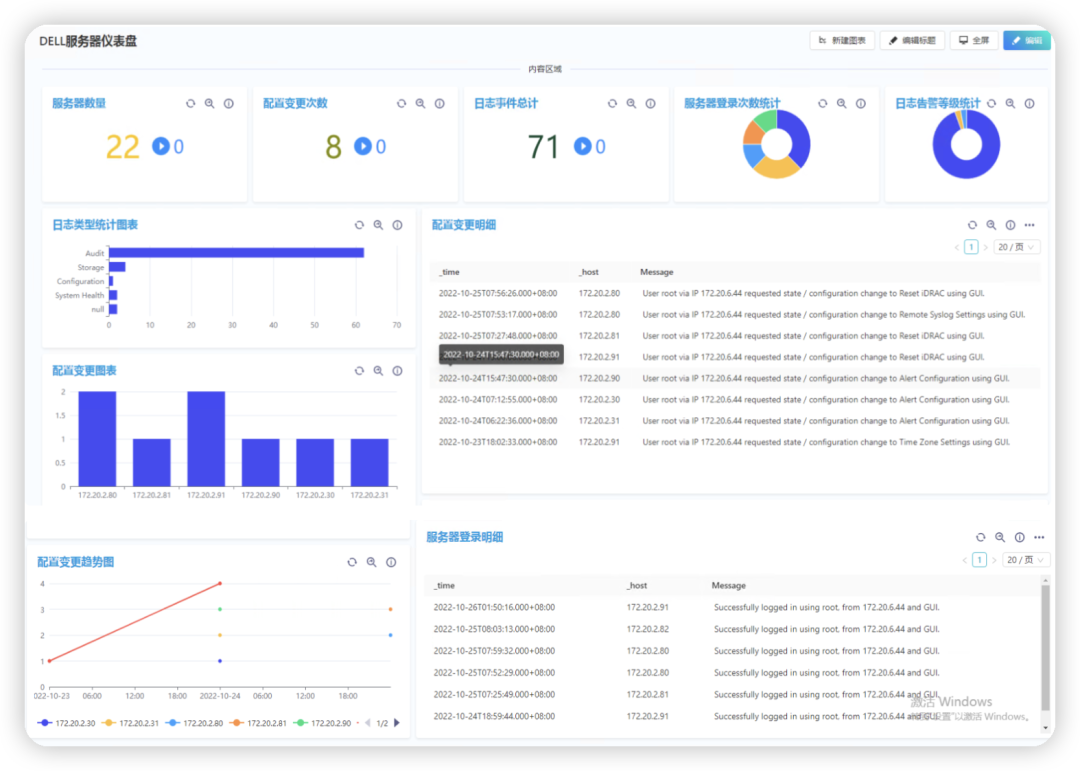
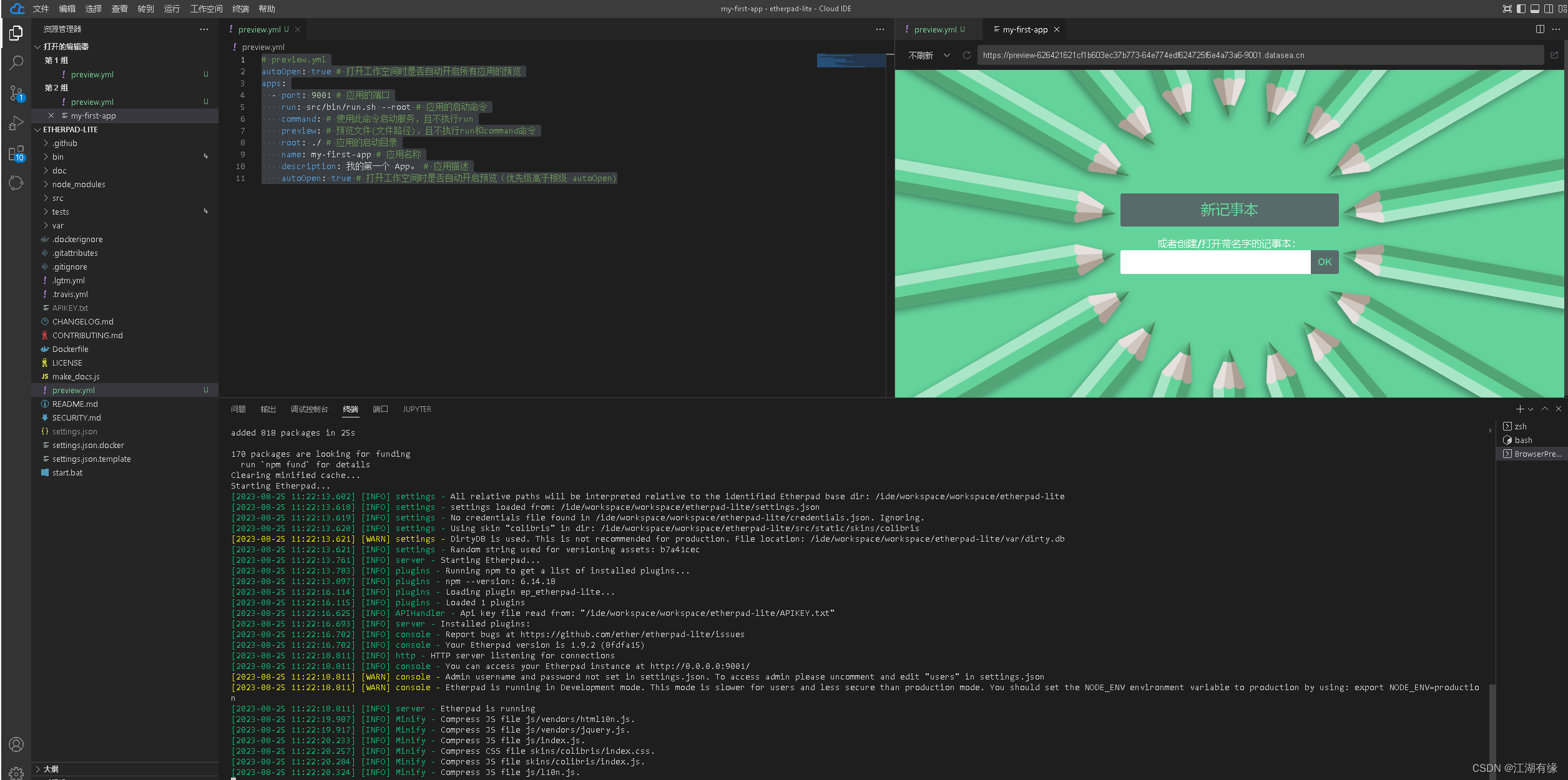
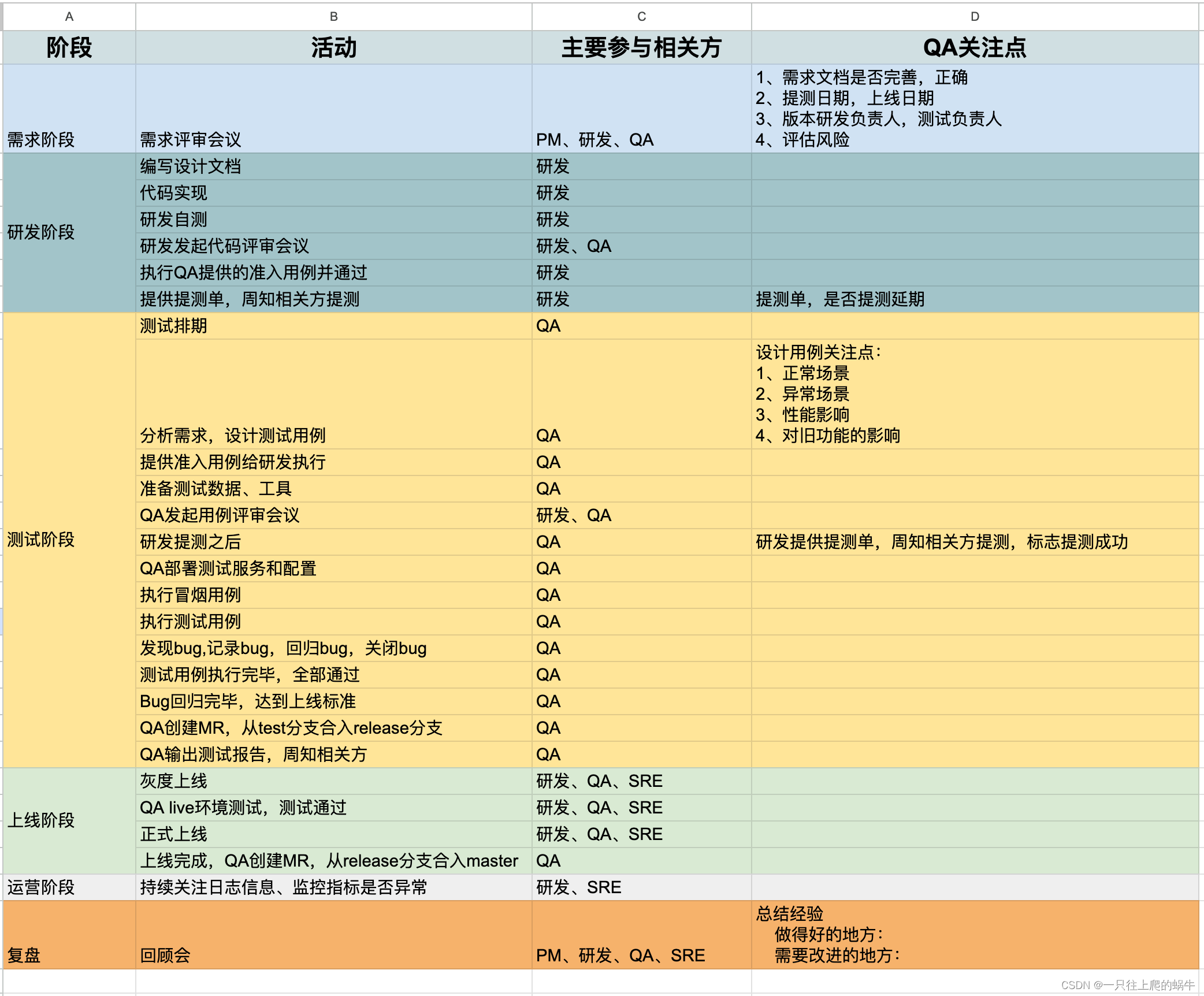
SMC状态机 讲解1.4 XX.sm文件
- 1、Task类
- 2、FSM任务
- 3、创建SMC.sm文件
- 4、定义FSM状态
- 5、定义转换 transition
- 6、定义FSM转换动作
- 7、定义FSM默认转换
- 8、定义状态Entry/Exit 动作
- 9、连接Task与Task FSM
1、Task类
SMC为对象(不是进程或应用程序,而是单个对象)生成有限状态机。如果有接收异步回调的对象,并且对象响应这些回调是基于对象状态的,那么SMC提供了一个强大的解决方案。
package com.acme.supercron;
public final class Task implements TaskEventListener,
TimerEventListener
{
public Task()
{
// 对象初始化
...
