文章目录
- 1.移除链表元素
- 2.反转链表
- 3.链表的中间结点
- 4.倒数第k个结点
- 5.合并两个有序链表
- 6.链表分割
- 7.链表的回文结构
- 8.相交链表
- 9.环形链表
- 10.环形链表Ⅱ
- 1.常规思路
- 2.新型思路【无码】
1.移除链表元素
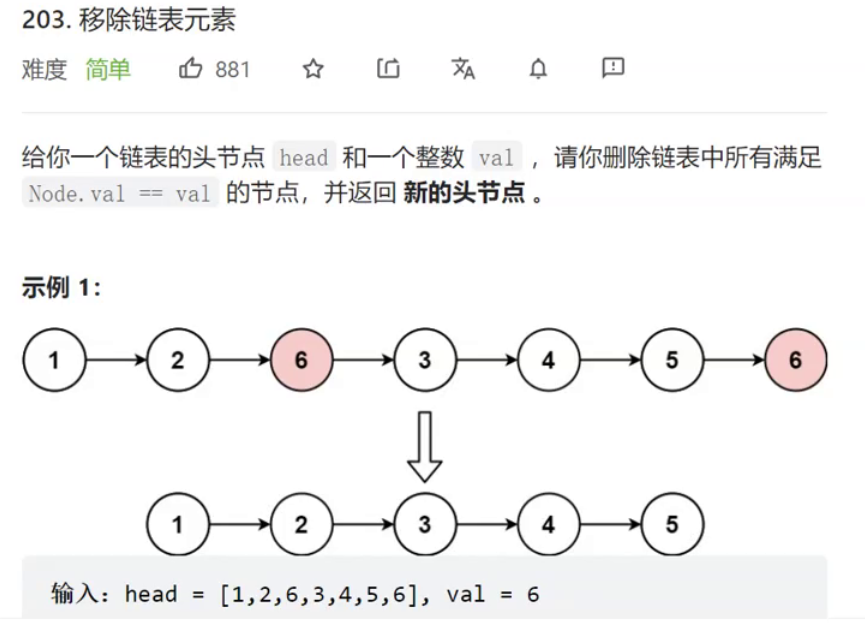
法一:遍历删除
struct ListNode
{
int val;
struct ListNode* next;
};
struct ListNode* rmele(struct ListNode* head, int val)
{
struct ListNode* prv = NULL;
struct ListNode* cp = head;
while (cp)
{
if (cp->val == val)
{
if (cp == head) //头删
{
//head自动指向cp的下一结点
head = cp->next;
//删除目标结点
free(cp);
//更新cp
cp = head;
}
else
{
//prv连接cp的next结点
prv->next = cp->next;
//删除目标值
free(cp);
//更新cp
cp = prv->next;
}
}
else //不是继续遍历
{
prv = cp;
cp = cp->next;
}
}
return head;
}
法二:循环尾插
struct ListNode
{
int val;
struct ListNode* next;
};
struct ListNode* rmele(struct ListNode* head, int n)
{
struct ListNode* tail = NULL;
struct ListNode* cp = head;
head = NULL;
//不置空 若遇到全是目标值的链表
//删除后--head应指向NULL--不置空head指向原头结点
while (cp)
{
if (cp->val == n) //是目标值删除
{
//obj指向要被删除的目标值
struct ListNode* obj = cp;
//cp后移
cp = cp->next;
//删除目标值
free(obj);
}
else //非目标值尾插
{
if (tail == NULL) //尾插首值
{
head = cp; //更新head 指向新的头结点
