目录
一,进程间通信
二,管道
匿名管道
命名管道
一,进程间通信
进程间通信(IPC,InterProcess Communication),即在不同进程之间进行信息的传播或交换;由于一般进程用户地址空间是独立的,不可直接访问其他进程地址空间,因此进程间进行信息交换必须通过系统内核进行;
进程间通信目的
- 数据传输,将一个进程的数据发送给另一个进程;
- 资源共享,多个进程间共享同样的资源;
- 通知事件,一个进程向另一个进程或一组进程发送信息,通知它们发生了某种事件(如进程终止时通知父进程);
- 进程控制,有些进程希望完全控制另一个进程的执行(如debug),此时进程希望能够拦截另一个进程的所有异常,并能够及时知道其状态的改变;
进程间通信的分类
- 管道
- 匿名管道pipe
- 命名管道
- System V IPC
- system V 消息队列
- system V 共享内存
- system V 信号量
- POSIX IPC
- 信息队列
- 共享内存
- 信息量
- 互斥量
- 调节变量
- 读写锁
二,管道
匿名管道pipe、命名管道;
匿名管道
Linux通过使用竖线(管道符 | )来连接多个命令,以形成一个管道;管道符前面命令的输出作为管道符后面命令的输入,管道中的数据只能单向流动(即半双工通信),要实现双向流动需创建两个管道;另外,此管道为匿名管道,用完即被自动销毁,且只能在父子进程间通信;
[wz@192 Desktop]$ cat test.c | grep main
int main() 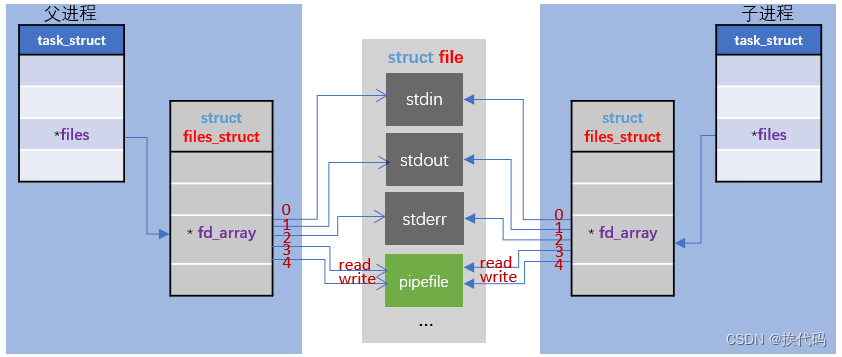
父进程需读写都打开文件,这样子进程继承时才会有读写,然后通过关闭父子进程对应的读写,来实现信息的传输;不关闭相应的读写,也可通信,但一般关闭防止误操作;
管道函数 pipe
- 创建匿名管道
- 创建成功,返回0;
- 创建失败,返回-1;
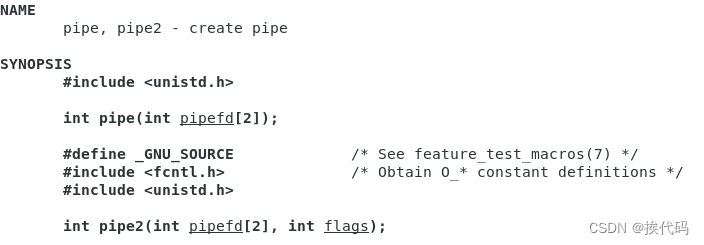
pipefd为文件描述符数组
- pipefd[0],指定管道读端,默认值为3;
- pipefd[1],指定管道写端,默认值为4;
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main()
{
int pipefd[2];
if(pipe(pipefd) < 0)
{
perror("pipe");
return 1;
}
printf("pipefd[0]: %d\n", pipefd[0]);
printf("pipefd[1]: %d\n", pipefd[1]);
return 0;
} [wz@192 pipe]$ ./test
pipefd[0]: 3
pipefd[1]: 4
int main()
{
int pipefd[2];
if(pipe(pipefd) < 0){
perror("pipe");
return 1;
}
char buf[32];
write(pipefd[1],"hellopipe",32); //向管道内写
read(pipefd[0],buf,32); //从管道内读
printf("buf: %s\n", buf);
return 0;
} [wz@192 pipe]$ ./test
buf: hellopipe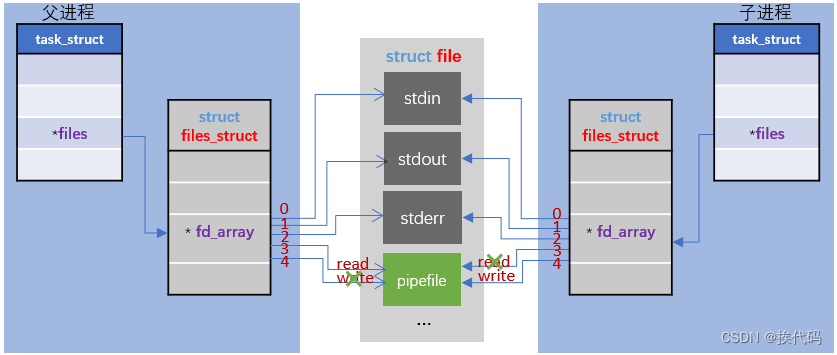
//子进程写入,父进程读取
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
int main()
{
int pipefd[2];
if(pipe(pipefd) < 0){
perror("pipe");
return 1;
}
pid_t id = fork();
if(id < 0){
perror("fork");
return 1;
}
else if(id == 0){
close(pipefd[0]);
char* msg = "child msg";
int count=5;
while(count){
printf("child write: %s\n",msg);
write(pipefd[1],msg,strlen(msg));
sleep(1);
count--;
}
close(pipefd[1]);
exit(0);
}
else{
char buf[64];
close(pipefd[1]);
while(1){
ssize_t sz=read(pipefd[0],buf,sizeof(buf)-1);
if(sz>0){
buf[sz]=0;
printf("father read: %s\n",buf);
}
else if(sz==0){
printf("pipe file empty!\n");
break;
}
}
close(pipefd[0]);
printf("close read\n");
int status = 0;
pid_t wait_pid = waitpid(id,&status,0);
if(WIFEXITED(status) && wait_pid==id)
printf("child exit normal, exit code: %d\n", WEXITSTATUS(status));
else
printf("child exit error, exit sig: %d\n", WTERMSIG(status));
}
return 0;
}
- 如管道为空,则读端需等待数据就绪,即read阻塞;
- 如管道在写端已写满,需等待管道有空闲空间才可继续写入,即write阻塞;
- 管道自带同步机制;
- 管道是单向通信的;
- 管道是面向字节流的;
- 管道只能保证具有血缘关系的进程通信;
- 管道可保证一定程度数据读取的原子性;
//子进程持续在写入,父进程关闭读
//此时OS会直接关闭子进程
else{
char buf[64];
close(pipefd[1]);
while(1){
ssize_t sz=read(pipefd[0],buf,sizeof(buf)-1);
