文章目录
- 一、静态文件和媒体文件
- 1.在django中使用静态文件
- 实践
- 2.在django中使用媒体文件
- 二、文件上传
- 单文件上传
- 实践
- 多文件上传
一、静态文件和媒体文件
媒体文件: 用户上传的文件,叫做media
静态文件:存放在服务器的css,js,image,font等 叫做static
1.在django中使用静态文件
1)首先确保django.contrib.staticfiles在 INSTALLED_APPS中
2)在settings中定义STATIC_URL
STATIC_URL = '/static/'
3)在你app的static目录中存放静态文件,比如
App/static/example.jpg
4)如果有别的静态资源文件,不在app下的static目录下,可以通过STATICFILES_DIRS来指定额外的静态文件搜索目录。
STATICFILES_DIRS = [
os.path.join(BASE_DIR, "static"),
...
]
5)在模板中使用load标签去加载静态文件
{% load static %}
<img src="{% static "App/example.jpg" %}" />
实践
创建一个新项目 Day06DjangoPro01
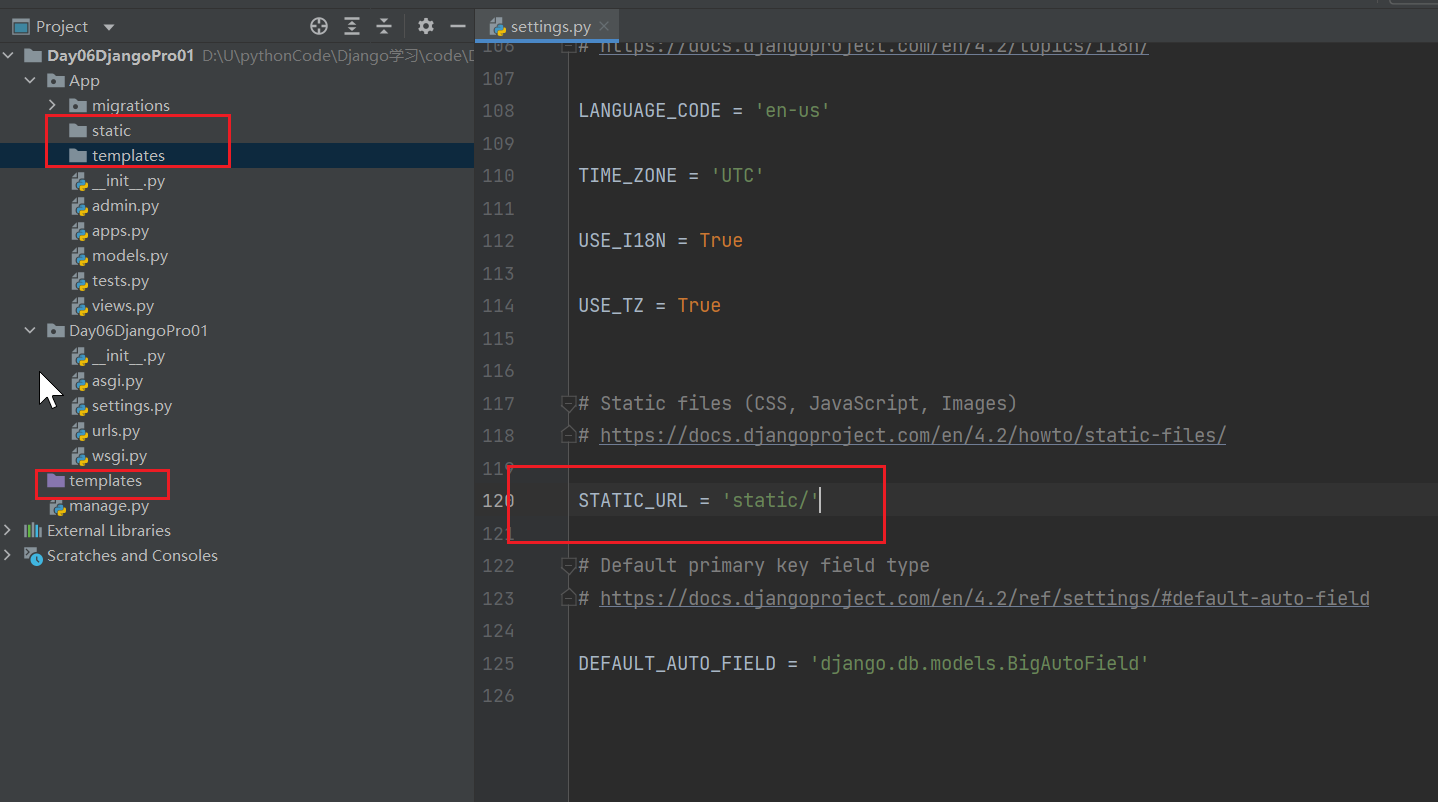
每一个应用中都可以新建一个static和templates

如果想要额外再加一些静态文件路径,就再加一个STATICFILES_DIRS
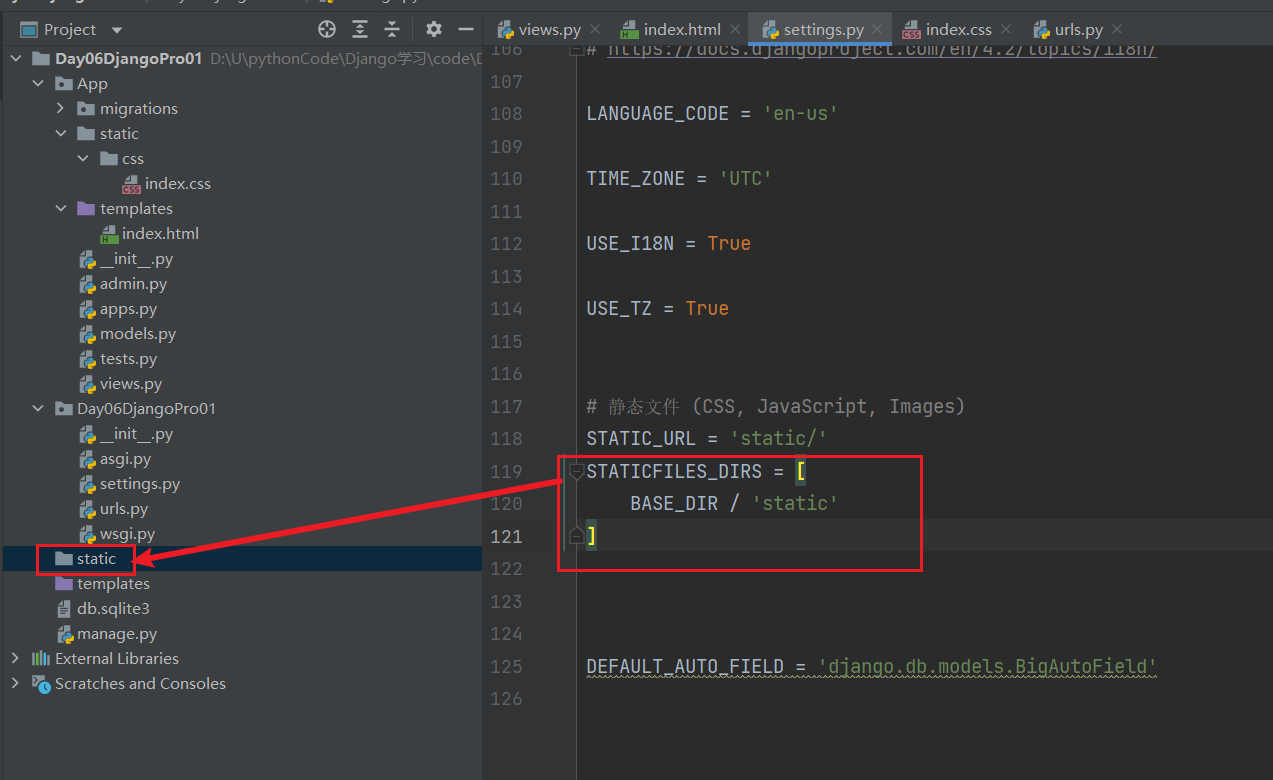
App\templates\index.html
一般用<link rel="stylesheet" href="{% static 'css/index.css' %}">
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>使用静态文件</title>
{% load static %}
{# <link rel="stylesheet" href="/static/css/index.css">#}
<link rel="stylesheet" href="{% static 'css/index.css' %}">
</head>
<body>
<h2>使用静态文件</h2>
<hr>
</body>
</html>
App\static\css\index.css
h2 {
color: #7FFF00FF;