tail = cp; //更新tail 指向新的尾结点
}
else //尾插非首值
{
//tail连接非目标值
tail->next = cp;
//更新tail
tail = cp; //更新tail 指向新的尾结点
}
//cp后移
cp = cp->next;
}
}
//遍历结束 尾结点的指针域须被置空
//若遇到空链表 tail初值为空 无法访问next
if (tail != NULL)
tail->next = NULL;
return head;
}
法三:带哨兵位的头结点
struct ListNode
{
int val;
struct ListNode* next;
};
struct ListNode* rmele(struct ListNode* head, int n)
{
struct ListNode* tail = NULL;
struct ListNode* cp = head;
head = tail = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
tail->next = NULL;
while (cp)
{
if (cp->val == n) //是目标值删除
{
//obj指向要被删除的目标值
struct ListNode* obj = cp;
//cp后移
cp = cp->next;
//删除目标值
free(obj);
}
else //非目标值尾插
{
//tail连接非目标值
tail->next = cp;
//更新tail
tail = cp; //更新tail 指向新的尾结点
//cp后移
cp = cp->next;
}
//尾插后将指针域置空
tail->next = NULL;
//sentinel:哨兵
struct ListNode* sp = head;
//更新head 指向非哨兵位的头结点
head = head->next;
//销毁哨兵位
free(sp);
return head;
}
}
2.反转链表
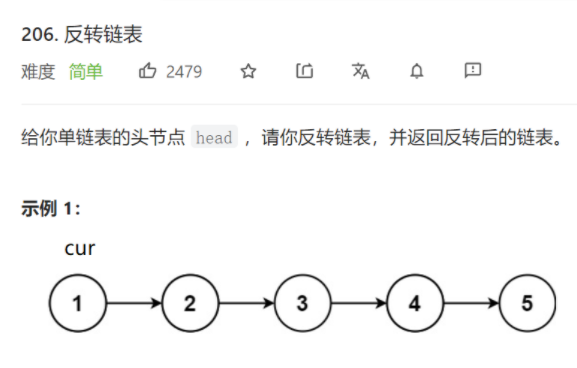
法一:循环头插
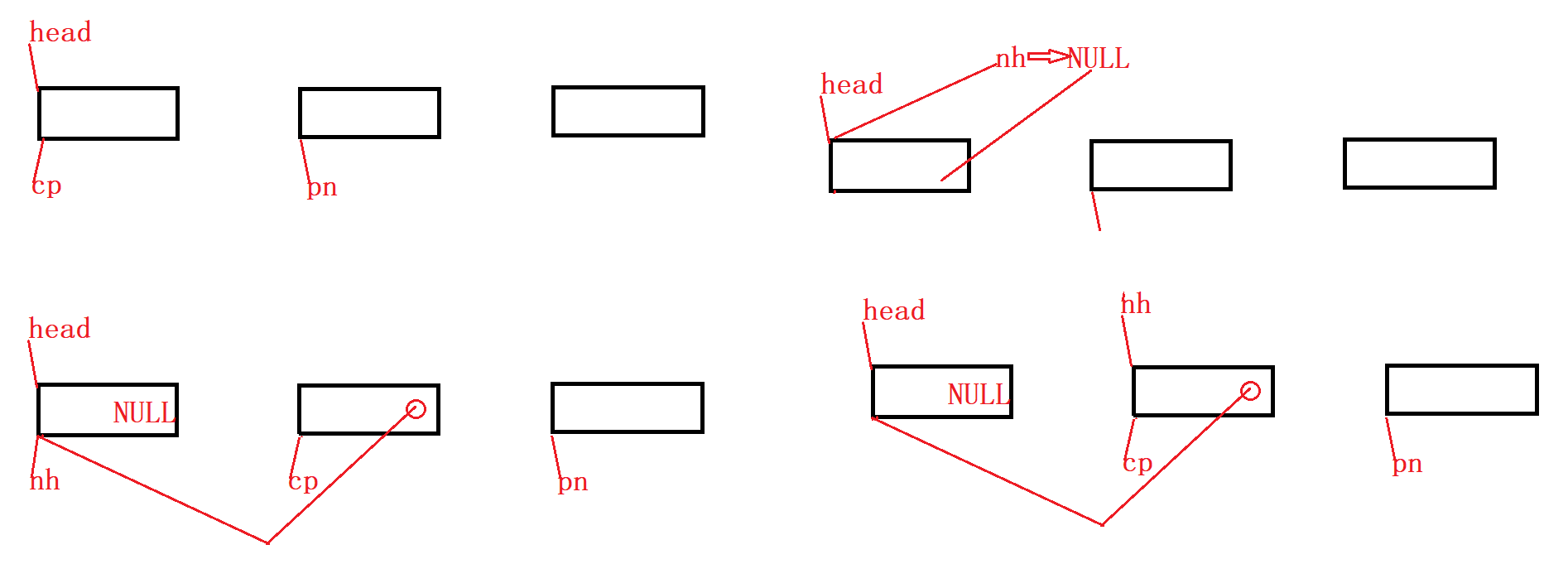
struct ListNode
{
int val;
struct ListNode* next;
};
//nh:newhead
