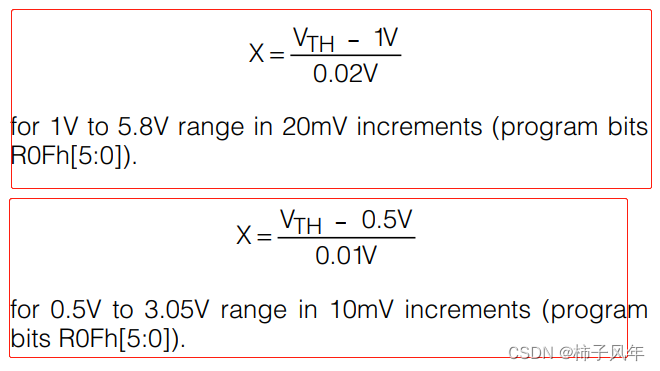
一个初中生自己编写的一个很LOW的“OS”,编写不易,不喜勿喷;耗时巨大,引用时请说明。






接下来,让我们一起学习使用cgyOS。
零、配置
下载本程序后,在Python3.10环境下使用pip安装pygame和keyboard的最新版本,然后双击“cos.py”即可完成配置并成功启动系统(本系统对Windows兼容性较强,对Linux兼容性较差,对Mac的兼容性不明。所以如果您使用Linux和Mac配置cgyos时出现问题,请自行解决)。
一、普通使用
普通使用和Windows差不多。运行本软件后,您将看到一个开机画面,结束后,您将看到一个“APP Starter”。您可以在文本框内输入(将鼠标光标放到文本框上,当鼠标指针变成“![]() ”时j即可输入。)应用程序的名称(所有应用程序都在apps文件夹中),在按回车键或点击“
”时j即可输入。)应用程序的名称(所有应用程序都在apps文件夹中),在按回车键或点击“![]() ”按钮,即可启动该软件。目前尚无法直接关闭软件,但是可以在软件中通过代码设置。
”按钮,即可启动该软件。目前尚无法直接关闭软件,但是可以在软件中通过代码设置。
二、编写软件
cgyOS具有非常强大的可拓展性,您可以轻易地编写软件并在cgyOS中运行。
2.1 基础框架与运行
接下来,请和我一起编写一个小程序:Hello World。
首先请看应用程序基本框架(apps\basic.py):
from apilib import *
from classes import *
import cos
# 导入包
def cosmain(): # 主函数
screen = cos.window # 绑定显示器
root = Tk(screen, 10, 105, 350, 450, "Basic") # 创建窗口
api_hook(root, 'Basic') # 绑定窗口
在这段代码中,1~3行代码导入了本程序要用的包。第8行“cosmain”是cgyOS应用程序的主函数,cgyOS应用程序应有且只有一个主函数。第九行绑定了cgyOS的显示器,它非常重要,几乎您在使用每个cgyOS的类时都要将其传入。第10行创建了一个GUI窗口(小白可能会误认为它是tkinter),它的实现方法为TK类。TK类的__init__的原型为:
def __init__(self,
screen: Any,
x: Any,
y: Any,
_w: Any,
_h: Any,
_title: Any,
bg: tuple[int, int, int] = lightgray) -> None第11行代码使用了apilib的api_hook函数,它可以让窗口正常显示。
接下来,在cgyOS\apps中新建文件,命名为“HelloWorld.py”。



并把应用程序基本框架复制与其中

再打开cgy-os\apps\__init__.py,把我们的程序名追加到第一行的后面。
原来:
改后:
from . import bosd, downloads, msgmaker, tfer, watch, hw, boyorgirl, canvas, cosver, HelloWorld接下来,我们运行cgy-os,在APP Starter中输入“HelloWorld”,然后点击“运行”。


接下来,让我们一起更改一些代码:
1.窗口的长、宽太大了,并且窗口标题应该为“Hello World”。为此,我们把
root = Tk(screen, 10, 105, 350, 450, "Basic")改成
root = Tk(screen, 10, 105, 200, 150, "Hello World!")
2.窗口中太空了。为了解决问题,我们可以在“root = TK(...)”那一行后面添加如下代码:
label = Label(screen, root, "Hello World!!", 5, 5)
label.pack()这里使用了Label类,Label类的__init__的原型为:
def __init__(self,
screen: Any,
root: Tk,
text: Any,
x: Any,
y: Any,
fg: tuple[int, int, int] = black,
bg: tuple[int, int, int] = white,
maxlength: int = -1) -> None它(和以后的大部分类都)是“Widget”类的子类。widget类的__init__函数的原型为:
def __init__(self,
screen: Any,
root: Tk) -> None一般地,在使用widget的子类时,第一个参数传入screen,第二个参数传入Tk类的实例(如:root)。
运行效果:
出现这种问题是因为Label中将文字的底色默认设为了白色,为解决这个问题,请将
label = Label(screen, root, "Hello World!!", 5, 5)改为
label = Label(screen, root, "Hello World!!", 5, 5, bg=None)这样就没有问题了。
接下来,让我们添加一个功能按钮:
from apilib import *
from classes import *
import cos
# 导入包
def cosmain(): # 主函数
def cmd(): # Here!