}
根路由Day06DjangoPro01\urls.py
from django.contrib import admin
from django.urls import path
from App.views import *
urlpatterns = [
path('admin/', admin.site.urls),
path('index/', index),
]
App\views.py
from django.shortcuts import render
# 静态文件的使用
def index(request):
return render(request, 'index.html')
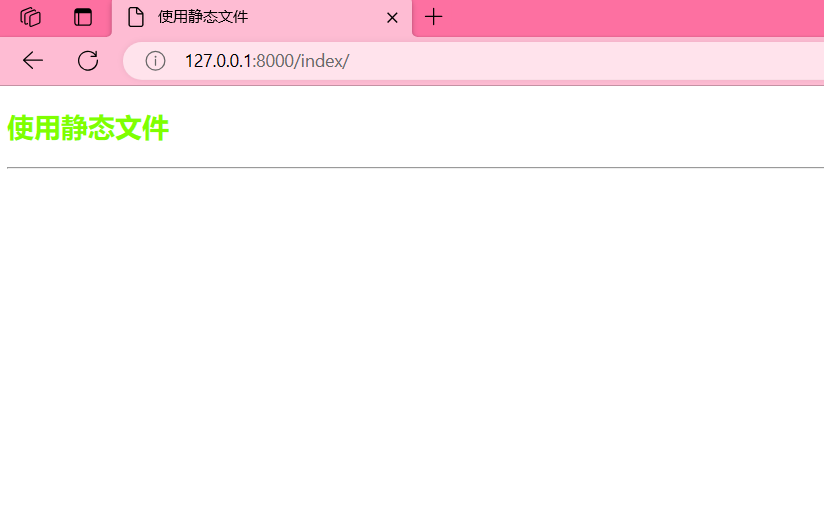
在项目根目录下的static和templates 也是可以这样用的
2.在django中使用媒体文件
在settings中配置 MEDIA_ROOT
MEDIA_ROOT = os.path.join(BASE_DIR, "media")
二、文件上传
单文件上传
文件上传要求form表单存在enctype="multipart/form-data"属性,并且提交方法是post。
<form enctype="multipart/form-data" action="/uploadFile/" method="post">
<input type="file"name="myfile" />
<br/>
<input type="submit" value="upload"/>
</form>
最简单的文件上传:
def file_upload(request):
if request.method =='POST':
# 获取上传的文件,如果没有文件,则默认为None
myFile = request.FILES.get( 'myfile', None)
if not myFile:
return HttpResponse("no files for upload")
file_path = os.path.join(settings.MEDIA_ROOT, '1.jpg')
with open(file_path, 'ab') as fp:
for part in myFile.chunks():
fp.write(part)
return HttpResponse("上传成功!")
else:
return render(request,'index.html')
实践