if(sz>0){
buf[sz]=0;
printf("father read: %s\n",buf);
close(pipefd[0]);
break;
}
else if(sz==0){
printf("pipe file empty!\n");
break;
}
}
printf("close read\n");
int status = 0;
pid_t wait_pid = waitpid(id,&status,0);
if(WIFEXITED(status) && wait_pid==id)
printf("child exit normal, exit code: %d\n", WEXITSTATUS(status));
else
printf("child exit error, exit sig: %d\n", WTERMSIG(status));
}//子进程退出信号为13,即SIGPIPE
[wz@192 pipe]$ ./test
child write: child msg
father read: child msg
close read
child write: child msg
child exit error, exit sig: 13
[wz@192 pipe]$ ulimit -a
core file size (blocks, -c) 0
data seg size (kbytes, -d) unlimited
scheduling priority (-e) 0
file size (blocks, -f) unlimited
pending signals (-i) 7154
max locked memory (kbytes, -l) 64
max memory size (kbytes, -m) unlimited
open files (-n) 1024
pipe size (512 bytes, -p) 8
POSIX message queues (bytes, -q) 819200
real-time priority (-r) 0
stack size (kbytes, -s) 8192
cpu time (seconds, -t) unlimited
max user processes (-u) 4096
virtual memory (kbytes, -v) unlimited
file locks (-x) unlimited
命名管道
命名管道是一种特殊类型的文件,可在不相关进程间交换数据,使用FIFO文件实现;
使用命令mkfifo,创建命名管道
[wz@192 pipe]$ mkfifo pipefile
[wz@192 pipe]$ ll pipefile
prw-rw-r--. 1 wz wz 0 8月 18 08:24 pipefile
使用函数mkfifo,创建命名管道

匿名管道与命名管道区别
- 匿名管道由函数pipe创建并打开;
- 命名管道由函数或命令mkfifo创建,再由open打开;
- 唯一区别即创建和打开方式不同;
[wz@192 pipe]$ echo abc > pipefile [wz@192 pipe]$ while :; do echo "1,##########"; cat pipefile; echo "2,#########"; sleep 1; done
1,##########
abc
2,#########
1,##########实现server&client通信
//makefile
.PHONY:all
all: server client
server:server.c
gcc -o $@ $^
client:client.c
gcc -o $@ $^
.PHONY:clean
clean:
rm -rf server client //server.c
//创建命名管道,并读
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
int main()
{
int ret = mkfifo("pipefile", 0644);
if(ret == -1){
perror("mkfifo");
return 1;
}
int pipefd = open("pipefile", O_RDONLY);
if(pipefd < 0){
perror("open");
return 2;
}
char msg[64]={0};
while(1){
printf("please wait ...\n");
ssize_t sz = read(pipefd, msg, sizeof(msg)-1);
if(sz > 0){
msg[sz]=0;
printf("server read: %s\n", msg);
}
else if(sz == 0){
printf("client quit!\n");
break;
}
else{
perror("read");
return 3;
}
}
close(pipefd);
return 0;
} //client.c
//向管道写入
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
int main()
{
int pipefd = open("pipefile", O_WRONLY);
if(pipefd < 0){
perror("open");
return 1;
}
char msg[64]={0};
while(1){
printf("please write ...\n");
ssize_t sz = read(0, msg, sizeof(msg)-1);
if(sz > 0){
msg[sz]=0;
write(pipefd, msg, strlen(msg));
}
else if(sz == 0){
printf("client read empty!\n");
break;
}
else{
perror("client read\n");
return 2;
}
}
close(pipefd);
return 0;
}