目录
- 一,状态管理Vuex
- 二,state状态
- 三,mutations
- 四,actions
- 五,modules
- 最后
一,状态管理Vuex
Vuex 是一个专为 Vue.js 应用程序开发的状态管理模式。它采用集中式存储管理应用的所有组件的状态,并以相应的规则保证状态以一种可预测的方式发生变化。
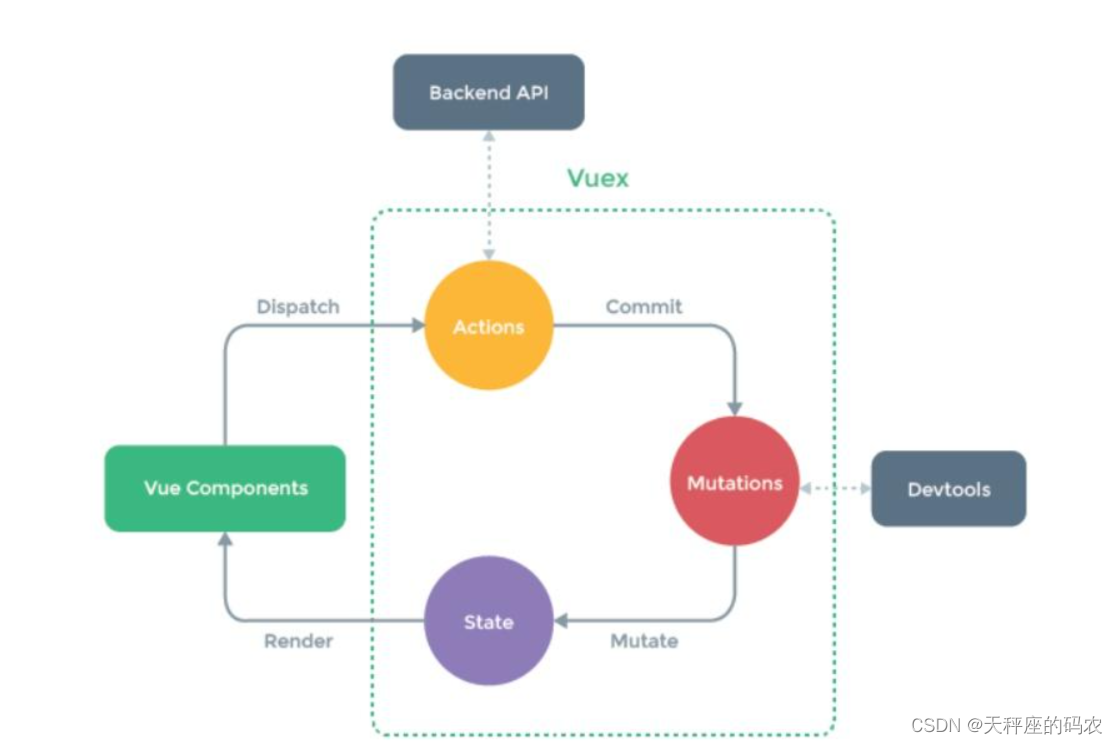
Vuex的核心:state、mutations、actions
state:存储公共的一些数据
mutations:定义一些方法来修改state中的数据,数据怎么改变
actions: 使用异步的方式来触发mutations中的方法进行提交。
此部分的代码我们在vue-cli中使用
二,state状态
声明
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count:11
},
mutations: {
},
actions: {
}
})
使用
// 直接在模板中使用
<template>
<div>
vuex中的状态数据count:{{ $store.state.count }}
</div>
</template>
// 在方法中使用
ceshi(){
console.log("Vuex中的状态数据count:",this.$store.state.count);
this.$router.push({
path:"/ceshi"
},()=>{},()=>{})
}
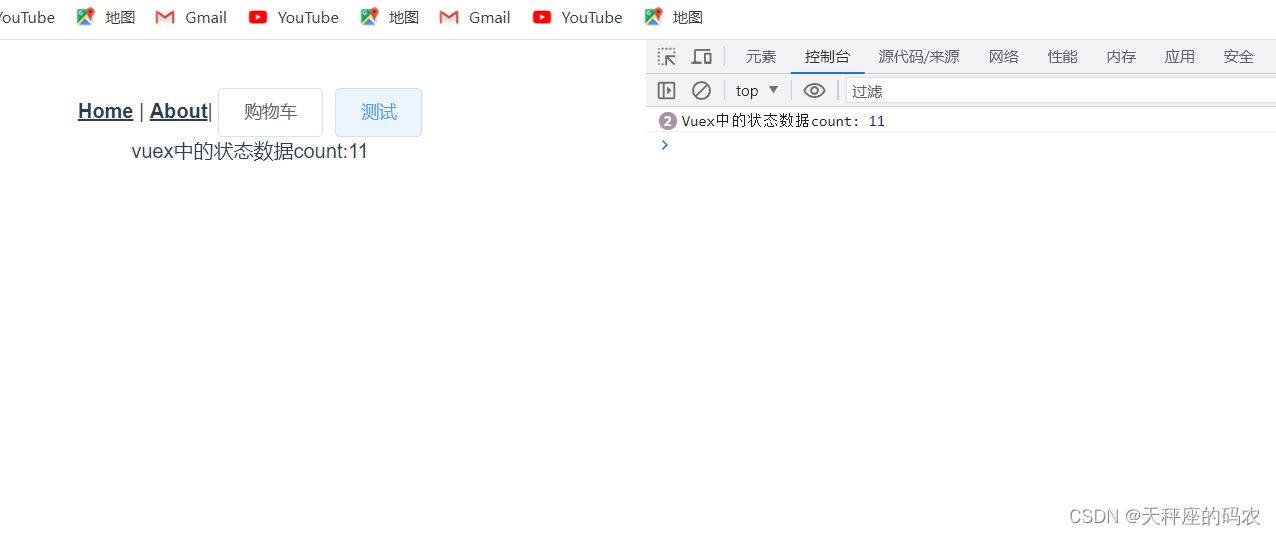
在计算属性中使用
当一个组件需要获取多个状态的时候,将这些状态都声明为计算属性会有些重复和冗余。为了解决这个问题,我们可以使用 mapState 辅助函数帮助我们生成计算属性,让你少按几次键。
// 在组件中导入mapState函数。mapState函数返回的是一个对象
import {mapState} from 'vuex'
// 在组件中导入mapState函数。mapState函数返回的是一个对象
<template>
<div id="app">
<div id="nav">
<router-link to="/">Home</router-link> |
<router-link to="/about">About</router-link>|
<el-button @click="gouwucheclick">购物车</el-button>
<el-button @click="ceshi">测试</el-button>
<br>
vuex中的状态数据count:{{ $store.state.count }}
<br>{{ count }}
<br> doubleCount:{{ doubleCount }}
</div>
<router-view/>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import {mapState} from 'vuex'
export default{
data(){
return{
baseCount:10
}
},
methods:{
gouwucheclick(){
this.$router.push({
path:"/gouwuche"
},()=>{},()=>{})
},
ceshi(){
console.log("Vuex中的状态数据count:",this.$store.state.count);
this.$router.push({
path:"/ceshi"