在settings中配置 MEDIA_ROOT
# 媒体文件
MEDIA_ROOT = BASE_DIR / 'static/upload'
templates\upload1.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>单文件上传</h2>
<form action="" enctype="multipart/form-data" method="post">
{% csrf_token %}
用户名:<input type="text" name="username"><br>
头像:<input type="file"name="icon" /><br/>
<button>上传图片</button>
</form>
</body>
</html>
App\models.py
from django.db import models
# 用户
class UserModel(models.Model):
# 名字
name = models.CharField(max_length=30, unique=True)
# 头像
icon = models.CharField(max_length=255)
写完之后记得做迁移
生成迁移文件: python manage.py makemigrations
执行迁移: python manage.py migrate
App\views.py
import os
import uuid
from django.conf import settings
from django.shortcuts import render
# 上传文件:媒体文件
# 单文件上传
from App.models import UserModel
def upload1(request):
if request.method == 'GET':
return render(request, 'upload1.html')
elif request.method == 'POST':
# 单文件上传
username = request.POST.get('username')
icon = request.FILES.get('icon') # 只有一个文件用get()
print(icon, type(icon)) # 文件对象
# picture3.jpg <class 'django.core.files.uploadedfile.TemporaryUploadedFile'>
print(icon.name) # picture3.jpg
