浅水方程
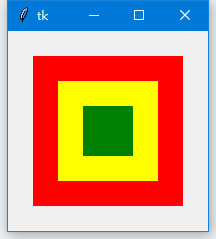
浅水方程可以建立起海啸和浴缸中波浪的数学模型。浅水方程建立了水或者其它不可压缩液体受扰动时传播的模型。隐含的假设是,液体的深度和波浪的长度、扰动等相比是很小的。
在这样的记号下,浅水方程为双曲守恒定律的一个例子。
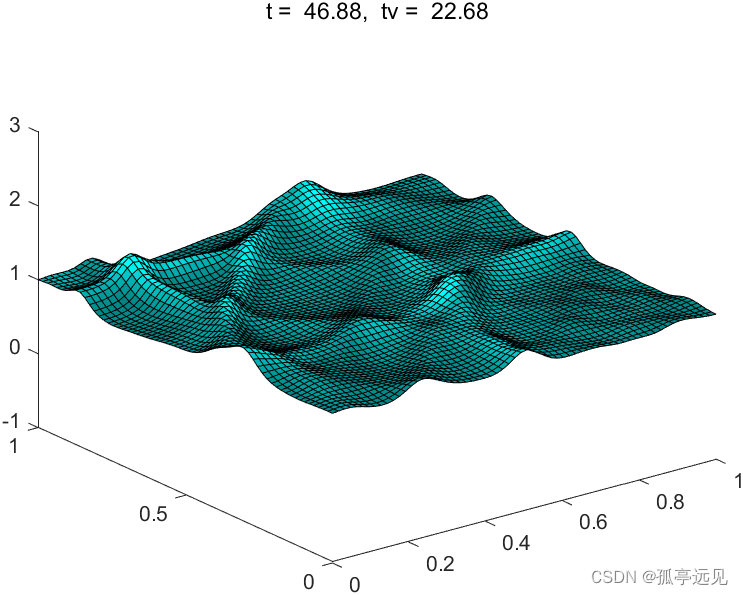
使用拉克斯-冯特洛夫方法计算方程的近似数值解。waterwave求解的区域为正方形区域,有反射的边界条件。在初始时刻,在整个区域都有h=1,u=0,v=0,这样解是静态的。然后在连续几个时间步长内,二维高斯型峰值添加到h处,用来模拟水滴滴到水面上的冲量扰动作用。
shading 设置颜色着色属性
function waterwave
% WATERWAVE 2D Shallow Water Model
%
% Lax-Wendroff finite difference method.
% Reflective boundary conditions.
% Random water drops initiate gravity waves.
% Surface plot displays height colored by momentum.
% Plot title shows t = simulated time and tv = a measure of total variation.
%t = 模拟时间,tv = 总变化量
% An exact solution to the conservation law would have constant tv.
% Lax-Wendroff produces nonphysical oscillations and increasing tv.
%
% See:
% http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Shallow_water_equations
% http://www.amath.washington.edu/~rjl/research/tsunamis
% http://www.amath.washington.edu/~dgeorge/tsunamimodeling.html
% http://www.amath.washington.edu/~claw/applications/shallow/www
% Parameters
n = 64; % grid size
g = 9.8; % gravitational constant
dt = 0.01; % hardwired timestep
dx = 1.0;
dy = 1.0;
nplotstep = 8; %绘图间隔
ndrops = 1; % 最大滴数
dropstep = 200; % 液滴间隔
D = droplet(1.5,21); % 模拟水滴
% Initialize graphics
[surfplot,top,restart,quit] = initgraphics(n); %启动图形
% Outer loop, restarts.
while get(quit,'value') == 0
set(restart,'value',0)
H = ones(n+2,n+2); U = zeros(n+2,n+2); V = zeros(n+2,n+2);
Hx = zeros(n+1,n+1); Ux = zeros(n+1,n+1); Vx = zeros(n+1,n+1);
Hy = zeros(n+1,n+1); Uy = zeros(n+1,n+1); Vy = zeros(n+1,n+1);
ndrop = ceil(rand*ndrops);
nstep = 0;
% Inner loop, time steps.