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------
// TaskEventListener Interface Implemenation.
//
// 未完成任务在指定时间片内继续工作的时间。
public void start(long timeSlice)
{
...
}
// 当一个正在运行的、未完成的任务应该暂停运行时调用,即使它的时间片没有过期。
// 注意:当时间片过期时,任务的运行也会暂停。
public void suspend()
{
...
}
// 当未完成的任务被阻塞时调用。被阻塞的任务在解除阻塞后能够继续运行。
public void block()
{
...
}
// 当阻塞的任务被解除阻塞并允许继续运行时调用。
public void unblock()
{
...
}
// 当一个未完成的任务被永久停止时调用。
// 然后删除已停止的任务。
public void stop()
{
...
}
// 当任务被删除时调用。出现以下情况之一调用:
//1.任务已经完成运行并且现在被停止
//2.系统正在关闭并且所有任务都将立即终止时,任务将被删除。
public void delete()
{
...
}
//
// end of TaskEventListener Interface Implemenation.
//-----------------------------------------------------------
//-----------------------------------------------------------
// TimerEventListener Interface Implementation.
//
// 当时间片计时器到期时调用。如果运行,任务挂起。
public void handleTimeout(TimerEvent event)
{
...
}
//
// end of TimerEventListener Interface Implementation.
//-----------------------------------------------------------
// Remainder of class definition.
...