# 1. 将上传的图片存储到后端对应的媒体文件夹中
# file_name = icon.name # 图片名称尽量不要使用原图名称
# file_name = gen_uuid_name() + icon.name[icon.name.rfind('.'):] # icon.name.rfind('.') 获得最后一个.的下标, 拿到的是 .jpg
file_name = gen_uuid_name() + os.path.splitext(icon.name)[-1] # os.path.splitext得到的是一个数组,取最后一个, 拿到的是 .jpg
# 后面可以加个时间戳
file_path = os.path.join(settings.MEDIA_ROOT, file_name) # settings.py 设置的文件路径 MEDIA_ROOT
print('file_path', file_path) # D:\xxx\pythonCode\Django学习\code\Day06DjangoPro01\static\upload\picture3.jpg
# 分段写入文件
with open(file_path, 'ab') as fp: # ab 追加写的方式
for part in icon.chunks(): # icon.chunks()方法 会一段一段的取,直到你取完为止,考虑到上传视频很大的话,一次性取会占很大一块内存,所以分段取
fp.write(part)
fp.flush() # 写一段,清空一次缓存
# 如果要把用户的图片存起来,不是直接把图片的二进制存起来,虽然可以存二进制,但是我们一般不存二进制
# 2. 存到本地。将该媒体文件的路径 存入到数据库中。因为图片视频的二进制都比较大,如果存二进制到数据库会很大
user = UserModel()
user.name = username
user.icon = 'upload/' + file_name
user.save() # 保存
return render(request, 'upload1.html')
# 得到一个图片名称(通过uuid来得到唯一的图片名称)
def gen_uuid_name():
return str(uuid.uuid4()) # 它会根据我们的时间还有随机数之类的东西去生成唯一的字符串
urls.py
# 上传文件
path('upload1/', upload1),
浏览器http://127.0.0.1:8000/upload1/