while get(restart,'value')==0 && get(quit,'value')==0
nstep = nstep + 1;
% Random water drops
if mod(nstep,dropstep) == 0 && nstep <= ndrop*dropstep
w = size(D,1);
i = ceil(rand*(n-w))+(1:w);
j = ceil(rand*(n-w))+(1:w);
H(i,j) = H(i,j) + (1+4*rand)/5*D;
end
% Reflective boundary conditions
H(:,1) = H(:,2); U(:,1) = U(:,2); V(:,1) = -V(:,2);
H(:,n+2) = H(:,n+1); U(:,n+2) = U(:,n+1); V(:,n+2) = -V(:,n+1);
H(1,:) = H(2,:); U(1,:) = -U(2,:); V(1,:) = V(2,:);
H(n+2,:) = H(n+1,:); U(n+2,:) = -U(n+1,:); V(n+2,:) = V(n+1,:);
% First half step
% x direction
i = 1:n+1;
j = 1:n;
% height
Hx(i,j) = (H(i+1,j+1)+H(i,j+1))/2 - dt/(2*dx)*(U(i+1,j+1)-U(i,j+1));
% x momentum
Ux(i,j) = (U(i+1,j+1)+U(i,j+1))/2 - ...
dt/(2*dx)*((U(i+1,j+1).^2./H(i+1,j+1) + g/2*H(i+1,j+1).^2) - ...
(U(i,j+1).^2./H(i,j+1) + g/2*H(i,j+1).^2));
% y momentum
Vx(i,j) = (V(i+1,j+1)+V(i,j+1))/2 - ...
dt/(2*dx)*((U(i+1,j+1).*V(i+1,j+1)./H(i+1,j+1)) - ...
(U(i,j+1).*V(i,j+1)./H(i,j+1)));
% y direction
i = 1:n;
j = 1:n+1;
% height
Hy(i,j) = (H(i+1,j+1)+H(i+1,j))/2 - dt/(2*dy)*(V(i+1,j+1)-V(i+1,j));
% x momentum
Uy(i,j) = (U(i+1,j+1)+U(i+1,j))/2 - ...
dt/(2*dy)*((V(i+1,j+1).*U(i+1,j+1)./H(i+1,j+1)) - ...
(V(i+1,j).*U(i+1,j)./H(i+1,j)));
% y momentum
Vy(i,j) = (V(i+1,j+1)+V(i+1,j))/2 - ...
dt/(2*dy)*((V(i+1,j+1).^2./H(i+1,j+1) + g/2*H(i+1,j+1).^2) - ...
(V(i+1,j).^2./H(i+1,j) + g/2*H(i+1,j).^2));
% Second half step
i = 2:n+1;
j = 2:n+1;
% height
H(i,j) = H(i,j) - (dt/dx)*(Ux(i,j-1)-Ux(i-1,j-1)) - ...
(dt/dy)*(Vy(i-1,j)-Vy(i-1,j-1));
% x momentum
U(i,j) = U(i,j) - (dt/dx)*((Ux(i,j-1).^2./Hx(i,j-1) + g/2*Hx(i,j-1).^2) - ...
(Ux(i-1,j-1).^2./Hx(i-1,j-1) + g/2*Hx(i-1,j-1).^2)) ...
- (dt/dy)*((Vy(i-1,j).*Uy(i-1,j)./Hy(i-1,j)) - ...
(Vy(i-1,j-1).*Uy(i-1,j-1)./Hy(i-1,j-1)));
% y momentum
V(i,j) = V(i,j) - (dt/dx)*((Ux(i,j-1).*Vx(i,j-1)./Hx(i,j-1)) - ...
(Ux(i-1,j-1).*Vx(i-1,j-1)./Hx(i-1,j-1))) ...
- (dt/dy)*((Vy(i-1,j).^2./Hy(i-1,j) + g/2*Hy(i-1,j).^2) - ...
(Vy(i-1,j-1).^2./Hy(i-1,j-1) + g/2*Hy(i-1,j-1).^2));
% Update plot
if mod(nstep,nplotstep) == 0
C = abs(U(i,j)) + abs(V(i,j)); % Color shows momemtum
t = nstep*dt;
tv = norm(C,'fro');
set(surfplot,'zdata',H(i,j),'cdata',C);
set(top,'string',sprintf('t = %6.2f, tv = %6.2f',t,tv))
drawnow
end
if all(all(isnan(H))), break, end % Unstable, restart
end
end
close(gcf)
% ------------------------------------
function D = droplet(height,width)
% DROPLET 2D Gaussian
% D = droplet(height,width)
[x,y] = ndgrid(-1:(2/(width-1)):1);
D = height*exp(-5*(x.^2+y.^2));
% ------------------------------------
function [surfplot,top,restart,quit] = initgraphics(n);
% INITGRAPHICS Initialize graphics for waterwave.
