说到Java集合,共有两大类分别是Collection和Map。今天就详细聊聊大家耳熟能详的List吧。
List接口实现自Collection接口,是Java的集合框架中的一员,List接口下又有ArrayList、LinkedList和线程安全的Vector,今天就简单分析一下ArrayList和LinkedList的异同以及各自的优势。

ArrayList
ArrayList的身世

- AbstractList:ArrayList继承自AbstractList,AbstractList提供了一个基于数组的动态列表实现,并且它提供了通用列表操作的默认实现。这其实是抽象类的最佳实现,通过继承,可以复用抽象类已实现的通过方法,子类无需重复实现,使子类只关注自身特性的方法。
- List: 表明ArrayList符合List接口的规范。
- Cloneable: 表明它具有拷贝能力,可以进行深拷贝或浅拷贝操作。
- Serializable: 使一个类可以进行序列化,即将对象转换为字节序列以便存储或传输,并在需要时将其反序列化为对象。
- RandomAccess: 标识接口,标识实现该接口的集合支持快速随机访问元素的能力,以告诉代码选择合适的访问方式。
引用ArrayList集合中的一段代码:
/**
* Default initial capacity.
*/
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;
/**
* Shared empty array instance used for empty instances.
*/
private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
/**
* Shared empty array instance used for default sized empty instances. We
* distinguish this from EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA to know how much to inflate when
* first element is added.
*/
private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
/**
* The array buffer into which the elements of the ArrayList are stored.
* The capacity of the ArrayList is the length of this array buffer. Any
* empty ArrayList with elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA
* will be expanded to DEFAULT_CAPACITY when the first element is added.
*/
transient Object[] elementData; // non-private to simplify nested class access
数据结构

构造方法
通过ArrayList的无参构造方法创建一个ArrayList对象时,Object类型的数组elementData会赋值一个空数组,我们调用ArrayList的add方法,给list插入数据时,我们才使用ArrayList的默认长度10。
/**
* Constructs an empty list with the specified initial capacity.
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity of the list
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the specified initial capacity
* is negative
*/
public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) {
if (initialCapacity > 0) {
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
} else if (initialCapacity == 0) {
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
}
}
/**
* Constructs an empty list with an initial capacity of ten.
*/
public ArrayList() {
this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
/**
* Constructs a list containing the elements of the specified
* collection, in the order they are returned by the collection's
* iterator.
*
* @param c the collection whose elements are to be placed into this list
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
*/
public ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) {
Object[] a = c.toArray();
if ((size = a.length) != 0) {
if (c.getClass() == ArrayList.class) {
elementData = a;
} else {
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(a, size, Object[].class);
}
} else {
// replace with empty array.
elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
}
扩容机制
构造一个初始长度是2的列表,调用add方法向列表中添加两个元素。查看源码调用情况:
插入指定元素到list的末尾。
/**
* Appends the specified element to the end of this list.
*
* @param e element to be appended to this list
* @return <tt>true</tt> (as specified by {@link Collection#add})
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}
ensureCapacityInternal:确保内部能力。
直译比较晦涩,可以理解为,在插入新的元素前,需要先确认当前List是否有足够的空间可以容纳新元素。
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {
ensureExplicitCapacity(calculateCapacity(elementData, minCapacity));
}
ensureCapacityInternal方法内部很简单,调用了ensureExplicitCapacity方法,入参是当前列表size+1作为当前列表的最小容量。
private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) {
modCount++;
// overflow-conscious code
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity);
}
- modCount的作用是记录结构性修改次数,当对ArrayList 进行添加或删除操作时,modCount 的值都会递增。而在迭代器进行迭代操作时,它会检查当前的 modCount 值是否与迭代器创建时记录的 expectedModCount 值相等,如果不相等,则立即抛出 ConcurrentModificationException 异常。即Fast-fail机制。
- 判断集合最小容量减去当前List的可变数组的长度是否大于0,用于判断当前List插入当前元素是否需要扩容。
/**
* Increases the capacity to ensure that it can hold at least the
* number of elements specified by the minimum capacity argument.
*
* @param minCapacity the desired minimum capacity
*/
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
增加容量以确保它至少可以容纳最小容量参数指定的元素数量。
扩容时先根据当前容量,通过右移运算符计算出扩容后的动态数组大小。
将一个数的二进制表示向右移动指定的位数。右移操作等效于将操作数除以 2 的移位次数次幂。
‘>>’ '<<'运算符相较于乘和除以的优势是性能更强。
oldCapacity >> 1等价于N除以2的一次幂,即oldCapacity/2。