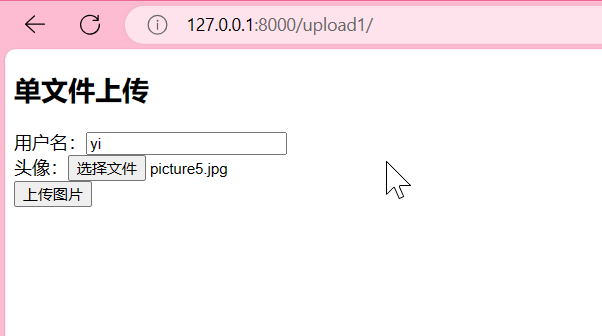
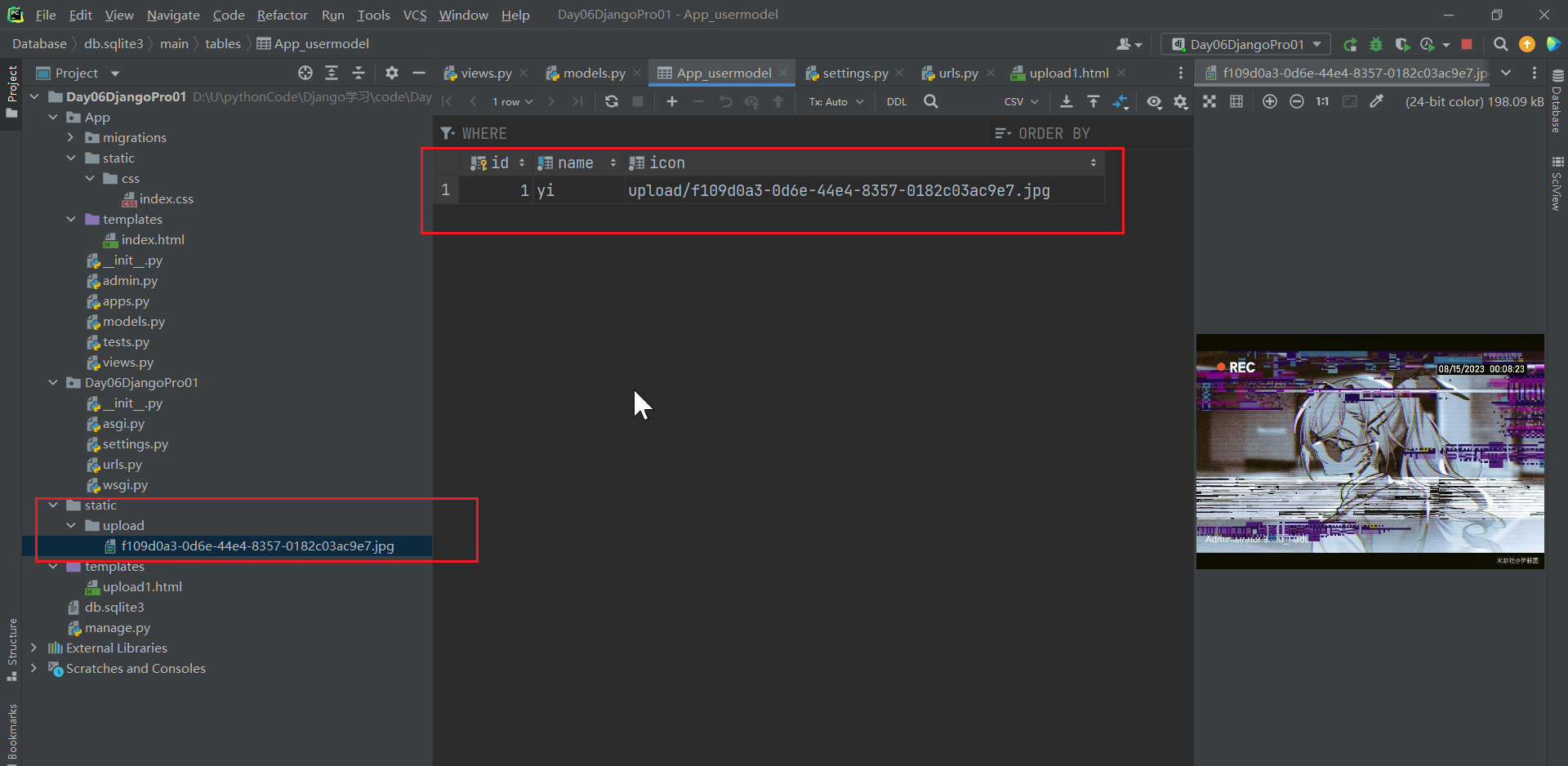
可以看到上传成功啦!!!
多文件上传
App\models.py
# 相册
class PhotoModel(models.Model):
img = models.CharField(max_length=255) # 图片地址
# 图片所属用户
user = models.ForeignKey(UserModel, on_delete=models.PROTECT) # 每一个照片只属于一个用户,一对多关系
写完之后记得做迁移
生成迁移文件: python manage.py makemigrations
执行迁移: python manage.py migrate
templates\upload2.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>多文件上传</h2>
{# enctype="multipart/form-data" : 支持文件上传 #}
{# multiple: 支持文件多选 #}
<form action="" enctype="multipart/form-data" method="post">
{% csrf_token %}
用户id:<input type="text" name="userid"><br>
请选择要上传的照片:<input type="file" name="imgs" multiple /><br/>
<button>上传图片</button>
</form>
</body>
</html>
App\views.py
import os
import uuid
from django.conf import settings
from django.shortcuts import render
from App.models import *
# 多文件上传
def upload2(request):
if request.method == 'GET':
return render(request, 'upload2.html')
elif request.method == 'POST':
userid = request.POST.get('userid')
imgs = request.FILES.getlist('imgs')
print('imgs: ', imgs)