},()=>{},()=>{})
}
},
computed:mapState({
count:'count',
doubleCount(state){
return state.count * 2 + this.baseCount
}
})
}
</script>
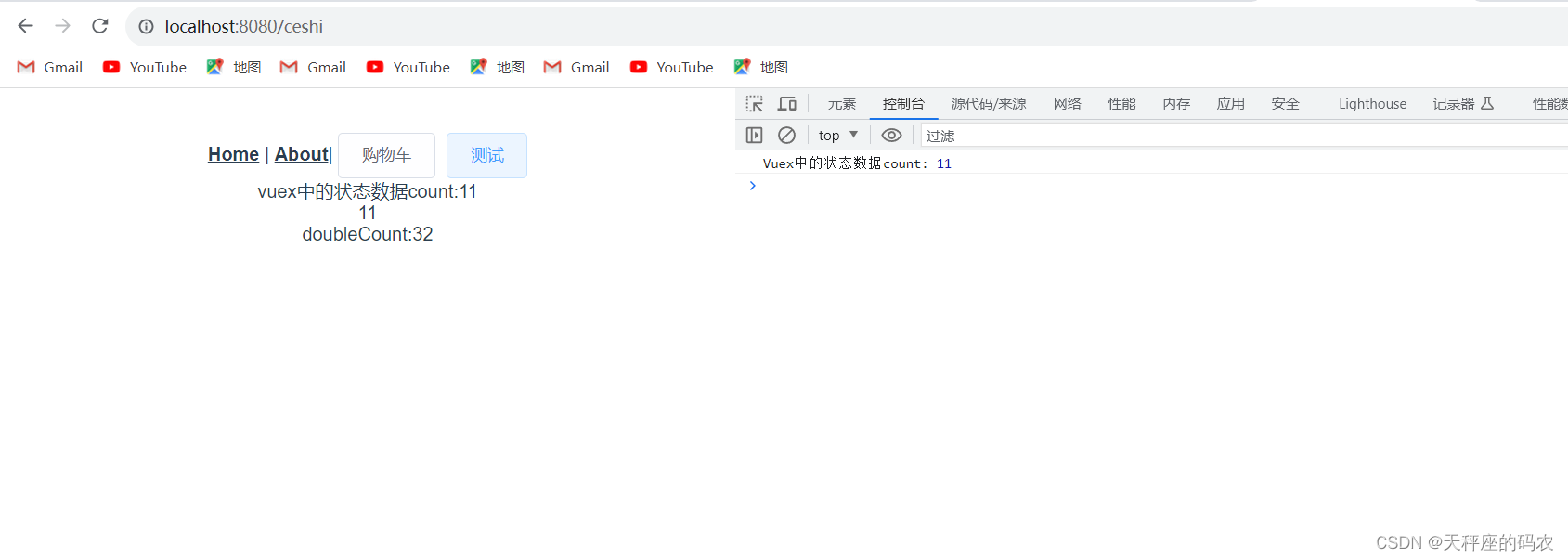
使用展开运算符
在之前的示例中,不方便和本地的计算属性混合使用,下面我们使用展开运算符,这样就可以和本地的计算属性一起使用。
<template>
<div id="app">
<div id="nav">
<router-link to="/">Home</router-link> |
<router-link to="/about">About</router-link>|
<el-button @click="gouwucheclick">购物车</el-button>
<el-button @click="ceshi">测试</el-button>
<br>本地的计算属性{{ localCount }}
<br>
vuex中的状态数据count:{{ $store.state.count }}
<br>{{ count }}
<br> doubleCount:{{ doubleCount }}
</div>
<router-view/>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import {mapState} from 'vuex'
export default{
data(){
return{
baseCount:10
}
},
methods:{
gouwucheclick(){
this.$router.push({
path:"/gouwuche"
},()=>{},()=>{})
},
ceshi(){
this.baseCount=5
console.log("Vuex中的状态数据count:",this.$store.state.count);
this.$router.push({
path:"/ceshi"
},()=>{},()=>{})
}
},
computed:{
localCount(){
// 本地的计算属性,没有vuex中的状态参与
return this.baseCount + 1
},
...mapState({
count:'count',
doubleCount(state){
return state.count * 2 + this.baseCount
}
})
}
}
</script>
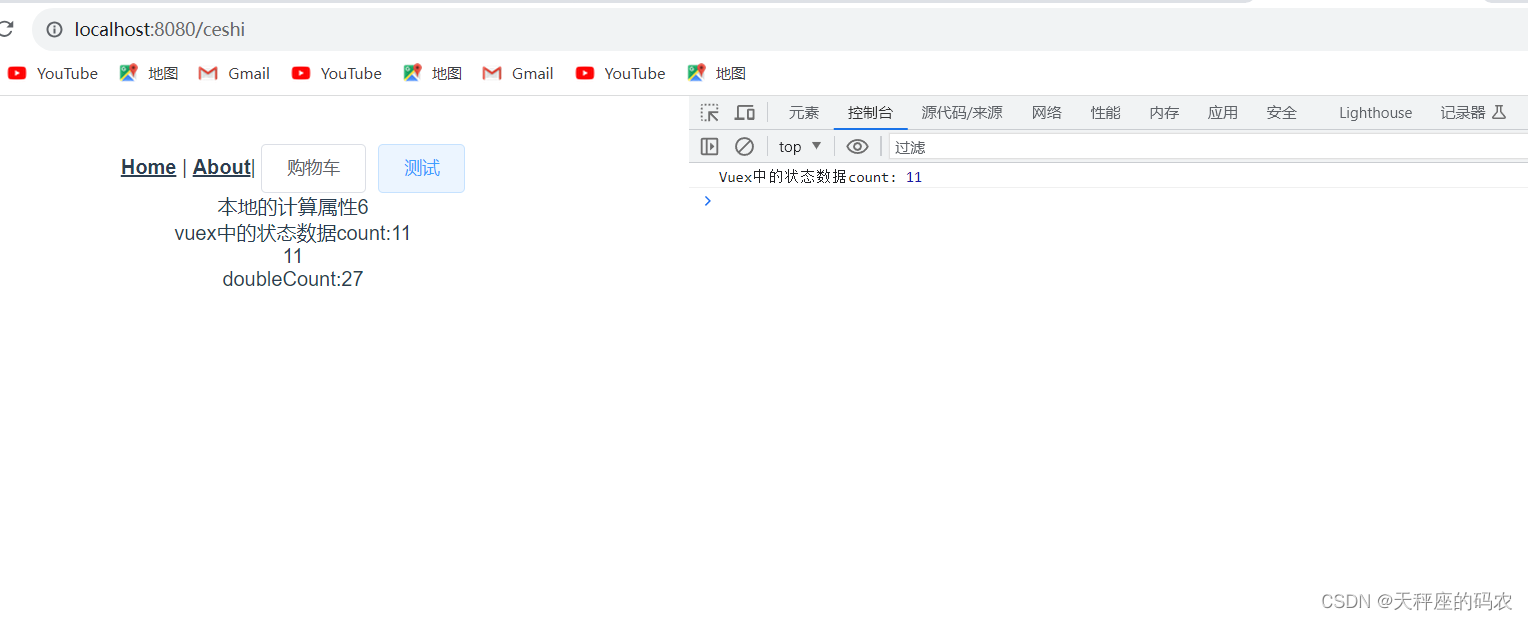
三,mutations
state中的数据是只读的,不能直接进行修改。想要修改state中数据的唯一途径就是调用mutation方法。
使用commit()函数,调用mutation函数。
注意:mutation中只能执行同步方法。
mutations: {
// 在mutations中定义方法,在方法中修改state
// state是状态,num是额外的参数
add(state,num){
state.count = state.count +num
}
},
直接调用
<template>
<div id="app">
<div id="nav">
<router-link to="/">Home</router-link> |
<router-link to="/about">About</router-link>|
