Spring
@Conditional
Spring 4.0+提供的注解。作用是给需要装载的Bean增加一个条件判断。只有满足条件才会装在到IoC容器中。而这个条件可以由自己去完成的,可以通过重写Condition接口重写matches()方法去实现自定义的逻辑。所以说这个注解增加了对Bean装载的灵活性。
源码
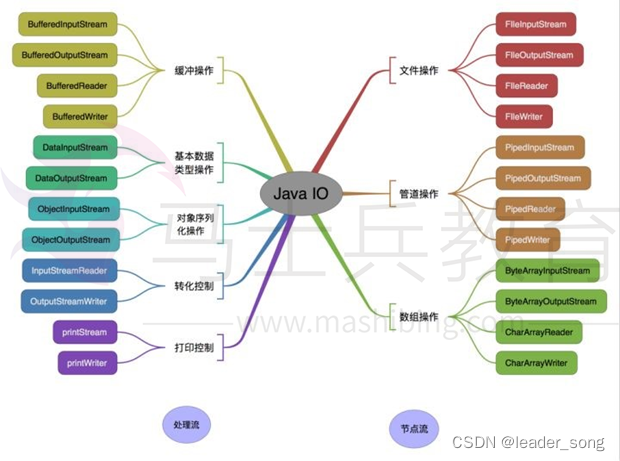
可以看出来首先可以修饰在类、接口、枚举以及方法上。并且可以接收一个或多个实现Condition接口的类。
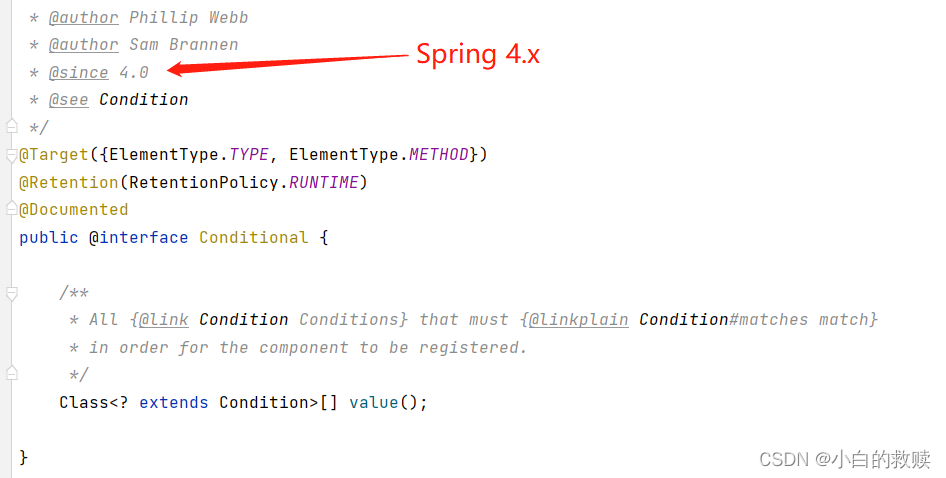
那么在Condition接口中只有一个返回布尔类型的matches()方法。从这个单词也看得出来这是匹配的意思,所以就是匹配校验Bean是否可以被加载进IoC容器中。Determine if the condition matches(确定条件是否匹配)。
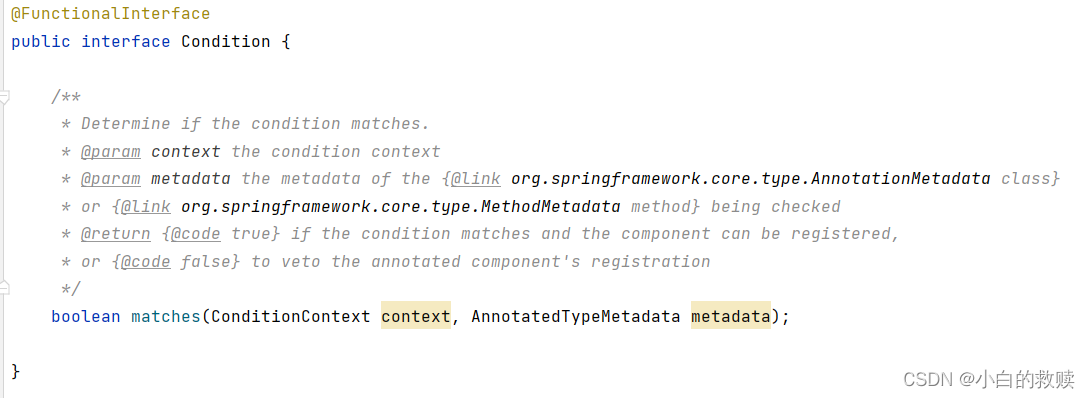
实战代码
以下先建两个Bean类、一个条件类、一个配置类、以及测试Main类。需要注意的是条件类中的参数并不是Spring的上下文ApplicationContext,所以其内容需要设置在-vm options中。至于这个-vm [options]中的options可以通过DOS窗口输入Java就可以看到有什么选项了。
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class Animal {
private String name;
private String sex;
}@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class Person {
private String name;
private Integer age;
}public class PersonCondition implements Condition {
/**
* @param context 上下文
* @param metadata 注解元信息
*/
@Override
public boolean matches(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) {
// 通过条件上下文获取环境中的配置文件信息
String property = context.getEnvironment().getProperty("spring.createBean");
if(null == property) {
return false;
}
return property.contains("person");
}
}public class AnimalCondition implements Condition {
/**
* @param context 上下文
* @param metadata 注解元信息
*/
@Override
public boolean matches(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) {
// 通过条件上下文获取环境中的配置文件信息
String property = context.getEnvironment().getProperty("spring.createBean");
if(null == property) {
return false;
}
return property.contains("animal");
}
}public class ConditionalTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 通过Spring上下文ApplicationContext传入配置类获取其中的Bean描述并输出
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(ConditionalConfig.class);
Arrays.stream(applicationContext.getBeanDefinitionNames()).forEach(System.out::println);
}
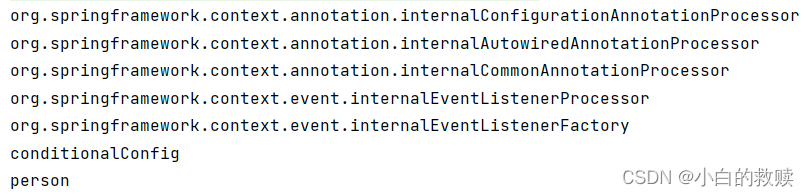
}测试结果
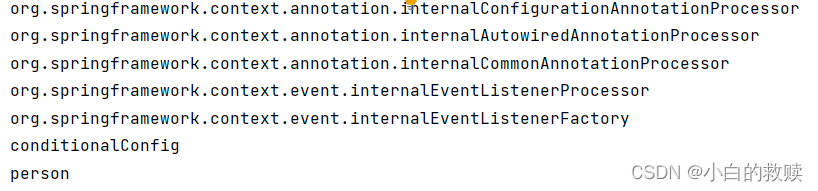
SpringBoot
关于@ConditionalOnXxx注解是在SpringBoot中拓展出来的,是原先Spring框架中没有存在的注解。那么以下就逐一去了解每个注解的作用。需要说的是这些注解全部都可以注解在类、接口、枚举和方法上。

