北邮22信通一枚~
跟随课程进度每周更新数据结构与算法的代码和文章
持续关注作者 解锁更多邮苑信通专属代码~
获取更多文章 请访问专栏:
北邮22信通_青山如墨雨如画的博客-CSDN博客
目录
一.总纲
二.构造函数
2.1构造函数讲解
2.2构造函数的书写
书上代码如下:
小编改进后的代码
三.深度优先遍历DFS
3.1书上重要语句提取:
3.2一个修饰
3.3 DFS完整代码
四.广度优先遍历BFS
4.1广度优先遍历注意事项
4.2广度优先遍历代码部分
4.2.1使用数组拟合队列描写BFS
4.2.2直接使用STL队列描写BFS
五.析构函数
5.1核心思路
5.2代码部分
六.总体代码
6.1代码效果图
6.2代码部分
6.3运行结果
一.总纲
***说明***
1.本篇文章使用邻接表的存储结构实现图,将分别介绍广度优先遍历和深度优先遍历两种图的遍历方法;
2.由于书中代码存在欠缺之处,本代码对书中代码做了修改、改进和修饰,具体将在后文讲解;
3.本篇文章测试用图为书169页图5-25(a)所呈现的图,广度优先遍历和深度优先遍历部分代码将对这张图进行测试。
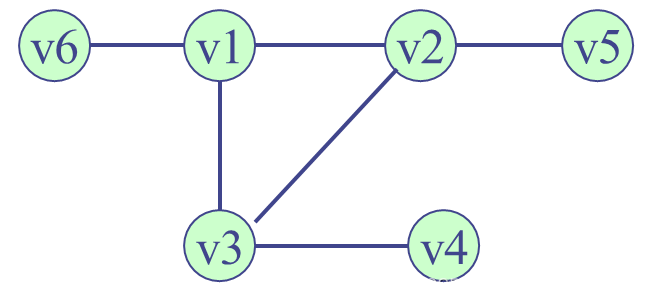
***说明完毕***
二.构造函数
2.1构造函数讲解
图的邻接表存储结构及其含义如下:
这里标一下英文单词及其释义:
vertex:顶点
arc:弧

图的构造实际上就是讲一张图的所有数据信息数字化。如何把一张图用最简洁的数字组合描述出来呢?
首先我们应该获取这张图结点个数和弧的个数。
对所有结点,我们使用一个数组(adjlist)将他们存储起来。如果用数组存储所有结点,那么每个结点所承载的数据,就变成了两个,一个是结点本身的数据域(传入为temp类型,主函数中具象化为student),另一个是它在数组中的位置(下标)。
对每条弧,显然,只要知道这条弧的起始顶点和指向顶点,就可以清晰且唯一地描述这条弧了。所以,我们需要传入所有弧的开始和指向结点的数据。通过上面分析,我们知道一个结点承载两个数据,那使用哪个数据会更加简洁呢?显然,传入数据应该使用数组下标。
综上分析,我们需要的数据有这些:结点个数,弧的个数,结点储存的temp类型数据,弧的首尾结点的数组下标。
我们通过上图所画出的邻接表来具体说明各种数据。
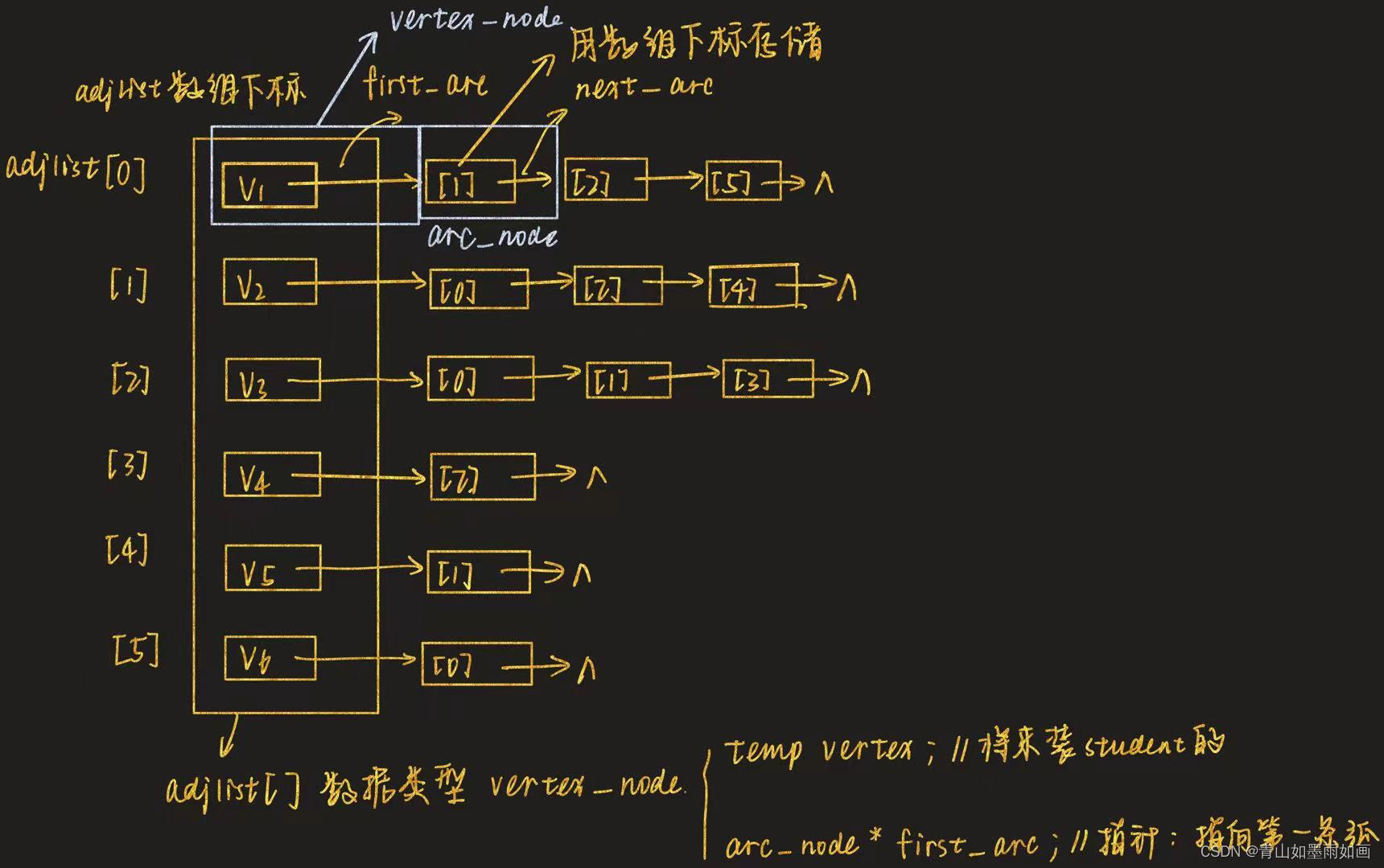
则对构造函数,首先传入结点个数和弧的个数;然后传入结点数据域存放的temp类型的数据,可以用传入temp类型数组来实现; 然后传入弧的数字化描述,具体需要传入数对,数对可以用结构体来整理,即传入整型结构体数组来实现对弧的数字化描述。
2.2一个修改和改进
书中代码对弧数据的传入采用的是头插法的方法,但是需要逆序输入数对才可以正确运行。修改方法一是增加一个形参,以结构体数组的形式逆序遍历传入数对,同时赋值和储存;修改方法二就是直接逆序输入,但是过程麻烦。
因为在大家普遍学习的C++课程中对文件的读写要求不高,所以小编将构造函数改成了传入正常参数的方式,这样也能同时使用上述提供的解决方法二,轻松地将弧数据输入到程序中。
2.2构造函数的书写
书上代码如下:
template<class temp>
al_graph<temp>::al_graph(ifstream& fin)
{
fin >> this->vnum;
fin >> this->arcnum;
for (int i = 0; i < vnum; i++)
{
fin >> this->adjlist[i].vertex;
this->adjlist[i].first_arc = nullptr;
}
for (int i = 0; i < arcnum; i++)
