介绍
用一个变量如何维护多种状态 在 ReentrantLock 中,使用 Sync ( 实际是 AQS )的 int 类型的 state 来表示同步状态,表示锁被一个线程重复获取的次数。
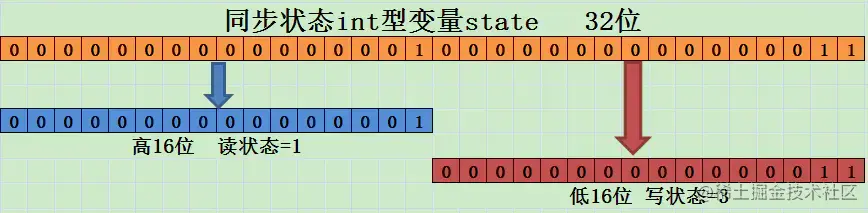
但是,读写锁 ReentrantReadWriteLock 内部维护着一对读写锁,如果要用一个变量维护多种状态,需要采用“按位切割使用”的方式来维护这个变量,将其切分为两部分:高16为表示读,低16为表示写。
分割之后,读写锁是如何迅速确定读锁和写锁的状态呢?通过位运算。假如当前同步状态为S,那么:
写状态,等于 S & 0x0000FFFF(将高 16 位全部抹去)。 当写状态加1,等于S+1.
读状态,等于 S >>> 16 (无符号补 0 右移 16 位)。当读状态加1,等于S+(1<<16),也就是S+0x00010000
根据状态的划分能得出一个推论:S不等于0时,当写状态(S&0x0000FFFF)等于0时,则读状态(S>>>16)大于0,即读锁已被获取。
public class ReentrantReadWriteLock
implements ReadWriteLock, java.io.Serializable
常量&变量
//序列化版本号
private static final long serialVersionUID = -6992448646407690164L;
/** Inner class providing readlock */
//读锁
private final ReentrantReadWriteLock.ReadLock readerLock;
/** Inner class providing writelock */
//写锁
private final ReentrantReadWriteLock.WriteLock writerLock;
/** Performs all synchronization mechanics */
//同步器
final Sync sync;
// Unsafe mechanics
private static final sun.misc.Unsafe UNSAFE;
private static final long TID_OFFSET;
static {
try {
UNSAFE = sun.misc.Unsafe.getUnsafe();
Class<?> tk = Thread.class;
TID_OFFSET = UNSAFE.objectFieldOffset
(tk.getDeclaredField("tid"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new Error(e);
}
}
内部类
Sync
ReentrantReadWriteLock将状态码state分为高16位和低16位。状态码state的高16位用于存储并发读取的线程数(读线程重入的次数也加入计数),即状态码state的高16位=(线程1的重入次数+线程2的重入次数+…+线程n的重入次数)。状态码state的低16位用于存储单个写线程的重入次数(写锁为互斥锁,只有一个线程能获取写锁)。
/**
* Synchronization implementation for ReentrantReadWriteLock.
* Subclassed into fair and nonfair versions.
*/
abstract static class Sync extends AbstractQueuedSynchronizer {
//版本序列号
private static final long serialVersionUID = 6317671515068378041L;
/*
* Read vs write count extraction constants and functions.
* Lock state is logically divided into two unsigned shorts:
* The lower one representing the exclusive (writer) lock hold count,
* and the upper the shared (reader) hold count.
*/
// 共享锁偏移量 state共32位 高16位为读锁,低16位为写锁
static final int SHARED_SHIFT = 16;
//高16位,用于存储并发读取的线程数 00000000 00000001 00000000 00000000
static final int SHARED_UNIT = (1 << SHARED_SHIFT);
//持有读锁的读线程的最大数量 00000000 00000000 11111111 11111111即65535
static final int MAX_COUNT = (1 << SHARED_SHIFT) - 1;
//用于计算低16位的单个写进程重入次数 00000000 00000000 11111111 11111111
static final int EXCLUSIVE_MASK = (1 << SHARED_SHIFT) - 1;
/** Returns the number of shared holds represented in count */
//计算共享的数量(读锁) 高16位表示。
// 读锁可以同时被多个线程持有,每个线程持有的读锁支持重入的特性,所以需要对每个线程持有的读锁的数量单独计数,这就需要用到 HoldCounter 计数器
static int sharedCount(int c) { return c >>> SHARED_SHIFT; }
/** Returns the number of exclusive holds represented in count */
//计算独占的重入数量(写锁):低16位表示。
static int exclusiveCount(int c) { return c & EXCLUSIVE_MASK; }
/**
* A counter for per-thread read hold counts.
* Maintained as a ThreadLocal; cached in cachedHoldCounter
*/
/**
* 读锁的本质是共享锁,一次共享锁的操作就相当于对HoldCounter 计数器的操作。
* 获取共享锁,则该计数器 + 1,释放共享锁,该计数器 - 1。只有当线程获取共享锁后才能对共享锁进行释放、重入操作。
* HoldCounter是用来记录读锁重入数的对象
*/
static final class HoldCounter {
int count = 0;
// Use id, not reference, to avoid garbage retention
final long tid = getThreadId(Thread.currentThread());
}
/**
* ThreadLocal subclass. Easiest to explicitly define for sake
* of deserialization mechanics.
*/
/**
* 通过 ThreadLocalHoldCounter 类,HoldCounter 与线程进行绑定。
* HoldCounter 是绑定线程的一个计数器,而 ThreadLocalHoldCounter 则是线程绑定的 ThreadLocal。
* ThreadLocalHoldCounter是ThreadLocal变量,用来存放不是第一个获取读锁的线程的其他线程的读锁重入数对象
*/
static final class ThreadLocalHoldCounter
extends ThreadLocal<HoldCounter> {
public HoldCounter initialValue() {
return new HoldCounter();
}
}
/**
* The number of reentrant read locks held by current thread.
* Initialized only in constructor and readObject.
* Removed whenever a thread's read hold count drops to 0.
*/
private transient ThreadLocalHoldCounter readHolds;
/**
* The hold count of the last thread to successfully acquire
* readLock. This saves ThreadLocal lookup in the common case
* where the next thread to release is the last one to
* acquire. This is non-volatile since it is just used
* as a heuristic, and would be great for threads to cache.
*
* <p>Can outlive the Thread for which it is caching the read
* hold count, but avoids garbage retention by not retaining a
* reference to the Thread.
*
* <p>Accessed via a benign data race; relies on the memory
* model's final field and out-of-thin-air guarantees.
*/
private transient HoldCounter cachedHoldCounter;
/**
* firstReader is the first thread to have acquired the read lock.
* firstReaderHoldCount is firstReader's hold count.
*
* <p>More precisely, firstReader is the unique thread that last
* changed the shared count from 0 to 1, and has not released the
* read lock since then; null if there is no such thread.
