目标检测 pytorch复现Yolov4目标检测项目
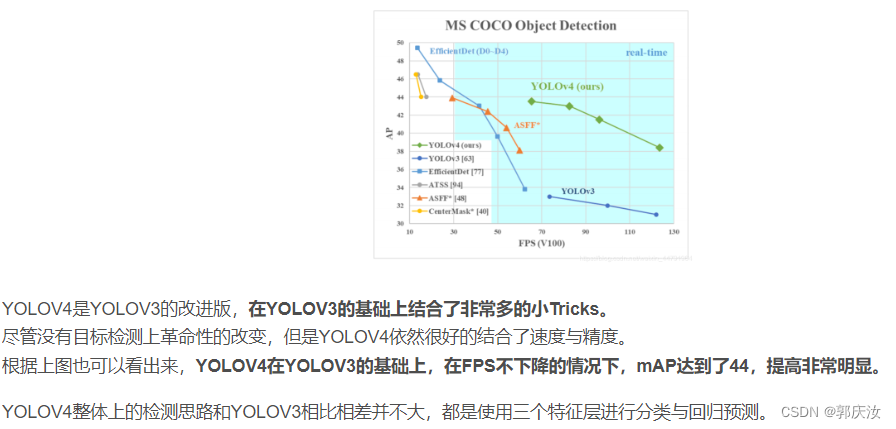
- YOLOV4介绍
- YOLOV4结构解析
- 1、主干特征提取网络Backbone
- 2、特征金字塔
- 3、YoloHead利用获得到的特征进行预测
- 4、预测结果的解码
- YOLOV4的训练
- 1、YOLOV4的改进训练技巧
- 2、loss组成
- 训练自己的YoloV4模型
YOLOV4介绍

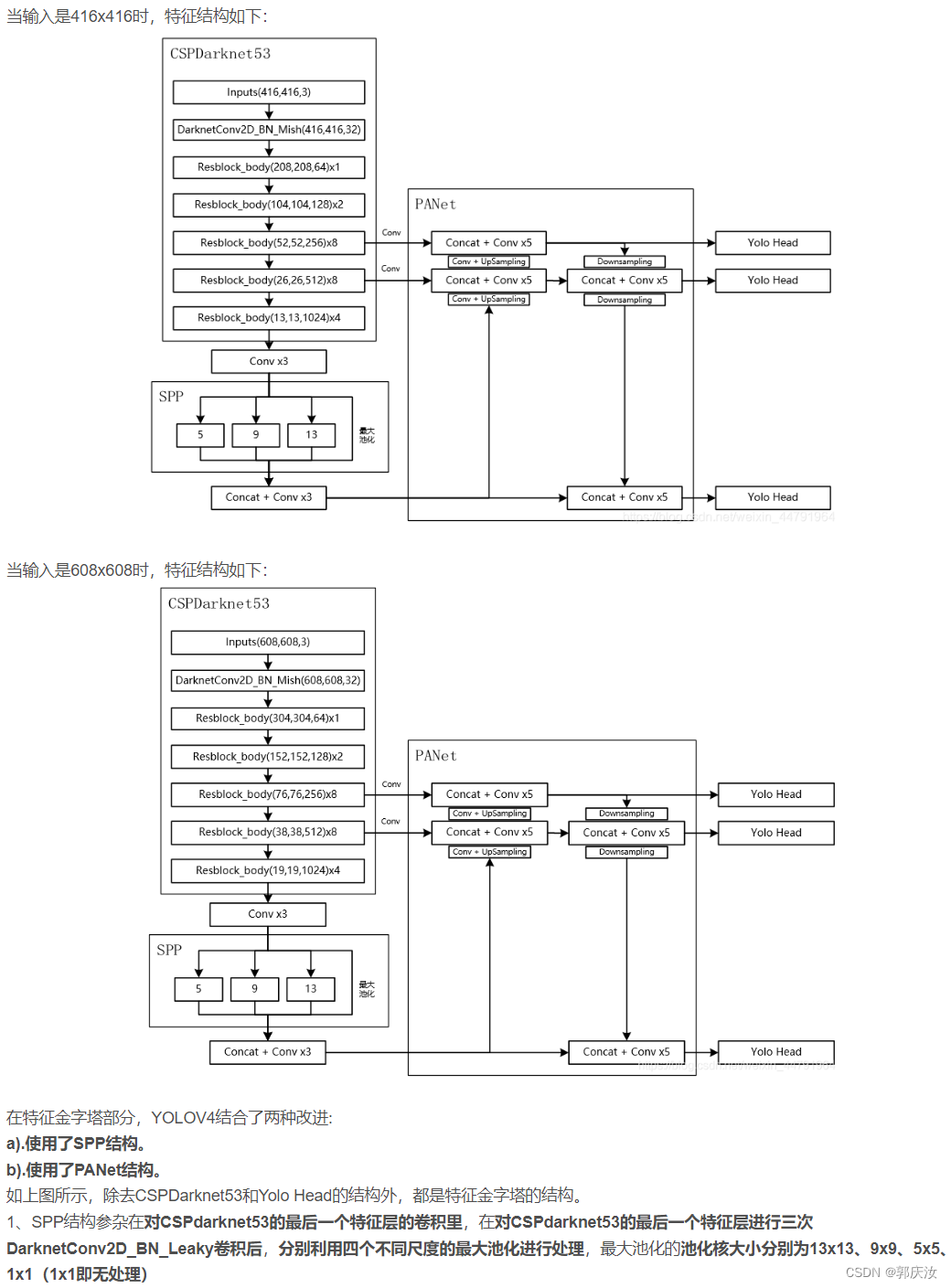
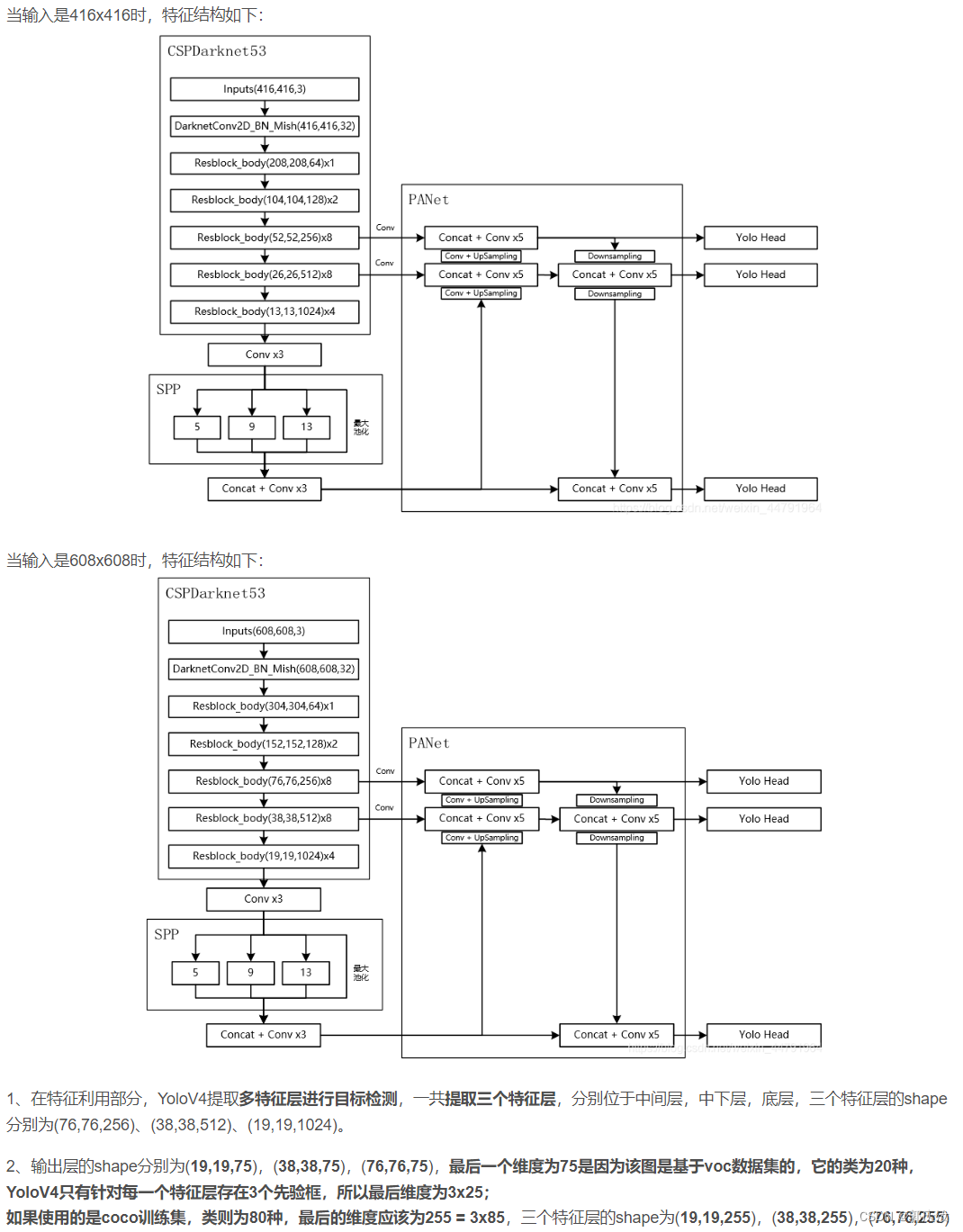
YOLOV4结构解析
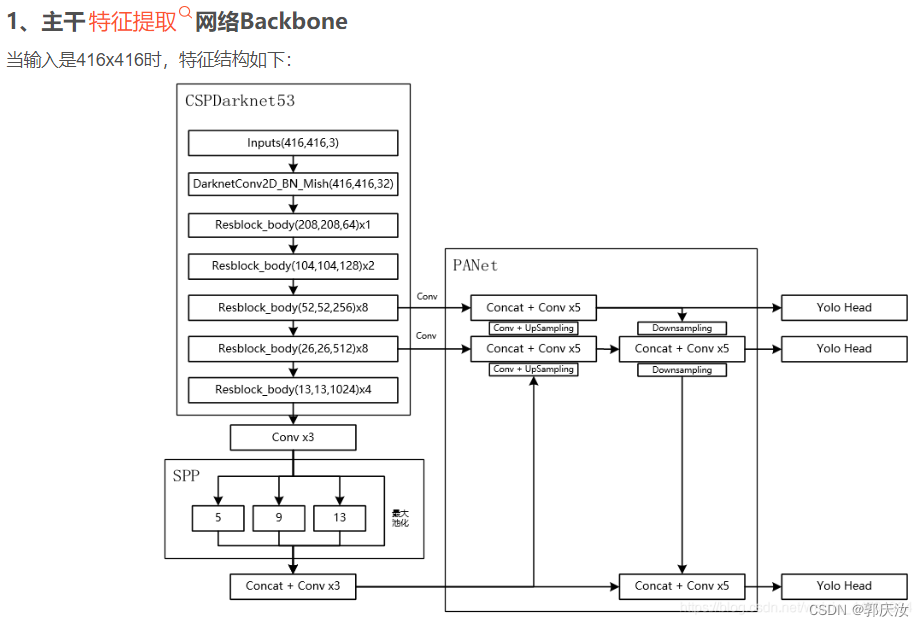
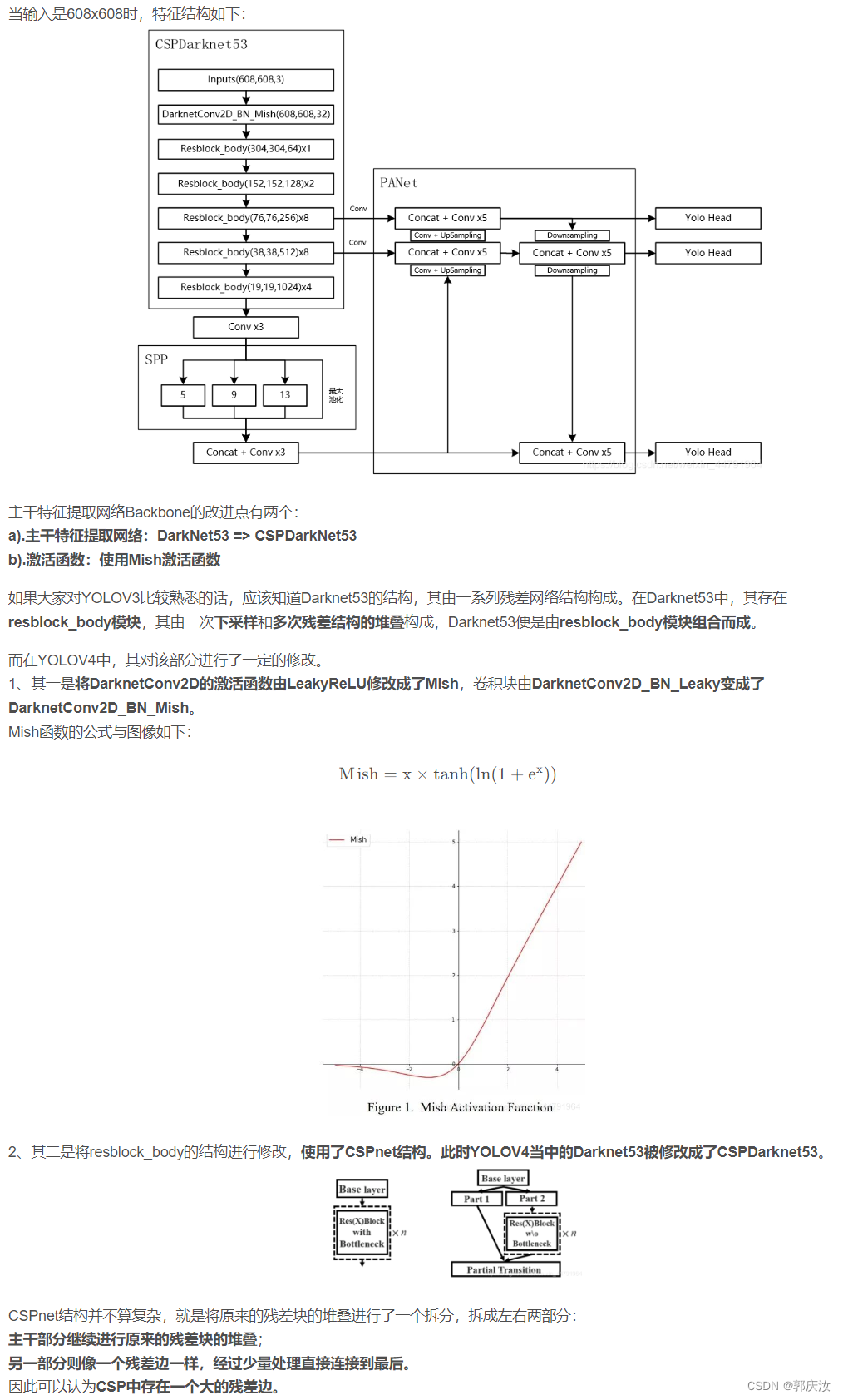
1、主干特征提取网络Backbone
#---------------------------------------------------#
# CSPdarknet的结构块
# 存在一个大残差边
# 这个大残差边绕过了很多的残差结构
#---------------------------------------------------#
class Resblock_body(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, num_blocks, first):
super(Resblock_body, self).__init__()
self.downsample_conv = BasicConv(in_channels, out_channels, 3, stride=2)
if first:
self.split_conv0 = BasicConv(out_channels, out_channels, 1)
self.split_conv1 = BasicConv(out_channels, out_channels, 1)
self.blocks_conv = nn.Sequential(
Resblock(channels=out_channels, hidden_channels=out_channels//2),
BasicConv(out_channels, out_channels, 1)
)
self.concat_conv = BasicConv(out_channels*2, out_channels, 1)
else:
self.split_conv0 = BasicConv(out_channels, out_channels//2, 1)
self.split_conv1 = BasicConv(out_channels, out_channels//2, 1)
self.blocks_conv = nn.Sequential(
*[Resblock(out_channels//2) for _ in range(num_blocks)],
BasicConv(out_channels//2, out_channels//2, 1)
)
self.concat_conv = BasicConv(out_channels, out_channels, 1)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.downsample_conv(x)
x0 = self.split_conv0(x)
x1 = self.split_conv1(x)
x1 = self.blocks_conv(x1)
x = torch.cat([x1, x0], dim=1)
x = self.concat_conv(x)
return x
全部实现代码为:
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch.nn as nn
import math
from collections import OrderedDict
#-------------------------------------------------#
# MISH激活函数
#-------------------------------------------------#
class Mish(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Mish, self).__init__()
def forward(self, x):
return x * torch.tanh(F.softplus(x))
#-------------------------------------------------#
# 卷积块
# CONV+BATCHNORM+MISH
#-------------------------------------------------#
class BasicConv(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride=1):
super(BasicConv, self).__init__()
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride, kernel_size//2, bias=False)