//cp:pointer to current
//pnext:pointer to next
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head)
{
struct ListNode* nh = NULL;
struct ListNode* cp = head;
while (cp)
{
//pn永远指向cp的下一个结点
struct ListNode* pnext = cp->next;
//nh指向上一个结点-->初始为空
cp->next = nh; //cp的指针域存储上一个结点空间地址 ==》cp连接nh(上一个结点)
//nh指向更新 指向现结点空间地址
nh = cp;
//cp后移
cp = pnext;
}
return nh;
}
法二:改变指针指向
struct ListNode
{
int val;
struct ListNode* next;
};
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head)
{
if (head == NULL)
return NULL;
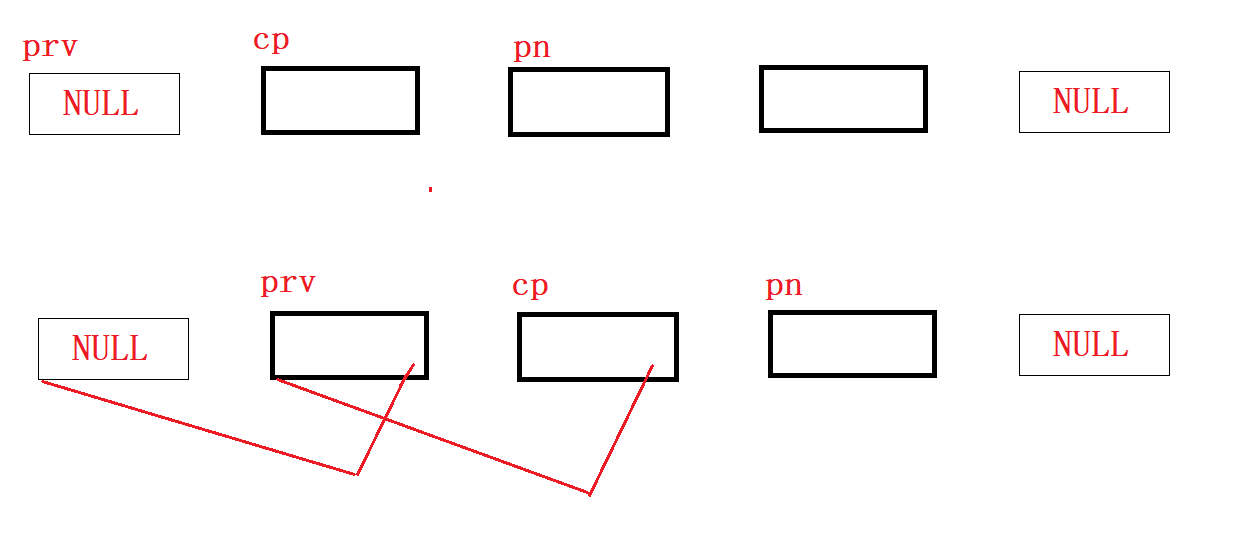
struct ListNode* prv, * cp, * pn;
prv = NULL;
cp = head;
pn = cp->next;
while (cp)
{
//cp连接前结点
cp->next = prv;
//前结点指针后移
prv = cp;
//现结点指针后移
cp = pn;
//原pn非空
if (pn != NULL)
{
pn = pn->next;
}
}
return prv;
}
3.链表的中间结点
struct ListNode
{
int val;
struct ListNode* next;
};
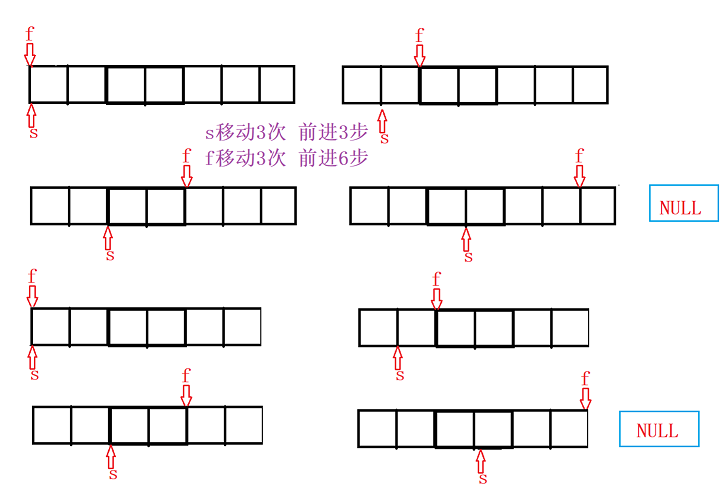
struct ListNode* middleNode(struct ListNode* head)
{
struct ListNode* s,* f;
s = f = head;
while (f && f->next)
{
s = s -> next;
f = f -> next -> next;
}
return s;
}
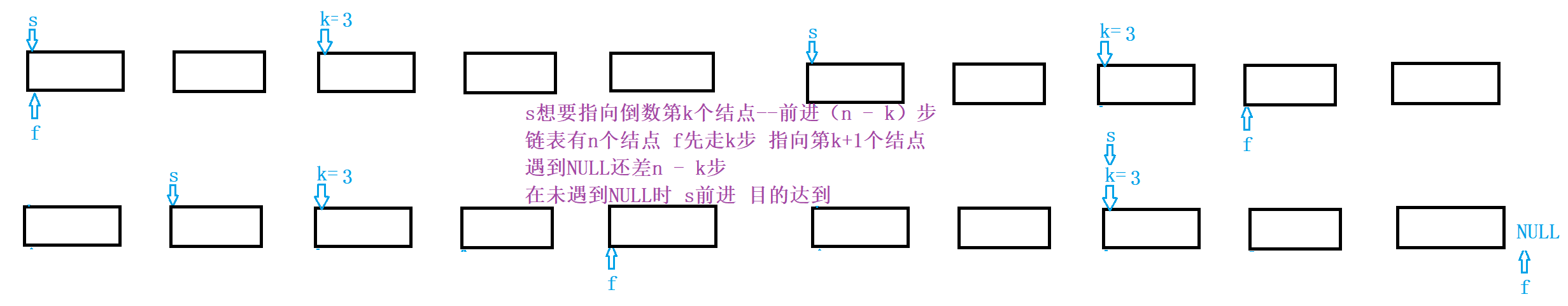