% [surfplot,top,restart,quit] = initgraphics(n)
% returns handles to a surface plot, its title, and two uicontrol toggles.
clf
shg
set(gcf,'numbertitle','off','name','Shallow_water')
x = (0:n-1)/(n-1);
surfplot = surf(x,x,ones(n,n),zeros(n,n));
grid off
axis([0 1 0 1 -1 3])
caxis([-1 1])
shading faceted
c = (1:64)'/64;
cyan = [0*c c c];
colormap(cyan)
top = title('xxx');
restart = uicontrol('position',[20 20 80 20],'style','toggle','string','restart');
quit = uicontrol('position',[120 20 80 20],'style','toggle','string','close');
摩尔斯电码
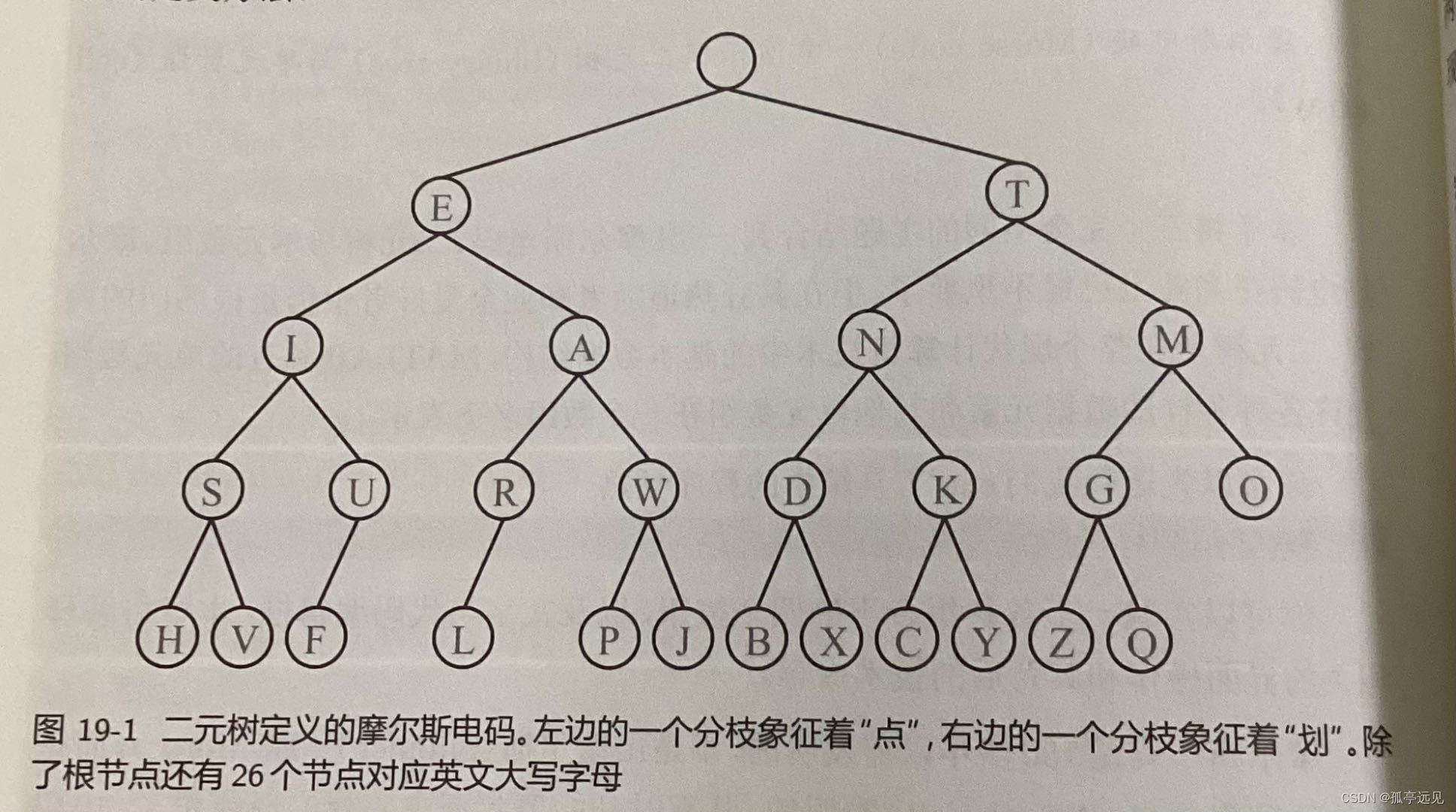
摩尔斯电码演示了二元树(binary tree)和单元数组(cell array)。电码由短的点(dot或‘.’)或者长的停顿(dash或‘-’)分隔。
'...---...'表示SOS,‘...--...’表示SMS。
摩尔斯树
采用二元树来定义摩尔斯电码。从根节点开始向左移动一个链接表示一个“点”,向右表示一个“划”。如可以用“.-”来表示字母A。
function M = morse_tree
% MORSE_TREE
% M = morse_tree is a cell array of cell arrays, the binary
% tree for the Morse code of the 26 Latin characters.