pass # Here!
screen = cos.window # 绑定显示器
root = Tk(screen, 10, 105, 200, 150, "Hello World!") # 创建窗口
label = Label(screen, root, "Hello World!!", 5, 5, bg=None)
label.pack()
btn = Button(screen, root, "exit", 5, 25, len("exit") * 10 + 5, cmd) # Here!
btn.pack() # Here!
api_hook(root, 'Basic') # 绑定窗口

这里使用了Button类,它的原型为:
def __init__(self,
screen: Any,
root: Tk,
text: Any,
x: Any,
y: Any,
_w: Any,
command: Any,
fg: tuple[int, int, int] = black,
bg: tuple[int, int, int] = lightgray) -> None其中command参数指定了当按钮被按下时所运行的函数/类的方法。它不应该加小括号,如果必须传参,请使用lambda语句。
现在按下按钮程序没有动作,这是由于cmd函数中没有函数体导致的。接下来,我们来“充实”一下cmd函数。
def cmd(): # Here!
root.set_disabled(True) # 取消显示窗口
在摁下按钮,窗口就消失了。
#Hello World完整代码
from apilib import *
from classes import *
import cos
# 导入包
def cosmain(): # 主函数
def cmd(): # Here!
root.set_disabled(True) # 取消显示窗口
screen = cos.window # 绑定显示器
root = Tk(screen, 10, 105, 200, 150, "Hello World!") # 创建窗口
label = Label(screen, root, "Hello World!!", 5, 5, bg=None)
label.pack()
btn = Button(screen, root, "exit", 5, 25, len("exit") * 10 + 5, cmd) # Here!
btn.pack() # Here!
api_hook(root, 'Basic') # 绑定窗口
2.2 内核详解
本来不应该现在将这个的,只能假定看这个的都是大佬了…
最重要的内核在cos/cpu.py中。它(现在)提供了绘图函数、按键绑定和计时器。代码如下:
import sys
import time
import pygame
import hankaku # font
import keyboard
now_key = ""
lk = None
def callback(event):
global now_key, lk
a = str(event)
if a[-5:] == 'down)':
if a[14:-6] not in ("shift", "right shift", "ctrl", "right ctrl", "caps lock"):
now_key = a[14:-6]
time.sleep(0.0001)
now_key = ''
keyboard.hook(callback)
# import keyboard
class Io:
def __init__(self):
# keyboard.hook(lambda e: self.io_check_key(e))
pass
@staticmethod
def io_init(w, h, title):
pygame.init()
screen = pygame.display.set_mode((w, h))
pygame.display.set_caption(title)
return screen
@staticmethod
def io_check_mouse():
b = pygame.mouse.get_pressed()
if b:
return b
@staticmethod
def io_check_exit():
for event in pygame.event.get():
if event.type == pygame.QUIT:
pygame.quit()
sys.exit()
@staticmethod
def io_put_line(screen, x1, y1, x2, y2, color):
pygame.draw.line(screen, color, (x1, y1), (x2, y2))
@staticmethod
def io_put_bg(screen, color):
screen.fill(color)
@staticmethod
def io_put_box(screen, x, y, w, h, color, is_fill=True):
if is_fill:
pygame.draw.rect(screen, color, (x, y, w, h))
else:
pygame.draw.rect(screen, color, (x, y, w, h), 1)
@staticmethod
def io_put_point(screen, x, y, color):
pygame.draw.rect(screen, color, (x, y, 1, 1))
@staticmethod
def io_update():
pygame.display.flip()
def io_put_str(self, screen, x, y, color, text, bg_color=None):
for i in range(len(list(text))):
self.io_put_chr(screen, x + i * 10, y, color, text[i], bg_color)
return len(text) * 10
def io_put_chr(self, screen, x, y, color, char, bg_color=None):
hex_char = hex(ord(char))
for i in range(len(hankaku.font[hex_char])):
for j in range(len(hankaku.font[hex_char][i])):
if hankaku.font[hex_char][i][j] == '.':
if bg_color is None:
pass
else:
self.io_put_point(screen, x + j, y + i, bg_color)
elif hankaku.font[hex_char][i][j] == '*':
self.io_put_point(screen, x + j, y + i, color)
# @staticmethod
# def io_check_key(e=None):
# return
class Time:
def __init__(self):
self.sec = 0
self.start = time.time()
def sleep(self, sec):
self.start = time.time()
self.sec = sec
def is_sleeping(self):
return (time.time() - self.start) < self.sec
@staticmethod
def time():
return time.time()
没什么可以说的,会pygame的人都能看懂,主要是看懂也没必要。字体文件是cos/hankaku.py,抄的30天的源文件,自己写了一个编译器(虽然只有30行)把它的源文件编译成.py了。现在只支持英文(中文实在太难了,理解万岁)。
font = {
'0x01': [['.', '.', '.', '.', '.', '.', '.', '.'], ['.', '.', '*', '*', '*', '.', '.', '.'],
['.', '*', '.', '.', '.', '*', '.', '.'], ['*', '.', '.', '.', '.', '.', '*', '.'],
['*', '.', '*', '.', '*', '.', '*', '.'], ['*', '.', '*', '.', '*', '.', '*', '.'],
['*', '.', '.', '.', '.', '.', '*', '.'], ['*', '.', '.', '.', '.', '.', '*', '.'],
['*', '.', '*', '.', '*', '.', '*', '.'], ['*', '.', '.', '*', '.', '.', '*', '.'],
['.', '*', '.', '.', '.', '*', '.', '.'], ['.', '.', '*', '*', '*', '.', '.', '.'],
['.', '.', '.', '.', '.', '.', '.', '.'], ['.', '.', '.', '.', '.', '.', '.', '.'],
......