<el-button @click="gouwucheclick">购物车</el-button>
<el-button @click="ceshi">测试</el-button>
<el-button @click="addcount">调用add</el-button>
<br>本地的计算属性{{ localCount }}
<br>
vuex中的状态数据count:{{ $store.state.count }}
<br>{{ count }}
<br> doubleCount:{{ doubleCount }}
</div>
<router-view/>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import {mapState} from 'vuex'
export default{
data(){
return{
baseCount:10
}
},
methods:{
gouwucheclick(){
this.$router.push({
path:"/gouwuche"
},()=>{},()=>{})
},
ceshi(){
this.baseCount=5
console.log("Vuex中的状态数据count:",this.$store.state.count);
this.$router.push({
path:"/ceshi"
},()=>{},()=>{})
},
addcount(){
this.$store.commit('add',1)
}
},
computed:{
localCount(){
// 本地的计算属性,没有vuex中的状态参与
return this.baseCount + 1
},
...mapState({
count:'count',
doubleCount(state){
return state.count * 2 + this.baseCount
}
})
}
}
</script>
演示2
使用辅助函数(mapMutations)简化
import {mapMutations} from 'vuex'
四,actions
actions中执行的方法可以是异步的
actions中要修改状态state中的内容,需要通过mutation。
在组件中调用action需要调用dispatch()函数。
步骤如下:
声明action方法
actions: {
delayAdd(countext,num){
// 在action中调用mutation中的方法
setTimeout(()=>{
countext.commit('add',num)
},2000)
}
},
直接调用action方法
<template>
<div id="app">
<div id="nav">
<router-link to="/">Home</router-link> |
<router-link to="/about">About</router-link>|
<el-button @click="gouwucheclick">购物车</el-button>
<el-button @click="ceshi">测试</el-button>
<el-button @click="addcount">调用add</el-button>
<el-button @click="addcountAction">调用actions中的方法</el-button>
<br>本地的计算属性{{ localCount }}
<br>
vuex中的状态数据count:{{ $store.state.count }}
<br>{{ count }}