}
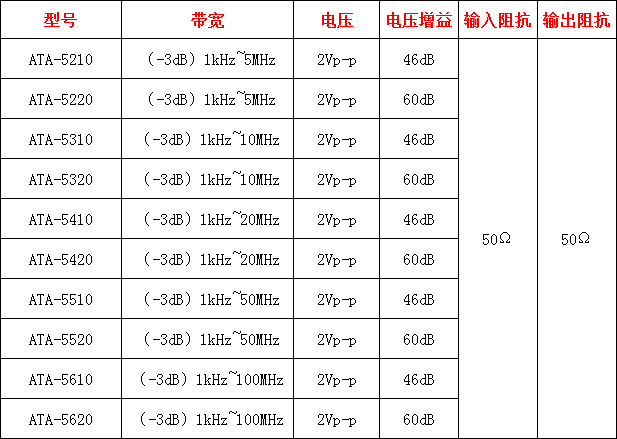
2、FSM任务
任务FSM示意图如下:
 任务的状态是:
任务的状态是:
- Running:任务正在运行。允许任务在指定的时间限制内运行。
- Suspended:任务尚未完成,正在等待再次运行。
- Stopped:任务已完成运行或外部停止。
- Blocked:未完成的任务被外部阻止再次运行。它将保持这种状态,直到停止或解除阻塞。
- Stopping:任务在进入停止状态前,正在清理已分配的资源。
- Deleted:任务完全停止,关联资源全部返回。现在可以安全地删除任务了。FSM的结束状态。
3、创建SMC.sm文件
XX.sm 文件是一个没有定义状态或转换的框架。包含以下特性:
| 关键字 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| %package | 指定此FSM所属的类包,与关联的Task类包相同。 |
| %fsmclass | 指定生成的有限状态机类名。如果未指定%fsmclass,则有限状态机类名默认为TaskContext。这个关键字不是必需的。 |
| %fsmfile | 指定生成的有限状态机类文件名 |
| %access | 指定生成的类的可访问级别(只在生成Java和c#代码时有效) |
| %start | 指定FSM的启动状态 |
| %map | FSM的名称 |
| %{ %} | 编写注释 |
代码实现:
%{
//编写注释
//...
%}
// This FSM works for the Task class only and only the Task
// class may instantiate it.
%class Task
%package com.acme.supercron
%fsmclass TaskFSM
%fsmfile TaskFSM
%access package
// A %map name cannot be the same as the FSM class name.
%start TaskMap::Suspended
%map TaskMap
%%
...
%%
4、定义FSM状态
在%map TaskFSM %% … %% 分隔符中定义FSM状态
// 此FSM只对Task类起作用
// class可以实例化.
%class Task
%package com.acme.supercron
%fsmclass TaskFSM
%fsmfile TaskFSM
%access package
// %map 名字不能与FSM类名相同
%start TaskMap::Suspended
%map TaskMap
%%
Suspended
{
...
}
Running
{
...
}
// 此处等待解锁、停止、删除
Blocked
{
...
}
Stopping
{
...
}
Stopped
{
...
}
Deleted
{
...
}
...
%%
5、定义转换 transition
转换由四个部分组成:
- transition name:转换名称
- transition guard:转换保护(可选)
- 转换结束时的状态
- transition action:转换动作
下面介绍Stop、Block和Delete转换:
// 该FSM只对Task类工作,并且只对Task类工作
// 类可以实例化
%class Task
%package com.acme.supercron
%package package
%fsmclass TaskFSM
%fsmfile TaskFSM
%access package
// %map名称不能与FSM的类名相同
%start TaskMap::Suspended
%map TaskMap
%%
Suspended
{
// Time to do more work.
// 时间片持续时间作为转换传入
// argument.
Start(timeslice: long) // 转换名称
Running // 转换结束后的状态
{
... // 执行动作
}
}
Running
{
// 等待时间片
Suspend //转换名称
Suspended //转换结束后的状态
{
...
}
// Task已经完成.
Done
Stopped
{
...
}
}
// 等待解锁、停止或删除
Blocked
{
// The task may continue working now.
Unblock
Suspended
{
...
}
}
Stopping
{
// task结束
Stopped
Stopped
{
...
}
}
Stopped
{
...
}
Deleted
{
...
}
...
%%
6、定义FSM转换动作
转换操作是FSM和应用程序类Task之间的第一次耦合。actions是Task的方法。这些方法必须具有以下属性:
- FSM可访问,这意味着至少有public方法。或者如果在同一个package中,则有package方法。
- 有void返回类型。如果该方法确实返回值,则FSM将忽略该值。
SMC对转换参数没有语法限制,只是将它们用“()”括号括起来并以逗号分隔。
// This FSM works for the Task class only and only the Task
// class may instantiate it.
%class Task
%package com.acme.supercron
%fsmclass TaskFSM
%fsmfile TaskFSM
%access package
// A %map name cannot be the same as the FSM class name.
%start TaskMap::Suspended
%map TaskMap
%%
Suspended
{
// Time to do more work.
// The timeslice duration is passed in as a transition
// argument.
Start(timeslice: long)
Running
{
continueTask();
startSliceTimer(timeslice);
}
}
Running
{
// Wait for another time slice.