{
int i, j;
fin >> i >> j;//依次输入本初结点,邻接顶点
arc_node* s = new arc_node;
s->adj_vertex = j;//j是邻接顶点的下标
s->next_arc = this->adjlist[i].first_arc;
this->adjlist[i].first_arc = s;
}
}小编改进后的代码
(其中relation数组即为传入的整型结构体形参,用来数字化弧)
template<class temp>
al_graph<temp>::al_graph(temp a[], relation r[], int vnum, int arcnum)
{
this->vnum = vnum;
this->arcnum = arcnum;
for (int i = 0; i < vnum; i++)
{
this->adjlist[i].vertex = a[i];
this->adjlist[i].first_arc = nullptr;
}
for (int i = arcnum - 1; i >= 0; i--)//逆序输入
{
arc_node* s = new arc_node;
s->adj_vertex = r[i].end;
s->next_arc = this->adjlist[r[i].start].first_arc;
this->adjlist[r[i].start].first_arc = s;
}
}三.深度优先遍历DFS
3.1书上重要语句提取:
“为避免重复访问同一个顶点,必须记住每个顶点是否已经被访问过,所以,图的遍历算法必须添加一个布尔向量bool visited[n],初始值为FALSE,一旦访问了顶点vi,则visited[ i - 1 ]设置为TRUE。”
“深度优先遍历类似于树的前序遍历。”
3.2一个修饰
书上代码固然可以实现深度优先遍历,但是遍历一次之后数组visited各个元素都将被标记,无法进行第二次深度遍历。所以在这里小编添加了一个return0函数,方便将各个visited数组全部返回FALSE值。
template<class temp>
void al_graph<temp>::return0(bool x[])
{
for (int i = 0; i < maxsize; i++)
x[i] = 0;
}使用完DFS方法后引用此函数,就可以实现visited数组的格式化了。
3.3 DFS完整代码
DFS完整代码如下:
template<class temp>
void al_graph<temp>::return0(bool x[])
{
for (int i = 0; i < maxsize; i++)
x[i] = 0;
}
bool DFS_visited[maxsize];
template<class temp>
void al_graph<temp>::DFS_core(int v)
{
this->adjlist[v].vertex.print();
DFS_visited[v] = 1;
arc_node* p = this->adjlist[v].first_arc;
while (p != NULL)
{
int j = p->adj_vertex;
if (DFS_visited[j] == 0)
DFS_core(j);
p = p->next_arc;
}
}
template<class temp>
void al_graph<temp>::DFS(int v)
{
cout << "从"<<v+1<<"开始,深度优先遍历结果为:" << endl;