*
* <p>Cannot cause garbage retention unless the thread terminated
* without relinquishing its read locks, since tryReleaseShared
* sets it to null.
*
* <p>Accessed via a benign data race; relies on the memory
* model's out-of-thin-air guarantees for references.
*
* <p>This allows tracking of read holds for uncontended read
* locks to be very cheap.
*/
private transient Thread firstReader = null;
private transient int firstReaderHoldCount;
Sync() {
readHolds = new ThreadLocalHoldCounter();
setState(getState()); // ensures visibility of readHolds
}
/*
* Acquires and releases use the same code for fair and
* nonfair locks, but differ in whether/how they allow barging
* when queues are non-empty.
*/
/**
* Returns true if the current thread, when trying to acquire
* the read lock, and otherwise eligible to do so, should block
* because of policy for overtaking other waiting threads.
*/
abstract boolean readerShouldBlock();
/**
* Returns true if the current thread, when trying to acquire
* the write lock, and otherwise eligible to do so, should block
* because of policy for overtaking other waiting threads.
*/
abstract boolean writerShouldBlock();
/*
* Note that tryRelease and tryAcquire can be called by
* Conditions. So it is possible that their arguments contain
* both read and write holds that are all released during a
* condition wait and re-established in tryAcquire.
*/
protected final boolean tryRelease(int releases) {
//若锁的持有者不是当前线程,抛出异常
if (!isHeldExclusively())
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
//state的预期值
int nextc = getState() - releases;
//当前写状态是否为0,为0则释放写锁
boolean free = exclusiveCount(nextc) == 0;
//当前写状态为0
if (free)
//设置锁的持有者为null
setExclusiveOwnerThread(null);
//同步状态state
setState(nextc);
return free;
}
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
/*
* Walkthrough:
* 1. If read count nonzero or write count nonzero
* and owner is a different thread, fail.
* 2. If count would saturate, fail. (This can only
* happen if count is already nonzero.)
* 3. Otherwise, this thread is eligible for lock if
* it is either a reentrant acquire or
* queue policy allows it. If so, update state
* and set owner.
*/
//当前线程
Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
//aqs的state值 存在读锁或者写锁,状态就不为0
int c = getState();
//获取写锁的重入数
int w = exclusiveCount(c);
//当前同步状态state != 0,说明已经有其他线程获取了读锁或写锁
if (c != 0) {
// (Note: if c != 0 and w == 0 then shared count != 0)
// c!=0 && w==0 表示存在读锁
// 当前存在读锁或者写锁已经被其他写线程获取,则写锁获取失败
if (w == 0 || current != getExclusiveOwnerThread())
return false;
//最大可重入次数 超出最大范围 65535
if (w + exclusiveCount(acquires) > MAX_COUNT)
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
// Reentrant acquire
//同步state状态
setState(c + acquires);
return true;
}
// writerShouldBlock有公平与非公平的实现, 非公平返回false,会尝试通过cas加锁
//c==0 写锁未被任何线程获取,当前线程是否阻塞或者cas尝试获取锁
if (writerShouldBlock() ||
!compareAndSetState(c, c + acquires))
return false;
//获取写锁成功 设置写锁为当前线程所有
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
protected final boolean tryReleaseShared(int unused) {
Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
//当前线程是第一个获取读锁的线程
if (firstReader == current) {
// assert firstReaderHoldCount > 0;
// 第一个获取读锁的线程的重入次数为1
if (firstReaderHoldCount == 1)
//第一个获取对锁的线程为null
firstReader = null;
else
//重入次数大于1,重入次数-1
firstReaderHoldCount--;
} else {
//不是第一个获取读锁的线程
HoldCounter rh = cachedHoldCounter;
if (rh == null || rh.tid != getThreadId(current))
//获取线程的计数器
rh = readHolds.get();
//重入次数
int count = rh.count;
//重入次数小于等于1 ,移除该线程的读锁
if (count <= 1) {
readHolds.remove();
if (count <= 0)
throw unmatchedUnlockException();
}
//重入次数大于1,计数器减1
--rh.count;
}
for (;;) {
int c = getState();
int nextc = c - SHARED_UNIT;
if (compareAndSetState(c, nextc))
// Releasing the read lock has no effect on readers,
// but it may allow waiting writers to proceed if
// both read and write locks are now free.
return nextc == 0;
}
}
private IllegalMonitorStateException unmatchedUnlockException() {
return new IllegalMonitorStateException(
"attempt to unlock read lock, not locked by current thread");
}
protected final int tryAcquireShared(int unused) {
/*
* Walkthrough:
* 1. If write lock held by another thread, fail.
* 2. Otherwise, this thread is eligible for
* lock wrt state, so ask if it should block
* because of queue policy. If not, try
* to grant by CASing state and updating count.
* Note that step does not check for reentrant
* acquires, which is postponed to full version
* to avoid having to check hold count in
* the more typical non-reentrant case.
* 3. If step 2 fails either because thread
* apparently not eligible or CAS fails or count
* saturated, chain to version with full retry loop.
*/
Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
// 如果写锁已经被获取并且获取写锁的线程不是当前线程,当前线程获取读锁失败返回-1 判断锁降级
if (exclusiveCount(c) != 0 &&
getExclusiveOwnerThread() != current)
return -1;
//读锁的数量
int r = sharedCount(c);
//获取读锁的线程是否该被阻塞
if (!readerShouldBlock() &&
r < MAX_COUNT &&
compareAndSetState(c, c + SHARED_UNIT)) {//当前线程获取读锁
//如果是第一个获取读锁的线程
if (r == 0) {
firstReader = current;
firstReaderHoldCount = 1;//设置第一个获取读锁线程的重入数
// 表示第一个获取读锁的线程重入
} else if (firstReader == current) {
//第一个获取读锁的线程重入次数+ 1
firstReaderHoldCount++;
} else {
// 非第一个获取读锁的线程
HoldCounter rh = cachedHoldCounter;
if (rh == null || rh.tid != getThreadId(current))
cachedHoldCounter = rh = readHolds.get();
else if (rh.count == 0)
readHolds.set(rh);
//记录其他获取读锁的线程的重入次数
rh.count++;
}
return 1;
}
//尝试通过自旋的方式获取读锁,实现了重入逻辑
return fullTryAcquireShared(current);
}
/**
* Full version of acquire for reads, that handles CAS misses
* and reentrant reads not dealt with in tryAcquireShared.
*/
final int fullTryAcquireShared(Thread current) {
/*
* This code is in part redundant with that in
* tryAcquireShared but is simpler overall by not
* complicating tryAcquireShared with interactions between
* retries and lazily reading hold counts.
*/
HoldCounter rh = null;
for (;;) {
int c = getState();
if (exclusiveCount(c) != 0) {
if (getExclusiveOwnerThread() != current)
return -1;
// else we hold the exclusive lock; blocking here
// would cause deadlock.