Suspend
Suspended
{
stopSliceTimer();
suspendTask();
}
// Task has completed.
Done
Stopped
{
stopSliceTimer();
releaseResources();
}
}
// Wait here to be either unblocked, stopped or deleted.
Blocked
{
// The task may continue working now.
// No actions needed.
Unblock
Suspended
{}
}
Stopping
{
// The task is now stopped.
Stopped
Stopped
{
releaseResources();
}
}
Stopped
{
...
}
Deleted
{
...
}
...
%%
Task中的转换动作方法为:
package com.acme.supercron;
public final class Task implements TaskEventListener, TimerEventListener
{
public Task()
{
// 对象初始化
...
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------
// TaskEventListener Interface Implemenation.
//
<snip>
//
// end of TaskEventListener Interface Implemenation.
//-----------------------------------------------------------
//-----------------------------------------------------------
// TimerEventListener Interface Implementation.
//
<snip>
//
// end of TimerEventListener Interface Implementation.
//-----------------------------------------------------------
//-----------------------------------------------------------
// State Machine Actions.
//
// Activate the underlying task and get it running again.
/* package */ void continueTask()
{
...
return;
}
// Inactivate the underlying task.
/* package */ void suspendTask()
{
...
return;
}
// Start the timeslice timer for the given milliseconds.
/* package */ void startSliceTimer(long timeslice)
{
...
return;
}
// Stop the timeslice timer.
/* package */ void stopSliceTimer()
{
...
return;
}
// Return system resources from whence they came.
/* package */ void releaseResources()
{
...
return;
}
//
// end of State Machine Actions.
//-----------------------------------------------------------
// Remainder of class definition.
...
}
7、定义FSM默认转换
现在已经定义了转换“Stop”、“Block”和“Delete”。这些转换没有开始状态的原因是,无论当前状态如何,都要进行转换。
- Stop:如果task仍然是alive的(处于Suspended、Running或Blocked状态),那么它必须立即转换到stop状态。如果任务为not alive(在其他三种状态下),则忽略此转换,因为task不再alive。
- Block:如果task处于Suspended或running状态,那么它将转换到Bolcked状态。否则该请求将被忽略。
- Delete:如果task处于除Deleted之外的任何状态,那么它必须转换到Deleted状态。
SMC提供了两种定义默认转换的方法:Default状态和Default转换。sm更新了默认的Stop, Block和Delete转换定义:
// This FSM works for the Task class only and only the Task
// class may instantiate it.
%class Task
%package com.acme.supercron
%fsmclass TaskFSM
%fsmfile TaskFSM
%access package
// A %map name cannot be the same as the FSM class name.
%start TaskMap::Suspended
%map TaskMap
%%
Suspended
{
// Time to do more work.
// The timeslice duration is passed in as a transition
// argument.
Start(timeslice: long)
Running
{
continueTask();
startSliceTimer(timeslice);
}
Block
Blocked
{
blockTask();
}
Running
{
// Wait for another time slice.
Suspend
Suspended
{
stopSliceTimer();
suspendTask();
}
Block
Blocked
{
stopSliceTimer();
blockTask();
}
// Task has completed.
Done
Stopped
{
stopSliceTimer();
releaseResources();
}
}
// Wait here to be either unblocked, stopped or deleted.
Blocked
{
// The task may continue working now.
// No actions needed.
Unblock
Suspended
{}
}
Stopping
{
// The task is now stopped.
Stopped
Stopped
{
releaseResources();
}
// We are stopping.
Stop
nil
{}
}
Stopped
{
// We are stopping.
Stop
nil
{}
// Ignore all transitions until deleted.
Default
nil
{}
}
Deleted
{
// Define all known transitions as loopbacks.
Start(timeslice: long)
nil
{}
Suspend()
nil
{}
Block()
nil
{}
Unblock()
nil
{}
Done()
nil
{}
Stop()
nil
{}
Stopped()
nil
{}
Delete()
nil
{}
}
Default
{
// Three states follow this transition, three states ignore.
// So define the active definition.
Stop
Stopping
{
stopTask();
}
// Block is ignored by four of six states.
// Force the other two states to define this.
// Note the "nil" end state. This is a loopback transition
Block
nil
{}
// All but the Delete state follow this transition. Define it here.
Delete
Deleted
{}
// Ignore a transition by default.
Default
nil
{}
}
%%
blockTask()和stopTask()方法被添加到Task类中:
package com.acme.supercron;
public final class Task implements TaskEventListener, TimerEventListener
{
public Task()
{
// Object initialization.