从上图可以发现有十三种是@ConditionalOnXxx。其中就不了解@ConditionalOnCloudPlatform与@ConditionOnJndi这两个注解了。
上面的扩展注解我们可以简单的分为以下几类:
- Bean作为条件:@ConditionalOnBean、@ConditionalOnMissingBean、@ConditionalOnSingleCandidate。
- 类作为条件:@ConditionalOnClass、@ConditionalOnMissingClass。
- SpEL表达式作为条件:@ConditionalOnExpression。
- Java版本作为条件: @ConditionalOnJava
- 配置属性作为条件:@ConditionalOnProperty。
- 资源文件作为条件:@ConditionalOnResource。
- 是否Web应用作为判断条件:@ConditionalOnWebApplication、@ConditionalOnNotWebApplication。
条件为Bean的情况
@ConditionalOnBean
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Conditional({OnBeanCondition.class})
public @interface ConditionalOnBean {
/**
* 需要作为条件的类的Class对象数组
*/
Class<?>[] value() default {};
/**
* 需要作为条件的类的Name, Class.getName()
*/
String[] type() default {};
/**
* (用于指定注解修饰的Bean)条件所需的注解类
*/
Class<? extends Annotation>[] annotation() default {};
/**
* Spring容器中Bean的名字
*/
String[] name() default {};
/**
* 搜索容器层级,当前容器,父容器
*/
SearchStrategy search() default SearchStrategy.ALL;
/**
* 可能在其泛型参数中包含指定Bean类型的其他类
*/
Class<?>[] parameterizedContainer() default {};
}源码中的属性就不一一展示测试了,这里就测试value于name即可,value传入的是Class类型。而这个注解的含义很简单:如果IoC容器中存在该注解中value属性对应的Bean,那么就加载被该注解注解的Bean。否则不加载。测试代码采用上面Spring目录下的测试结果中的代码。这里主要展示配置类中的逻辑。
@Configuration
public class ConditionalConfig {
@Bean
public Person person() {
return new Person();
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnBean(Person.class)
//@ConditionalOnBean(name = "com.gok.entity.Person")
public Animal animal() {
return new Animal();
}
}
这里需要注意的是,Spring加载Bean是在配置类中自上而下加载的,所以说如果person()与animal()两个方法换位置的话Animal是不会被加载到IoC容器中的,因为在它加载时Person还没被加载入IoC容器。
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
@Target({ ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD })
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Conditional(OnBeanCondition.class)
public @interface ConditionalOnMissingBean {
/**
* 需要作为条件的类的Class对象数组
*/
Class<?>[] value() default {};
/**
* 需要作为条件的类的Name, Class.getName()
*/
String[] type() default {};
/**
* 匹配Bean的时候需要忽视的Class对象数组,一般是父类
* @ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = JdbcFactory.class, ignored = MySqlDefaultFactory.class)