%
% M = morse_tree_extended is a larger cell array of cell arrays,
% the binary tree for the Morse code of the 26 Latin characters
% plus digits, punctuation marks, and several non-Latin characters.
%
% _____ root _____
% / \
% _ E _ _ T _
% / \ / \
% I A N M
% / \ / \ / \ / \
% S U R W D K G O
% / \ / / / \ / \ / \ / \
% H V F L P J B X C Y Z Q
%
global extend
if extend==1
M = morse_tree_extended;
return
end
% Level 4
h = {'H' {} {}};
v = {'V' {} {}};
f = {'F' {} {}};
l = {'L' {} {}};
p = {'P' {} {}};
j = {'J' {} {}};
b = {'B' {} {}};
x = {'X' {} {}};
c = {'C' {} {}};
y = {'Y' {} {}};
z = {'Z' {} {}};
q = {'Q' {} {}};
% Level 3
s = {'S' h v};
u = {'U' f {}};
r = {'R' l {}};
w = {'W' p j};
d = {'D' b x};
k = {'K' c y};
g = {'G' z q};
o = {'O' {} {}};
% Level 2
i = {'I' s u};
a = {'A' r w};
n = {'N' d k};
m = {'M' g o};
% Level 1
e = {'E' i a};
t = {'T' n m};
% Level 0
M = {'' e t};树的搜索
反复选择树上的不同分支对应着遍历这个树的不同顺序。在众多可能的排序中,有两种有着标准的名字:深度优先搜索方法(depth-first search)和广度优先搜索(breadth-first search)。
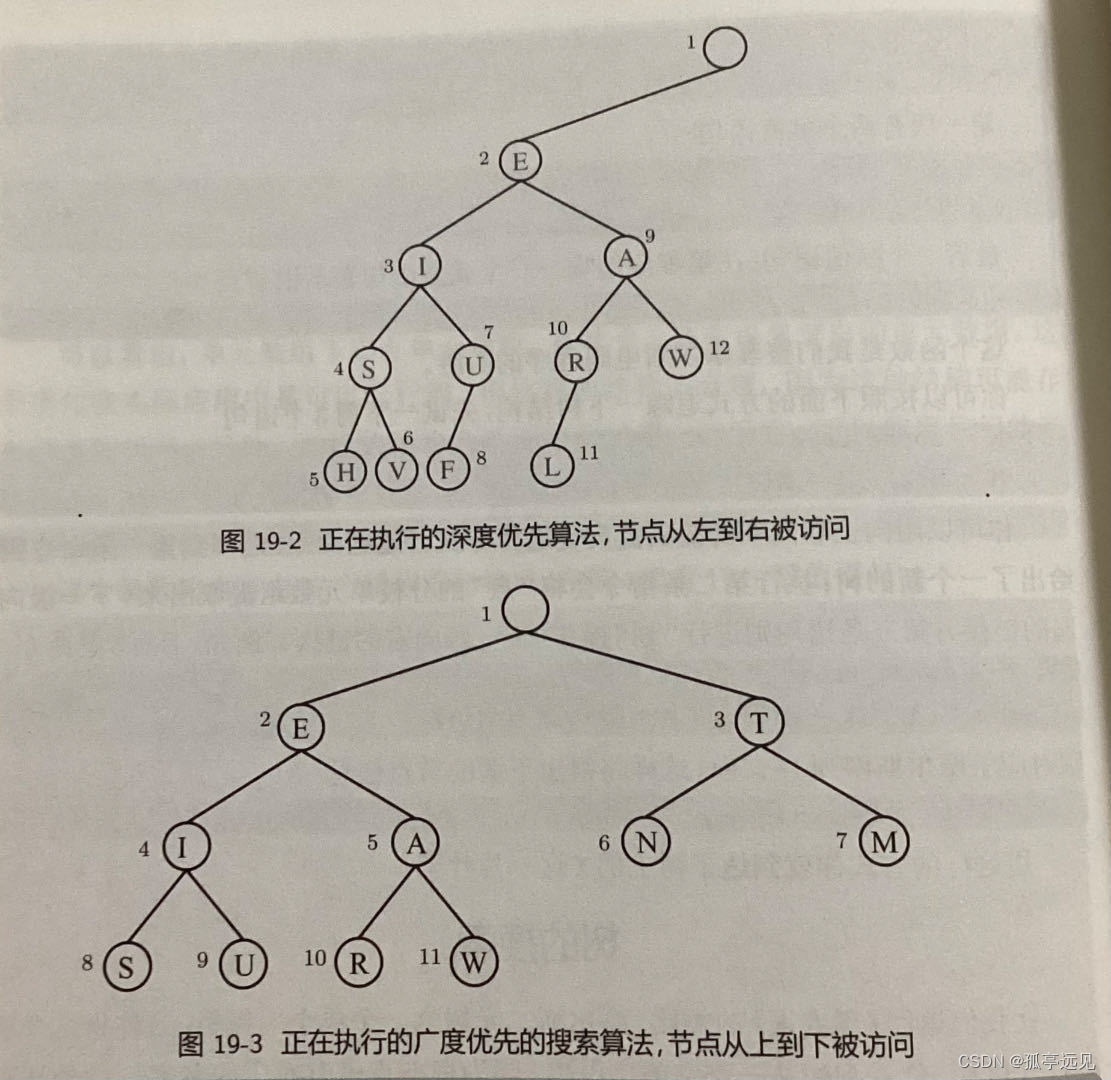
深度优先的方法使用的是成为栈(stack)的数据结构。栈S为单元数组,只要栈是非空的,while循环就一直进行下去。