...
}
<snip>
//-----------------------------------------------------------
// State Machine Actions.
//
<snip>
// Block the underlying task from running.
/* package */ void blockTask()
{
...
return;
}
// Permanently stop the underlying task.
/* package */ void stopTask()
{
...
return;
}
<snip>
//
// end of State Machine Actions.
//-----------------------------------------------------------
// Remainder of class definition.
...
}
8、定义状态Entry/Exit 动作
当不处于Running状态时,应该停止时间片定时器。实现这一点的方法是在Running中添加一个Exit块,并将stopSliceTimer()动作移动到那里。
由于正在定义状态的Exit动作,因此将startSliceTimer()动作放入Entry块中似乎是很自然的。但反对的理由有两点:
- 进入运行状态的转换只有一次。将startSliceTimer()从Suspended的Start过渡移动到Running的entry动作没有任何好处。
- startSliceTimer()接受Start转换的时间片参数。如果startSliceTimer()是一个入口操作,那么它不能访问转换参数。解决这个问题的唯一方法是将切片时间存储在Task类中,然后在entry动作(startSliceTimer(ctext . getslicetime()))中立即检索它。现在,将动作移动到entry块比什么都不做还要糟糕。
// This FSM works for the Task class only and only the Task
// class may instantiate it.
%class Task
%package com.acme.supercron
%fsmclass TaskFSM
%fsmfile TaskFSM
%access package
// A %map name cannot be the same as the FSM class name.
%start TaskMap::Suspended
%map TaskMap
%%
<snip>
Running
Exit
{
stopSliceTimer();
}
{
// Wait for another time slice.
Suspend
Suspended
{
// stopSliceTimer(); moved.
suspendTask();
}
Block
Blocked
{
// stopSliceTimer(); moved.
blockTask();
}
// Task has completed.
Done
Stopped
{
// stopSliceTimer(); moved.
releaseResources();
}
}
<snip>
}
%%
9、连接Task与Task FSM
将FSMs连接到它们的应用程序类非常简单:
- 在Task类中添加数据成员TaskFSM _fsm
- 在Task的构造函数中实例化TaskFSM。
- 如果start状态有必须在创建FSM时执行的entry动作,那么在Task的构造函数之外调用_fsm.enterStartState()
- 当你需要发出一个转换时,调用_fsm相应的转换方法:
_fsm.Start(timeSlice);
package com.acme.supercron;
public final class Task
implements TaskEventListener,
TimerEventListener
{
public Task()
{
// Object initialization.
...
// Instantiate the FSM here but perform the initial
// state's entry actions outside of the constructor
// to prevent referencing this object before its
// initialization is complete.
_fsm = new TaskFSM(this);
}
// Execute the start state's entry actions by calling this
// method. This method should be called only once and prior to
// issuing any transitions. Therefore this method should be
// called before registering this Task instance as a task and
// timer event listener.
public void startFSM()
{
_fsm.enterStartState();
TaskManager.addListener(this);
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------
// TaskEventListener Interface Implemenation.
//
// Time for the incomplete task to continue its work for the
// specified time slice.
public void start(long timeSlice)
{
_fsm.Start(timeSlice);
}
// Called when a running, incomplete task should suspend
// running even though its time slice is not expired.
// Note: the task's running is also suspended when the time
// slice expires.
public void suspend()
{
_fsm.Suspend();
}
// Called when an incomplete task is blocked. Blocked tasks
// are able to continue running when unblocked.
public void block()
{
_fsm.Block();
}
// Called when a blocked task is unblocked and allowed
// to continue running.
public void unblock()
{
_fsm.Unblock();
}
// Called when an incomplete task is permanently stopped.
// Stopped tasks are then deleted.
public void stop()
{
_fsm.Stop();
}
// Called when the task is deleted. Tasks are deleted when
// either 1) the task has completed running and is now
// stopped or 2) when the system is shutting down and all
// are to terminate immediately.
public void delete()
{
_fsm.Delete();
}
//
// end of TaskEventListener Interface Implemenation.
//-----------------------------------------------------------
//-----------------------------------------------------------
// TimerEventListener Interface Implementation.
//
// Called with the time slice timer has expired. If running,
// the task is suspended.
public void handleTimeout(TimerEvent event)
{
_fsm.Suspend();
}
//
// end of TimerEventListener Interface Implementation.
//-----------------------------------------------------------
<snip>
// The associated finite state machine.
private final TaskFSM _fsm;
}