4.倒数第k个结点
struct ListNode
{
int val;
struct ListNode* next;
};
struct ListNode* FindKthToTail(struct ListNode* pListHead, int k)
{
struct ListNode* s, * f;
s = f = pListHead;
//f先前进k步
while (k--)
{
if (f != NULL) //防止输入的值k > 链表长度
f = f->next; //即f还未走完k步 链表已结束
else
return NULL;
}
while (f)
{
s = s->next;
f = f->next;
}
return s;
}
5.合并两个有序链表
法一:归并插入
struct ListNode
{
int val;
struct ListNode* next;
};
struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* list1, struct ListNode* list2)
{
if (list1 == NULL)
return list2;
if (list2 == NULL)
return list1;
struct ListNode* head, * tail;
head = tail = NULL;
while (list1 && list2)
{
if (list1->val < list2->val)
{
if (tail == NULL)
{
//头插--直接指向obj
head = tail = list1;
}
else
{
tail->next = list1;
//后移
tail = tail->next;
}
//后移
list1 = list1->next;
}
else
{
if (tail == NULL)
{
head = tail = list2;
}
else
{
tail->next = list2;
tail = tail->next;
}
//后移
list2 = list2->next;
}
}
if (list1)
tail->next = list1;
if (list2)
tail->next = list2;
//新链表头结点
return head;
}
法二:带哨兵位的头结点
struct ListNode
{
int val;
