【动手学习深度学习】逐行代码解析合集
17使用块的网络(VGG)
视频链接:动手学习深度学习–使用块的网络(VGG)
课程主页:https://courses.d2l.ai/zh-v2/
教材:https://zh-v2.d2l.ai/
1、VGG网络
与AlexNet、LeNet一样,VGG网络可以分为两部分:第一部分主要由卷积层和汇聚层组成,第二部分由全连接层组成。

2、定义VGG块
import torch
from torch import nn
from d2l import torch as d2l
import os
os.environ["KMP_DUPLICATE_LIB_OK"]="TRUE"
"====================1、VGG===================="
# VGG块:指定卷积层个数、输入通道数、输出通道数
def vgg_block(num_convs, in_channels, out_channels):
layers = []
# n个卷积层,重复n次
for _ in range(num_convs):
# 指定每个卷积层的输入通道数、输出通道数,卷积核大小,padding
layers.append(nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels,
kernel_size=3, padding=1))
# 在每个卷积层后加ReLU激活函数
layers.append(nn.ReLU())
# 这一层的输出 = 下一层的输入
in_channels = out_channels
# 最大池化层
layers.append(nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2,stride=2))
# 放入Sequential中构造一个VGG块
return nn.Sequential(*layers)
3、VGG-11
原始VGG网络有5个卷积块,其中前两个块各有一个卷积层,后三个块各包含两个卷积层。 第一个模块有64个输出通道,每个后续模块将输出通道数量翻倍,直到该数字达到512。由于该网络使用8个卷积层和3个全连接层,因此它通常被称为VGG-11。
# 超参数变量conv_arch,指定了每个VGG块里卷积层个数和输出通道数。
conv_arch = ((1, 64), (1, 128), (2, 256), (2, 512), (2, 512))
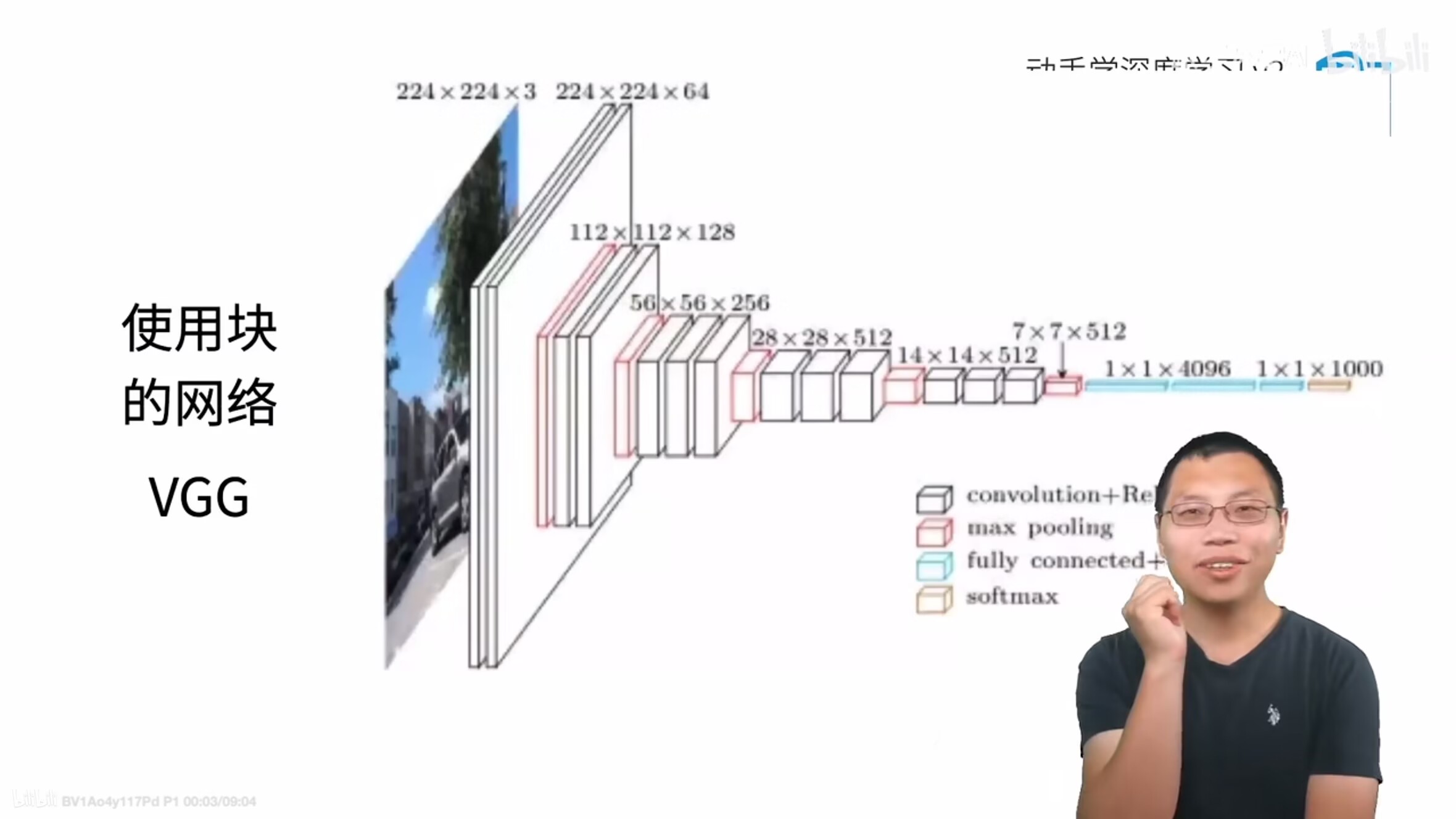
5个卷积块
"====================2、VGG-11===================="
def vgg(conv_arch):
conv_blks = [] # 卷积块
in_channels = 1
# 卷积层部分,遍历卷积层个数和输出通道数
for (num_convs, out_channels) in conv_arch:
conv_blks.append(vgg_block(num_convs, in_channels, out_channels))
in_channels = out_channels
return nn.Sequential(
*conv_blks, nn.Flatten(),
# 全连接层部分
nn.Linear(out_channels * 7 * 7, 4096), nn.ReLU(), nn.Dropout(0.5),
nn.Linear(4096, 4096), nn.ReLU(), nn.Dropout(0.5),
nn.Linear(4096, 10))
net = vgg(conv_arch)
print(net)
VGG网络输出:
Sequential(
(0): Sequential(
(0): Conv2d(1, 64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(1): ReLU()
(2): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
)
(1): Sequential(
(0): Conv2d(64, 128, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(1): ReLU()
(2): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
)
(2): Sequential(
(0): Conv2d(128, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(1): ReLU()
(2): Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(3): ReLU()
(4): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