self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels)
self.activation = Mish()
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv(x)
x = self.bn(x)
x = self.activation(x)
return x
#---------------------------------------------------#
# CSPdarknet的结构块的组成部分
# 内部堆叠的残差块
#---------------------------------------------------#
class Resblock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, channels, hidden_channels=None, residual_activation=nn.Identity()):
super(Resblock, self).__init__()
if hidden_channels is None:
hidden_channels = channels
self.block = nn.Sequential(
BasicConv(channels, hidden_channels, 1),
BasicConv(hidden_channels, channels, 3)
)
def forward(self, x):
return x+self.block(x)
#---------------------------------------------------#
# CSPdarknet的结构块
# 存在一个大残差边
# 这个大残差边绕过了很多的残差结构
#---------------------------------------------------#
class Resblock_body(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, num_blocks, first):
super(Resblock_body, self).__init__()
self.downsample_conv = BasicConv(in_channels, out_channels, 3, stride=2)
if first:
self.split_conv0 = BasicConv(out_channels, out_channels, 1)
self.split_conv1 = BasicConv(out_channels, out_channels, 1)
self.blocks_conv = nn.Sequential(
Resblock(channels=out_channels, hidden_channels=out_channels//2),
BasicConv(out_channels, out_channels, 1)
)
self.concat_conv = BasicConv(out_channels*2, out_channels, 1)
else:
self.split_conv0 = BasicConv(out_channels, out_channels//2, 1)
self.split_conv1 = BasicConv(out_channels, out_channels//2, 1)
self.blocks_conv = nn.Sequential(
*[Resblock(out_channels//2) for _ in range(num_blocks)],
BasicConv(out_channels//2, out_channels//2, 1)
)
self.concat_conv = BasicConv(out_channels, out_channels, 1)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.downsample_conv(x)
x0 = self.split_conv0(x)
x1 = self.split_conv1(x)
x1 = self.blocks_conv(x1)
x = torch.cat([x1, x0], dim=1)
x = self.concat_conv(x)
return x
class CSPDarkNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, layers):
super(CSPDarkNet, self).__init__()
self.inplanes = 32
self.conv1 = BasicConv(3, self.inplanes, kernel_size=3, stride=1)
self.feature_channels = [64, 128, 256, 512, 1024]
self.stages = nn.ModuleList([
Resblock_body(self.inplanes, self.feature_channels[0], layers[0], first=True),