}接下来,进入正式的系统:cos/cos.py。
开头先导入包:
import threading
import time as wintime
import random
from cpu import *
from sysset import *
import datetime
import cell
import sysset
import os
import osapp
# import ostest
import classes然后设置显示屏、系统计时器、初始化鼠标位置和确认debug模式(这里说一下:DEBUG若为TRUE,则不会显示开机动画,并且会直接全部报错信息,若DEBUG设置为FALSE则会显示开机动画,若有错误则会显示一个红屏错误界面(ROSD))。
window = Io.io_init(w, h, title)
os_timer = Time()
mx, my = pygame.mouse.get_pos()
DEBUG = False接下来一堆函数,先跳过,直接来到200多行:
if __name__ == "__main__":
_dir = os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__)))
if _dir not in sys.path:
sys.path.insert(0, _dir)
main()
第2-4行可以让cgyOS所在目录下的文件可以直接被import(否则在pycharm Professional等编辑器中应用程序的编写会很不顺利),第5行调用main函数,正式启动系统。
def main():
init()
osapp.cos_system_app_starter_cosmain(window)
while True:
if DEBUG:
oneloop()
else:
try:
oneloop()
except (Exception, ValueError) as e:
ROSD(e)
breakmain函数首先调用了init函数,它主要设置了窗口图标、鼠标显示和开机动画(对于shutup函数,请直接阅读源码)。
def init():
try:
img = pygame.image.load(r"lego.ico")
pygame.display.set_icon(img)
except:
pass
pygame.mouse.set_visible(False)
if not DEBUG:
shutup()然后它(main函数)调用了osapp里的一个函数(类似Windows的开机启动),它其实是一个标准的cgyOS的APP:
#cos\osapp.py
from classes import *
from apilib import *
from sysset import *
import apps
import cos
def cos_system_app_starter_cosmain(screen):
def cmd():
try:
exec("apps." + entry.get() + ".cosmain()")
except (ModuleNotFoundError, ImportError, Exception) as e:
if cos.DEBUG:
print(type(e), str(e))
msg.config(text=f"Error:APP \"{entry.get().lower()}\" IS NOT A FULL-COS APP.")