<br> doubleCount:{{ doubleCount }}
</div>
<router-view/>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import {mapState} from 'vuex'
export default{
data(){
return{
baseCount:10
}
},
methods:{
gouwucheclick(){
this.$router.push({
path:"/gouwuche"
},()=>{},()=>{})
},
ceshi(){
this.baseCount=5
console.log("Vuex中的状态数据count:",this.$store.state.count);
this.$router.push({
path:"/ceshi"
},()=>{},()=>{})
},
addcount(){
this.$store.commit('add',1)
},
addcountAction(){
this.$store.dispatch('delayAdd',2)
}
},
computed:{
localCount(){
// 本地的计算属性,没有vuex中的状态参与
return this.baseCount + 1
},
...mapState({
count:'count',
doubleCount(state){
return state.count * 2 + this.baseCount
}
})
}
}
</script>
五,modules
在复杂的项目中,我们不能把大量的数据堆积到store中,这样store的内容就太多,而且比较凌乱,不方便管理。所以就是出现了module。他将原有的store切割成了一个个的module。每个module中都有自己的store、mutation、actions和getter
store中定义一个module
const storeModuleA={
state:{
countA:10
},
mutations:{
addA(state){
state.countA++
console.log("moduleA:"+state.countA);
},
// 此方法和root中的方法名字一致
add(state){
console.log("moduleA:"+state.countA);
}
}
}
export default storeModuleA
在store.js中,导入并注册此module
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
import storeModuleA from './stroeModuleA'
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count:11,
},
mutations: {
// state是状态,num是额外的参数
add(state,num){
console.log('root中的add');
state.count = state.count +num
}
},
actions: {
delayAdd(countext,num){
// 在action中调用mutation中的方法
setTimeout(()=>{
countext.commit('add',num)
},2000)
}
},
modules: {
a:storeModuleA
}
})
在组件中使用子模块中的状态
<template>
<div id="app">