} else if (readerShouldBlock()) {
// Make sure we're not acquiring read lock reentrantly
if (firstReader == current) {
// assert firstReaderHoldCount > 0;
} else {
if (rh == null) {
rh = cachedHoldCounter;
if (rh == null || rh.tid != getThreadId(current)) {
rh = readHolds.get();
if (rh.count == 0)
readHolds.remove();
}
}
if (rh.count == 0)
return -1;
}
}
if (sharedCount(c) == MAX_COUNT)
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
if (compareAndSetState(c, c + SHARED_UNIT)) {
if (sharedCount(c) == 0) {
firstReader = current;
firstReaderHoldCount = 1;
} else if (firstReader == current) {
firstReaderHoldCount++;
} else {
if (rh == null)
rh = cachedHoldCounter;
if (rh == null || rh.tid != getThreadId(current))
rh = readHolds.get();
else if (rh.count == 0)
readHolds.set(rh);
rh.count++;
cachedHoldCounter = rh; // cache for release
}
return 1;
}
}
}
/**
* Performs tryLock for write, enabling barging in both modes.
* This is identical in effect to tryAcquire except for lack
* of calls to writerShouldBlock.
*/
final boolean tryWriteLock() {
Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
if (c != 0) {
int w = exclusiveCount(c);
if (w == 0 || current != getExclusiveOwnerThread())
return false;
if (w == MAX_COUNT)
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
}
if (!compareAndSetState(c, c + 1))
return false;
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
/**
* Performs tryLock for read, enabling barging in both modes.
* This is identical in effect to tryAcquireShared except for
* lack of calls to readerShouldBlock.
*/
final boolean tryReadLock() {
Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
for (;;) {
int c = getState();
if (exclusiveCount(c) != 0 &&
getExclusiveOwnerThread() != current)
return false;
int r = sharedCount(c);
if (r == MAX_COUNT)
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
if (compareAndSetState(c, c + SHARED_UNIT)) {
if (r == 0) {
firstReader = current;
firstReaderHoldCount = 1;
} else if (firstReader == current) {
firstReaderHoldCount++;
} else {
HoldCounter rh = cachedHoldCounter;
if (rh == null || rh.tid != getThreadId(current))
cachedHoldCounter = rh = readHolds.get();
else if (rh.count == 0)
readHolds.set(rh);
rh.count++;
}
return true;
}
}
}
protected final boolean isHeldExclusively() {
// While we must in general read state before owner,
// we don't need to do so to check if current thread is owner
return getExclusiveOwnerThread() == Thread.currentThread();
}
// Methods relayed to outer class
final ConditionObject newCondition() {
return new ConditionObject();
}
final Thread getOwner() {
// Must read state before owner to ensure memory consistency
return ((exclusiveCount(getState()) == 0) ?
null :
getExclusiveOwnerThread());
}
final int getReadLockCount() {
return sharedCount(getState());
}
final boolean isWriteLocked() {
return exclusiveCount(getState()) != 0;
}
final int getWriteHoldCount() {
return isHeldExclusively() ? exclusiveCount(getState()) : 0;
}
final int getReadHoldCount() {
if (getReadLockCount() == 0)
return 0;
Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
if (firstReader == current)
return firstReaderHoldCount;
HoldCounter rh = cachedHoldCounter;
if (rh != null && rh.tid == getThreadId(current))
return rh.count;
int count = readHolds.get().count;
if (count == 0) readHolds.remove();
return count;
}
/**
* Reconstitutes the instance from a stream (that is, deserializes it).
*/
private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
s.defaultReadObject();
readHolds = new ThreadLocalHoldCounter();
setState(0); // reset to unlocked state
}
final int getCount() { return getState(); }
}
NonfairSync
在NonfairSync类中,读锁和写锁都被实现为可重入锁。具体来说,它通过维护一个线程持有的读写锁数量来实现可重入性,因此一个线程可以多次获取读写锁而不会被阻塞。
另外,NonfairSync类中还有一些方法用于实现读写锁的获取、释放和降级等操作。其中最重要的方法是tryAcquireShared(int arg)和tryAcquire(int arg)方法,它们分别用于获取读锁和写锁。这些方法会根据当前锁的状态来判断线程是否可以获取锁,并且在获取锁的同时更新锁状态。
/**
* Nonfair version of Sync
* 非公平锁,继承Sync
*/
static final class NonfairSync extends Sync {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -8159625535654395037L;
final boolean writerShouldBlock() {
return false; // writers can always barge
}
final boolean readerShouldBlock() {
/* As a heuristic to avoid indefinite writer starvation,
* block if the thread that momentarily appears to be head
* of queue, if one exists, is a waiting writer. This is
* only a probabilistic effect since a new reader will not
* block if there is a waiting writer behind other enabled
* readers that have not yet drained from the queue.
*/
return apparentlyFirstQueuedIsExclusive();
}
}
FairSync
在FairSync中,读写锁的获取是基于“先到先得”的原则,即先请求锁的线程先获得锁,保证了锁的获取是公平的。FairSync实现了公平性的方式是通过维护等待队列实现的,当有线程请求锁时,FairSync会将其添加到等待队列的尾部,当锁可用时,会从队列的头部选择一个线程获得锁。因此,FairSync在保证公平性的同时,可能会导致额外的上下文切换开销,影响锁的性能表现。
/**
* Fair version of Sync
* 公平锁,继承Sync
*/
static final class FairSync extends Sync {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -2274990926593161451L;
final boolean writerShouldBlock() {
return hasQueuedPredecessors();
}
final boolean readerShouldBlock() {
return hasQueuedPredecessors();
}
}
ReadLock
ReadLock是一个读锁,用于控制读取操作的并发访问。它实现了Lock接口中的lock()、unlock()方法,以及Condition接口中的newCondition()方法。
当一个线程获取了ReadLock之后,其他线程可以继续获取ReadLock,但不能获取WriteLock。只有当所有线程释放了ReadLock,才能有一个线程获取WriteLock。
使用ReentrantReadWriteLock可以提高程序的并发性能,因为它允许多个线程同时读取数据,但只允许一个线程写入数据,从而避免了读写冲突的问题。
/**
* The lock returned by method {@link ReentrantReadWriteLock#readLock}.
* 读锁
*/
public static class ReadLock implements Lock, java.io.Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -5992448646407690164L;
private final Sync sync;
/**
* Constructor for use by subclasses
*
* @param lock the outer lock object
* @throws NullPointerException if the lock is null
*/
protected ReadLock(ReentrantReadWriteLock lock) {
sync = lock.sync;
}
/**
* Acquires the read lock.
*
* <p>Acquires the read lock if the write lock is not held by
* another thread and returns immediately.