)
(3): Sequential(
(0): Conv2d(256, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(1): ReLU()
(2): Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(3): ReLU()
(4): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
)
(4): Sequential(
(0): Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(1): ReLU()
(2): Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(3): ReLU()
(4): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
)
(5): Flatten(start_dim=1, end_dim=-1)
(6): Linear(in_features=25088, out_features=4096, bias=True)
(7): ReLU()
(8): Dropout(p=0.5, inplace=False)
(9): Linear(in_features=4096, out_features=4096, bias=True)
(10): ReLU()
(11): Dropout(p=0.5, inplace=False)
(12): Linear(in_features=4096, out_features=10, bias=True)
)
构建一个高度和宽度为224的单通道数据样本,以观察每个层输出的形状。
# 构建一个高度和宽度为224的单通道数据样本,以观察每个层输出的形状。
X = torch.randn(size=(1, 1, 224, 224))
for blk in net:
X = blk(X)
print(blk.__class__.__name__,'output shape:\t',X.shape)
'''
输出:
Sequential output shape: torch.Size([1, 64, 112, 112])
Sequential output shape: torch.Size([1, 128, 56, 56])
Sequential output shape: torch.Size([1, 256, 28, 28])
Sequential output shape: torch.Size([1, 512, 14, 14])
Sequential output shape: torch.Size([1, 512, 7, 7])
Flatten output shape: torch.Size([1, 25088])
Linear output shape: torch.Size([1, 4096])
ReLU output shape: torch.Size([1, 4096])
Dropout output shape: torch.Size([1, 4096])
Linear output shape: torch.Size([1, 4096])
ReLU output shape: torch.Size([1, 4096])
Dropout output shape: torch.Size([1, 4096])
Linear output shape: torch.Size([1, 10])
'''
正如从代码中所看到的,我们在每个块的高度和宽度减半,最终高度和宽度都为7。最后再展平表示,送入全连接层处理。
4、训练模型
"====================3、训练模型===================="
# 由于VGG-11比AlexNet计算量更大,因此我们构建了一个通道数较少的网络,足够用于训练Fashion-MNIST数据集。
ratio = 4
small_conv_arch = [(pair[0], pair[1] // ratio) for pair in conv_arch]
net = vgg(small_conv_arch)
lr, num_epochs, batch_size = 0.05, 10, 128
train_iter, test_iter = d2l.load_data_fashion_mnist(batch_size, resize=224)
d2l.train_ch6(net, train_iter, test_iter, num_epochs, lr, d2l.try_gpu())
5、运行结果
虽然使用了很小的VGG网络(VGG-11且通道数除以4)计算量减少了16倍,但是运行速度还是比AlexNet慢了很多,所以运行VGG网络是一件很贵的事情。但是精度得到了提升。