<div id="nav">
<router-link to="/">Home</router-link> |
<router-link to="/about">About</router-link>|
<el-button @click="gouwucheclick">购物车</el-button>
<el-button @click="ceshi">测试</el-button>
<el-button @click="addcount">调用add</el-button>
<el-button @click="addcountAction">调用actions中的方法</el-button>
<br>本地的计算属性{{ localCount }}
<br>
vuex中的状态数据count:{{ $store.state.count }}
<br>{{ count }}
<br> doubleCount:{{ doubleCount }}
<hr>
{{ $store.state.a.countA }}
<el-button @click="addMoudleAaddA">调用a模块中的mutation-addA</el-button>
</div>
<router-view/>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import {mapState} from 'vuex'
export default{
data(){
return{
baseCount:10
}
},
methods:{
gouwucheclick(){
this.$router.push({
path:"/gouwuche"
},()=>{},()=>{})
},
ceshi(){
this.baseCount=5
console.log("Vuex中的状态数据count:",this.$store.state.count);
this.$router.push({
path:"/ceshi"
},()=>{},()=>{})
},
addcount(){
this.$store.commit('add',1)
},
addcountAction(){
this.$store.dispatch('delayAdd',2)
},
addMoudleAaddA(){
this.$store.commit('addA')
},
},
computed:{
localCount(){
// 本地的计算属性,没有vuex中的状态参与
return this.baseCount + 1
},
...mapState({
count:'count',
doubleCount(state){
return state.count * 2 + this.baseCount
}
})
}
}
</script>
示例4
在store.js中,导入并注册此module
在组件中使用子模块中的状态
没有声明namespace的情况
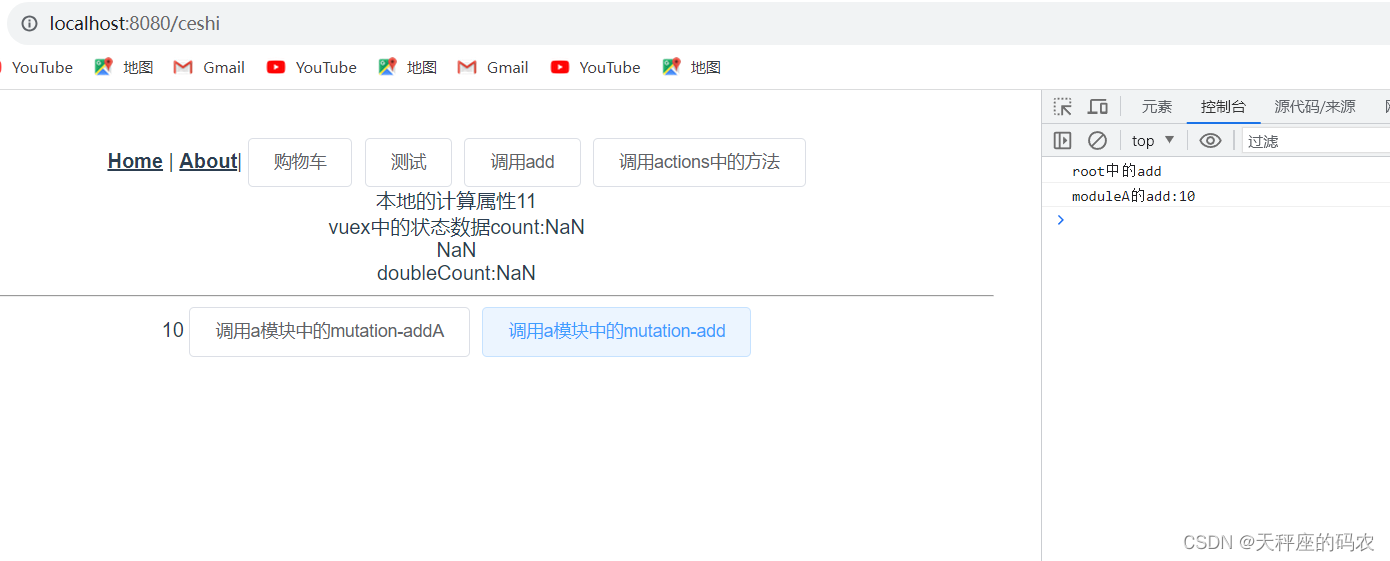
子模块中的mutation在没有使用namespace的情况下,这些方法会注册到root中。
如果子模块中的mutation和root中的一样。则都会被调用。
<template>
<div id="app">
<div id="nav">
<router-link to="/">Home</router-link> |
<router-link to="/about">About</router-link>|