Resblock_body(self.feature_channels[0], self.feature_channels[1], layers[1], first=False),
Resblock_body(self.feature_channels[1], self.feature_channels[2], layers[2], first=False),
Resblock_body(self.feature_channels[2], self.feature_channels[3], layers[3], first=False),
Resblock_body(self.feature_channels[3], self.feature_channels[4], layers[4], first=False)
])
self.num_features = 1
# 进行权值初始化
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
n = m.kernel_size[0] * m.kernel_size[1] * m.out_channels
m.weight.data.normal_(0, math.sqrt(2. / n))
elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):
m.weight.data.fill_(1)
m.bias.data.zero_()
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.stages[0](x)
x = self.stages[1](x)
out3 = self.stages[2](x)
out4 = self.stages[3](out3)
out5 = self.stages[4](out4)
return out3, out4, out5
def darknet53(pretrained, **kwargs):
model = CSPDarkNet([1, 2, 8, 8, 4])
if pretrained:
if isinstance(pretrained, str):
model.load_state_dict(torch.load(pretrained))
else:
raise Exception("darknet request a pretrained path. got [{}]".format(pretrained))
return model
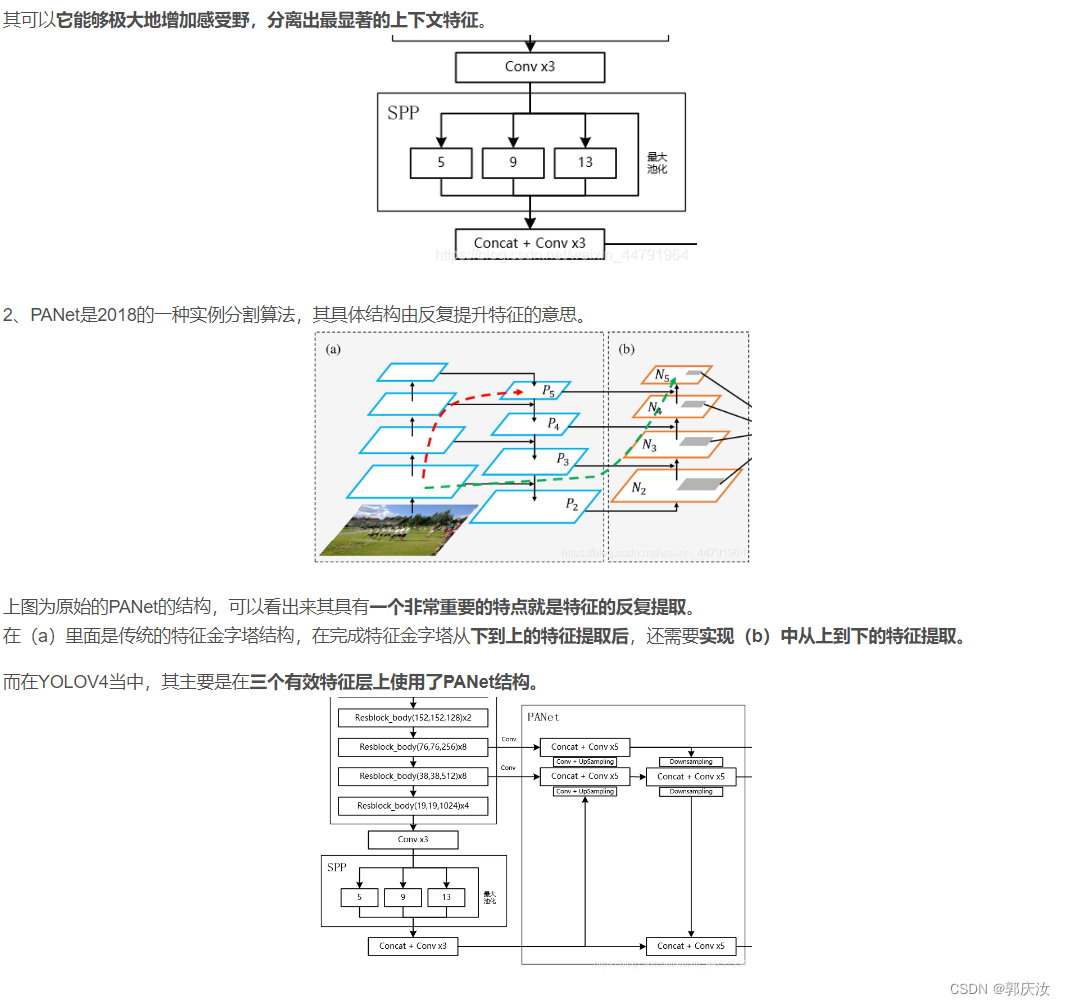
2、特征金字塔
#---------------------------------------------------#
# SPP结构,利用不同大小的池化核进行池化
# 池化后堆叠
#---------------------------------------------------#
class SpatialPyramidPooling(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, pool_sizes=[5, 9, 13]):
super(SpatialPyramidPooling, self).__init__()
self.maxpools = nn.ModuleList([nn.MaxPool2d(pool_size, 1, pool_size//2) for pool_size in pool_sizes])
def forward(self, x):
features = [maxpool(x) for maxpool in self.maxpools[::-1]]
features = torch.cat(features + [x], dim=1)
return features
代码如下所示:
#---------------------------------------------------#
# yolo_body
#---------------------------------------------------#
class YoloBody(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, config):
super(YoloBody, self).__init__()
self.config = config
# backbone
self.backbone = darknet53(None)
self.conv1 = make_three_conv([512,1024],1024)
self.SPP = SpatialPyramidPooling()
self.conv2 = make_three_conv([512,1024],2048)
self.upsample1 = Upsample(512,256)
self.conv_for_P4 = conv2d(512,256,1)
self.make_five_conv1 = make_five_conv([256, 512],512)
self.upsample2 = Upsample(256,128)
self.conv_for_P3 = conv2d(256,128,1)
