文章目录
- 一、C++实现线程池
- 1. 头文件
- 2. 测试部分
- 二、C++11实现线程池
- 1. 头文件
- 2. 测试部分
一、C++实现线程池
1. 头文件
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
#include<string.h>
#include<string>
#include<pthread.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<queue>
#include<unistd.h>
using namespace std;
using callback = void(*)(void*);
//任务的结构体
template<typename T>
struct Task
{
Task()
{
function = nullptr;
args = nullptr;
}
Task(callback fun, void* args)
{
function = fun;
this -> args = (T*)args;
}
callback function;
T* args;
};
//任务队列
template<typename T>
class TaskQueue
{
public:
TaskQueue()
{
pthread_mutex_init(&mutex,NULL);
}
~TaskQueue()
{
pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex);
}
//添加任务
void AddTask(Task<T> task)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
queue.push(task);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
}
void AddTask(callback fun, void* args)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
Task<T> task(fun,args);
queue.push(task);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
}
//取出一个任务
Task<T> TakeTask()
{
Task<T> task;
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
if (queue.size() > 0)
{
task = queue.front();
queue.pop();
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
return task;
}
//获取当前队列中的任务个数
inline int GetTaskNum()
{
return queue.size();
}
private:
pthread_mutex_t mutex; //互斥锁
std::queue<Task<T>> queue;
};
//线程池
template<typename T>
class ThreadPool
{
public:
ThreadPool(int min , int max)
{
//实例化任务队列
taskqueue = new TaskQueue<T>;
//初始化线程池
min_num = min;
max_num = max;
busy_num = 0;
live_num = min;
//根据线程最大上限,给线程数组分配内存
threadID = new pthread_t[max];
if (threadID == nullptr)
{
cout << "new threadID fail" << endl;
}
//初始化线程ID
memset(threadID, 0, sizeof(pthread_t) * max);
//初始化互斥锁和条件变量
if (pthread_mutex_init(&mutex_pool, NULL) != 0 ||
pthread_cond_init(¬empty, NULL) != 0)
{
cout << "mutex or cond init fail" << endl;
}
//创建线程
for (size_t i = 0; i < min; ++i)
{
pthread_create(&threadID[i], NULL, Work, this);
cout << "create thread ID :" << to_string(threadID[i]) << endl;
}
pthread_create(&managerID, NULL, Manage, this);
}
~ThreadPool()
{
shutdown = true;
//销毁管理者进程
pthread_join(managerID, NULL);
//唤醒消费者
for (int i = 0; i < live_num; ++i)
{
pthread_cond_signal(¬empty);
}
if (taskqueue)
{
delete taskqueue;
}
if (threadID)
{
delete[] threadID;
}
pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex_pool);
pthread_cond_destroy(¬empty);
}
//添加任务
void Add_Task(Task<T> task)
{
if (shutdown)
return;
//添加任务,不需加锁,队列中有
taskqueue->AddTask(task);
//唤醒消费者
pthread_cond_signal(¬empty);
}
//获取忙线程个数
int Get_Busy_Num()
{
int busynum = 0;
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex_pool);
busynum = busy_num;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex_pool);
return busynum;
}
//获取存活线程个数
int Get_Live_Num()
{
int livenum = 0;
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex_pool);
livenum = live_num;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex_pool);
return livenum;
}
private:
//工作的线程任务函数
static void* Work(void* args)
{
ThreadPool* pool = static_cast<ThreadPool*>(args);
while (true)
{
//访问任务队列加锁
pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->mutex_pool);
//判断任务队列是否为空,空了就堵塞
while (pool->taskqueue->GetTaskNum() == 0 && !pool->shutdown)
{
cout << "thread :" << to_string(pthread_self()) << " waiting..." << endl;
pthread_cond_wait(&pool->notempty, &pool->mutex_pool);
//解除后 判断是否要销毁进程
if (pool->exit_num > 0)
{
pool->exit_num--;
if (pool->live_num > pool->min_num)
{
pool->live_num--;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mutex_pool);