S = {morse_tree}; while ~isempty(S) N = S{1}; S = S(2:end); if ~isempty(N) fprintf(' %s',N{1}) S = {N{2} N{3} S{:}}; end end fprintf('\n')广度优先搜索算法用了称为队列(queue)的数据结构。
%% Breadth first, with a queue. Q = {morse_tree}; while ~isempty(Q) N = Q{1}; Q = Q(2:end); if ~isempty(N) fprintf(' %s',N{1}) Q = {Q{:} N{2} N{3}}; end end fprintf('\n')
队列采用了先进先出(FIFO)的策略,而堆栈采用了后进先出(LIFO)的策略。
function morse_gui(arg)
% MORSE_GUI Interactive demonstration of Morse code and binary trees.
if nargin == 0
init_gui
elseif isequal(arg,'_depth')
depth
elseif isequal(arg,'_breadth')
breadth
else
translate
end
% ------------------------------------
function depth
% Depth first traversal of Morse code binary tree
% Stack, LIFO, last in first out.
% Insert new items at the top of the stack.
S = {morse_tree};
X = 0;
Y = 0;
while ~isempty(S)
N = S{1};
S = S(2:end);
x = X(1);
X = X(2:end);
y = Y(1);
Y = Y(2:end);
if ~isempty(N)
node(N{1},x,y)
S = {N{2} N{3} S{:}};
X = [2*x-(x>=0); 2*x+(x<=0); X];
Y = [y+1; y+1; Y];
end
end
end % depth
% ------------------------------------
function breadth
% Breadth first traversal of Morse code binary tree.
% Queue, FIFO, first in first out.
% Insert new items at the end of the queue.