self.make_five_conv2 = make_five_conv([128, 256],256)
# 3*(5+num_classes)=3*(5+20)=3*(4+1+20)=75
final_out_filter2 = len(config["yolo"]["anchors"][2]) * (5 + config["yolo"]["classes"])
self.yolo_head3 = yolo_head([256, final_out_filter2],128)
self.down_sample1 = conv2d(128,256,3,stride=2)
self.make_five_conv3 = make_five_conv([256, 512],512)
# 3*(5+num_classes)=3*(5+20)=3*(4+1+20)=75
final_out_filter1 = len(config["yolo"]["anchors"][1]) * (5 + config["yolo"]["classes"])
self.yolo_head2 = yolo_head([512, final_out_filter1],256)
self.down_sample2 = conv2d(256,512,3,stride=2)
self.make_five_conv4 = make_five_conv([512, 1024],1024)
# 3*(5+num_classes)=3*(5+20)=3*(4+1+20)=75
final_out_filter0 = len(config["yolo"]["anchors"][0]) * (5 + config["yolo"]["classes"])
self.yolo_head1 = yolo_head([1024, final_out_filter0],512)
def forward(self, x):
# backbone
x2, x1, x0 = self.backbone(x)
P5 = self.conv1(x0)
P5 = self.SPP(P5)
P5 = self.conv2(P5)
P5_upsample = self.upsample1(P5)
P4 = self.conv_for_P4(x1)
P4 = torch.cat([P4,P5_upsample],axis=1)
P4 = self.make_five_conv1(P4)
P4_upsample = self.upsample2(P4)
P3 = self.conv_for_P3(x2)
P3 = torch.cat([P3,P4_upsample],axis=1)
P3 = self.make_five_conv2(P3)
P3_downsample = self.down_sample1(P3)
P4 = torch.cat([P3_downsample,P4],axis=1)
P4 = self.make_five_conv3(P4)
P4_downsample = self.down_sample2(P4)
P5 = torch.cat([P4_downsample,P5],axis=1)
P5 = self.make_five_conv4(P5)
out2 = self.yolo_head3(P3)
out1 = self.yolo_head2(P4)
out0 = self.yolo_head1(P5)
return out0, out1, out2
3、YoloHead利用获得到的特征进行预测
实现代码如下:
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 最后获得yolov4的输出
#---------------------------------------------------#
def yolo_head(filters_list, in_filters):
m = nn.Sequential(
conv2d(in_filters, filters_list[0], 3),
nn.Conv2d(filters_list[0], filters_list[1], 1),
)
return m
#---------------------------------------------------#
# yolo_body
#---------------------------------------------------#
class YoloBody(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, config):
super(YoloBody, self).__init__()
self.config = config
# backbone
self.backbone = darknet53(None)
self.conv1 = make_three_conv([512,1024],1024)
self.SPP = SpatialPyramidPooling()
self.conv2 = make_three_conv([512,1024],2048)
self.upsample1 = Upsample(512,256)
self.conv_for_P4 = conv2d(512,256,1)
self.make_five_conv1 = make_five_conv([256, 512],512)