*
* <p>If the write lock is held by another thread then
* the current thread becomes disabled for thread scheduling
* purposes and lies dormant until the read lock has been acquired.
* 读锁加锁
*/
public void lock() {
sync.acquireShared(1);
}
/**
* Acquires the read lock unless the current thread is
* {@linkplain Thread#interrupt interrupted}.
*
* <p>Acquires the read lock if the write lock is not held
* by another thread and returns immediately.
*
* <p>If the write lock is held by another thread then the
* current thread becomes disabled for thread scheduling
* purposes and lies dormant until one of two things happens:
*
* <ul>
*
* <li>The read lock is acquired by the current thread; or
*
* <li>Some other thread {@linkplain Thread#interrupt interrupts}
* the current thread.
*
* </ul>
*
* <p>If the current thread:
*
* <ul>
*
* <li>has its interrupted status set on entry to this method; or
*
* <li>is {@linkplain Thread#interrupt interrupted} while
* acquiring the read lock,
*
* </ul>
*
* then {@link InterruptedException} is thrown and the current
* thread's interrupted status is cleared.
*
* <p>In this implementation, as this method is an explicit
* interruption point, preference is given to responding to
* the interrupt over normal or reentrant acquisition of the
* lock.
*
* @throws InterruptedException if the current thread is interrupted
*/
public void lockInterruptibly() throws InterruptedException {
sync.acquireSharedInterruptibly(1);
}
/**
* Acquires the read lock only if the write lock is not held by
* another thread at the time of invocation.
*
* <p>Acquires the read lock if the write lock is not held by
* another thread and returns immediately with the value
* {@code true}. Even when this lock has been set to use a
* fair ordering policy, a call to {@code tryLock()}
* <em>will</em> immediately acquire the read lock if it is
* available, whether or not other threads are currently
* waiting for the read lock. This "barging" behavior
* can be useful in certain circumstances, even though it
* breaks fairness. If you want to honor the fairness setting
* for this lock, then use {@link #tryLock(long, TimeUnit)
* tryLock(0, TimeUnit.SECONDS) } which is almost equivalent
* (it also detects interruption).
*
* <p>If the write lock is held by another thread then
* this method will return immediately with the value
* {@code false}.
*
* @return {@code true} if the read lock was acquired
*/
public boolean tryLock() {
return sync.tryReadLock();
}
/**
* Acquires the read lock if the write lock is not held by
* another thread within the given waiting time and the
* current thread has not been {@linkplain Thread#interrupt
* interrupted}.
*
* <p>Acquires the read lock if the write lock is not held by
* another thread and returns immediately with the value
* {@code true}. If this lock has been set to use a fair
* ordering policy then an available lock <em>will not</em> be
* acquired if any other threads are waiting for the
* lock. This is in contrast to the {@link #tryLock()}
* method. If you want a timed {@code tryLock} that does
* permit barging on a fair lock then combine the timed and
* un-timed forms together:
*
* <pre> {@code
* if (lock.tryLock() ||
* lock.tryLock(timeout, unit)) {
* ...
* }}</pre>
*
* <p>If the write lock is held by another thread then the
* current thread becomes disabled for thread scheduling
* purposes and lies dormant until one of three things happens:
*
* <ul>
*
* <li>The read lock is acquired by the current thread; or
*
* <li>Some other thread {@linkplain Thread#interrupt interrupts}
* the current thread; or
*
* <li>The specified waiting time elapses.
*
* </ul>
*
* <p>If the read lock is acquired then the value {@code true} is
* returned.
*
* <p>If the current thread:
*
* <ul>
*
* <li>has its interrupted status set on entry to this method; or
*
* <li>is {@linkplain Thread#interrupt interrupted} while
* acquiring the read lock,
*
* </ul> then {@link InterruptedException} is thrown and the
* current thread's interrupted status is cleared.
*
* <p>If the specified waiting time elapses then the value
* {@code false} is returned. If the time is less than or
* equal to zero, the method will not wait at all.
*
* <p>In this implementation, as this method is an explicit
* interruption point, preference is given to responding to
* the interrupt over normal or reentrant acquisition of the
* lock, and over reporting the elapse of the waiting time.
*
* @param timeout the time to wait for the read lock
* @param unit the time unit of the timeout argument
* @return {@code true} if the read lock was acquired
* @throws InterruptedException if the current thread is interrupted
* @throws NullPointerException if the time unit is null
*/
public boolean tryLock(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException {
return sync.tryAcquireSharedNanos(1, unit.toNanos(timeout));
}
/**
* Attempts to release this lock.
*
* <p>If the number of readers is now zero then the lock
* is made available for write lock attempts.
* 读锁解锁
*/
public void unlock() {
sync.releaseShared(1);
}
/**
* Throws {@code UnsupportedOperationException} because
* {@code ReadLocks} do not support conditions.
*
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException always
*/
public Condition newCondition() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
/**
* Returns a string identifying this lock, as well as its lock state.
* The state, in brackets, includes the String {@code "Read locks ="}
* followed by the number of held read locks.
*
* @return a string identifying this lock, as well as its lock state
*/
public String toString() {
int r = sync.getReadLockCount();
return super.toString() +
"[Read locks = " + r + "]";
}
}
WriteLock
WriteLock是一个可重入的独占锁,用于写操作的同步。该锁可以被多个读线程同时持有,但只能被一个写线程持有。如果试图在没有释放该锁的情况下重复获取WriteLock锁,则当前线程将一直被阻塞,直到锁被释放。
WriteLock对象可以通过调用ReentrantReadWriteLock的writeLock()方法来获取。获取WriteLock锁后,可以使用lock()方法进行锁定,使用unlock()方法进行解锁。和其他锁一样,为了避免死锁,建议在finally块中进行解锁操作。
WriteLock还提供了一些其他的方法,例如tryLock()方法尝试获取锁并立即返回结果,tryLock(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)方法尝试在指定时间内获取锁并返回结果。此外,WriteLock还可以通过调用getHoldCount()方法获取当前线程持有锁的数量,以支持可重入性。
/**
* The lock returned by method {@link ReentrantReadWriteLock#writeLock}.
* 写锁
*/
public static class WriteLock implements Lock, java.io.Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -4992448646407690164L;
private final Sync sync;
/**
* Constructor for use by subclasses
*
* @param lock the outer lock object
* @throws NullPointerException if the lock is null
*/
protected WriteLock(ReentrantReadWriteLock lock) {
sync = lock.sync;
}
/**
* Acquires the write lock.
*
* <p>Acquires the write lock if neither the read nor write lock
* are held by another thread
* and returns immediately, setting the write lock hold count to
* one.
*
* <p>If the current thread already holds the write lock then the
* hold count is incremented by one and the method returns
* immediately.
*
* <p>If the lock is held by another thread then the current
* thread becomes disabled for thread scheduling purposes and
* lies dormant until the write lock has been acquired, at which
* time the write lock hold count is set to one.
