原题代码:
package com.example.demo3;
public class InitializeDemo {
private static int k = 1;
private static InitializeDemo t1 = new InitializeDemo("t1");
private static InitializeDemo t2 = new InitializeDemo("t1");
private static int i = print("i");
private static int n = 99;
{
print("初始化块");
j=100;
}
public InitializeDemo(String str) {
System.out.println((k++) + ":" + str + " i=" + i + " n=" + n);
++i;
++n;
}
static {
print("静态块");
n=100;
}
private int j = print("j");
public static int print(String str){
System.out.println((k++) + ":" + str + " i=" + i + " n=" + n);
++n;
return ++i;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
InitializeDemo test1 = new InitializeDemo("test");
}
}
- 类运行时,从上至下先执行静态变量、静态代码块、静态main方法
- 执行静态变量或者静态代码块时,遇到创建实例的引用或者静态方法时,可以先创建实例、执行静态方法
- 创建实例时,执行构造方法前需要先执行实例代码块,每次实例化都会执行一次
- 最后,静态变量和静态代码块执行完毕之后,完成运行
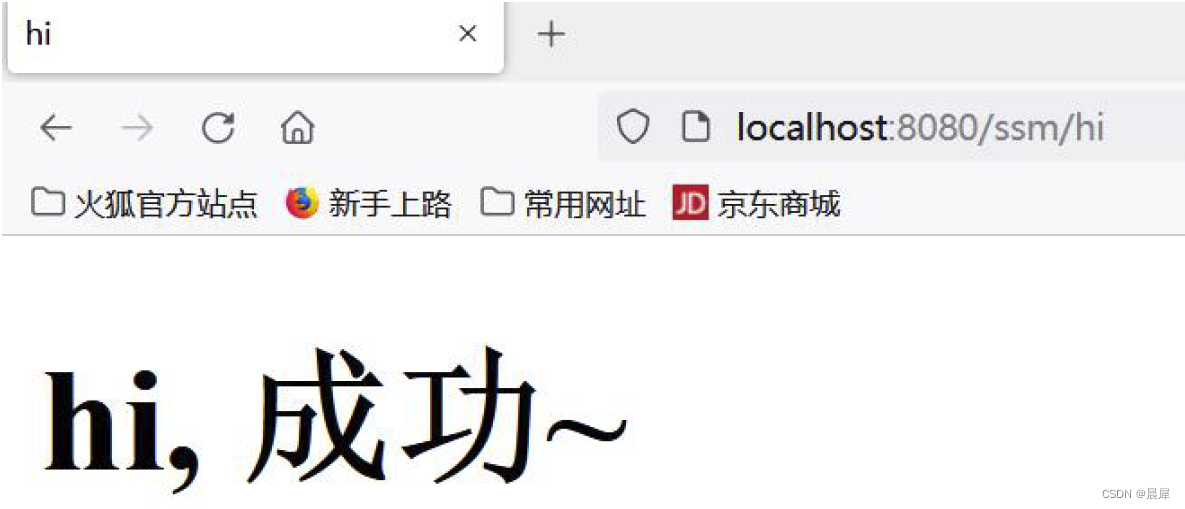
看一下运行结果










![[openCV]基于拟合中线的智能车巡线方案V4](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/6d6e0e96c2dc49d2b5af82306de736db.png)