pool->Thread_Exit();
}
}
}
//判断线程池是否要关闭了
if (pool->shutdown)
{
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mutex_pool);
pool->Thread_Exit();
}
//从任务队列取出任务
Task<T> task = pool->taskqueue->TakeTask();
pool->busy_num++;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mutex_pool);
cout << "thread :" << to_string(pthread_self()) << " start working..." << endl;
task.function(task.args);
delete task.args;
task.args = nullptr;
//任务结束
cout << "thread :" << to_string(pthread_self()) << " end working..." << endl;
pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->mutex_pool);
pool->busy_num--;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mutex_pool);
}
return nullptr;
}
//管理者线程任务函数
static void* Manage(void* args)
{
ThreadPool* pool = static_cast<ThreadPool*>(args);
while (!pool->shutdown)
{
//5秒检测一次
sleep(5);
pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->mutex_pool);
int livenum = pool->live_num;
int busynum = pool->busy_num;
int queuesize = pool->taskqueue->GetTaskNum();
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mutex_pool);
const int NUMBER = 2;
//创建
if (queuesize > livenum && livenum < pool->max_num)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->mutex_pool);
int num = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < pool->max_num &&
num < NUMBER &&
pool->live_num < pool->max_num ; ++i)
{
if (pool->threadID[i] == 0)
{
pthread_create(&pool->threadID[i], NULL, Work, pool);
num++;
pool->live_num++;
}
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mutex_pool);
}
//销毁
if (busynum * 2 < livenum && livenum > pool->min_num)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->mutex_pool);
pool->exit_num = NUMBER;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mutex_pool);
for (int i = 0; i < NUMBER; ++i)
{
pthread_cond_signal(&pool->notempty);
}
}
}
return nullptr;
}
void Thread_Exit()
{
pthread_t tid = pthread_self();
for (int i = 0; i < max_num; ++i)
{
if (threadID[i] == tid)
{
cout << "thread :" << to_string(pthread_self()) << "exiting" << endl;
threadID[i] = 0;
break;
}
}
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
private:
pthread_mutex_t mutex_pool;
pthread_cond_t notempty;
pthread_t* threadID;
pthread_t managerID;
TaskQueue<T>* taskqueue;
int min_num;
int max_num;
int busy_num;
int live_num;
int exit_num;
bool shutdown = false;
};
2. 测试部分
#include"ThreadPool.h"
void Task_Test(void* args)
{
int num = *(int*)args;
cout<<"thread :" << pthread_self() << " is working " << "number =" << num <<endl;
sleep(1);
return;
}
int main()
{
//创建线程池
ThreadPool<int> pool(3, 10);
for (int i = 0; i < 100; ++i)
{
int* num = new int(i+100);
pool.Add_Task(Task<int>(Task_Test,num));
}
sleep(40);
return 0;
}
以上只是基于C修改出对应于C++的代码
并且以上代码存在一个问题
输出的结果有时会因为线程原因出现混乱
可以通过加锁来解决,但锁的数量超过1就容易导致死锁问题,所以暂且搁置
二、C++11实现线程池
并非原创,摘于此处
1. 头文件
#pragma once
#include<queue>
#include<thread>
#include<condition_variable>
#include<atomic>
#include<stdexcept>
#include<future>
#include<vector>
#include<functional>
namespace std
{
#define THREADPOOL_MAX_NUM 16
class threadpool
{
unsigned short _initsize;
using Task = function<void()>;
vector<thread> _pool;
queue<Task> _tasks;
mutex _lock;
mutex _lockGrow;
condition_variable _task_cv;
atomic<bool> _run{true};
atomic<int> _spa_trd_num{0};
public:
inline threadpool(unsigned short size = 4)
{
_initsize = size;
Add_Thread(size);
}
inline ~threadpool()
{
_run = false;
_task_cv.notify_all();
for (thread& thread : _pool)
{
if (thread.joinable())
thread.join();
}
}
template<typename F,typename... Args>