* 写锁加锁
*/
public void lock() {
sync.acquire(1);
}
/**
* Acquires the write lock unless the current thread is
* {@linkplain Thread#interrupt interrupted}.
*
* <p>Acquires the write lock if neither the read nor write lock
* are held by another thread
* and returns immediately, setting the write lock hold count to
* one.
*
* <p>If the current thread already holds this lock then the
* hold count is incremented by one and the method returns
* immediately.
*
* <p>If the lock is held by another thread then the current
* thread becomes disabled for thread scheduling purposes and
* lies dormant until one of two things happens:
*
* <ul>
*
* <li>The write lock is acquired by the current thread; or
*
* <li>Some other thread {@linkplain Thread#interrupt interrupts}
* the current thread.
*
* </ul>
*
* <p>If the write lock is acquired by the current thread then the
* lock hold count is set to one.
*
* <p>If the current thread:
*
* <ul>
*
* <li>has its interrupted status set on entry to this method;
* or
*
* <li>is {@linkplain Thread#interrupt interrupted} while
* acquiring the write lock,
*
* </ul>
*
* then {@link InterruptedException} is thrown and the current
* thread's interrupted status is cleared.
*
* <p>In this implementation, as this method is an explicit
* interruption point, preference is given to responding to
* the interrupt over normal or reentrant acquisition of the
* lock.
*
* @throws InterruptedException if the current thread is interrupted
*/
public void lockInterruptibly() throws InterruptedException {
sync.acquireInterruptibly(1);
}
/**
* Acquires the write lock only if it is not held by another thread
* at the time of invocation.
*
* <p>Acquires the write lock if neither the read nor write lock
* are held by another thread
* and returns immediately with the value {@code true},
* setting the write lock hold count to one. Even when this lock has
* been set to use a fair ordering policy, a call to
* {@code tryLock()} <em>will</em> immediately acquire the
* lock if it is available, whether or not other threads are
* currently waiting for the write lock. This "barging"
* behavior can be useful in certain circumstances, even
* though it breaks fairness. If you want to honor the
* fairness setting for this lock, then use {@link
* #tryLock(long, TimeUnit) tryLock(0, TimeUnit.SECONDS) }
* which is almost equivalent (it also detects interruption).
*
* <p>If the current thread already holds this lock then the
* hold count is incremented by one and the method returns
* {@code true}.
*
* <p>If the lock is held by another thread then this method
* will return immediately with the value {@code false}.
*
* @return {@code true} if the lock was free and was acquired
* by the current thread, or the write lock was already held
* by the current thread; and {@code false} otherwise.
*/
public boolean tryLock( ) {
return sync.tryWriteLock();
}
/**
* Acquires the write lock if it is not held by another thread
* within the given waiting time and the current thread has
* not been {@linkplain Thread#interrupt interrupted}.
*
* <p>Acquires the write lock if neither the read nor write lock
* are held by another thread
* and returns immediately with the value {@code true},
* setting the write lock hold count to one. If this lock has been
* set to use a fair ordering policy then an available lock
* <em>will not</em> be acquired if any other threads are
* waiting for the write lock. This is in contrast to the {@link
* #tryLock()} method. If you want a timed {@code tryLock}
* that does permit barging on a fair lock then combine the
* timed and un-timed forms together:
*
* <pre> {@code
* if (lock.tryLock() ||
* lock.tryLock(timeout, unit)) {
* ...
* }}</pre>
*
* <p>If the current thread already holds this lock then the
* hold count is incremented by one and the method returns
* {@code true}.
*
* <p>If the lock is held by another thread then the current
* thread becomes disabled for thread scheduling purposes and
* lies dormant until one of three things happens:
*
* <ul>
*
* <li>The write lock is acquired by the current thread; or
*
* <li>Some other thread {@linkplain Thread#interrupt interrupts}
* the current thread; or
*
* <li>The specified waiting time elapses
*
* </ul>
*
* <p>If the write lock is acquired then the value {@code true} is
* returned and the write lock hold count is set to one.
*
* <p>If the current thread:
*
* <ul>
*
* <li>has its interrupted status set on entry to this method;
* or
*
* <li>is {@linkplain Thread#interrupt interrupted} while
* acquiring the write lock,
*
* </ul>
*
* then {@link InterruptedException} is thrown and the current
* thread's interrupted status is cleared.
*
* <p>If the specified waiting time elapses then the value
* {@code false} is returned. If the time is less than or
* equal to zero, the method will not wait at all.
*
* <p>In this implementation, as this method is an explicit
* interruption point, preference is given to responding to
* the interrupt over normal or reentrant acquisition of the
* lock, and over reporting the elapse of the waiting time.
*
* @param timeout the time to wait for the write lock
* @param unit the time unit of the timeout argument
*
* @return {@code true} if the lock was free and was acquired
* by the current thread, or the write lock was already held by the
* current thread; and {@code false} if the waiting time
* elapsed before the lock could be acquired.
*
* @throws InterruptedException if the current thread is interrupted
* @throws NullPointerException if the time unit is null
*/
public boolean tryLock(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException {
return sync.tryAcquireNanos(1, unit.toNanos(timeout));
}
/**
* Attempts to release this lock.
*
* <p>If the current thread is the holder of this lock then
* the hold count is decremented. If the hold count is now
* zero then the lock is released. If the current thread is
* not the holder of this lock then {@link
* IllegalMonitorStateException} is thrown.
*
* @throws IllegalMonitorStateException if the current thread does not
* hold this lock
* 写锁解锁
*/
public void unlock() {
sync.release(1);
}
/**
* Returns a {@link Condition} instance for use with this
* {@link Lock} instance.
* <p>The returned {@link Condition} instance supports the same
* usages as do the {@link Object} monitor methods ({@link
* Object#wait() wait}, {@link Object#notify notify}, and {@link
* Object#notifyAll notifyAll}) when used with the built-in
* monitor lock.
*
* <ul>
*
* <li>If this write lock is not held when any {@link
* Condition} method is called then an {@link
* IllegalMonitorStateException} is thrown. (Read locks are
* held independently of write locks, so are not checked or
* affected. However it is essentially always an error to
* invoke a condition waiting method when the current thread
* has also acquired read locks, since other threads that
* could unblock it will not be able to acquire the write
* lock.)
*
* <li>When the condition {@linkplain Condition#await() waiting}
* methods are called the write lock is released and, before
* they return, the write lock is reacquired and the lock hold
* count restored to what it was when the method was called.
*
* <li>If a thread is {@linkplain Thread#interrupt interrupted} while
* waiting then the wait will terminate, an {@link
* InterruptedException} will be thrown, and the thread's
* interrupted status will be cleared.
*
* <li> Waiting threads are signalled in FIFO order.