self.upsample2 = Upsample(256,128)
self.conv_for_P3 = conv2d(256,128,1)
self.make_five_conv2 = make_five_conv([128, 256],256)
# 3*(5+num_classes)=3*(5+20)=3*(4+1+20)=75
final_out_filter2 = len(config["yolo"]["anchors"][2]) * (5 + config["yolo"]["classes"])
self.yolo_head3 = yolo_head([256, final_out_filter2],128)
self.down_sample1 = conv2d(128,256,3,stride=2)
self.make_five_conv3 = make_five_conv([256, 512],512)
# 3*(5+num_classes)=3*(5+20)=3*(4+1+20)=75
final_out_filter1 = len(config["yolo"]["anchors"][1]) * (5 + config["yolo"]["classes"])
self.yolo_head2 = yolo_head([512, final_out_filter1],256)
self.down_sample2 = conv2d(256,512,3,stride=2)
self.make_five_conv4 = make_five_conv([512, 1024],1024)
# 3*(5+num_classes)=3*(5+20)=3*(4+1+20)=75
final_out_filter0 = len(config["yolo"]["anchors"][0]) * (5 + config["yolo"]["classes"])
self.yolo_head1 = yolo_head([1024, final_out_filter0],512)
def forward(self, x):
# backbone
x2, x1, x0 = self.backbone(x)
P5 = self.conv1(x0)
P5 = self.SPP(P5)
P5 = self.conv2(P5)
P5_upsample = self.upsample1(P5)
P4 = self.conv_for_P4(x1)
P4 = torch.cat([P4,P5_upsample],axis=1)
P4 = self.make_five_conv1(P4)
P4_upsample = self.upsample2(P4)
P3 = self.conv_for_P3(x2)
P3 = torch.cat([P3,P4_upsample],axis=1)
P3 = self.make_five_conv2(P3)
P3_downsample = self.down_sample1(P3)
P4 = torch.cat([P3_downsample,P4],axis=1)
P4 = self.make_five_conv3(P4)
P4_downsample = self.down_sample2(P4)
P5 = torch.cat([P4_downsample,P5],axis=1)
P5 = self.make_five_conv4(P5)
out2 = self.yolo_head3(P3)
out1 = self.yolo_head2(P4)
out0 = self.yolo_head1(P5)
return out0, out1, out2
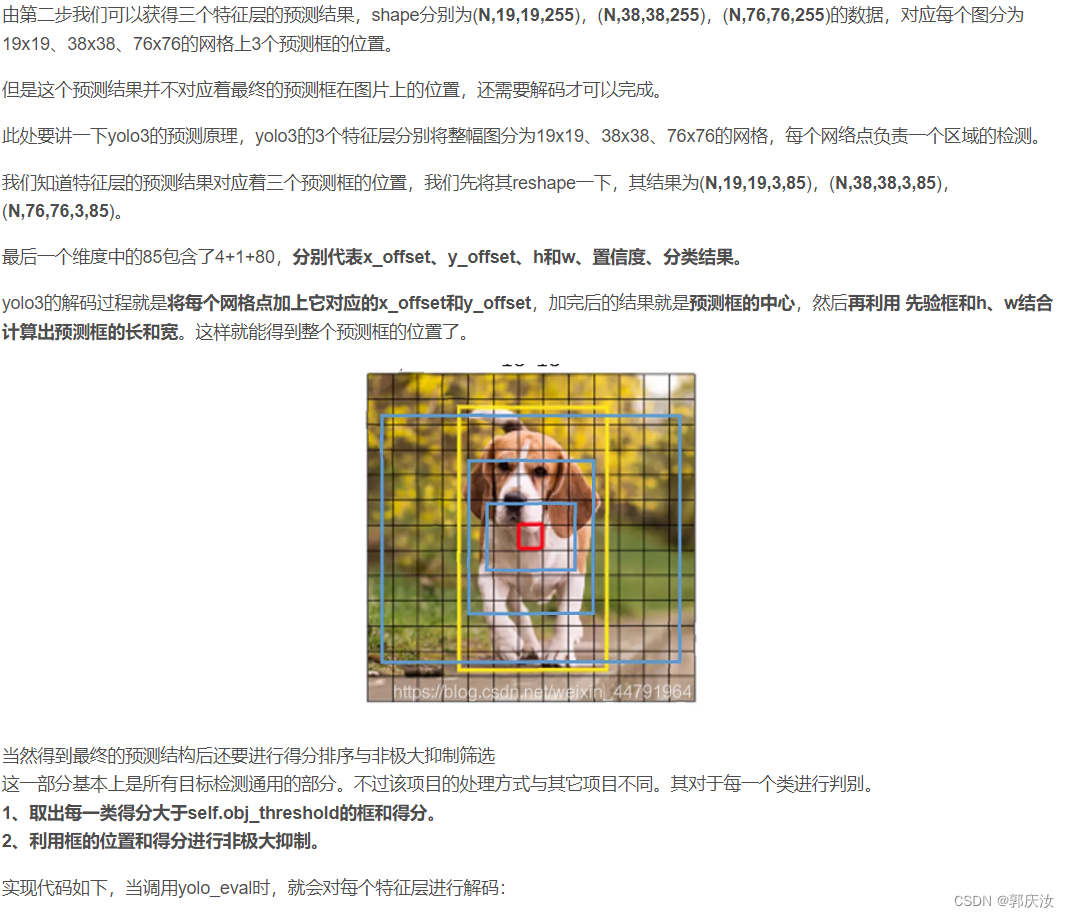
4、预测结果的解码
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from torchvision.ops import nms
import numpy as np
class DecodeBox():
def __init__(self, anchors, num_classes, input_shape, anchors_mask = [[6,7,8], [3,4,5], [0,1,2]]):
super(DecodeBox, self).__init__()
self.anchors = anchors
self.num_classes = num_classes
self.bbox_attrs = 5 + num_classes
self.input_shape = input_shape
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
# 13x13的特征层对应的anchor是[142, 110],[192, 243],[459, 401]
# 26x26的特征层对应的anchor是[36, 75],[76, 55],[72, 146]
# 52x52的特征层对应的anchor是[12, 16],[19, 36],[40, 28]
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
self.anchors_mask = anchors_mask
