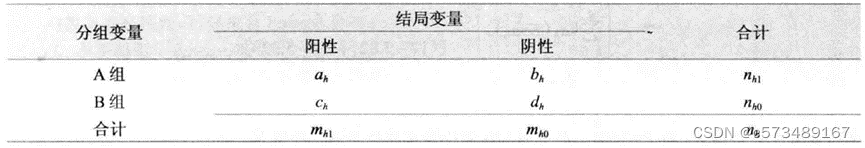

E(ah)、 Var(ah):基于H0,第h层的四格表第一行,第一列格子对应的理论频数及其方差。
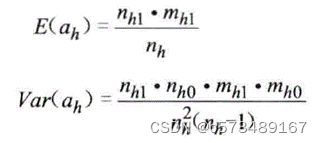
CMH χ2应用方法注意事项
proc freq CMH
The CMH option in the TABLES statement gives a stratified statistical analysis of the relationship between the row and column variables after controlling for the strata variables in a multiway table. For example, for the table request ABC*D, the CMH option provides an analysis of the relationship between C and D, after controlling for A and B. The stratified analysis provides a way to adjust for the possible confounding effects of A and B without being forced to estimate parameters for them.
tables ABC*D
A 、B为分层因素(混杂因素)
The CMH analysis produces Cochran-Mantel-Haenszel statistics, which include the correlation statistic, the ANOVA (row mean scores) statistic, and the general association statistic. For 2*2 tables, the CMH option also provides Mantel-Haenszel and logit estimates of the common odds ratio and the common relative risks, in addition to the Breslow-Day test for homogeneity of the odds ratios.
exact:Zelen’s相等比值比的精确检验
Exact statistics are also available for stratified 2*2 tables. If you specify the EQOR option in the EXACT statement, PROC FREQ provides Zelen’s exact test for equal odds ratios. If you specify the COMOR option in the EXACT statement, PROC FREQ provides exact confidence limits for the common odds ratio and an exact test that the common odds ratio equals one.
示例
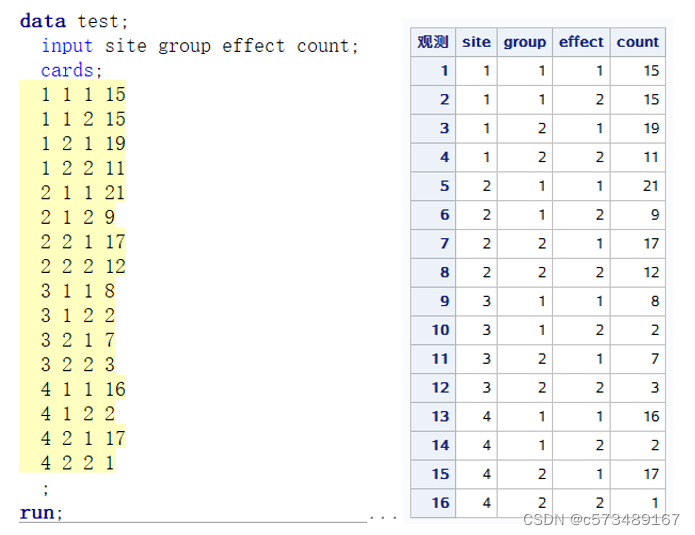

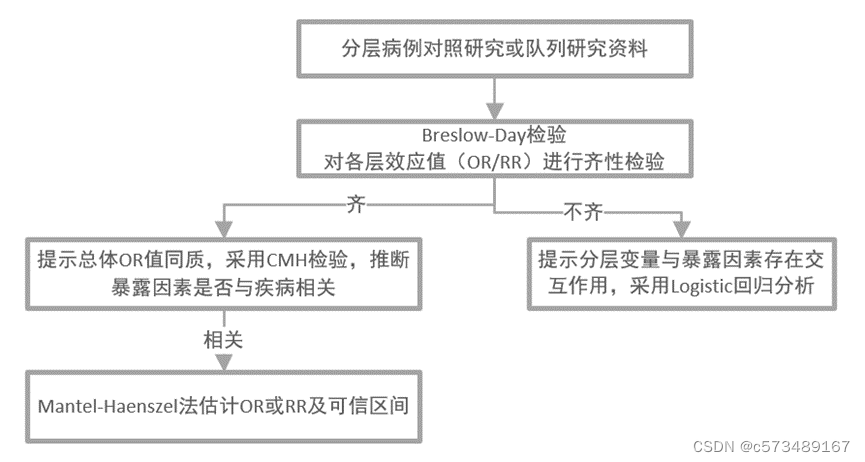
首先看 Breslow-Day test for homogeneity of odds ratios,同质性检验,对各层的效应值(OR/RR)进行齐性检验。若不拒绝齐性假设(P>0.05),才可依据CMH检验的结果推断出暴露因素是否与疾病相关。若拒绝了齐性假设,则提示分层变量与暴露因素存在交互作用,用CMH检验的结果不能说明问题,可进行多元Logistic回归分析。
其次看CMH χ2检验统计量,当结果变量为二分类时,3种统计量的数值结果一致。P>0.05,各Site的组间的效应无差异。
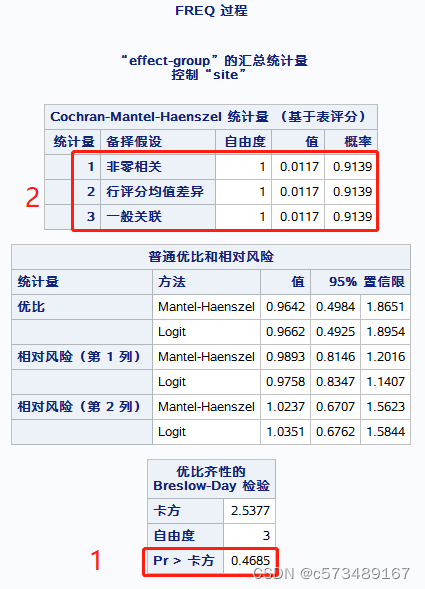
data test;
input site group effect count;
cards;
1 1 1 15
1 1 2 15
1 2 1 19
1 2 2 11
2 1 1 21
2 1 2 9
2 2 1 17
2 2 2 12
3 1 1 8
3 1 2 2
3 2 1 7
3 2 2 3
4 1 1 16
4 1 2 2
4 2 1 17
4 2 2 1
;
run;
proc print data=test;run;
proc freq data=test;
weight count;
tables site * group * effect / cmh ;
run;