那么举个例子,往一个当前长度是10的数组中插入一个新的元素,那么它扩容后的新数组长度便为:
10 + (10/2)= 15;
/**
* The maximum size of array to allocate.
* Some VMs reserve some header words in an array.
* Attempts to allocate larger arrays may result in
* OutOfMemoryError: Requested array size exceeds VM limit
*/
private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;
private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) {
if (minCapacity < 0) // overflow
throw new OutOfMemoryError();
return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ?
Integer.MAX_VALUE :
MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;
}
这段代码的作用是确保在需要扩展 ArrayList 的容量时,不会超过预定义的最大数组大小 MAX_ARRAY_SIZE。如果需要分配更大的容量,则会使用 hugeCapacity() 方法计算一个巨大的容量值,以满足需求。这样可以避免分配过大的内存而导致异常或性能问题。
复制
完成以上判断是否需要扩容的操作,现在需要将旧数组的数据复制到新扩容的数组中。
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public static <T> T[] copyOf(T[] original, int newLength) {
return (T[]) copyOf(original, newLength, original.getClass());
}
public static <T,U> T[] copyOf(U[] original, int newLength, Class<? extends T[]> newType) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T[] copy = ((Object)newType == (Object)Object[].class)
? (T[]) new Object[newLength]
: (T[]) Array.newInstance(newType.getComponentType(), newLength);
System.arraycopy(original, 0, copy, 0,
Math.min(original.length, newLength));
return copy;
}
/**
* 复制数组
* @param src 源数组
* @param srcPos 源数组中的起始位置
* @param dest 目标数组
* @param destPos 目标数组中的起始位置
* @param length 要复制的数组元素的数量
*/
public static native void arraycopy(Object src, int srcPos,
Object dest, int destPos,
int length);
Java native关键字用于表示一个方法是由外部的本地代码(通常是由其他边城语言如C/C++编写的)实现的。它常用于与底层系统或硬件进行交互、调用操作系统特定的功能或访问本地库等情况。native 方法的声明只包含方法名和参数列表,没有方法体。它告诉编译器该方法的实现不是在 Java 代码中,而是在外部的本地代码中。
最终ArrayList的数组复制功能通过调用C/C++实现。
以上,便完成了ArrayList复制与扩容功能,再此,留下一个思考题:新增元素,ArrayList和LinkedList那个性能更高?
搜索
/**
* Returns the element at the specified position in this list.
*
* @param index index of the element to return
* @return the element at the specified position in this list
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E get(int index) {
rangeCheck(index);
return elementData(index);
}
/**
* Checks if the given index is in range. If not, throws an appropriate
* runtime exception. This method does *not* check if the index is
* negative: It is always used immediately prior to an array access,
* which throws an ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException if index is negative.
*/
private void rangeCheck(int index) {
if (index >= size)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
E elementData(int index) {
return (E) elementData[index];
}
ArrayList的get方法首先校验入参Index在本ArrayList是否数组越界,如果没有数组越界,使用数组的方法定位到特定位置的元素,所以ArrayList的get方法时间复杂度是O(1)。
LinkedList
LinkedList的身世
数据结构