*/
Class<?>[] ignored() default {};
/**
* 匹配Bean的时候需要忽视的类的Name, Class.getName()
*/
String[] ignoredType() default {};
/**
* (用于指定注解修饰的Bean)条件所需的注解类
*/
Class<? extends Annotation>[] annotation() default {};
/**
* Spring容器中Bean的名字
*/
String[] name() default {};
/**
* 搜索容器层级,当前容器,父容器
*/
SearchStrategy search() default SearchStrategy.ALL;
/**
* 可能在其泛型参数中包含指定Bean类型的其他类
*/
Class<?>[] parameterizedContainer() default {};
}理解了上面注解的作用,那这个注解就游刃有余了,miss单词意为错过、没有的意思。所以这个注解的作用就是:如果IoC容器中不存在该注解中value属性对应的Bean,那么就加载被该注解注解的Bean。否则不加载。
@Configuration
public class ConditionalConfig {
@Bean
public Person person() {
return new Person();
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(Person.class)
//@ConditionalOnMissingBean(name = "com.gok.entity.Person")
public Animal animal() {
return new Animal();
}
}@ConditionalOnSingleCandidate
@Target({ ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD })
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Conditional(OnBeanCondition.class)
public @interface ConditionalOnSingleCandidate {
/**
* 需要作为条件的类的Class对象
*/
Class<?> value() default Object.class;
/**
* 需要作为条件的类的Name, Class.getName()
*/
String type() default "";
/**
* 搜索容器层级,当前容器,父容器
*/
SearchStrategy search() default SearchStrategy.ALL;
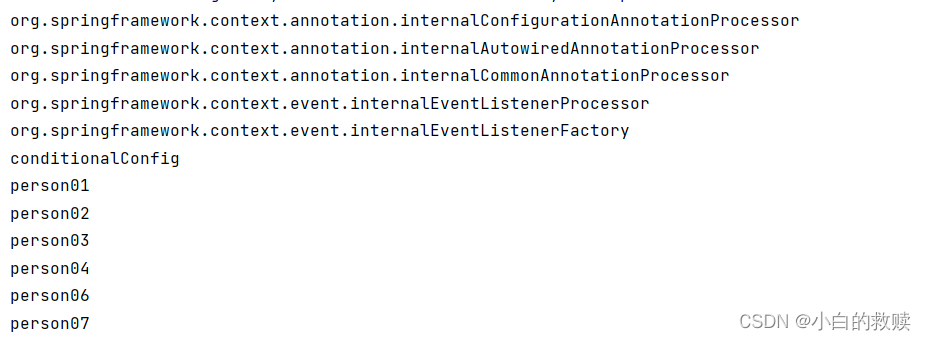
}此注解从单词single与candidate可以得出是单个候选人的意思。大致可以猜测是存在相同类型的Bean的话只会对单个有效。我尝试将其放到person02()上,还是一样将这两个Bean加载到了IoC当中,但是放在第一个person01()上,导致person01没有被加载到IoC容器当中。所以此Bean的作用就是:如果当指定Bean在容器中只有一个,或者虽然有多个但是指定首选Bean的时候则生效。即同类型的Bean中,首选Bean无法被加载入IoC容器中。
@Configuration
public class ConditionalConfig {
@Bean
@ConditionalOnSingleCandidate
public Person person01() {
return new Person();
}
@Bean
public Person person02() {
return new Person();
}
}条件为类的情况
@ConditionalOnClass
@Target({ ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD })
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Conditional(OnClassCondition.class)
public @interface ConditionalOnClass {
/**
* 需要作为条件的类的Class对象数组
*/
Class<?>[] value() default {};
/**
* 需要作为条件的类的Name, Class.getName()
*/
String[] name() default {};
