如何利用OpenAI的函数调用特性
函数调用能实现哪些功能?
简单来说,函数调用功能可以助你在请求方法时构建结构化的数据。因为生成模型的特性,它产生的数据往往是无结构的,即使在提示(prompt)中指定了输出格式,但实际输出的结果往往偏离预期。
如果你曾经使用过Langchain,那么你一定知道其中有一个叫做OutputParser的模块,这个模块中定义了许多用于快速结构化数据的工具。

然而,面对大规模的模型,这些工具并不总是那么有效。因为模型的输出结果难以预测,这使得在一些复杂场景下,模型输出的结果总是无法被正确解析。即使是使用了Langchain中的OutputFixingParser,也难以让整个流程变得流畅。
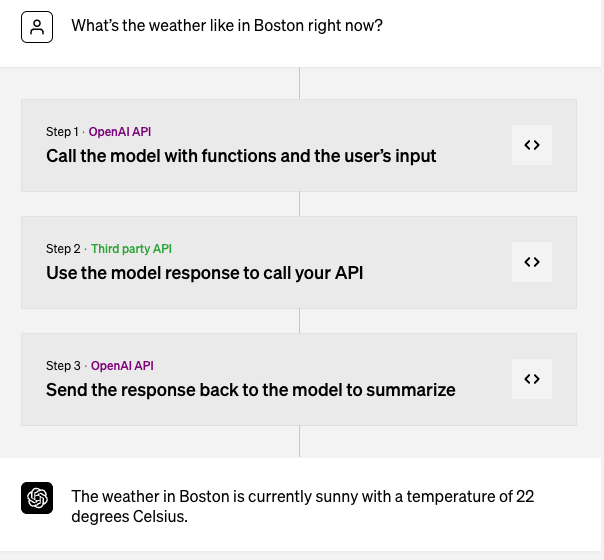
因此,我们仍然需要回归到OpenAI官方推出的函数调用特性。在官方提供的一个示例中,它使用function calling让GPT模型提取自然语言中可用于函数调用的信息,然后利用第三方接口获取实时信息,最后生成一个全新的总结。
如何使用函数调用以及其工作原理?
接下来,让我们借助官方的示例来解析一下如何使用function calling这个特性,以及它究竟是如何运作的。
第一步:携带函数调用去请求GPT接口
首先,你需要把一个问题和函数调用一起,作为请求提交到GPT的接口。
messages = [{"role": "user", "content": "What's the weather like in Boston?"}]
functions = [
{
"name": "get_current_weather",
"description": "Get the current weather in a given location",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"location": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The city and state, e.g. San Francisco, CA",
},
"unit": {"type": "string", "enum": ["celsius", "fahrenheit"]},
},
"required": ["location"],
},
}
]
response = openai.ChatCompletion.create(
model="gpt-3.5-turbo-0613",
messages=messages,
functions=functions,
function_call="auto", # auto is default, but we'll be explicit
)
response_message = response["choices"][0]["message"]
"""
输出:
<OpenAIObject at 0x7a90d69f1620> JSON: {
"role": "assistant",
"content": null,
"function_call": {
"name": "get_current_weather",
"arguments": "{\n \"location\": \"Boston, MA\"\n}"
}
}
"""
在这个例子中,先是定义了一个问题: What's the weather like in Boston?, 这个是我们想要回答的问题,其中Boston是问题中的地名,weather是我们想要知道的信息。在下面的function中,我们定义了一个function来指明我们在获取三方的api时需要哪些参数,进而让gpt知道它应该从What's the weather like in Boston? 这句话中提取什么样的信息,以及什么格式的信息。
第二步:拿着解析出来的信息请求接口
import json
# 这是一个虚假的函数,用来模拟三方接口的返回值
def get_current_weather(location, unit="fahrenheit"):
"""Get the current weather in a given location"""
weather_info = {
"location": location,
"temperature": "72",
"unit": unit,
"forecast": ["sunny", "windy"],
}
return json.dumps(weather_info)
if response_message.get("function_call"):
# Step 3: call the function
# Note: the JSON response may not always be valid; be sure to handle errors
available_functions = {
"get_current_weather": get_current_weather,
} # only one function in this example, but you can have multiple
function_name = response_message["function_call"]["name"]
fuction_to_call = available_functions[function_name]
function_args = json.loads(response_message["function_call"]["arguments"])
function_response = fuction_to_call(
location=function_args.get("location"),
unit=function_args.get("unit"),
)
"""
输出的function_response:
{"location": "Boston, MA", "temperature": "72", "unit": null, "forecast": ["sunny", "windy"]}
"""
在这一步中,我们通过 function_name = response_message["function_call"]["name"] 这个来获取到了gpt模型解析出的函数名,因为在更复杂的场景中,我们可能一次性让gpt解析更多的方法,因此我们需要获取到所有的函数名。
接着我们又通过response_message["function_call"]["arguments"]这个获取到了解析出来的参数。这边的参数其实就gpt通过我们的问题提取到的能够被用到get_current_weather这个函数中作为参数的内容。比如现在我们需要的两个参数是location和unit, gpt就会根据现有的这个问题来提取是localtion和unit意思的信息。
第三步生成一个summary
messages.append(response_message) # extend conversation with assistant's reply
messages.append(
{
"role": "function",
"name": function_name,
"content": function_response,
}
) # extend conversation with function response
second_response = openai.ChatCompletion.create(
model="gpt-3.5-turbo-0613",
messages=messages,
) # get a new response from GPT where it can see the function response
在最后一步只是单纯的根据上下文信息生成一个新的句子,其实没有什么更多的信息。
接下来我们通过另一个稍微复杂一点点的案例再来解释下function calling的用法
举个栗子 让GPT机器翻译
现在我们想让GPT帮我做一个翻译的功能,并且翻译的信息可以结构化的输出,于是我写了这么一个prompt:
prompt_template = """
Now you have to translate the following text into {lang}:
### Text to translate:
{text}
### Target language:
{lang}
### Output format:
your translation should in the following format:
{{'res': 'your translation'}}
"""
其实,在大部分情况只下,这个prompt就已经可以输出一份结构化的数据了,但是在复杂场景比如你的文本较长,或者尝试翻译大量文本的时候,模型总会出现一些额外的信息,不仅仅只有你想要的这个json格式,可能还有其他连带出来的输出。