*
* <li>The ordering of lock reacquisition for threads returning
* from waiting methods is the same as for threads initially
* acquiring the lock, which is in the default case not specified,
* but for <em>fair</em> locks favors those threads that have been
* waiting the longest.
*
* </ul>
*
* @return the Condition object
*/
public Condition newCondition() {
return sync.newCondition();
}
/**
* Returns a string identifying this lock, as well as its lock
* state. The state, in brackets includes either the String
* {@code "Unlocked"} or the String {@code "Locked by"}
* followed by the {@linkplain Thread#getName name} of the owning thread.
*
* @return a string identifying this lock, as well as its lock state
*/
public String toString() {
Thread o = sync.getOwner();
return super.toString() + ((o == null) ?
"[Unlocked]" :
"[Locked by thread " + o.getName() + "]");
}
/**
* Queries if this write lock is held by the current thread.
* Identical in effect to {@link
* ReentrantReadWriteLock#isWriteLockedByCurrentThread}.
*
* @return {@code true} if the current thread holds this lock and
* {@code false} otherwise
* @since 1.6
*/
public boolean isHeldByCurrentThread() {
return sync.isHeldExclusively();
}
/**
* Queries the number of holds on this write lock by the current
* thread. A thread has a hold on a lock for each lock action
* that is not matched by an unlock action. Identical in effect
* to {@link ReentrantReadWriteLock#getWriteHoldCount}.
*
* @return the number of holds on this lock by the current thread,
* or zero if this lock is not held by the current thread
* @since 1.6
*/
public int getHoldCount() {
return sync.getWriteHoldCount();
}
}
写锁的获取
写锁是一个支持重进入的排它锁。如果当前线程已经获取了写锁,则增加写状态。如果当前线程在获取写锁时,读锁已经被获取(读状态不为0)或者该线程不是已经获取写锁的线程, 则当前线程进入等待状态。
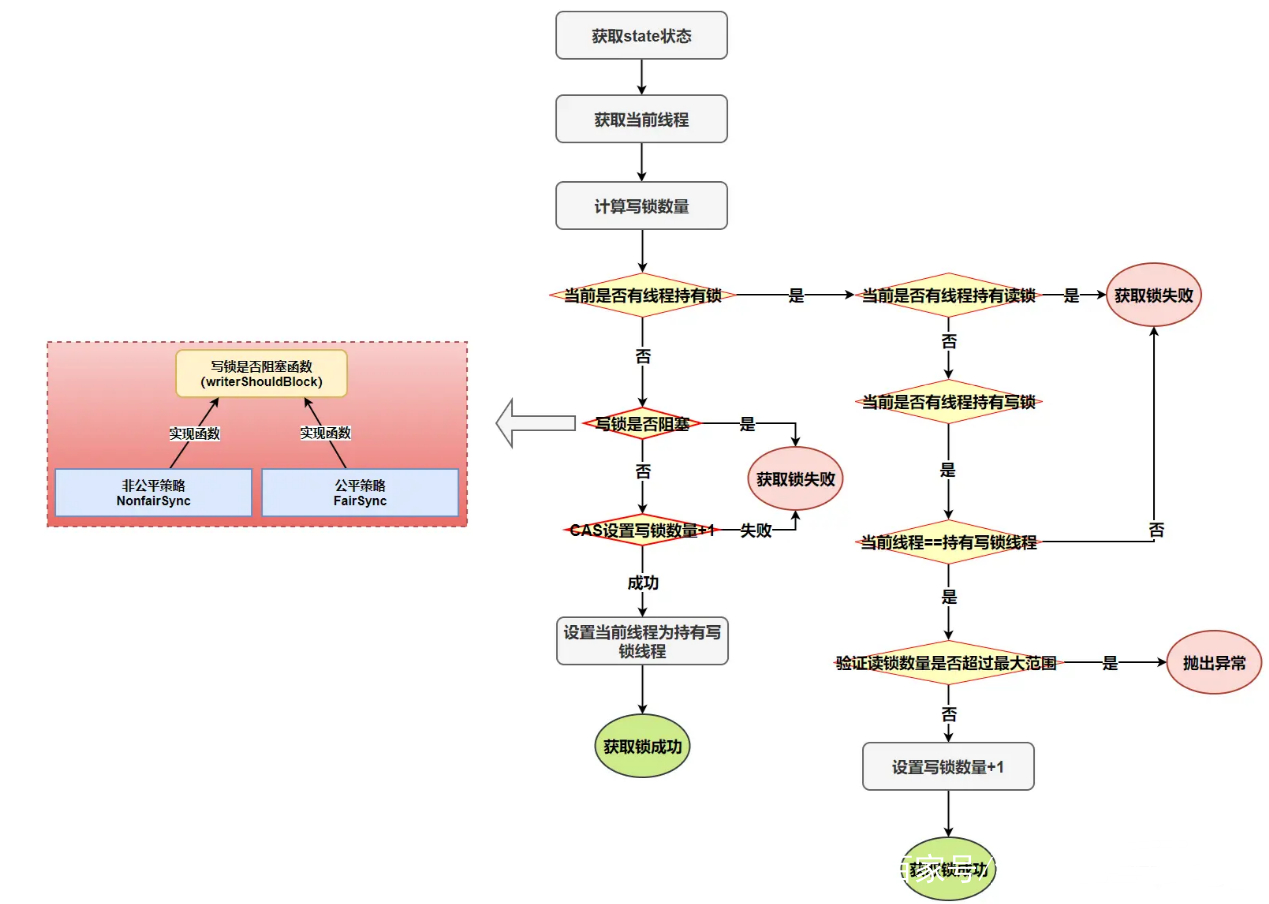
写锁的获取是通过重写AQS中的tryAcquire方法实现的。
writeLock.lock()
用于获取写锁的方法。该方法会阻塞当前线程直到获取到写锁。
当一个线程获取到写锁时,其他线程无法获取到读锁或写锁,直到当前线程释放该写锁。这意味着写锁的获取是独占的,一次只能有一个线程获得写锁。
如果当前线程已经持有写锁,那么该方法会增加锁的重入次数,并立即返回。这允许线程对同一段代码进行多次写操作,而不会被其他线程打断。
注意:在使用ReentrantReadWriteLock时,使用写锁时需要保证不能出现死锁的情况。因为如果一个线程获取到了写锁,其他线程都无法获得锁,如果该线程又尝试获取读锁,则会造成死锁。因此,在使用该锁时需要格外小心,避免出现死锁情况。
ReentrantReadWriteLock内部类WriteLock的lock方法
/**
* Acquires the write lock.
*
* <p>Acquires the write lock if neither the read nor write lock
* are held by another thread
* and returns immediately, setting the write lock hold count to
* one.
*
* <p>If the current thread already holds the write lock then the
* hold count is incremented by one and the method returns
* immediately.