<el-button @click="gouwucheclick">购物车</el-button>
<el-button @click="ceshi">测试</el-button>
<el-button @click="addcount">调用add</el-button>
<el-button @click="addcountAction">调用actions中的方法</el-button>
<br>本地的计算属性{{ localCount }}
<br>
vuex中的状态数据count:{{ $store.state.count }}
<br>{{ count }}
<br> doubleCount:{{ doubleCount }}
<hr>
{{ $store.state.a.countA }}
<el-button @click="addMoudleAaddA">调用a模块中的mutation-addA</el-button>
<el-button @click="addMoudleAadd">调用a模块中的mutation-add</el-button>
</div>
<router-view/>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import {mapState} from 'vuex'
export default{
data(){
return{
baseCount:10
}
},
methods:{
gouwucheclick(){
this.$router.push({
path:"/gouwuche"
},()=>{},()=>{})
},
ceshi(){
this.baseCount=5
console.log("Vuex中的状态数据count:",this.$store.state.count);
this.$router.push({
path:"/ceshi"
},()=>{},()=>{})
},
addcount(){
this.$store.commit('add',1)
},
addcountAction(){
this.$store.dispatch('delayAdd',2)
},
addMoudleAaddA(){
this.$store.commit('addA')
},
addMoudleAadd(){
this.$store.commit('add')
}
},
computed:{
localCount(){
// 本地的计算属性,没有vuex中的状态参与
return this.baseCount + 1
},
...mapState({
count:'count',
doubleCount(state){
return state.count * 2 + this.baseCount
}
})
}
}
</script>
声明namespace的情况
在module中添加
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
import storeModuleA from './stroeModuleA'
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count:11,
},
mutations: {
// state是状态,num是额外的参数
add(state,num){
console.log('root中的add');
state.count = state.count +num
}
},
actions: {
delayAdd(countext,num){