struct ListNode* next;
};
struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* list1, struct ListNode* list2)
{
struct ListNode* head, * tail;
//哨兵位
head = tail = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
tail->next = NULL;
while (list1 && list2)
{
if (list1->val < list2->val)
{
tail->next = list1;
tail = tail->next;
list1 = list1->next;
}
else
{
tail->next = list2;
tail = tail->next;
list2 = list2->next;
}
}
//有剩余结点--连接
if (list1)
tail->next = list1;
if (list2)
tail->next = list2;
struct ListNode* realhead = head->next;
free(head);
return realhead;
}
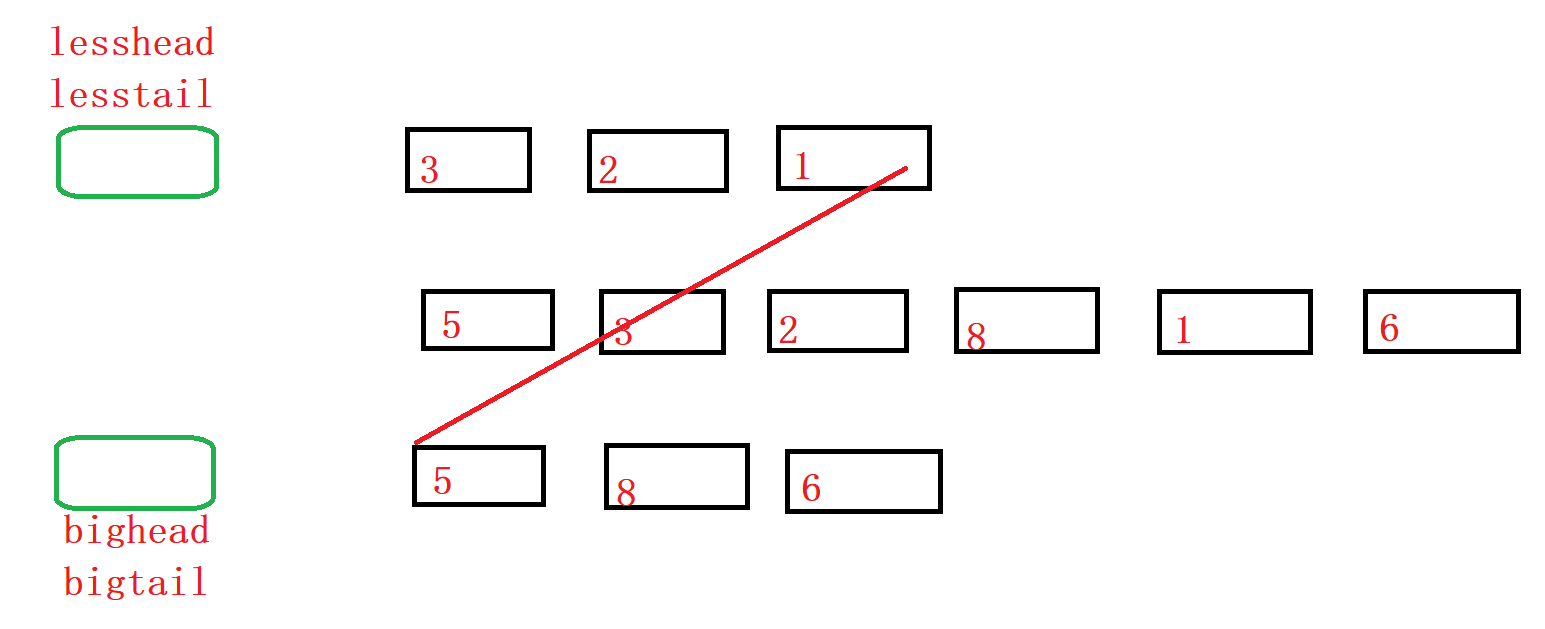
6.链表分割
struct ListNode
{
int val;
struct ListNode* next;
ListNode(int x)
:val(x)
,next(nullptr)
{
}
};
class Partition
{
public:
ListNode* partition(ListNode* pHead, int x)
{
//创建哨兵位
struct ListNode* big_head, * big_tail, * less_head, * less_tail;
big_head = big_tail = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
less_head = less_tail = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
big_tail->next = nullptr;
less_tail->next = nullptr;