Q = {morse_tree};
X = 0;
Y = 0;
while ~isempty(Q)
N = Q{1};
Q = Q(2:end);
x = X(1);
X = X(2:end);
y = Y(1);
Y = Y(2:end);
if ~isempty(N)
node(N{1},x,y);
Q = {Q{:} N{2} N{3}};
X = [X; 2*x-(x>=0); 2*x+(x<=0)];
Y = [Y; y+1; y+1];
end
end
end % breadth
% ------------------------------------
function translate
% Translate to and from Morse code.
e = findobj('style','edit');
s = findobj('string','sound');
t = get(e,'string');
if all(t=='.' | t=='-' | t==' ' | t=='*')
t = decode(t);
set(e,'string',t);
else
code = encode(t);
set(e,'string',code);
if get(s,'value') == 1
morse_sound(code)
end
end
if length(t)>=3 && isequal(t(1:3),'SOS')
scream
end
end
% ------------------------------------
function code = encode(text)
% ENCODE Translate text to dots and dashes.
% encode('text')
code = '';
text = upper(text);
for k = 1:length(text);
ch = text(k);
% A blank in the text is worth three in the code.
if ch == ' '
code = [code ' '];
else
code = [code encode_ch(ch) ' '];
end
end
end % encode
% ------------------------------------
function dd = encode_ch(ch)
% ENCODE_CH Translate one character to dots and dashes.
S = {morse_tree};
D = {''};
while ~isempty(S)
N = S{1};
dd = D{1};
S = S(2:end);
D = D(2:end);
if ~isempty(N)
if N{1} == ch;
return
else
S = {N{2} N{3} S{:}};
D = {[dd '.'] [dd '-'] D{:}};
end
end
end
dd = '*';
end % encode_ch
% ------------------------------------
function text = decode(code)
% DECODE Translate strings of dots and dashes to text.
% decode('string of dots, dashes and spaces')
text = [];
code = [code ' '];
while ~isempty(code);
k = find(code == ' ',1);
ch = decode_dd(code(1:k));
text = [text ch];
code(1:k) = [];
% Many blanks in the code is worth one in the text.
if ~isempty(code) && code(1) == ' '
text = [text ' '];
while ~isempty(code) && code(1) == ' '
code(1) = [];
end
end
end
end % decode
% ------------------------------------
function ch = decode_dd(dd)
% DECODE_DD Translate one character's worth of dots
% and dashes to a single character of text.
M = morse_tree;
for k = 1:length(dd)
if dd(k) == '.'
M = M{2};
elseif dd(k) == '-'
M = M{3};
end
if isempty(M)
ch = '*';
return
end
end
ch = M{1};
end % decode_dd
% ------------------------------------
function init_gui
% Initialize Morse code gui.
global extend
extend = 0;
clf reset
axes('pos',[0 0 1 1])
axis(16*[-1 1 0 2])
axis square off
set(gcf,'color','white')
set(gca,'ydir','rev')
uicontrol('style','push','string','depth', ...
'units','normal','pos',[0.16 0.20 0.12 0.06], ...
'callback','cla, morse_gui(''_depth'')')
uicontrol('style','push','string','breadth', ...
'units','normal','pos',[0.35 0.20 0.12 0.06], ...
'callback','cla, morse_gui(''_breadth'')')
uicontrol('style','toggle','string','sound','value',1, ...
'units','normal','pos',[0.54 0.20 0.12 0.06]);
uicontrol('style','toggle','string','extend','value',0, ...
'units','normal','pos',[0.72 0.20 0.12 0.06], ...
'callback', ['global extend, extend=get(gcbo,''value'');' ...
'if extend==0, cla, end, axis(2^(4+extend)*[-1 1 0 2])']);
uicontrol('style','edit','string', ...
'Enter text or code to translate', ...
'units','normal','pos',[0.16 0.04 0.68 0.08], ...
'callback','cla, morse_gui(''_translate'')')
end
% ------------------------------------
function node(ch,x,y)
% Plot, and possibly play, node of Morse code binary tree.
global extend
r = 0.90;
z = r*exp(2*pi*i*(0:32)/32);
delta = 1/3;
dkgreen = [0 1/2 0];
lw = get(0,'defaultlinelinewidth')+0.5;
fs = get(0,'defaulttextfontsize');
if ~extend
lw = lw+1;
fs = fs+2;
end
p = 2^(4+extend-y);
u = (x~=0)*(2*x+2*(x<=0)-1)*p;
v = 4*(y+1);
% Circle
line(u+real(z),v+imag(z),'color','black','linewidth',lw)
% Character
text(u-delta,v,ch,'fontweight','bold','color',dkgreen,'fontsize',fs);
% Connect node to parent
if (x~=0)
if y==1
w = 0;
elseif rem(x,2)==(x>0)
w = u+p;
else
w = u-p;
end
line([u w],[v-r v+r-4],'color','black','linewidth',lw)
end
if get(findobj('string','sound'),'value') == 1
morse_sound(encode_ch(ch))
pause(0.2)
end
pause(0.1)
end
% ------------------------------------
function morse_sound(code,delta,note)
% MORSE_SOUND Play sound for dots and dashes.