else:
msg.config(text=f"APP \"{entry.get().upper()}\" STARTED SUCCESSFULLY")
root = Tk(screen, w / 2 - 125, h / 2 - 50, 250, 100, "APP Starter")
entry = Entry(screen, root, 5, 5, 180, cmd)
msg = Label(screen, root, "Welcome to CGY-OS!", 5, 30, bg=None,maxlength=24)
msg.pack()
entry.pack()
btn = Button(screen, root, "Start", 190, 5, 55, cmd)
btn.pack()
api_hook(root, "cos_system_app_starter_cosmain")
不错,它就是传说中的APP Starter。
然后我们的main函数用不同的两种方式调用了oneloop函数,一种是debug开启后的无防护版,一种是非debug下的“安全”版(其实也不安全)。oneloop函数:
def oneloop():
Io().io_check_exit()
Io.io_put_bg(window, darkgreen)
mousecheck()
explorer()
apps()
if not classes.s_mode: # update mouse
cell.m_state = mouse0
else:
classes.s_mode = False
mouse(cell.m_state)
Io.io_update()第2行和倒数第一行的“Io().io_check_exit()”和“Io.io_update()”是pygame的必要过程,只是被封装了一下;第3行把整个背景染成绿色(护眼从我做起);mousecheck主要控制窗口的拖动;explorer使用CPU的绘图函数绘制一个没用的任务栏;if...else...语句结合cos\classes.py控制鼠标样式;mouse函数负责在合适的位置绘制鼠标。apps函数负责控制程序。
def apps():
if len(cell.windows) >= 1:
cell.windows = sorted(cell.windows, key=lambda x: x['level'])
for i in cell.windows:
if not i['istop']:
# print(i['win'].level)
i['win'].mainloop()
# threading.Thread(target=lambda: i['win'].mainloop()).start()
函数体的第1、2行对窗口进行排序(关键字是它的层级);后面就是启动程序了。关于为什么要使用“i['istop']”,详见第3节“GUI类详解”。
2.3 GUI类详解
cos的所有内置GUI类都在cos\classes.py中。
2.3.1 TK类
Tk类不同于其他的GUI类,它是一个容器,而不是一个控件。
print(dir(classes.Tk))
['__class__', '__delattr__', '__dict__', '__dir__', '__doc__', '__eq__', '__format__',
'__ge__', '__getattribute__', '__gt__', '__hash__', '__init__', '__init_subclass__',
'__le__', '__lt__', '__module__', '__ne__', '__new__', '__reduce__', '__reduce_ex__',
'__repr__', '__setattr__', '__sizeof__', '__str__', '__subclasshook__', '__weakref__',
'add_hook', 'add_unapply_hook', 'config', 'del_hook', 'del_unapply_hook', 'mainloop',
'mkwindow', 'set_disabled', 'setlevel']每个GUI类都有以下方法:__init__(废话)、config(用来重设参数)。
2.3.1.1 Tk.__init__
Tk.__init__接受以下参数:
1.screen:它接受一个显示器,所有GUI类都要传递这个参数,它应该为cos.csreen。
2.x,y,_w,_h,_title:分别是窗口的x坐标、y坐标、长度、宽度和标题(cos中,屏幕或窗口的左上角为0,0)。
3.bg:背景色
2.3.1.2 Tk.config 所有的config函数均用于重设参数,无需解释。
2.3.1.3 Tk.setlevel: 此函数为系统负责调用的,暂时无需解释(因为系统中关于层级的设置尚不完善)
2.3.1.4 Tk.add_hook 和 Tk.del_hook:
它接受一个函数(也不能加括号),如果窗口显示(Tk.disabled is True)则执行函数,否则不执行。del_hook可以取消此函数的执行。一般用于控件的挂载。
2.3.1.5 Tk.add_unapply_hook 和 Tk.del_unapply_hook:
它接受一个函数(也不能加括号),不管窗口是否显示,都执行函数。del_unapply_hook可以取消此函数的执行。一般用于程序函数的挂载。
2.3.1.6 Tk.set_disabled:
它接受一个布尔值,若该值为TRUE,则显示窗口,否则不显示。
2.3.1.7 Tk.mainloop:
它是Tk类中最主要的函数,主要通过调用cpu.py中的函数完成窗口的绘制。
global s_mode
if not self.disabled:
Io.io_put_box(self.screen, self.x + 1, self.y - 21, self.w, self.h + 21, white)
Io.io_put_box(self.screen, self.x - 1, self.y - 19, self.w, self.h + 21, black)
Io.io_put_box(self.screen, self.x, self.y - 20, self.w, 20, lightblue)
# for i in range(self.w):
# Io.io_put_line(self.screen,self.x + i, self.y - 20, self.x + i, self.y,
# colorsys.hsv_to_rgb(240, 1-1.0/(i+1), 0))
Io().io_put_str(self.screen, self.x + 2, self.y - 20 + 3, black, self.title)#以上标题栏
for i in range(len(close)):
for j in range(len(close[i])):
if close[i][j] == 1:
Io.io_put_point(self.screen, self.x + self.w - 15 + i, self.y - 20 + 14 - j, black)
elif close[i][j] == 2:
Io.io_put_point(self.screen, self.x + self.w - 15 + i, self.y - 20 + 14 - j, white)
elif close[i][j] == 3:
Io.io_put_point(self.screen, self.x + self.w - 15 + i, self.y - 20 + 14 - j, lightgray)#以上关闭按钮(虽然没用)
Io.io_put_box(self.screen, self.x, self.y, self.w, self.h, self.bg)#窗口主体
for root_app_hook in self.hook:#控件钩子
root_app_hook()
for root_unapply_hook in self.unapply_hook:#程序钩子
root_unapply_hook()
return2.3.2 Widget类
widget类是所有控件的父类。除__init__、config外,它(和其他控件)还有以下几种共有方法:
2.3.2.1 Widget.pack、Widget.unpack
它们分别调用了Tk的add_hook和del_hook函数,将该控件的draw函数当做钩子钩入Tk中,使Tk在执行mainloop是自动执行它。
2.3.2.2 Widget.draw:
它类似于Tk.mainloop,可以将控件通过cpu.py的绘图函数绘制出来。
2.3.3 Label 类
print(dir(classes.Label))
['_Label__set_max_length', '__class__', '__delattr__', '__dict__', '__dir__', '__doc__',
'__eq__', '__format__', '__ge__', '__getattribute__', '__gt__', '__hash__', '__init__',
'__init_subclass__', '__le__', '__lt__', '__module__', '__ne__', '__new__', '__reduce__',
'__reduce_ex__', '__repr__', '__setattr__', '__sizeof__', '__str__', '__subclasshook__',
'__weakref__', 'config', 'draw', 'pack', 'unpack']
2.3.3.1 Label.__init__
Label.__init__接受以下形参:
1.screen:略。
2.root:一个Tk类的实例,希望这个控件显示到哪个root上,就把哪个root传入该形参(以下控件均需screen和root形参,所以以下所有控件都不写这两个形参。)
3.text:该控件显示的文本。
4.x,y:该控件在root内的位置(左上角为(0,0),以后也不解释)
5.fg、bg:fg为文字颜色,bg为背景颜色,如果bg=None,则将背景设为透明。
6.maxlenth:高级属性,意思为每当text的长度到达maxlenth时,label就会自动换行。(为高级功能)。
2.3.3.2 Label.__set_max_lenth 此函数为累的私有方法,主要负责实现maxlenth的功能,无需了解
2.3.3.3 Label.draw
def draw(self):
if self.maxlength == -1:
Io().io_put_str(self.screen, self.x + self.root.x, self.y + self.root.y, self.fg, self.text, self.bg)
else:
for i in self.labels:
Io().io_put_str(self.screen, i[1] + self.root.x, i[2] + self.root.y, color=self.fg, text=i[0],
bg_color=self.bg)很简单,懒得讲了。
2.3.4 Button类
print(dir(classes.Button))
['__class__', '__delattr__', '__dict__', '__dir__', '__doc__', '__eq__', '__format__',
'__ge__', '__getattribute__', '__gt__', '__hash__', '__init__', '__init_subclass__',
'__le__', '__lt__', '__module__', '__ne__', '__new__', '__reduce__', '__reduce_ex__',
'__repr__', '__setattr__', '__sizeof__', '__str__', '__subclasshook__', '__weakref__',
'check_click', 'config', 'draw', 'on', 'pack', 'runcmd', 'unpack']
2.3.4.1 Button.__init__
Button.__init__接受以下参数:
1.w: 按钮的宽,一般为“len(text)*10+5”
2.command:按钮点击时执行的函数
3. fg、bg:fg为按钮文字颜色。bg为按钮底色
注:Io.io_check_mouse()返回一个列表,[0]为是否按下左键;[1]为是否触碰滚轮;[2]为是否触碰右键。
2.3.4.2 Button.check_click:
返回一个布尔值,用于确定鼠标是否悬停于该按钮上并左键单击。
2.3.4.3 Button.on:
返回一个布尔值,用于确定鼠标是否悬停于该按钮上。(以后不讲)
2.3.4.4 Button.runcmd:
返回一个布尔值,可以据此确定是否运行“command”。它的作用是保证在长按按钮时不重复执行command、
2.3.4.5 Button.draw
它的主要功能为绘制窗口、更新指针并执行函数,代码和注释见下。
def draw(self):
global s_mode
mx, my = pygame.mouse.get_pos()#获取鼠标位置
if self.check_click(mx, my):#如果被点击,使用样式1
Io.io_put_box(self.screen, self.x - 1 + self.root.x, self.y - 1 + self.root.y, self.w + 1, self.h + 1,
black)
Io.io_put_box(self.screen, self.x + self.root.x, self.y + self.root.y, self.w + 1, self.h + 1, white)
Io.io_put_box(self.screen, self.x + self.root.x, self.y + self.root.y, self.w, self.h, self.bg)
Io().io_put_str(self.screen, self.x + 1 + self.root.x, self.y + 1 + self.root.y, self.fg, self.text,
self.bg)
else:#否则使用样式2
Io.io_put_box(self.screen, self.x - 1 + self.root.x, self.y - 1 + self.root.y, self.w + 1, self.h + 1,
white)
Io.io_put_box(self.screen, self.x + self.root.x, self.y + self.root.y, self.w + 1, self.h + 1, black)