//遍历
struct ListNode* cp = pHead;
while (cp)
{
if (cp->val < x)
{
less_tail->next = cp;
less_tail = less_tail->next;
}
else
{
big_tail->next = cp;
big_tail = big_tail->next;
}
cp = cp->next;
}
//连接两段链表
less_tail->next = big_head->next;
//注意尾结点指针域置空
big_tail->next = nullptr;
struct ListNode* newhead = less_head->next;
free(big_head);
free(less_head);
return newhead;
}
};
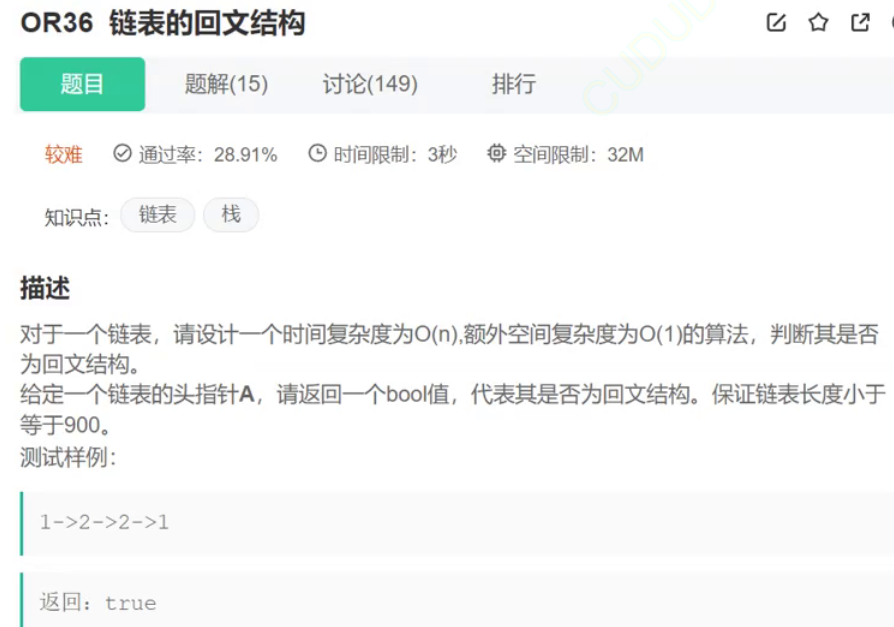
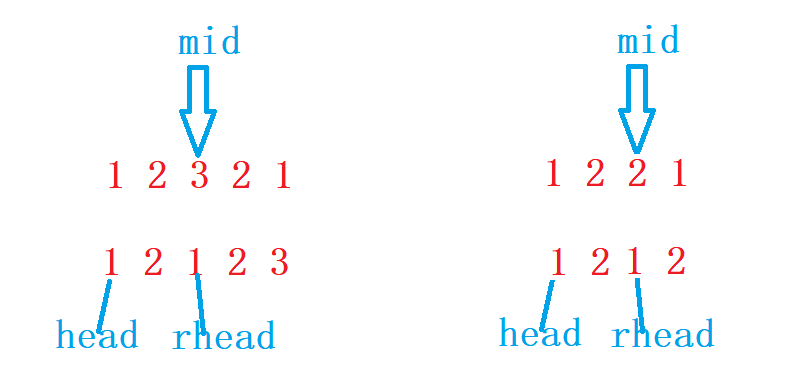
7.链表的回文结构
struct ListNode
{
int val;
struct ListNode* next;
};
//寻找中间结点
struct ListNode* middleNode(struct ListNode* head)
{
struct ListNode* s, * f;
s = f = head;
while (f && f->next)
{
s = s->next;
f = f->next->next;
}
return s;
}
//后半段逆置
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head)
{
struct ListNode* nh = NULL;
struct ListNode* cp = head;
while (cp)
{
//pn永远指向cp的下一个结点
struct ListNode* pnext = cp->next;
//nh指向上一个结点-->初始为空
cp->next = nh; //cp的指针域存储上一个结点空间地址 ==》cp连接nh(上一个结点)
//nh指向更新 指向现结点空间地址
nh = cp;
//cp后移
cp = pnext;
}
return nh;
}
//判断回文
bool isPalindrome(struct ListNode* head)
{