def decode_box(self, inputs):
outputs = []
for i, input in enumerate(inputs):
#-----------------------------------------------#
# 输入的input一共有三个,他们的shape分别是
# batch_size, 255, 13, 13
# batch_size, 255, 26, 26
# batch_size, 255, 52, 52
#-----------------------------------------------#
batch_size = input.size(0)
input_height = input.size(2)
input_width = input.size(3)
#-----------------------------------------------#
# 输入为416x416时
# stride_h = stride_w = 32、16、8
#-----------------------------------------------#
stride_h = self.input_shape[0] / input_height
stride_w = self.input_shape[1] / input_width
#-------------------------------------------------#
# 此时获得的scaled_anchors大小是相对于特征层的
#-------------------------------------------------#
scaled_anchors = [(anchor_width / stride_w, anchor_height / stride_h) for anchor_width, anchor_height in self.anchors[self.anchors_mask[i]]]
#-----------------------------------------------#
# 输入的input一共有三个,他们的shape分别是
# batch_size, 3, 13, 13, 85
# batch_size, 3, 26, 26, 85
# batch_size, 3, 52, 52, 85
#-----------------------------------------------#
prediction = input.view(batch_size, len(self.anchors_mask[i]),
self.bbox_attrs, input_height, input_width).permute(0, 1, 3, 4, 2).contiguous()
#-----------------------------------------------#
# 先验框的中心位置的调整参数
#-----------------------------------------------#
x = torch.sigmoid(prediction[..., 0])
y = torch.sigmoid(prediction[..., 1])
#-----------------------------------------------#
# 先验框的宽高调整参数
#-----------------------------------------------#
w = prediction[..., 2]
h = prediction[..., 3]
#-----------------------------------------------#
# 获得置信度,是否有物体
#-----------------------------------------------#
conf = torch.sigmoid(prediction[..., 4])
#-----------------------------------------------#
# 种类置信度
#-----------------------------------------------#
pred_cls = torch.sigmoid(prediction[..., 5:])
FloatTensor = torch.cuda.FloatTensor if x.is_cuda else torch.FloatTensor
LongTensor = torch.cuda.LongTensor if x.is_cuda else torch.LongTensor
#----------------------------------------------------------#
# 生成网格,先验框中心,网格左上角
# batch_size,3,13,13
#----------------------------------------------------------#
grid_x = torch.linspace(0, input_width - 1, input_width).repeat(input_height, 1).repeat(
batch_size * len(self.anchors_mask[i]), 1, 1).view(x.shape).type(FloatTensor)
