文章目录
- VGG Loss 的基础概念
- VGG 的网络结构
- VGG LOSS 的代码解析
- 参考
VGG Loss 的基础概念
VGG Loss 是content Loss中的一种。
为了评价图像的perceptual quality,《Perceptual losses for real time style transfer and super-resolution》 和 《GeneratingImageswithPerceptualSimilarityMetricsbasedonDeepNetworks》将content loss引入到SR中。
Content Loss利用预先训练的图像分类网络来度量图像之间的语义差异。将该网络表示为
φ
φ
φ,提取的第
l
l
l层high-level representation为
φ
(
l
)
(
I
)
φ^{(l)}(I)
φ(l)(I),Content Loss表示为两幅图像high-level representation之间的欧氏距离,如下:
L
content
(
I
^
,
I
;
ϕ
,
l
)
=
1
h
l
w
l
c
l
∑
i
,
j
,
k
(
ϕ
i
,
j
,
k
(
l
)
(
I
^
)
−
ϕ
i
,
j
,
k
(
l
)
(
I
)
)
2
,
\mathcal{L}_{\text {content }}(\hat{I}, I ; \phi, l)=\frac{1}{h_l w_l c_l} \sqrt{\sum_{i, j, k}\left(\phi_{i, j, k}^{(l)}(\hat{I})-\phi_{i, j, k}^{(l)}(I)\right)^2},
Lcontent (I^,I;ϕ,l)=hlwlcl1i,j,k∑(ϕi,j,k(l)(I^)−ϕi,j,k(l)(I))2,
其中
h
l
h_l
hl、
w
l
w_l
wl和
c
l
c_l
cl分别为
l
l
l层上表示的高度、宽度和通道数。
Content Loss 本质上是将learned knowledge of hierarchical image features从分类网络
φ
φ
φ转移到SR网络中。
与像素损失相比,内容损失促使输出图像
I
^
\hat I
I^在感知上与目标图像
I
I
I相似,而不是强迫它们精确匹配像素。因此,它产生的结果在视觉上更加直观,其中VGG和ResNet是最常用的预训练CNN。
VGG 的网络结构
VGG的论文:《Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition》
VGG网络采用重复堆叠的小卷积核替代大卷积核,在保证具有相同感受野的条件下,提升了网络的深度,从而提升网络特征提取的能力。
可以把VGG网络看成是数个vgg_block的堆叠,每个vgg_block由几个卷积层+ReLU层,最后加上一层池化层组成。VGG网络名称后面的数字表示整个网络中包含参数层的数量(卷积层或全连接层,不含池化层),如图所示。

- VGG16
5个VGG块的卷积层数量分别为(2, 2, 3, 3, 3),再加上3个全连接层,总的参数层数量为16,因此命名为VGG16。 - VGG19
5个VGG块的卷积层数量分别为(2, 2, 4, 4, 4),再加上3个全连接层,总的参数层数量为19,因此命名为VGG19。
VGG LOSS 的代码解析
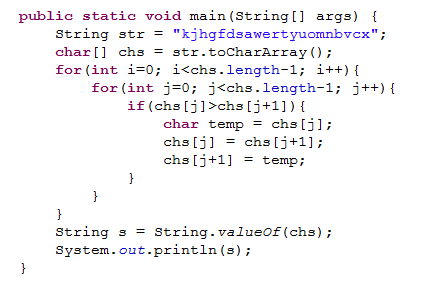
VGG19的代码实现
class VGG19(torch.nn.Module): # VGG19的网络
def __init__(self, requires_grad=False):
super().__init__()
vgg_pretrained_features = torchvision.models.vgg19(pretrained=True).features
self.slice1 = torch.nn.Sequential()
self.slice2 = torch.nn.Sequential()
self.slice3 = torch.nn.Sequential()
self.slice4 = torch.nn.Sequential()
self.slice5 = torch.nn.Sequential()
for x in range(2):
self.slice1.add_module(str(x), vgg_pretrained_features[x])
for x in range(2, 7):
self.slice2.add_module(str(x), vgg_pretrained_features[x])
for x in range(7, 12):
self.slice3.add_module(str(x), vgg_pretrained_features[x])
for x in range(12, 21):
self.slice4.add_module(str(x), vgg_pretrained_features[x])
for x in range(21, 30):
self.slice5.add_module(str(x), vgg_pretrained_features[x])
if not requires_grad:
for param in self.parameters():
param.requires_grad = False
def forward(self, X):
h_relu1 = self.slice1(X)
h_relu2 = self.slice2(h_relu1)
h_relu3 = self.slice3(h_relu2)
h_relu4 = self.slice4(h_relu3)
h_relu5 = self.slice5(h_relu4)
out = [h_relu1, h_relu2, h_relu3, h_relu4, h_relu5]
return out
首先我们先打印出vgg_pretrained_features,对应着VGG19中的各个网络层。

然后分别打印出sclie1,sclie2,sclie3,sclie4, sclie5。可以看出就是把VGG网络的前30层拆分成不同的分组。

VGG LOSS的代码实现
上文定义的vgg的输出分别是5个sclice输出组成的列表。
假设输入分别是x和y,vgg loss 的值就是分别将x和y将5个sclice输出计算loss,一共有5个loss。然后再将这5个loss按照一定的权重加权求和得到最终的loss 。
# VGG 特征距离损失
class VGGLoss(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(VGGLoss, self).__init__()
self.vgg = VGG19().cuda()
# self.criterion = nn.L1Loss()
self.criterion = nn.L1Loss(reduction='sum') # 求和
self.criterion2 = nn.L1Loss()# 求平均
self.weights = [1.0 / 32, 1.0 / 16, 1.0 / 8, 1.0 / 4, 1.0] # 各个slice的输出权重
def forward(self, x, y):
x_vgg, y_vgg = self.vgg(x), self.vgg(y)
loss = 0
for i in range(len(x_vgg)):
# print(x_vgg[i].shape, y_vgg[i].shape)
loss += self.weights[i] * self.criterion(x_vgg[i], y_vgg[i].detach()) # 不同slice的loss的加权和
return loss
def forward2(self, x, y):
x_vgg, y_vgg = self.vgg(x), self.vgg(y)
loss = 0
for i in range(len(x_vgg)):
# print(x_vgg[i].shape, y_vgg[i].shape)
loss += self.weights[i] * self.criterion2(x_vgg[i], y_vgg[i].detach())
return loss
参考
《SR中的常见的损失函数》