}这个其实和@ConditionalOnBean类似,但是那个注解是在IoC容器中或者是类全限定名找是否存在该Spring Bean。而@ConditionalOnClas是在IoC容器中或者是类全限定名找到是否存在该类。如果存在就加载,不存在就不加载到IoC容器中。
@ConditionalMissingClass
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Conditional({OnClassCondition.class})
public @interface ConditionalOnMissingClass {
/**
* 需要作为条件的类的Name, Class.getName()
*/
String[] value() default {};
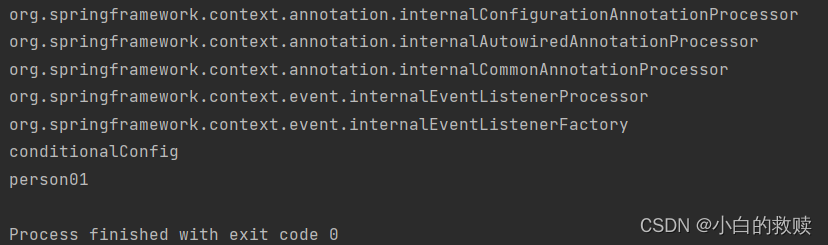
}与@ConditionalOnClass相反。会在这里一起展示代码以及测试的结果。Plant类是真实存在的,所以说person01被加载到IoC容器中,而person02没有被加载到IoC当中。
@Configuration
public class ConditionalConfig {
@Bean
@ConditionalOnClass(Animal.class)
public Person person01() {
return new Person();
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingClass("com.gok.entity.Animal")
public Person person02() {
return new Person();
}
}
条件为SpEL表达式的情况
@ConditionalOnExpression
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({ ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD })
@Documented
@Conditional(OnExpressionCondition.class)
public @interface ConditionalOnExpression {
/**
* 要作为条件的SpEL表达式
*/
String value() default "true";
}这个注解就是用来判断该Bean是否符合SpEL表达式,至于什么是SpEL表达式就自行百度学习了,就不多放篇幅去详细说明了。这里我设置person01为true,而person02为false。
@Configuration
public class ConditionalConfig {
@Bean
@ConditionalOnExpression("true")
public Person person01() {
return new Person();
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnExpression("false")
public Person person02() {
return new Person();
}
}条件为Java的情况
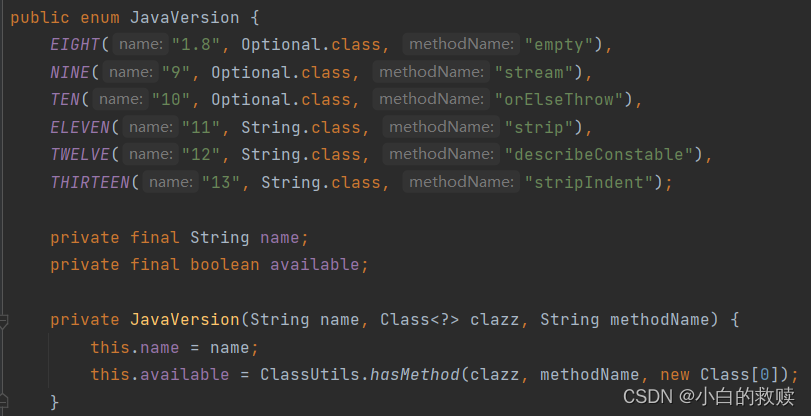
@ConditionalOnJava
@Target({ ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD })
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Conditional(OnJavaCondition.class)
public @interface ConditionalOnJava {
/**
* 比较方式,Range.EQUAL_OR_NEWER:当前版本等于或高于、Range.OLDER_THAN:当前版本老于,越早的版本越老
*/
ConditionalOnJava.Range range() default ConditionalOnJava.Range.EQUAL_OR_NEWER;
/**
* 指定JAVA版本
*/
JavaVersion value();
/**
* Range options.
*/
public static enum Range {
/**
* Equal to, or newer than the specified {@link JavaVersion}.
*/
EQUAL_OR_NEWER,
/**
* Older than the specified {@link JavaVersion}.