this->DFS_core(v);
return0(DFS_visited);
cout << endl;
}四.广度优先遍历BFS
4.1广度优先遍历注意事项
同样需要visited数组来记录是否标记过;
应用了队列思想,每一个元素出队,与这个元素直接相邻的元素依次入队,直至队空为止;
广度优先遍历类似于树的层序遍历。
4.2广度优先遍历代码部分
4.2.1使用数组拟合队列描写BFS
template<class temp>
void al_graph<temp>::return0(bool x[])
{
for (int i = 0; i < maxsize; i++)
x[i] = 0;
}
bool BFS_visited[maxsize];
template<class temp>
void al_graph<temp>::BFS_core(int v)
{
int queue[maxsize];
int front = 0, rear = 0;
this->adjlist[v].vertex.print();
BFS_visited[v] = 1;
queue[++rear] = v;
while (front != rear)
{
v = queue[++front];
arc_node* p = adjlist[v].first_arc;
while (p != nullptr)
{
int j = p->adj_vertex;
if (BFS_visited[j] == 0)
{
this->adjlist[j].vertex.print();
BFS_visited[j] = 1;
queue[++rear] = j;
}
p = p->next_arc;
}
}
}
template<class temp>
void al_graph<temp>::BFS(int v)
{
cout << "从" << v + 1 << "开始,广度优先遍历的结果为:" << endl;
BFS_core(v);
return0(BFS_visited);
cout << endl;
}4.2.2直接使用STL队列描写BFS
template<class temp>
void al_graph<temp>::return0(bool x[])
{
for (int i = 0; i < maxsize; i++)
x[i] = 0;
}
template<class temp>
void al_graph<temp>::BFS_core_for_queue(int v)
{
queue<int>q;
this->adjlist[v].vertex.print();
BFS_visited[v] = 1;
q.push(v);
while (!q.empty())
{
v = q.front();
q.pop();
arc_node* p = adjlist[v].first_arc;
while (p != nullptr)
{
int j = p->adj_vertex;
if (BFS_visited[j] == 0)
{
this->adjlist[j].vertex.print();
BFS_visited[j] = 1;
q.push(j);
}
p = p->next_arc;
}
}
}
template<class temp>
void al_graph<temp>::BFS_for_queue(int v)
{
cout << "从" << v + 1 << "开始,利用队列存储,广度优先遍历结果为:" << endl;
BFS_core_for_queue(v);
return0(BFS_visited);