grid_y = torch.linspace(0, input_height - 1, input_height).repeat(input_width, 1).t().repeat(
batch_size * len(self.anchors_mask[i]), 1, 1).view(y.shape).type(FloatTensor)
#----------------------------------------------------------#
# 按照网格格式生成先验框的宽高
# batch_size,3,13,13
#----------------------------------------------------------#
anchor_w = FloatTensor(scaled_anchors).index_select(1, LongTensor([0]))
anchor_h = FloatTensor(scaled_anchors).index_select(1, LongTensor([1]))
anchor_w = anchor_w.repeat(batch_size, 1).repeat(1, 1, input_height * input_width).view(w.shape)
anchor_h = anchor_h.repeat(batch_size, 1).repeat(1, 1, input_height * input_width).view(h.shape)
#----------------------------------------------------------#
# 利用预测结果对先验框进行调整
# 首先调整先验框的中心,从先验框中心向右下角偏移
# 再调整先验框的宽高。
#----------------------------------------------------------#
pred_boxes = FloatTensor(prediction[..., :4].shape)
pred_boxes[..., 0] = x.data + grid_x
pred_boxes[..., 1] = y.data + grid_y
pred_boxes[..., 2] = torch.exp(w.data) * anchor_w
pred_boxes[..., 3] = torch.exp(h.data) * anchor_h
#----------------------------------------------------------#
# 将输出结果归一化成小数的形式
#----------------------------------------------------------#
_scale = torch.Tensor([input_width, input_height, input_width, input_height]).type(FloatTensor)
output = torch.cat((pred_boxes.view(batch_size, -1, 4) / _scale,
conf.view(batch_size, -1, 1), pred_cls.view(batch_size, -1, self.num_classes)), -1)
outputs.append(output.data)
return outputs
def yolo_correct_boxes(self, box_xy, box_wh, input_shape, image_shape, letterbox_image):
#-----------------------------------------------------------------#
# 把y轴放前面是因为方便预测框和图像的宽高进行相乘
#-----------------------------------------------------------------#
box_yx = box_xy[..., ::-1]
box_hw = box_wh[..., ::-1]
input_shape = np.array(input_shape)
image_shape = np.array(image_shape)
if letterbox_image:
#-----------------------------------------------------------------#
# 这里求出来的offset是图像有效区域相对于图像左上角的偏移情况
# new_shape指的是宽高缩放情况
#-----------------------------------------------------------------#
new_shape = np.round(image_shape * np.min(input_shape/image_shape))
offset = (input_shape - new_shape)/2./input_shape
scale = input_shape/new_shape
box_yx = (box_yx - offset) * scale
box_hw *= scale
box_mins = box_yx - (box_hw / 2.)