auto commit(F&& f, Args&& ...args) -> future<decltype(f(args...)) >
{
if (!_run)
throw runtime_error{"commit auto stop"};
using RetType = decltype(f(args...));
auto task = make_shared<packaged_task<RetType()>>(bind(forward<F>(f), forward<Args>(args)...));
future<RetType> future = task->get_future();
{
lock_guard<mutex> lock{_lock};
_tasks.emplace([task]() {(*task)(); });
}
if (_spa_trd_num < 1 && _pool.size() < THREADPOOL_MAX_NUM)
Add_Thread(1);
_task_cv.notify_one();
return future;
}
template<typename F>
void commit2(F&& f)
{
if (!_run)
return;
{
lock_guard<mutex> lock{_lock};
_tasks.emplace(forward<F>(f));
}
if (_spa_trd_num < 1 && _pool.size() < THREADPOOL_MAX_NUM)
Add_Thread(1);
_task_cv.notify_one();
}
int idlCount() { return _spa_trd_num; }
int thrCount() { return _pool.size(); }
private:
void Add_Thread(unsigned short size)
{
if (!_run)
throw runtime_error{"Add_Thread stop"};
unique_lock<mutex> lockgrow{_lockGrow};
for (; _pool.size() < THREADPOOL_MAX_NUM && size > 0; --size)
{
_pool.emplace_back([this]
{
while (true)
{
Task task;
{
unique_lock<mutex> lock{_lock};
_task_cv.wait(lock, [this] {return !_run || !_tasks.empty(); });
if (!_run && _tasks.empty())
return;
_spa_trd_num--;
task = move(_tasks.front());
_tasks.pop();
}
task();
if (_spa_trd_num > 0 && _pool.size() > _initsize)
return;
{
unique_lock<mutex> lock{_lock};
_spa_trd_num++;
}
}
});
{
unique_lock<mutex> lock{_lock};
_spa_trd_num++;
}
}
}
};
}
要使用pthread依赖库
2. 测试部分
#include"ThreadPool.hpp"
#include<iostream>
void fun1(int slp)
{
printf("fun1 %ld\n", std::this_thread::get_id());
if (slp > 0)
{
printf("fun1 sleep %ld ========= %ld\n", slp, std::this_thread::get_id());
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(slp));
}
}
struct gfun
{
int operator()(int n)
{
printf("gfun %ld\n", n, std::this_thread::get_id());
return 42;
}
};
class A
{
public:
static int Afun(int n = 0) //函数必须是 static 的才能直接使用线程池
{
std::cout << n << "Afun " << std::this_thread::get_id() << std::endl;
return n;
}
static std::string Bfun(int n, std::string str, char c)
{
std::cout << n << "Bfun " << str.c_str() << " " << (int)c << " " << std::this_thread::get_id() << std::endl;
return str;
}
};
int main()
try {
std::threadpool executor{ 50 };
std::future<void> ff = executor.commit(fun1, 0);
std::future<int> fg = executor.commit(gfun{}, 0);
//std::future<int> gg = executor.commit(A::Afun, 9999); //IDE提示错误,但可以编译运行
std::future<std::string> gh = executor.commit(A::Bfun, 9998, "mult args", 123);
std::future<std::string> fh = executor.commit([]()->std::string { std::cout << "hello, fh ! " << std::this_thread::get_id() << std::endl; return "hello,fh ret !\n"; });
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::seconds(1));
std::cout << fg.get() << " " << fh.get().c_str() << " " << std::this_thread::get_id() << std::endl;
std::cout << " ======= fun1,55 ========= " << std::this_thread::get_id() << std::endl;
executor.commit(fun1, 55).get(); //调用.get()获取返回值会等待线程执行完
std::threadpool pool(4);
std::vector< std::future<int> > results;
for (int i = 0; i < 8; ++i)
{
results.emplace_back(
pool.commit([i] {
std::cout << "hello " << i << std::endl;
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::seconds(3));
std::cout << "world " << i << std::endl;
return i * i;
})
);
}
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::seconds(15));
for (auto&& result : results)
std::cout << result.get() << ' ';
std::cout << std::endl;
return 0;
}
catch (std::exception& e)
{
std::cout << "some error " << std::this_thread::get_id() << e.what() << std::endl;
}
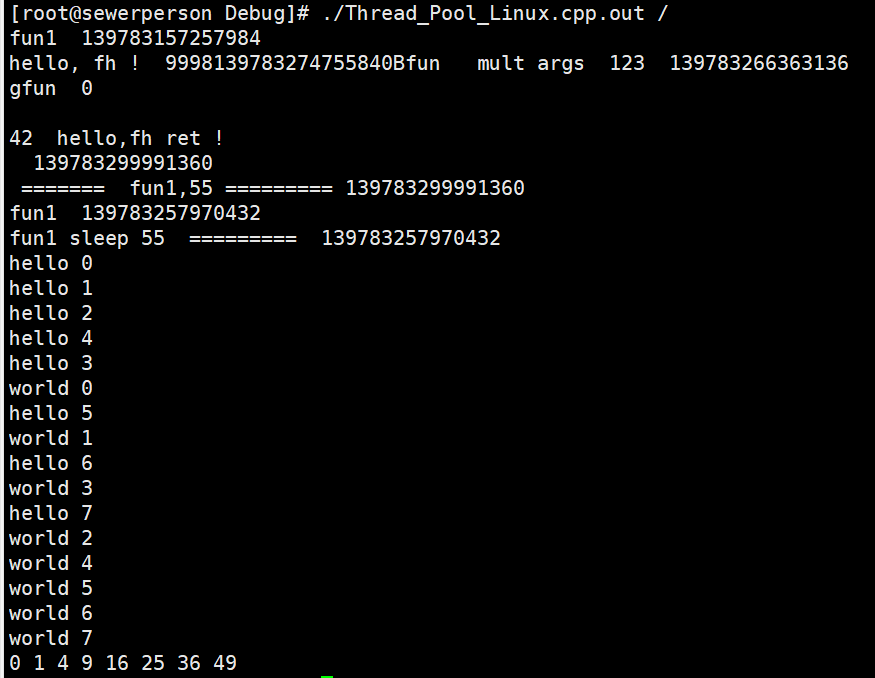
- 测试结果