struct ListNode* mid = middleNode(head);
struct ListNode* rhead = reverseList(mid);
while (head && rhead)
{
if (head->val != rhead->val)
{
return false;
}
else
{
head = head->next;
rhead = rhead->next;
}
}
return true;
}
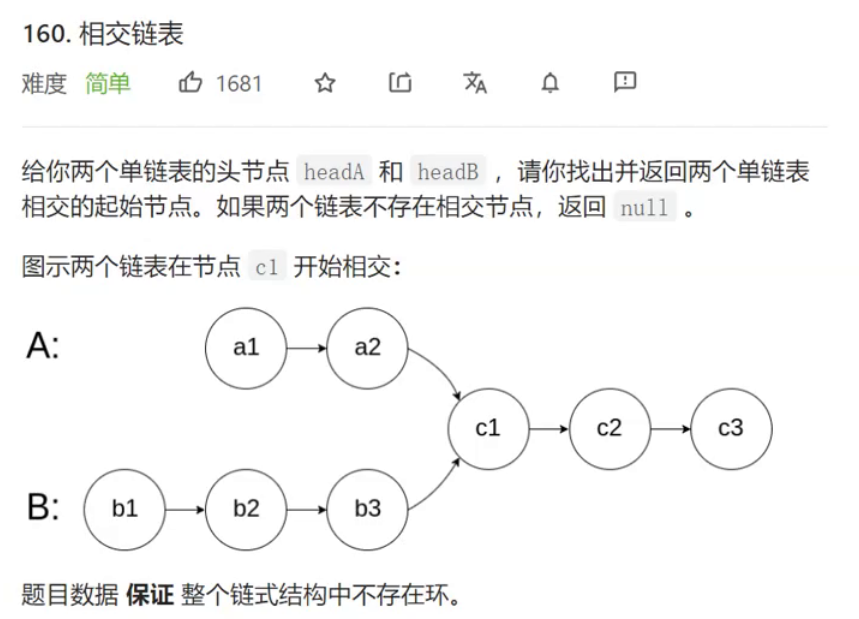
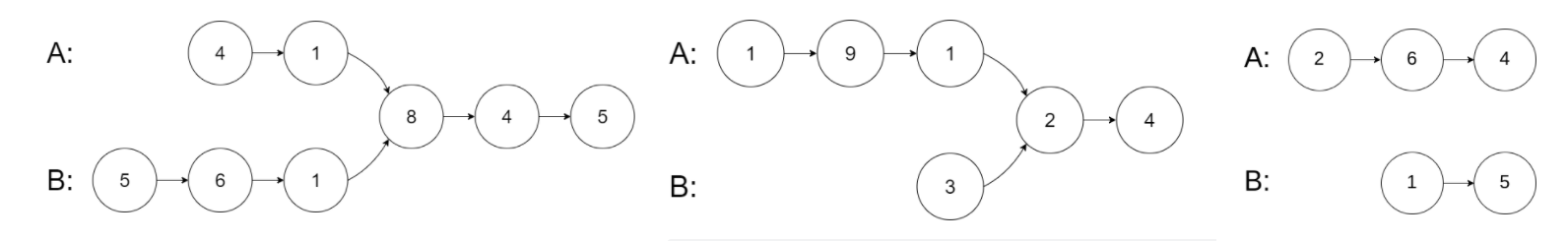
8.相交链表
struct ListNode
{
int val;
struct ListNode* next;
};
struct ListNode* getIntersectionNode(struct ListNode* headA, struct ListNode* headB)
{
if (headA == NULL || headB == NULL)
return NULL;
struct ListNode* cpA = headA, * cpB = headB;
//求链表长度
int lenA = 1, lenB = 1;
while (cpA->next)
{
cpA = cpA->next;
lenA++;
}
while (cpB->next)
{
cpB = cpB->next;
lenB++;
}
//若链表相交 尾结点空间地址定相同
if (cpA != cpB)
return NULL;
//定位长短链表
struct ListNode* S_list = headA, * L_list = headB;
if (lenA > lenB)
{
S_list = headB;
L_list = headA;
}
//求长度差
int gap = abs(lenA - lenB);
//长链表前进gap步
while (gap--)
{
L_list = L_list->next;
}
while (S_list != L_list)
{
S_list = S_list->next;
L_list = L_list->next;
}
return S_list;
}
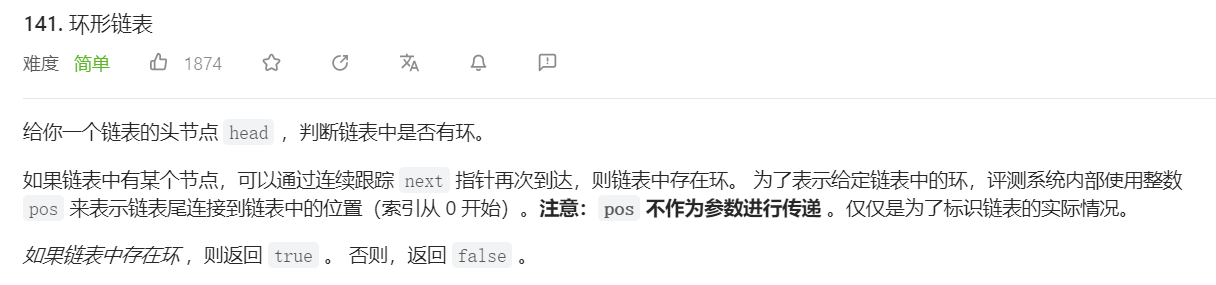
9.环形链表
struct ListNode