cout << endl;
}五.析构函数
因为邻接表存储结构中链表数量不单一,所以单独拿出来讲一下。
5.1核心思路
按顺序析构。因为有adjlist数组,按照下标依次对每一条链表析构。
5.2代码部分
template<class temp>
al_graph<temp>::~al_graph()
{
int i = 0;
while (i < this->vnum)
{
arc_node* p = this->adjlist[i++].first_arc;
while (p != nullptr)
{
arc_node* q = p->next_arc;
delete p;
p = q;
}
}
}六.总体代码
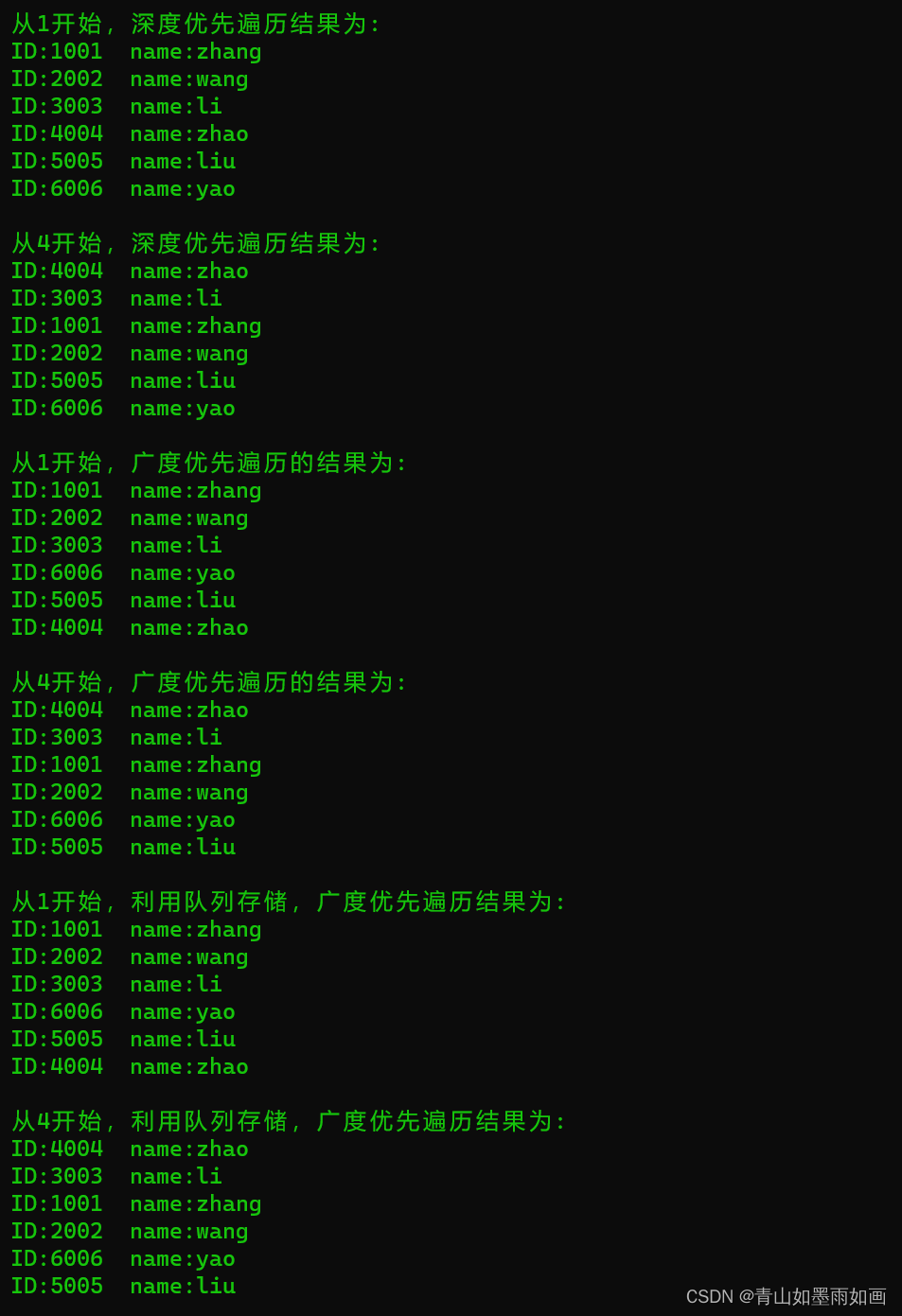
6.1代码效果图
6.2代码部分
#include<iostream>
#include<fstream>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
class student
{
private:
int ID;
string name;
public:
student()
{
this->ID = 0;
this->name = "un_known name";
}
student(int ID, string name)
{
this->ID = ID;
this->name = name;
}
void print()
{
cout << "ID:" << this->ID << " name:" << this->name << endl;
}
friend fstream& operator>>(fstream& fin, student& s)
{
fin >> s.ID;
fin >> s.name;
return fin;
}
};
struct arc_node
{
int adj_vertex;//数据域 邻接顶点的下标
arc_node* next_arc;//指针域 指向下一条弧结点
};
template<class temp>
struct vertex_node
{
temp vertex;//数据域 顶点信息
arc_node* first_arc;//指针域 指向第一条弧
};
struct relation//整型结构体数组,用来传递弧数据
{
int start;
int end;
};
const int maxsize = 10;
template<class temp>
class al_graph
{
private:
vertex_node<temp> adjlist[maxsize];
int vnum, arcnum;
public:
al_graph(ifstream& fin);
al_graph(temp a[],relation r[],int vnunm,int arcnum);
void return0(bool x[]);
void DFS_core(int v);
void DFS(int v);
void BFS_core(int v);
void BFS(int v);
void BFS_core_for_queue(int v);
void BFS_for_queue(int v);
~al_graph();
};
template<class temp>
al_graph<temp>::al_graph(ifstream& fin)
{
fin >> this->vnum;
fin >> this->arcnum;
for (int i = 0; i < vnum; i++)
{