// 在action中调用mutation中的方法
setTimeout(()=>{
countext.commit('add',num)
},2000)
}
},
modules: {
a:{
namespaced:true,
...storeModuleA
}
}
})
在组件中调用,加上别名即可
this.$store.commit('a/addA');
<template>
<div id="app">
<div id="nav">
<router-link to="/">Home</router-link> |
<router-link to="/about">About</router-link>|
<el-button @click="gouwucheclick">购物车</el-button>
<el-button @click="ceshi">测试</el-button>
<el-button @click="addcount">调用add</el-button>
<el-button @click="addcountAction">调用actions中的方法</el-button>
<br>本地的计算属性{{ localCount }}
<br>
vuex中的状态数据count:{{ $store.state.count }}
<br>{{ count }}
<br> doubleCount:{{ doubleCount }}
<hr>
{{ $store.state.a.countA }}
<el-button @click="addMoudleAaddA">调用a模块中的mutation-addA</el-button>
<el-button @click="addMoudleAadd">调用a模块中的mutation-add</el-button>
</div>
<router-view/>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import {mapState} from 'vuex'
export default{
data(){
return{
baseCount:10
}
},
methods:{
gouwucheclick(){
this.$router.push({
path:"/gouwuche"
},()=>{},()=>{})
},
ceshi(){
this.baseCount=5
console.log("Vuex中的状态数据count:",this.$store.state.count);
this.$router.push({
path:"/ceshi"
},()=>{},()=>{})
},
addcount(){
this.$store.commit('add',1)
},
addcountAction(){
this.$store.dispatch('delayAdd',2)
},
addMoudleAaddA(){
this.$store.commit('addA')
},
addMoudleAadd(){
this.$store.commit('a/add')
}
},
computed:{
localCount(){
// 本地的计算属性,没有vuex中的状态参与
return this.baseCount + 1
},
...mapState({
count:'count',
doubleCount(state){
return state.count * 2 + this.baseCount
}
})
}
}
</script>

最后
送大家一句话:不是井里没有水,而是挖的不够深