Io.io_put_box(self.screen, self.x + self.root.x, self.y + self.root.y, self.w, self.h, self.bg)
Io().io_put_str(self.screen, self.x + 1 + self.root.x, self.y + 1 + self.root.y, self.fg, self.text,
self.bg)
if self.on(mx, my): #如果鼠标悬停于其上
cell.m_state = mouse3 #切换鼠标指针
s_mode = True #标记切换
if self.runcmd() and self.check_click(mx, my): #如果可以运行command
self.command() #运行2.3.5 Entry 类
说明:Entry类BUG(特性)较多,使用entry可能会造成一些难以预防的错误。目前cgyos正在抓紧修复该问题。
print(dir(classes.Entry))
['__class__', '__delattr__', '__dict__', '__dir__', '__doc__', '__eq__', '__format__',
'__ge__', '__getattribute__', '__gt__', '__hash__', '__init__', '__init_subclass__',
'__le__', '__lt__', '__module__', '__ne__', '__new__', '__reduce__', '__reduce_ex__',
'__repr__', '__setattr__', '__sizeof__', '__str__', '__subclasshook__', '__weakref__',
'check_click', 'check_key', 'config', 'draw', 'get', 'insert', 'key', 'on', 'pack', 'set',
'unpack']
2.3.5.1 Entry.__init__
Entry.__init 接受以下参数:
1.w: 文本框的宽
2.fg、bg:输入文本的颜色、文本框的底色
3.command:按下回车键时执行的函数
2.3.5.2 Entry.insert
def insert(self, text, start): # start从0开始
self.text = self.text[:start] + text + self.text[start:]在文本的start处插入text(start从0开始)。
2.3.5.3 Entry.set、Entry.get:
set为直接将文本框内全部文本替换为形参“text”,get返回输入的文本。
2.3.5.4 Entry.check_click和Entry.on :同“Button”
2.3.5.5 Entry.key
负责通过cpu.py中的数据返回输入文本应更改的部分、处理退格。
2.3.5.6 Entry.check_key
否则通过Entry.key对显示的文本、光标做出反应和处理。
def check_key(self):
a = self.key()
if len(a) == 1: #如果是一个字符
self.text = self.text[:self.course] + a + self.text[self.course:] #在光标处增加字符
# self.showtext = self.text[abs(int(self.w / 10) - self.course):int(self.w / 10)]
if self.course >= self.w // 10:
self.showtext = self.text[self.course - self.w // 10 + 1:self.course]
else:
if len(self.text) <= self.w // 10:
self.showtext = self.text
else:
self.showtext = self.text[:self.w // 10]#更新显示文本
self.course += 1 #更新光标
else:
if a == 'left':
if self.course > 0:
self.course -= 1#更新光标
elif a == 'right':
if self.course < int(self.w / 10) and self.course < len(self.showtext):
self.course += 1#更新光标
elif a == 'up':
pass
elif a == 'down':
pass
elif a == 'enter':
if self.command is not None:
self.command()#处理回车键2.3.5.7 Entry.draw
如果鼠标悬停于其上,它才会获取输入。
def draw(self):
global s_mode
mx, my = pygame.mouse.get_pos() #获取鼠标坐标
if self.on(mx, my): #如果鼠标悬停于其上
self.check_key() #处理文本
s_mode = True
cell.m_state = mouse1
Io.io_put_box(self.screen, self.x - 2 + self.root.x, self.y - 1 + self.root.y, self.w + 1, self.h + 1,
black)
Io.io_put_box(self.screen, self.x + self.root.x - 1, self.y + self.root.y, self.w + 1, self.h + 1, white)
Io.io_put_box(self.screen, self.x + self.root.x - 1, self.y + self.root.y, self.w, self.h, self.bg) #画图
Io().io_put_str(self.screen, self.x + 2 + self.root.x, self.y + 1 + self.root.y, self.fg, self.showtext,
self.bg) #写字
if not self.timer.is_sleeping() or self.timer.sec == 0: #画光标
self.timer.sleep(0.5)
self.state = not self.state
if self.state and self.on(mx, my):
aa = self.course * 10
if self.course * 10 > self.w:
aa = self.w
Io.io_put_line(self.screen, self.x + self.root.x + aa,
self.y + self.root.y + 1,
self.x + self.root.x + aa,
self.y + self.root.y + 14 - 1, self.fg) #光标画完了
2.3.6 Message 类
message主要可以在窗口上显示一个小窗口(但是无法关闭,所以显得有些“鸡肋”,不过正在修复),它虽然像是一个容器,但实际是一个控件。
message类建立后,会自动将该控件作为窗口注册到apilib中。为了区分真的窗口和message,每个窗口在注册时要带一个【istop】属性,若为message,istop=TRUE。
print(dir(classes.Messagebox))