*/
OLDER_THAN
private Range() {}
}
}
此注解用来判断当前运行环境的Java版本是多少。符合范围内的条件才会加载Bean。
@Configuration
public class ConditionalConfig {
@Bean
@ConditionalOnJava(JavaVersion.EIGHT)
public Person person01() {
return new Person();
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnJava(JavaVersion.NINE)
public Person person02() {
return new Person();
}
}

条件为配置条件的情况
@ConditionalOnProperty
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({ ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD })
@Documented
@Conditional(OnPropertyCondition.class)
public @interface ConditionalOnProperty {
/**
* 对应property名称的值
*/
String[] value() default {};
String[] name() default {};
/**
* property名称的前缀,可有可无
*/
String prefix() default "";
/**
* 与name组合使用,比较获取到的属性值与havingValue给定的值是否相同,相同才加载配置
*/
String havingValue() default "";
/**
* 缺少该property时是否可以加载。如果为true,没有该property也会正常加载;反之报错
*/
boolean matchIfMissing() default false;
}此注解用于条件配置中读取peoperties文件中的信息。本人测试读取yml无效,需要在配置类上多添加个@PropertySource注解读取文件才能够使用配置条件注解。
# application.properties中的内容
com.gok.test=true
com.gok.password=123456@Configuration
// 读取properties文件的方式 可以配合@Value注解读取详细信息
@PropertySource(value = "classpath:application.properties", encoding = "UTF-8")
//@PropertySources({@PropertySource(value = "classpath:application.properties", encoding = "UTF-8")})
public class ConditionalConfig {
@Bean
@ConditionalOnProperty("com.gok.test")
public Person person01() {
return new Person();
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnProperty(name = "com.gok.test")
public Person person02() {
return new Person();
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnProperty("com.gok.password")
public Person person03() {
return new Person();
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnProperty(name = "com.gok.password", havingValue = "123456")
public Person person04() {
return new Person();
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnProperty(name = "com.gok.password", havingValue = "123456789")
public Person person05() {
return new Person();
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnProperty(value = "com.gok.password=123456", matchIfMissing = true)
public Person person06() {
return new Person();
}
@Bean
// 这里要注意如果要使用prefix前缀的话 必须带上name或者value
// 或者会报错:The name or value attribute of @ConditionalOnProperty must be specified
// 以下拼接即为:是否存在com.gok.password这个属性
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "com.gok", name = "password")
public Person person07() {
return new Person();
}
}条件为资源条件的情况
@ConditionalOnResource
@Target({ ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD })
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Conditional(OnResourceCondition.class)
public @interface ConditionalOnResource {
/**
* 要作为判断条件的资源文件名称 @ConditionalOnResource(resources = ”mybatis.xml”)
*/
String[] resources() default {};
}查询指定的资源,不仅仅可以查找classpath下的文件,还可以用来查找外部资源是否存在。
@Configuration
public class ConditionalConfig {
@Bean
@ConditionalOnResource(resources = "https://www.baidu.com")
public Person person01() {
return new Person();
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnResource(resources = "classpath:application.properties")
public Person person02() {
return new Person();
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnResource(resources = "https://www.baiduhaha.com")
public Person person03() {
return new Person();
}
}
条件为Web应用的情况
@ConditionalOnWebApplication
@Target({ ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD })
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Conditional(OnWebApplicationCondition.class)
public @interface ConditionalOnWebApplication {
/**
* 需要作为条件的Web应用程序的必需类型
*/
ConditionalOnWebApplication.Type type() default ConditionalOnWebApplication.Type.ANY;
/**
* Available application types.
*/
public static enum Type {
/**
* 任何web应用都将匹配
*/
ANY,
/**
* 仅基于servlet的Web应用程序将匹配
*/
SERVLET,
/**
* 仅基于反应式的Web应用程序将匹配
*/
REACTIVE;
private Type() {}
}
}判断当前是否为Web项目/Web环境。主要就是从是否有导入Web的依赖。这里简单介绍以下三种不同情况的依赖引入情况。
<!-- 无Web容器 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- 使用Tomcat/Servlet Web容器 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- 使用Netty 响应式的Web容器 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webflux</artifactId>
</dependency>@ConditionalOnNotWebApplication
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Conditional({OnWebApplicationCondition.class})
public @interface ConditionalOnNotWebApplication {
}参考文章
https://www.cnblogs.com/dusucyy/p/16609736.html
@ConditionalOnBean详解_你就像甜甜的益达的博客-CSDN博客