- AbstractSequentialList: 该类提供了基于链表结构的有序访问操作。
- Deque: Double Ended Queue,双端队列,支持在队列两端插入和删除操作。
- List: 表明ArrayList符合List接口的规范。
- Cloneable: 表明它具有拷贝能力,可以进行深拷贝或浅拷贝操作。
- Serializable: 使一个类可以进行序列化,即将对象转换为字节序列以便存储或传输,并在需要时将其反序列化为对象。
构造方法
/**
* Constructs an empty list.
*/
public LinkedList() {
}
/**
* Constructs a list containing the elements of the specified
* collection, in the order they are returned by the collection's
* iterator.
*
* @param c the collection whose elements are to be placed into this list
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
*/
public LinkedList(Collection<? extends E> c) {
this();
addAll(c);
}
LinkedList构造方法很简洁,有参构造方法调用了addAll()方法,方法内通过内部类Node去存储数据和上一个、下一个元素。
private static class Node<E> {
E item;
Node<E> next;
Node<E> prev;
Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}
添加元素
add
transient Node<E> last;
/**
* Links e as last element.
*/
void linkLast(E e) {
final Node<E> l = last;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);
last = newNode;
if (l == null)
first = newNode;
else
l.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
LinkedList会记录当前列表的最后一个元素,将最后一个元素赋值,用于创建新的节点,通过内部类Node构造方法创建一个新的节点,当新的节点创建成功后,将最新的节点赋值给当前最后一个元素。当LinkedList还未添加元素时,新插入的元素即为第一个元素,如果当前LinkedList不是第一次添加元素,那么建立最后一个元素和新插入元素的连接关系。而后当前LinkedList的size自增,modCount自增。
addAll
public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) {
return addAll(size, c);
}
LinkedList的addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c)方法有两个地方调用:
- LinkedList构造方法
- 公共方法addAll
public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) {
checkPositionIndex(index);
Object[] a = c.toArray();
int numNew = a.length;
if (numNew == 0)
return false;
Node<E> pred, succ;
if (index == size) {
succ = null;
pred = last;
} else {
succ = node(index);
pred = succ.prev;
}
for (Object o : a) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E e = (E) o;
Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, null);
if (pred == null)
first = newNode;
else
pred.next = newNode;
pred = newNode;
}
if (succ == null) {
last = pred;
} else {
pred.next = succ;
succ.prev = pred;
}
size += numNew;
modCount++;
return true;
}
private void checkPositionIndex(int index) {
if (!isPositionIndex(index))
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
/**
* Tells if the argument is the index of a valid position for an
* iterator or an add operation.
*/
private boolean isPositionIndex(int index) {
return index >= 0 && index <= size;
}
在执行正式逻辑前,会先校验插入的集合列表是否存在数组越界问题。
将传入的collection对象转化为数组,判断数组的长度,以确定需要构造多少个Node节点,创建两个Node节点对象:
- pred:当前索引位置的前一个节点(predecessor),用于在插入新节点时连接前一个节点和新节点之间的关系。
- succ:当前索引位置的节点本身(successor)用于在插入新节点时连接新节点和当前节点之间的关系。
随后判断index和size是否相等,当新初始化一个LinkedList时,index和size都是0,那么这个判断的意义就是:给当前LinkedList的last元素赋值。
当不相等时,根据index的值定位到当前元素的Node节点信息,给当前节点维护上一个节点的关系。
随后是遍历数组信息,创建节点,维护节点间上一个、下一个关系。
/**
* Returns the (non-null) Node at the specified element index.
*/
Node<E> node(int index) {
// assert isElementIndex(index);
if (index < (size >> 1)) {
Node<E> x = first;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++)
x = x.next;
return x;
} else {
Node<E> x = last;
for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--)
x = x.prev;
return x;
}
}
这个是LinkedList内部类Node的根据当前index查询对应元素的方法,首先判断当前要查询的index在列表中前半段还是后半段(通过index < (size >> 1)判断实现),位于前半段时,正序循环查询,位于后半段时,逆序循环查询,时间复杂度是O(n)。
获取元素
/**
* Returns the element at the specified position in this list.
*
* @param index index of the element to return
* @return the element at the specified position in this list
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E get(int index) {
checkElementIndex(index);
return node(index).item;
}
private void checkElementIndex(int index) {
if (!isElementIndex(index))
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
/**
* Tells if the argument is the index of an existing element.
*/
private boolean isElementIndex(int index) {
return index >= 0 && index < size;
}
LinkedList的get方法很简洁,首先判断index在LinkedList是否合法(数组越界),随后调用Node的node(index)即可,因此LinkedList的get方法时间复杂度同样是O(n)。
明明N/2,为什么还是O(n)?
当n->∞时,∞/2依然是∞,因此时间复杂度是O(n)。
测试
talk is cheap,show me your code.
public class StringSub {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int numElements = 1000000; // 要插入的元素数量
// 测试 ArrayList 插入性能
List<Integer> arrayList = new ArrayList<>();
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < numElements; i++) {
arrayList.add(i);
}
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("ArrayList 插入 " + numElements + " 个元素耗时:" + (endTime - startTime) + " 毫秒");
// 测试 LinkedList 插入性能
List<Integer> linkedList = new LinkedList<>();
startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < numElements; i++) {
linkedList.add(i);
}
endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("LinkedList 插入 " + numElements + " 个元素耗时:" + (endTime - startTime) + " 毫秒");
// 测试 ArrayList 查询性能
startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < numElements; i++) {
int element = arrayList.get(i);
}
endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("ArrayList 查询 " + numElements + " 个元素耗时:" + (endTime - startTime) + " 毫秒");
// 测试 LinkedList 查询性能
startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < numElements; i++) {
int element = linkedList.get(i);
}
endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("LinkedList 查询 " + numElements + " 个元素耗时:" + (endTime - startTime) + " 毫秒");
}
}
基于JDK 8的测试结果

