1 快速排序基本过程
快速排序的是将分治法运用到排序问题的典型例子。力扣912题,给你一个整数数组 nums,请你将该数组升序排列。
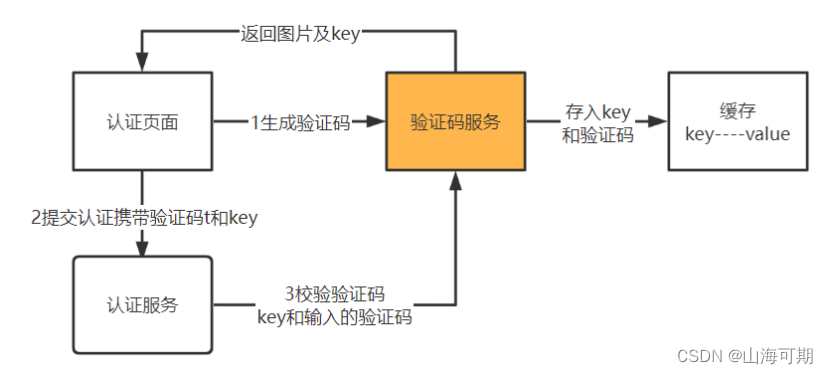
基本思想:是通过随机标记一个pivot元素将含有n个元素的序列划分为左右两个子序列left和right,其中left的元素都比pivot小,right的元素都比pivot大,然后再次对left和right分别执行快速排序,这样将左右两个子序列排列完后,整个序列也就是有序的了。这里以序列[28,36,35,38,34,25]为例,示意一下一轮快速排序的过程:

代码如下:
/**
* @param {number[]} nums
* @return {number[]}
*/
var sortArray = function(nums) {
quickSort(nums, 0, nums.length - 1);
return nums;
};
function quickSort(nums, start, end) {
if (start >= end) {
return;
}
const mid = partition(nums, start, end);
quickSort(nums, start, mid - 1);
quickSort(nums, mid + 1, end);
}
function partition(nums, start, end) {
let pivot = nums[start];
// 选择第一个数作为pivot,那么left就从第二个数开始进行比较
let left = start + 1;
let right = end;
while (left <= right) {
// 如果nums[left]一直小于pivot,left就向右移动
while (left <= right && nums[left] <= pivot) {
left++;
}
// 如果nums[right]一直大于pivot,right就向左移动
while (left <= right && nums[right] >= pivot) {
right--;
}
// 如果出现 nums[left] > pivot 或者 nums[right] < pivot 的情况,
// 就交换 nums[left] 和 nums[right]的位置
if (left < right) {
[nums[left], nums[right]] = [nums[right], nums[left]];
left++;
right--;
}
}
// 把pivot交换到合适位置
[nums[start], nums[right]] = [nums[right], nums[start]];
return right;
}
但是当数组中包含大量重复元素时,会出现性能下降的现象,此时我们可以使用三路快速排序算法。
三路快速排序的基本思想是将数组划分为三个区域:小于、等于和大于 pivot 的区域。这样可以将相同元素聚集在一起,从而减少交换的次数,提高性能。
代码如下:
/**
* @param {number[]} nums
* @return {number[]}
*/
var sortArray = function(nums) {
threeWayQuickSort(nums, 0, nums.length - 1);
return nums;
};
function threeWayQuickSort(nums, start, end) {
if (start >= end) {
return;
}
// 缩写解释 lt: less than(小于) gt: greater than(大于)
// 使用partitionThree函数进行三路划分
const [lt, gt] = partitionThree(nums, start, end);
threeWayQuickSort(nums, start, lt - 1);
threeWayQuickSort(nums, gt + 1, end);
}
function partitionThree(nums, start, end) {
let pivot = nums[start];
// lt指向小于pivot的区域的末尾
let lt = start;
// gt指向大于pivot的区域的起始
let gt = end;
// 用于遍历数组的指针
let i = start;
while (i <= gt) {
if (nums[i] < pivot) {
// 将当前元素交换到小于pivot区域末尾,并扩展小于区域
[nums[lt], nums[i]] = [nums[i], nums[lt]];
lt++;
i++;
} else if (nums[i] > pivot) {
// 将当前元素交换到大于pivot区域起始,并扩展大于区域
[nums[gt], nums[i]] = [nums[i], nums[gt]];
gt--;
} else {
// 相等情况,直接扩展等于区域
i++;
}
}
// 将pivot元素交换到适当位置
[nums[start], nums[lt]] = [nums[lt], nums[start]];
// 返回等于区域的起始和末尾
return [lt, gt];
}
这段代码中的 partitionThree 函数实现了三路划分,将数组划分为小于、等于和大于 pivot 的三个区域,从而有效处理重复元素。在每次递归中,通过 lt 和 gt 两个指针来维护三个区域的边界。相同元素会被直接放入等于区域,从而避免了不必要的交换操作。这种方法可以显著提高处理包含大量重复元素的数组的性能。
2 数组中第K大的数字
力扣215 题,数组中的第K个最大元素。给定整数数组 nums 和整数 k,请返回数组中第 k 个最大的元素。请注意,你需要找的是数组排序后的第 k 个最大的元素,而不是第 k 个不同的元素。
基于快速排序来解决这个问题,当我们完成快速排序后,序列是一个升序序列,我们只需要在排好序的序列中找到nums.length - k个元素即为最大的第k个元素。同样如果数组里包含海量重复元素那么就可以使用三路快速排序思想,将数组分为小于、等于和大于 pivot 的三个区域,以减少不必要的交换操作和递归。
代码如下:
var findKthLargest = function(nums, k) {
// 使用快速选择算法,在索引范围 [0, nums.length - 1] 中寻找第 k 个最大元素
return quickSelect(nums, 0, nums.length - 1, nums.length - k);
};
/**
* 快速选择函数
* */
function quickSelect(nums, start, end, targetIndex) {
// 如果区间中只有一个元素,则该元素就是第 k 个最大元素
if (start === end) {
return nums[start];
}
// 使用三路快速排序的方式进行划分
const { left, right } = threeWayPartition(nums, start, end);
// 如果 targetIndex 在 [left, right] 区间内,则说明第 k 个最大元素就在该区间内
if (targetIndex >= left && targetIndex <= right) {
return nums[targetIndex];
} else if (targetIndex < left) {
// 否则,在左侧区域寻找第 k 个最大元素
return quickSelect(nums, start, left - 1, targetIndex);
} else {
// 在右侧区域寻找第 k 个最大元素
return quickSelect(nums, right + 1, end, targetIndex);
}
}
/**
* 三路快速排序划分函数
*
* */
function threeWayPartition(nums, start, end) {
// 选取最后一个元素作为 pivot
const pivot = nums[end];
let i = start; // 当前元素索引
let lt = start; // lt指向小于pivot的区域的末尾
let gt = end; // gt指向大于pivot的区域的起始
while (i <= gt) {
if (nums[i] < pivot) {
// 将当前元素交换到小于 pivot 区域
[nums[i], nums[lt]] = [nums[lt], nums[i]];
i++;
lt++;
} else if (nums[i] > pivot) {
// 将当前元素交换到大于 pivot 区域
[nums[i], nums[gt]] = [nums[gt], nums[i]];
gt--;
} else {
// 相等的情况,直接跳过
i++;
}
}
// 返回小于 pivot 区域的右边界和大于 pivot 区域的左边界
return { left: lt, right: gt };
}