% morse_sound(code) plays code, a string of dots, dashes and spaces.
% morse_sound(code,delta,note) time slice is delta and tone is note.
% Default delta = 1/16 second.
% Default note = 6, which is F above middle C. See play_note.
if nargin < 2
delta = 1/16;
end
if nargin < 3
note = 6;
end
s = findobj('string','sound');
for k = 1:length(code)
if get(s,'value') == 1
switch code(k)
case '.'
play_note(note,delta)
case '-'
play_note(note,3*delta)
case ' '
pause(3*delta)
otherwise
% Skip the character
end
pause(delta)
end
end
end % morse_sound
% ------------------------------------
function play_note(note,T)
% PLAY_NOTE Play a musical note.
% play_note(note,T) Play a note for T seconds.
% note is an integer specifying semitones above and below middle C.
% There are 12 notes per octave.
% play_note(0,1/2) plays middle C (~261.625 Hz) for 1/2 second.
C4 = 440/2^(3/4); % Middle C, hertz
Fs = 44100; % Sample rate, hertz
t = (0:1/Fs:T); % Linear time ramp
f = C4 * 2^(note/12); % Frequency, hertz
y = sin(2*pi*f*t); % Sinusoidal signal
k = 1:1000; % Attack and release
r = (k/1000);
y(k) = r.*y(k);
y(end+1-k) = r.*y(end+1-k);
sound(y,Fs) % Play
end % play_note
end % morse_gui
解码和编码
解码是将 “点和划” 描述的东西变成文字;编码过程正好反过来。
function text = decode(code)
% DECODE Translate strings of dots and dashes to text.
% decode('string of dots, dashes and spaces')
text = [];
code = [code ' '];
while ~isempty(code);
k = find(code == ' ',1);
ch = decode_dd(code(1:k));
text = [text ch];
code(1:k) = [];
% Many blanks in the code is worth one in the text.
if ~isempty(code) && code(1) == ' '
text = [text ' '];
while ~isempty(code) && code(1) == ' '
code(1) = [];
end
end
end
end % decode function dd = encode_ch(ch)
% ENCODE_CH Translate one character to dots and dashes.
S = {morse_tree};
D = {''};
while ~isempty(S)
N = S{1};
dd = D{1};
S = S(2:end);
D = D(2:end);
if ~isempty(N)
if N{1} == ch;
return
else
S = {N{2} N{3} S{:}};
D = {[dd '.'] [dd '-'] D{:}};
end
end
end
dd = '*';
end % encode_ch摩尔斯电码表
morse_code使用了递归算法函数traverse,这种递归调用的结果把C表格和含有“点”和“划”的dd字符串合并。在matlab中,可以使用char函数将数字转换成字母,如char(65)命令转换为A。
function C = morse_code(C,M,dd)
% MORSE_CODE
% C = morse_code
% C = morse_code(morse_tree)
% C = morse_code(morse_tree_extended)
% Generate tables of the ASCII and Morse codes
% for the characters defined by the binary trees.
if nargin < 3 % Choose binary tree
if nargin == 0
M = morse_tree;
else
M = C;
end
C = cell(256,1); % The temporary code table
dd = ''; % dots and dashes
end
if ~isempty(M) % Depth first search
if ~isempty(M{1})
C{double(M{1})} = dd; % Use ASCII value as an index
end
C = morse_code(C,M{2},[dd '.']); % Recursive call
C = morse_code(C,M{3},[dd '-']); % Recursive call
end
if nargin < 3 % Final processing, convert to char.
c = char(C{:});
k = find(c(:,1) ~= ' '); % Find the nonblank entries.
b = blanks(length(k))';
C = [char(k) b b int2str(k) b b char(C{k})];
end