现在我想要做的是,使用function calling 来解析我们的输出,我只想要最后的翻译结果。比较省钱但是费力的方法就是我直接提取最终返回数据中的 {res : xxx} 这个字符串,并获得它的值。 但是在这里我们还是打算使用function calling来帮我们解析这个数据。
现在我们的翻译的执行是这样的:
text = 'Collection of Open Source Projects Related to GPT,GPT相关开源项目合集🚀、精选🔥🔥'
lang = 'en'
prompt = prompt_template.format(text=text, lang=lang)
# completion是我们封装的一个转发openai请求的函数,没有什么特别的实现
response = completion(model_name="gpt-3.5-turbo-0613", prompt=prompt)
response.content
"""
输出:
{'res': 'Collection of Open Source Projects Related to GPT, Compilation of open source projects related to GPT 🚀, selected 🔥🔥'}
"""
现在我们定义一个ResponseSchema来代表这个输出。 因为在复杂的生产场景中,我们往往需要解析的对象是很复杂的,是有多个字段以及不同类型的,我们不可能像官方的例子一样手动去去写每一个parameters。
在这里我使用了python的pydantic包来实现这么一个功能。
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field
import json
class ResponseSchema(BaseModel):
result: str = Field(..., description="the translated value")
@classmethod
def schema(cls, by_alias=True):
schema = super().schema(by_alias)
schema.pop('title', None)
return schema
@classmethod
def schema_json(cls, by_alias=True, **dumps_kwargs):
schema_str = json.dumps(cls.schema(by_alias), **dumps_kwargs)
return json.loads(schema_str)
在这里我手动的实现了schema和 schema_json 函数,因为 pydantic的模型类总会自带一个title的属性,这个属性很大程度上会影响GPT对我们最终想要的输出的理解。
我们执行ResponseSchema.schema_json()就可以获取到和上面官方例子一样的一个关于字段描述的结果:
{'type': 'object',
'properties': {'result': {'title': 'Result',
'description': 'the translated value',
'type': 'string'}},
'required': ['result']}
于是我们的function只需要写成这样就可以了:
functions=[
{
"name": "print_translation",
"description": "print the translated value from value of res",
"parameters": ResponseSchema.schema_json(),
},
]
在这个function中,我们的print_translation 函数其实是虚假的函数,我们只是给他起了一个合理的名字以及合理的描述,这样GPT就可以知道我们的参数的上下文是什么样的了。
完整的一个flow如下:
import openai
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field
import json
def completion(model_name, prompt):
completion = openai.ChatCompletion.create(
stream=False,
model=model_name,
messages=[
{"role": "user", "content": prompt}
]
)
return completion.choices[0].message
class ResponseSchema(BaseModel):
result: str = Field(..., description="the translated value")
@classmethod
def schema(cls, by_alias=True):
schema = super().schema(by_alias)
schema.pop('title', None)
return schema
@classmethod
def schema_json(cls, by_alias=True, **dumps_kwargs):
schema_str = json.dumps(cls.schema(by_alias), **dumps_kwargs)
return json.loads(schema_str)
### 让GPT帮我生成对应语句的翻译,并返回成json
prompt_template = """
Now you have to translate the following text into {lang}:
### Text to translate:
{text}
### Target language:
{lang}
### Output format:
your translation should in the following format:
{{'res': 'your translation'}}
"""
text = 'Collection of Open Source Projects Related to GPT,GPT相关开源项目合集🚀、精选🔥🔥'
lang = 'en'
functions=[
{
"name": "print_translation",
"description": "print the translated value from value of res",
"parameters": ResponseSchema.schema_json(),
},
]
prompt = prompt_template.format(text=text, lang=lang)
response = completion(model_name="gpt-3.5-turbo-0613", prompt=prompt)
final_result = openai.ChatCompletion.create(
model="gpt-3.5-turbo-0613",
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": prompt}],
functions=functions,
function_call="auto",
)
message = final_result["choices"][0]["message"]
eval(message['function_call']['arguments'])['result']
"""
最终输出:
Collection of Open Source Projects Related to GPT, GPT Related Open Source Project Collection 🚀, Selected 🔥🔥
"""
总结
在本文中,我们深入探索了OpenAI的函数调用特性,并解析了其在实现结构化数据生成中的巨大价值。虽然我们通常认为生成模型产生的数据是无结构的,但在文章中证明,借助函数调用特性,我们完全有可能创建出结构化的数据。
通过编程示例,我们详细解释了函数调用的工作原理,包括如何向GPT接口提交带有问题和函数调用的请求,如何利用模型提取出的信息去请求第三方接口获取实时数据,以及如何生成一个全新的总结。
接着,我们展示了如何借助函数调用特性实现机器翻译功能,并结构化输出翻译的信息。本文向大家展示了,通过为虚拟函数定义合理的名字和描述,GPT模型能够理解参数的上下文,并按照预设的格式生成结构化的翻译结果。
总的来说,本文为大家提供了一个实用的、结构化的数据生成方法,希望这对于您在大规模模型的数据解析以及多样化的信息提取上能够带来实质性的帮助。