fin >> this->adjlist[i].vertex;
this->adjlist[i].first_arc = nullptr;
}
for (int i = 0; i < arcnum; i++)
{
int i, j;
fin >> i >> j;//依次输入本初结点,邻接顶点
arc_node* s = new arc_node;
s->adj_vertex = j;//j是邻接顶点的下标
s->next_arc = this->adjlist[i].first_arc;
this->adjlist[i].first_arc = s;
}
}
template<class temp>
al_graph<temp>::al_graph(temp a[],
relation r[], int vnum, int arcnum)
{
this->vnum = vnum;
this->arcnum = arcnum;
for (int i = 0; i < vnum; i++)
{
this->adjlist[i].vertex = a[i];
this->adjlist[i].first_arc = nullptr;
}
for (int i = arcnum - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
arc_node* s = new arc_node;
s->adj_vertex = r[i].end;
s->next_arc = this->adjlist[r[i].start].first_arc;
this->adjlist[r[i].start].first_arc = s;
}
}
template<class temp>
void al_graph<temp>::return0(bool x[])
{
for (int i = 0; i < maxsize; i++)
x[i] = 0;
}
bool DFS_visited[maxsize];
template<class temp>
void al_graph<temp>::DFS_core(int v)
{
this->adjlist[v].vertex.print();
DFS_visited[v] = 1;
arc_node* p = this->adjlist[v].first_arc;
while (p != NULL)
{
int j = p->adj_vertex;
if (DFS_visited[j] == 0)
DFS_core(j);
p = p->next_arc;
}
}
template<class temp>
void al_graph<temp>::DFS(int v)
{
cout << "从"<<v+1<<"开始,深度优先遍历结果为:" << endl;
this->DFS_core(v);
return0(DFS_visited);
cout << endl;
}
bool BFS_visited[maxsize];
template<class temp>
void al_graph<temp>::BFS_core(int v)
{
int queue[maxsize];
int front = 0, rear = 0;
this->adjlist[v].vertex.print();
BFS_visited[v] = 1;
queue[++rear] = v;
while (front != rear)
{
v = queue[++front];
arc_node* p = adjlist[v].first_arc;
while (p != nullptr)