['__class__', '__delattr__', '__dict__', '__dir__', '__doc__', '__eq__', '__format__',
'__ge__', '__getattribute__', '__gt__', '__hash__', '__init__', '__init_subclass__',
'__le__', '__lt__', '__module__', '__ne__', '__new__', '__reduce__', '__reduce_ex__',
'__repr__', '__setattr__', '__sizeof__', '__str__', '__subclasshook__', '__weakref__',
'calc', 'config', 'draw', 'draw_msg', 'pack', 'setlevel', 'unpack']
2.3.6.1 Message.__init__
Message.__init__接受以下参数:
1.type:"info"、“error”、“question”、“warning”中任意一种。他们主要区分图标的区别。
2. x、y、title:同Tk类。
3.text:显示的文本
4.bg:窗口背景
2.3.6.2 Message.calc 和Label的__set_max_lenth方法类似,主要为了让文本自动换行并处理图标的位置。
2.3.6.3 Message.draw_msg
通过传入的参数(来自settings.py的二维数组)绘制消息框的图标。
def draw_msg(self, _type): #type 为2维数组
for i in range(len(_type)):
for j in range(len(_type[i])):
if _type[i][j] == 0: #透明
pass
elif _type[i][j] == 1: #白色标记,为百色点
Io.io_put_point(self.screen, self.root.x + 25 + j,
(self.y - 65) / 2 + (self.root.y - self.y) / 2 + (
self.root.y + self.root.h) / 2 + len(
_type) / 2 + i,
white)
elif _type[i][j] == 2: #蓝色标记,为蓝色点
Io.io_put_point(self.screen, self.root.x + 25 + j,
(self.y - 65) / 2 + (self.root.y - self.y) / 2 + (
self.root.y + self.root.h) / 2 + len(
_type) / 2 + i, blue)
elif _type[i][j] == 3: #黄色标记,为黄色点
Io.io_put_point(self.screen, self.root.x + 25 + j,
(self.y - 65) / 2 + (self.root.y - self.y) / 2 + (
self.root.y + self.root.h) / 2 + len(
_type) / 2 + i, yellow)
elif _type[i][j] == 4: #红色标记,为红色点
Io.io_put_point(self.screen, self.root.x + 25 + j,
(self.y - 65) / 2 + (self.root.y - self.y) / 2 + (
self.root.y + self.root.h) / 2 + len(
_type) / 2 + i, red)
elif _type[i][j] == 5: #黑色标记,为黑色点
Io.io_put_point(self.screen, self.root.x + 25 + j,
(self.y - 65) / 2 + (self.root.y - self.y) / 2 + (
self.root.y + self.root.h) / 2 + len(
_type) / 2 + i, black)
2.3.6.4 Message.draw:显示而已,没什么可说的。
2.3.7 ProgressBar类
显示一个标准的进度条。
print(dir(classes.ProgressBar))
['__class__', '__delattr__', '__dict__', '__dir__', '__doc__', '__eq__', '__format__',
'__ge__', '__getattribute__', '__gt__', '__hash__', '__init__', '__init_subclass__',
'__le__', '__lt__', '__module__', '__ne__', '__new__', '__reduce__', '__reduce_ex__',
'__repr__', '__setattr__', '__sizeof__', '__str__', '__subclasshook__', '__weakref__',
'calc', 'config', 'draw', 'get', 'get_int', 'on', 'pack', 'set', 'unpack']
2.3.7.1 PrograssBar.__init__:
它接受的参数:full:进度条到100%时表示的数据
2.3.7.2 ProgressBar.get、ProgressBar.set、ProgressBar.get_int:
set接受一个数字,可将现在的值设为该数字(显示计算方法:now_w=w*now/full);get返回当前数字。get_int 返回一个2位小数,为now和full之比。
2.3.7.3 ProgressBar.calc:
计算now和full之比,若now和full之比大于1,则返回w*1,否则返回w*now/full。
2.3.7.4 ProgressBar.draw:
def draw(self):
global s_mode
mx, my = pygame.mouse.get_pos() #获取鼠标位置
if self.on(mx, my):
cell.m_state = mouse2 #将鼠标指针改为“等待”
s_mode = True
Io.io_put_box(self.screen, self.x - 2 + self.root.x, self.y - 1 + self.root.y, self.w + 1, self.h + 1,
black)
Io.io_put_box(self.screen, self.x + self.root.x - 1, self.y + self.root.y, self.w + 1, self.h + 1, white)
Io.io_put_box(self.screen, self.x + self.root.x - 1, self.y + self.root.y, self.w, self.h, self.bg)
Io.io_put_box(self.screen, self.x + self.root.x - 1, self.y + self.root.y, self.calc(), self.h, darkblue) #绘制
2.3.8 RadioButton类
一个单选框。
print(dir(classes.RadioButton))
['__class__', '__delattr__', '__dict__', '__dir__', '__doc__', '__eq__', '__format__',