*
* <p>If the lock is held by another thread then the current
* thread becomes disabled for thread scheduling purposes and
* lies dormant until the write lock has been acquired, at which
* time the write lock hold count is set to one.
*/
public void lock() {
sync.acquire(1);
}
acquire
获取锁,调用aqs中的acquire方法
/**
* Acquires in exclusive mode, ignoring interrupts. Implemented
* by invoking at least once {@link #tryAcquire},
* returning on success. Otherwise the thread is queued, possibly
* repeatedly blocking and unblocking, invoking {@link
* #tryAcquire} until success. This method can be used
* to implement method {@link Lock#lock}.
*
* @param arg the acquire argument. This value is conveyed to
* {@link #tryAcquire} but is otherwise uninterpreted and
* can represent anything you like.
*/
public final void acquire(int arg) {
//尝试获取锁
if (!tryAcquire(arg) &&
//addWaiter:将线程封装到 Node 节点并添加到队列尾部
//acquireQueued查看当前排队的 Node 是否在队列的前面,如果在前面,尝试获取锁资源。如果没在前面,线程进入到阻塞状态。
acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg))
//中断当前线程,唤醒
selfInterrupt();
}
tryAcquire
尝试获取锁,ReentrantReadWriteLock内部类sync重写了aqs的tryAcquire方法
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
/*
* Walkthrough:
* 1. If read count nonzero or write count nonzero
* and owner is a different thread, fail.
* 2. If count would saturate, fail. (This can only
* happen if count is already nonzero.)
* 3. Otherwise, this thread is eligible for lock if
* it is either a reentrant acquire or
* queue policy allows it. If so, update state
* and set owner.
*/
//当前线程
Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
//aqs的state值 存在读锁或者写锁,状态就不为0
int c = getState();
//获取写锁的重入数
int w = exclusiveCount(c);
//当前同步状态state != 0,说明已经有其他线程获取了读锁或写锁
if (c != 0) {
// (Note: if c != 0 and w == 0 then shared count != 0)
// c!=0 && w==0 表示存在读锁
// 当前存在读锁或者写锁已经被其他写线程获取,则写锁获取失败
if (w == 0 || current != getExclusiveOwnerThread())
return false;
//最大可重入次数 超出最大范围 65535
if (w + exclusiveCount(acquires) > MAX_COUNT)
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
// Reentrant acquire
//同步state状态
setState(c + acquires);
return true;
}
// writerShouldBlock有公平与非公平的实现, 非公平返回false,会尝试通过cas加锁
//c==0 写锁未被任何线程获取,当前线程是否阻塞或者cas尝试获取锁
if (writerShouldBlock() ||
!compareAndSetState(c, c + acquires))
return false;
//获取写锁成功 设置写锁为当前线程所有
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
写锁的释放
写锁释放通过重写AQS的tryRelease方法实现
writeLock.unlock()
用于释放当前线程持有的写锁。在调用此方法之前,线程必须已经获得了相应的写锁才能释放。
具体地说,当线程调用此方法时,它会将当前线程持有的写锁的计数器减1。如果计数器减为0,则表示当前线程已经完全释放了写锁,其他线程可以获得写锁进行写操作。如果计数器减为负数,则表示当前线程没有完全释放写锁,还有其他线程持有写锁,则会抛出IllegalMonitorStateException异常。
需要注意的是,如果当前线程没有持有写锁,调用此方法会抛出IllegalMonitorStateException异常。因此,在调用此方法之前,必须确保当前线程已经获得了相应的写锁
/**
* Attempts to release this lock.
*
* <p>If the current thread is the holder of this lock then
* the hold count is decremented. If the hold count is now
* zero then the lock is released. If the current thread is
* not the holder of this lock then {@link
* IllegalMonitorStateException} is thrown.
*
* @throws IllegalMonitorStateException if the current thread does not
* hold this lock
*/
public void unlock() {
sync.release(1);
}
release
释放锁,调用aqs中的release方法
/**
* Releases in exclusive mode. Implemented by unblocking one or
* more threads if {@link #tryRelease} returns true.
* This method can be used to implement method {@link Lock#unlock}.
*
* @param arg the release argument. This value is conveyed to
* {@link #tryRelease} but is otherwise uninterpreted and
* can represent anything you like.
* @return the value returned from {@link #tryRelease}
* release利用tryRelease先进行释放锁,tryRealse是由子类实现的方法,可以确保线程是获取到锁的,并进行释放锁,
* unparkSuccessor主要是利用LockSupport.unpark唤醒线程;
*/
public final boolean release(int arg) {
//尝试释放锁,这个方法是由子类实现的方法
if (tryRelease(arg)) {
Node h = head;
//头节点不为如果节点状态不是CANCELLED,也就是线程没有被取消,也就是不为0的,就进行唤醒
if (h != null && h.waitStatus != 0)
//唤醒线程
unparkSuccessor(h);
return true;
}
return false;
}
tryRelease
尝试释放锁,ReentrantReadWriteLock内部类sync重写了aqs的tryRelease方法
/*
* Note that tryRelease and tryAcquire can be called by
* Conditions. So it is possible that their arguments contain
* both read and write holds that are all released during a
* condition wait and re-established in tryAcquire.
*/
protected final boolean tryRelease(int releases) {
//若锁的持有者不是当前线程,抛出异常
if (!isHeldExclusively())
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
//state的预期值
int nextc = getState() - releases;
//当前写状态是否为0,为0则释放写锁
boolean free = exclusiveCount(nextc) == 0;
//当前写状态为0
if (free)
//设置锁的持有者为null
setExclusiveOwnerThread(null);
//同步状态state
setState(nextc);
return free;
}
读锁的获取
实现共享式同步组件的同步语义需要通过重写AQS的tryAcquireShared方法和tryReleaseShared方法。
readLock.lock()
获取读锁的方法。当调用这个方法时,如果当前并没有线程持有写锁,则当前线程可以获取读锁,并允许其它读线程同时获取锁并读取数据。但如果已有一个线程持有写锁,则所有的读线程都将阻塞,直到写锁被释放。
在获取了读锁之后,需要在合适的时候释放它,以避免出现死锁。
/**
* Acquires the read lock.
*
* <p>Acquires the read lock if the write lock is not held by
* another thread and returns immediately.
*
* <p>If the write lock is held by another thread then
* the current thread becomes disabled for thread scheduling
* purposes and lies dormant until the read lock has been acquired.
*/
public void lock() {
sync.acquireShared(1);
}
acquireShared
aqs中的acquireShared方法
获取共享锁。它的实现方式是通过CAS(Compare And Set)原子操作来实现的,在获取锁之前会先判断当前线程是否可以获取锁,如果不能获取,则会将当前线程加入到等待队列中,并将其阻塞。
/**
* Acquires in shared mode, ignoring interrupts. Implemented by
* first invoking at least once {@link #tryAcquireShared},
* returning on success. Otherwise the thread is queued, possibly
* repeatedly blocking and unblocking, invoking {@link
* #tryAcquireShared} until success.