基于JDK 17的测试结果
内存测试
使用JProfiler测试,对比两者创建100万个对象内存差异:

可以看到,LinkedList创建100万个对象,使用内存39997KB,ArrayList创建100万个对象,使用内存20859KB。为什么LinkedList需要比ArrayList近一半的内存?
打个断点,我们看一下:
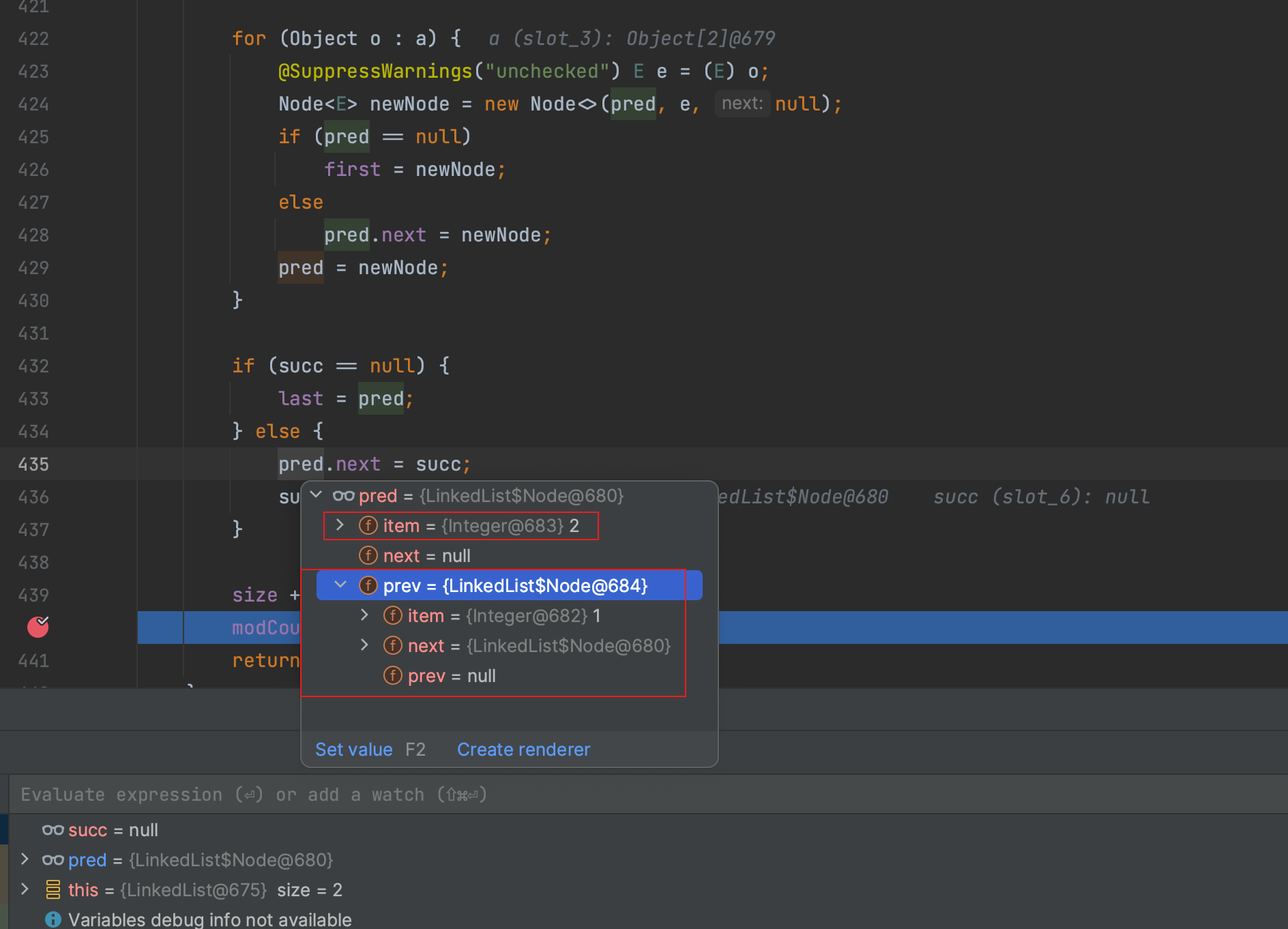
再回到LinkedList的结构图,我们可以看到,每个LinkedList元素所在的节点,都有三部分组成,一个node节点存储上一个节点信息,一个node节点存储下一个节点信息,只有还一个item存储当前信息,因此,同样一个数据存在LinkedList中占用的内存要比ArrayList更大。