{
int j = p->adj_vertex;
if (BFS_visited[j] == 0)
{
this->adjlist[j].vertex.print();
BFS_visited[j] = 1;
queue[++rear] = j;
}
p = p->next_arc;
}
}
}
template<class temp>
void al_graph<temp>::BFS(int v)
{
cout << "从" << v + 1 << "开始,广度优先遍历的结果为:" << endl;
BFS_core(v);
return0(BFS_visited);
cout << endl;
}
template<class temp>
void al_graph<temp>::BFS_core_for_queue(int v)
{
queue<int>q;
this->adjlist[v].vertex.print();
BFS_visited[v] = 1;
q.push(v);
while (!q.empty())
{
v = q.front();
q.pop();
arc_node* p = adjlist[v].first_arc;
while (p != nullptr)
{
int j = p->adj_vertex;
if (BFS_visited[j] == 0)
{
this->adjlist[j].vertex.print();
BFS_visited[j] = 1;
q.push(j);
}
p = p->next_arc;
}
}
}
template<class temp>
void al_graph<temp>::BFS_for_queue(int v)
{
cout << "从" << v + 1 << "开始,利用队列存储,广度优先遍历结果为:" << endl;
BFS_core_for_queue(v);
return0(BFS_visited);
cout << endl;
}
template<class temp>
al_graph<temp>::~al_graph()
{
int i = 0;
while (i < this->vnum)
{
arc_node* p = this->adjlist[i++].first_arc;
while (p != nullptr)
{
arc_node* q = p->next_arc;
delete p;
p = q;
}
}
}
student stu[6] =
{
{1001,"zhang"},{2002,"wang"},{3003,"li"},
{4004,"zhao"},{5005,"liu"},{6006,"yao"}
};
//写入文本对象的构造函数因为是头插法,所以连接方式需要倒序输入
relation r1[12] =
{
{0,1},{0,2},{0,5},
{1,0},{1,2},{1,4},
{2,0},{2,1},{2,3},
{3,2},
{4,1},
{5,0}
};
relation r2[12] =
{
{0,5},{0,2},{0,1},
{1,4},{1,2},{1,0},
{2,3},{2,1},{2,0},
{3,2},
{4,1},
{5,0}
};
int main()
{
system("color 0A");
al_graph<student>aa(stu, r1, 6, 12);
aa.DFS(0);
aa.DFS(3);
aa.BFS(0);
aa.BFS(3);
aa.BFS_for_queue(0);
aa.BFS_for_queue(3);
return 0;
}
6.3运行结果