{
int val;
struct ListNode* next;
};
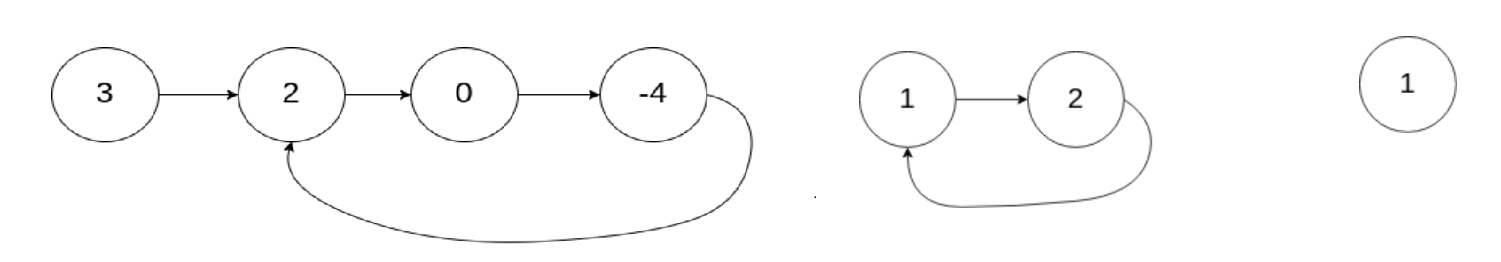
bool has_cycle(struct ListNode* head)
{
struct ListNode* f = head, * s = head;
while (f && f->next)
{
s = s->next;
f = f -> next->next;
if (s == f)
return true;
}
return false;
}



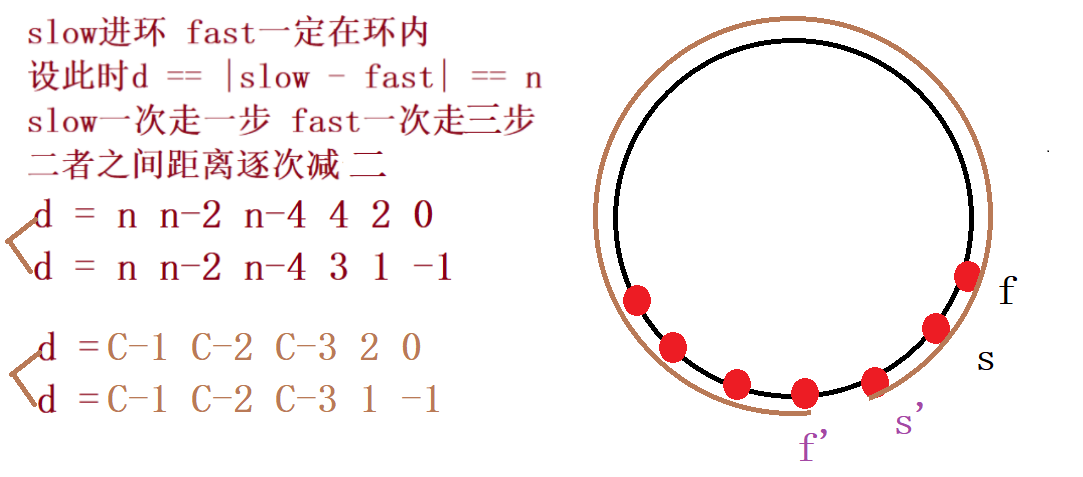
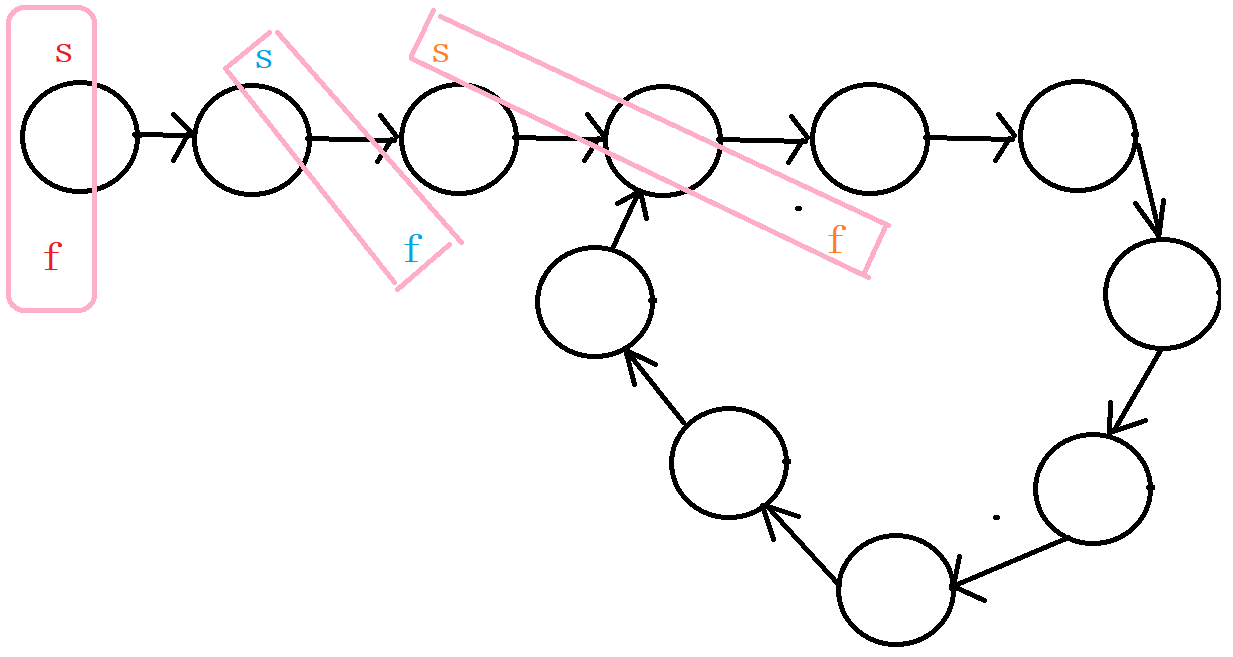
n是偶数能追上
n是奇数 C-1是偶数能追上
n是奇数 C-1是奇数追不上
10.环形链表Ⅱ
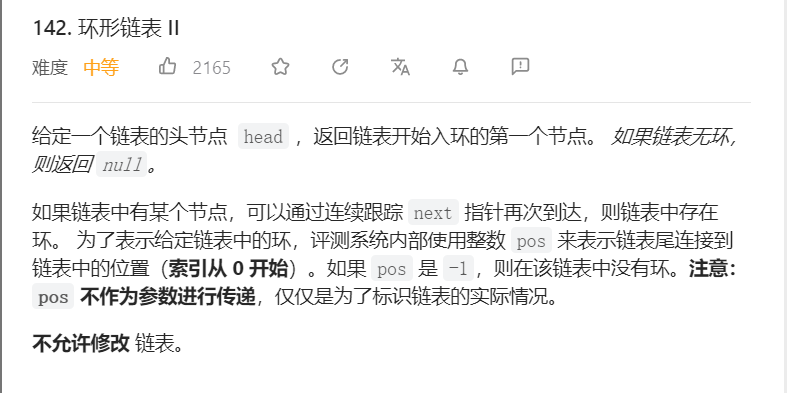
1.常规思路
slow进环后在一圈内一定会被fast追上:slow进环后 fast一定在slow前面 二者之间最大距离为一圈 slow走1圈 fast会走2圈 超出的这一圈绝对会碰到slow ==》 fast最多走2圈就会追上slow【fast比slow每次多走一步的前提下】
struct ListNode
{
int val;
struct ListNode* next;
};
struct ListNode* detectCycle(struct ListNode* head)
{
struct ListNode* s, * f;
s = f = head;
//若f 、 f->next二者有一为空 == 定不存在环
while (f && f->next)
{
//s走1步 f走2步
s = s->next;
f = f -> next->next;
//s == f :定有环
if (s == f)
{
struct ListNode* meet = s;
while (meet != head)
{
meet = meet->next;
head = head -> next;
}
//相等即二者相遇 相遇点即为交点
return meet;
}
}
return NULL;
}
2.新型思路【无码】
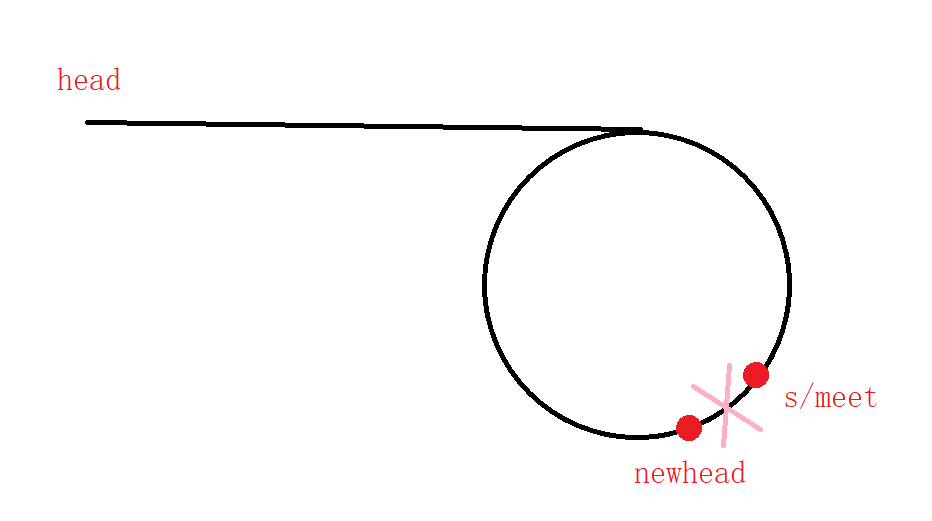
问题变成了:newhead的链表和head的链表的寻找交点的问题