# [<TemporaryUploadedFile: picture2.jpg (image/jpeg)>,
# <TemporaryUploadedFile: picture3.jpg (image/jpeg)>,...]
for img in imgs:
# 1. 把图片存储到uploads中
file_name = gen_uuid_name() + os.path.splitext(img.name)[-1]
file_path = os.path.join(settings.MEDIA_ROOT, file_name) # 得到一个绝对文件路径
with open(file_path, 'ab') as fp:
for part in img.chunks():
fp.write(part)
fp.flush()
# 2. 将图片路径存入到数据库中
photo = PhotoModel()
photo.img = 'uploads/' + file_name
photo.user_id = userid # photo.user = UserModel.objects.filter(pk=userid).first()# 没查到就是None,暂时不考虑其他问题None
photo.save()
return render(request, 'upload2.html')
urls.py
path('upload2/', upload2), # 多文件上传
浏览器 http://127.0.0.1:8000/upload2/
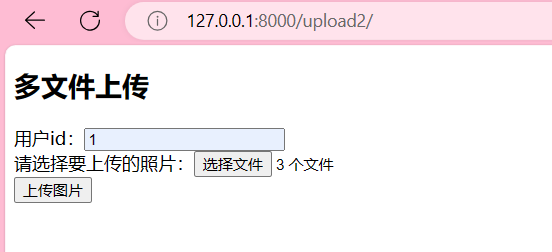
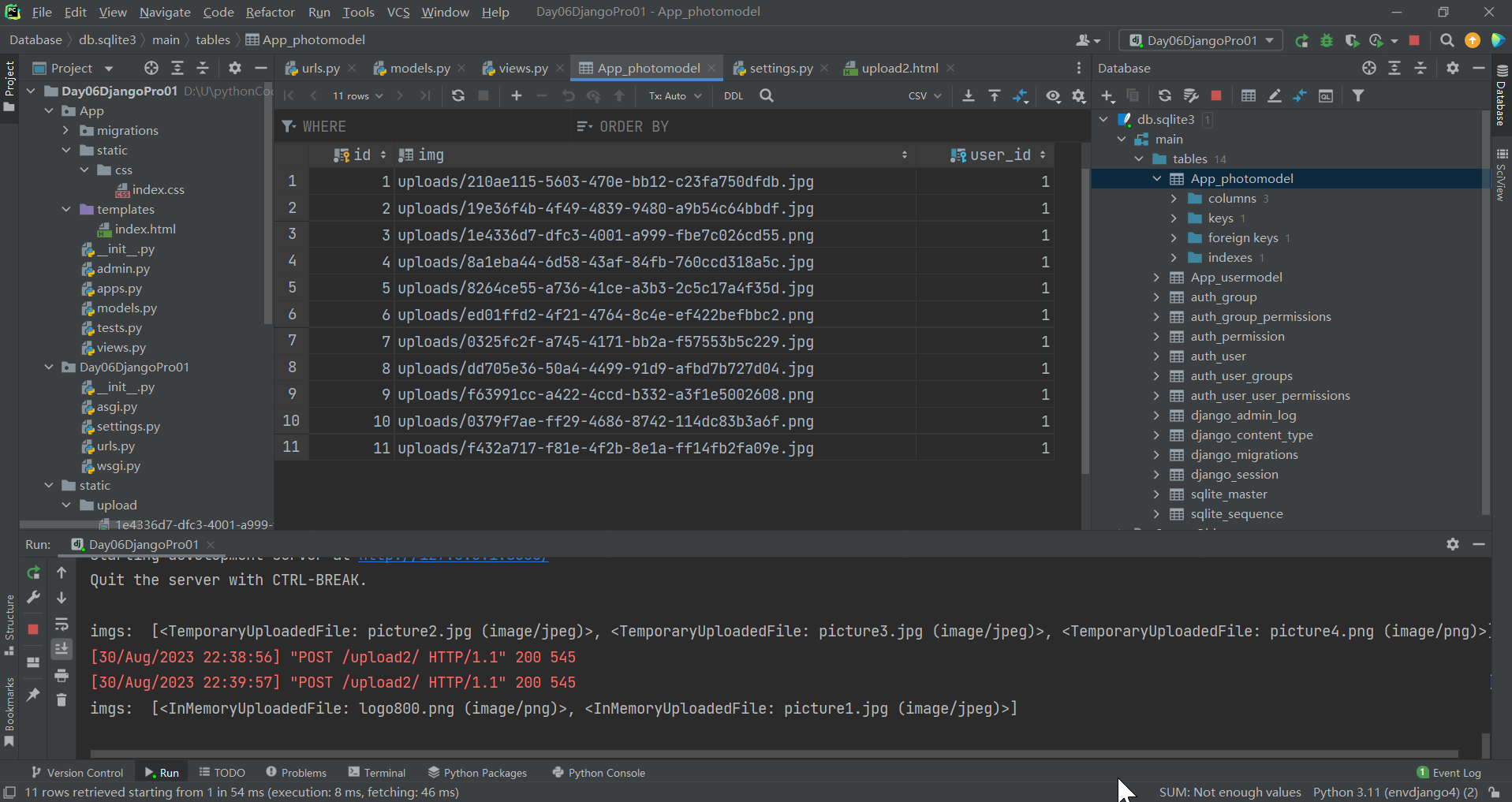
可以看到,图片保存成功啦,数据也存到数据库啦