*
* @param arg the acquire argument. This value is conveyed to
* {@link #tryAcquireShared} but is otherwise uninterpreted
* and can represent anything you like.
*/
public final void acquireShared(int arg) {
//尝试获取锁
if (tryAcquireShared(arg) < 0)
//获取锁失败则加入队列,自旋获取锁
doAcquireShared(arg);
}
tryAcquireShared
ReentrantReadWriteLock内部类sync重写了aqs的
tryAcquireShared方法是用来尝试获取读锁的方法。读锁是共享锁,多个线程可以同时获取读锁,但是当有一个线程获取写锁时,其他线程不能获取读锁。
tryAcquireShared方法的实现如下:
首先,判断当前线程是否已经获取了写锁,如果是,则可以直接获取读锁,增加读锁的计数并返回。
如果当前没有获取写锁,那么就需要检查是否有其他线程正在获取写锁,如果是,则不能获取读锁,返回负数。
如果当前既没有获取写锁,也没有其他线程在获取写锁,那么就可以尝试获取读锁了。首先获取读锁的计数值,如果当前读锁的计数为0,则可以直接获取读锁,增加读锁计数并返回。否则,判断当前线程是否是最后一个持有读锁的线程,如果是,则可以直接获取读锁,增加读锁计数并返回。否则,不能获取读锁,返回负数。
总的来说,tryAcquireShared方法的实现就是先判断是否有写锁,如果没有则尝试获取读锁,如果其他线程正在获取写锁,则不能获取读锁,否则等待。
protected final int tryAcquireShared(int unused) {
/*
* Walkthrough:
* 1. If write lock held by another thread, fail.
* 2. Otherwise, this thread is eligible for
* lock wrt state, so ask if it should block
* because of queue policy. If not, try
* to grant by CASing state and updating count.
* Note that step does not check for reentrant
* acquires, which is postponed to full version
* to avoid having to check hold count in
* the more typical non-reentrant case.
* 3. If step 2 fails either because thread
* apparently not eligible or CAS fails or count
* saturated, chain to version with full retry loop.
*/
Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
//获取aqs中的状态码state
int c = getState();
// 如果写锁已经被获取并且获取写锁的线程不是当前线程,当前线程获取读锁失败返回-1 判断锁降级
if (exclusiveCount(c) != 0 &&
getExclusiveOwnerThread() != current)
return -1;
//读锁的数量
int r = sharedCount(c);
//获取读锁的线程是否该被阻塞
if (!readerShouldBlock() &&
r < MAX_COUNT &&
compareAndSetState(c, c + SHARED_UNIT)) {//当前线程获取读锁
//如果是第一个获取读锁的线程,则使用firstReader记录第一个获取读锁的线程对象,并设置第一个获取读锁的线程的重入次数firstReaderHoldCount为1。
if (r == 0) {
firstReader = current;
firstReaderHoldCount = 1;//设置第一个获取读锁线程的重入数
// 表示第一个获取读锁的线程重入
} else if (firstReader == current) {
//第一个获取读锁的线程重入次数+ 1
firstReaderHoldCount++;
} else {
// 非第一个获取读锁的线程
// 获取上一次获取读锁的线程的相关记录(上次获取读锁的线程的id和重入次数)
HoldCounter rh = cachedHoldCounter;
// 如果没有上一个获取获取读锁的线程的信息(第一个获取读锁的线程不算)||上一个获取读锁的线程id不等于当前的线程的id
if (rh == null || rh.tid != getThreadId(current))
// 从TreadLocal中获取当前线程的信息(重入信息),将上次获取读锁的线程信息设置为当前获取读锁的线程信息。
cachedHoldCounter = rh = readHolds.get();
else if (rh.count == 0)
readHolds.set(rh);
//记录其他获取读锁的线程的重入次数
rh.count++;
}
return 1;
}
//尝试通过自旋的方式获取读锁,实现了重入逻辑
return fullTryAcquireShared(current);
}
读锁的释放
获取到读锁,执行完临界区后,要记得释放读锁(如果重入多次要释放对应的次数),不然会阻塞其他线程的写操作。
读锁释放的实现主要通过方法tryReleaseShared
readLock.unlock()
释放当前线程持有的读锁。如果当前线程没有持有读锁,则该方法不执行任何操作。
/**
* Attempts to release this lock.
*
* <p>If the number of readers is now zero then the lock
* is made available for write lock attempts.
*/
public void unlock() {
sync.releaseShared(1);
}
releaseShared
释放共享锁,aqs中的releaseShared方法
/**
* Releases in shared mode. Implemented by unblocking one or more
* threads if {@link #tryReleaseShared} returns true.
*
* @param arg the release argument. This value is conveyed to
* {@link #tryReleaseShared} but is otherwise uninterpreted
* and can represent anything you like.
* @return the value returned from {@link #tryReleaseShared}
* 共享模式下的释放。如果『tryReleaseShared』返回true的话,会使一个或多个线程重新启动
*/
public final boolean releaseShared(int arg) {
if (tryReleaseShared(arg)) {
doReleaseShared();
return true;
}
return false;
}
tryReleaseShared
ReentrantReadWriteLock内部类sync重写了aqs的
tryReleaseShared方法首先获取当前线程。如果当前线程是第一个读取器(即firstReader),则将其移除。否则,将当前线程的读取计数器减1。接下来,使用自旋来减少共享锁的状态,直到成功减少到0。最后,返回是否成功释放了共享锁。
protected final boolean tryReleaseShared(int unused) {
Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
//当前线程是第一个获取读锁的线程
if (firstReader == current) {
// assert firstReaderHoldCount > 0;
// 第一个获取读锁的线程的重入次数为1
if (firstReaderHoldCount == 1)
//第一个获取对锁的线程为null
firstReader = null;
else
//重入次数大于1,重入次数-1
firstReaderHoldCount--;
} else {
//不是第一个获取读锁的线程
HoldCounter rh = cachedHoldCounter;
if (rh == null || rh.tid != getThreadId(current))
//获取线程的计数器
rh = readHolds.get();
//重入次数
int count = rh.count;
//重入次数小于等于1 ,移除该线程的读锁
if (count <= 1) {
readHolds.remove();
if (count <= 0)
throw unmatchedUnlockException();
}
//重入次数大于1,计数器减1
--rh.count;
}
for (;;) {
int c = getState();
int nextc = c - SHARED_UNIT;
if (compareAndSetState(c, nextc))
// Releasing the read lock has no effect on readers,
// but it may allow waiting writers to proceed if
// both read and write locks are now free.
return nextc == 0;
}
}