'__ge__', '__getattribute__', '__gt__', '__hash__', '__init__', '__init_subclass__',
'__le__', '__lt__', '__module__', '__ne__', '__new__', '__reduce__', '__reduce_ex__',
'__repr__', '__setattr__', '__sizeof__', '__str__', '__subclasshook__', '__weakref__',
'check_click', 'config', 'draw', 'draw_pic', 'friend', 'get', 'on', 'pack', 'set',
'unpack']
2.3.8.1 RadioButton.__init__:
RadioButton.__init__接受以下参数:
text:按钮后显示的文本
command:点击时执行的函数,正在开发中,现在还是鸡肋。
2.3.8.2 RadioButton.friend:
接受一个RadioButton类,将他们添加至一个“组”中,一个组中必须有且只有一个RadioButton被选中。
2.3.8.3 RadioButton.get、RadioButton.set:
def set(self, value):
self.onclick = value #先设置
a = False
for i in self.friends:
if i.onclick: #如果有一个为真
a = True
if a: #如果有一个为真
self.onclick = True #它必须为假
if self.onclick:#它要是真的
for i in self.friends:
i.onclick = False #其他的全是假
set接受一个参数,并依据这个参数把本组的全部RadioButton的值进行调整。get返回是否被选中。
2.3.8.4 RadioButton.draw_pic:
通过本RadioButton是否被选中适当的选择图片并显示。
2.3.8.5 RadioButton.draw:
def draw(self):
global s_mode
mx, my = pygame.mouse.get_pos()
if self.check_click(mx, my): #如果被点击
self.onclick = not self.onclick
a = False
for i in self.friends:
if i.onclick:
a = True
if a:
self.onclick = True
if self.onclick:
for i in self.friends:
i.onclick = False #更新点击状态
self.draw_pic() #绘图
Io().io_put_str(self.screen, self.x + len(self.pic) + 5 + self.root.x, self.y + self.root.y, self.fg, self.text)
if self.on(mx, my):
cell.m_state = mouse3 #更改鼠标指针
s_mode = True2.3.9 ChickButton类
本类除了没有friends的设定外,和RadioButton大同小异,不在叙述。
2.3.10 Canvas类
一个绘图类,每个绘图函数会返回一个句柄,可以通过canvas的函数对该句柄进性操作。
print(dir(classes.Canvas))
['__class__', '__delattr__', '__dict__', '__dir__', '__doc__', '__eq__', '__format__',
'__ge__', '__getattribute__', '__gt__', '__hash__', '__init__', '__init_subclass__',
'__le__', '__lt__', '__module__', '__ne__', '__new__', '__reduce__', '__reduce_ex__',
'__repr__', '__setattr__', '__sizeof__', '__str__', '__subclasshook__', '__weakref__',
'config', 'draw', 'line', 'mouse_is_on', 'pack', 'point', 'put_str', 'rect', 'remove_all',
'remove_pen', 'unpack']
2.3.10.1 Canvas.__init__:
Canvas.__init 接受的参数之前以全部讲解过。
2.3.10.2 Canvas.line、Canvas.point、Canvas.rect、Canvas.put_str:
绘图函数,每个函数返回一个句柄。
2.3.10.3 Canvas.remove_pen、Canvas.remove_all:
remove_pen 接受一个句柄并删除该句柄,remove_all将清空所有句柄。
2.3.10.4 Canvas.mouse_is_on:
返回一个布尔值,表示鼠标是否悬停于其上。
2.3.10.5 Canvas.draw:
绘制背景和所有句柄。
2.3.10.6 用Canvas绘制的假窗口
算是个小彩蛋吧,注释免了,直接App_starter输入“canvas”即可运行。
from apilib import *
from classes import *
import cos
def cosmain():
screen = cos.window
root = Tk(screen, 10, 105, 250, 250, "Canvas Test")
canvas = Canvas(screen, root, 0, 0, 250, 250)
canvas.pack()
title = "A False Window!"
x = 5
y = 30
w = 240
h = 200
canvas.rect(x + 1, y - 21, w, h + 21, white)
canvas.rect(x - 1, y - 19, w, h + 21, black)
canvas.rect(x, y - 20, w, 20, lightblue)
canvas.put_str(x + 2, y - 17, title, black)
for i in range(len(close)):
for j in range(len(close[i])):
if close[i][j] == 1:
canvas.point(x + w - 15 + i, y - 20 + 14 - j, black)
elif close[i][j] == 2:
canvas.point(x + w - 15 + i, y - 20 + 14 - j, white)
elif close[i][j] == 3:
canvas.point(x + w - 15 + i, y - 20 + 14 - j, lightgray)
canvas.rect(x, y, w, h, lightgray)
def run():
is_on, mx, my = canvas.mouse_is_on()
if is_on:
# print(mx, my)
canvas.point(mx, my, black)
root.add_unapply_hook(run)
api_hook(root, 'Canvas')