box_maxes = box_yx + (box_hw / 2.)
boxes = np.concatenate([box_mins[..., 0:1], box_mins[..., 1:2], box_maxes[..., 0:1], box_maxes[..., 1:2]], axis=-1)
boxes *= np.concatenate([image_shape, image_shape], axis=-1)
return boxes
def non_max_suppression(self, prediction, num_classes, input_shape, image_shape, letterbox_image, conf_thres=0.5, nms_thres=0.4):
#----------------------------------------------------------#
# 将预测结果的格式转换成左上角右下角的格式。
# prediction [batch_size, num_anchors, 85]
#----------------------------------------------------------#
box_corner = prediction.new(prediction.shape)
box_corner[:, :, 0] = prediction[:, :, 0] - prediction[:, :, 2] / 2
box_corner[:, :, 1] = prediction[:, :, 1] - prediction[:, :, 3] / 2
box_corner[:, :, 2] = prediction[:, :, 0] + prediction[:, :, 2] / 2
box_corner[:, :, 3] = prediction[:, :, 1] + prediction[:, :, 3] / 2
prediction[:, :, :4] = box_corner[:, :, :4]
output = [None for _ in range(len(prediction))]
for i, image_pred in enumerate(prediction):
#----------------------------------------------------------#
# 对种类预测部分取max。
# class_conf [num_anchors, 1] 种类置信度
# class_pred [num_anchors, 1] 种类
#----------------------------------------------------------#
class_conf, class_pred = torch.max(image_pred[:, 5:5 + num_classes], 1, keepdim=True)
#----------------------------------------------------------#
# 利用置信度进行第一轮筛选
#----------------------------------------------------------#
conf_mask = (image_pred[:, 4] * class_conf[:, 0] >= conf_thres).squeeze()
#----------------------------------------------------------#
# 根据置信度进行预测结果的筛选
#----------------------------------------------------------#
image_pred = image_pred[conf_mask]
class_conf = class_conf[conf_mask]
class_pred = class_pred[conf_mask]
if not image_pred.size(0):
continue
#-------------------------------------------------------------------------#
# detections [num_anchors, 7]
# 7的内容为:x1, y1, x2, y2, obj_conf, class_conf, class_pred
#-------------------------------------------------------------------------#
detections = torch.cat((image_pred[:, :5], class_conf.float(), class_pred.float()), 1)
#------------------------------------------#
# 获得预测结果中包含的所有种类
#------------------------------------------#
unique_labels = detections[:, -1].cpu().unique()
if prediction.is_cuda:
unique_labels = unique_labels.cuda()
detections = detections.cuda()
for c in unique_labels:
#------------------------------------------#
# 获得某一类得分筛选后全部的预测结果
#------------------------------------------#
detections_class = detections[detections[:, -1] == c]
#------------------------------------------#
# 使用官方自带的非极大抑制会速度更快一些!
#------------------------------------------#
keep = nms(
detections_class[:, :4],
detections_class[:, 4] * detections_class[:, 5],
nms_thres
)
max_detections = detections_class[keep]
# # 按照存在物体的置信度排序
# _, conf_sort_index = torch.sort(detections_class[:, 4]*detections_class[:, 5], descending=True)
# detections_class = detections_class[conf_sort_index]
# # 进行非极大抑制
# max_detections = []
# while detections_class.size(0):
# # 取出这一类置信度最高的,一步一步往下判断,判断重合程度是否大于nms_thres,如果是则去除掉
# max_detections.append(detections_class[0].unsqueeze(0))
# if len(detections_class) == 1:
# break
# ious = bbox_iou(max_detections[-1], detections_class[1:])
# detections_class = detections_class[1:][ious < nms_thres]
# # 堆叠
# max_detections = torch.cat(max_detections).data
# Add max detections to outputs
output[i] = max_detections if output[i] is None else torch.cat((output[i], max_detections))
if output[i] is not None:
output[i] = output[i].cpu().numpy()
box_xy, box_wh = (output[i][:, 0:2] + output[i][:, 2:4])/2, output[i][:, 2:4] - output[i][:, 0:2]
output[i][:, :4] = self.yolo_correct_boxes(box_xy, box_wh, input_shape, image_shape, letterbox_image)
return output
YOLOV4的训练
1、YOLOV4的改进训练技巧
def merge_bboxes(self, bboxes, cutx, cuty):
merge_bbox = []
for i in range(len(bboxes)):
for box in bboxes[i]:
tmp_box = []
x1, y1, x2, y2 = box[0], box[1], box[2], box[3]
if i == 0:
if y1 > cuty or x1 > cutx:
continue
if y2 >= cuty and y1 <= cuty:
y2 = cuty
if x2 >= cutx and x1 <= cutx:
x2 = cutx
if i == 1:
if y2 < cuty or x1 > cutx:
continue
if y2 >= cuty and y1 <= cuty:
y1 = cuty
if x2 >= cutx and x1 <= cutx:
x2 = cutx
if i == 2:
if y2 < cuty or x2 < cutx:
continue
if y2 >= cuty and y1 <= cuty:
y1 = cuty
if x2 >= cutx and x1 <= cutx:
x1 = cutx
if i == 3:
if y1 > cuty or x2 < cutx:
continue
if y2 >= cuty and y1 <= cuty:
y2 = cuty
if x2 >= cutx and x1 <= cutx:
x1 = cutx
tmp_box.append(x1)
tmp_box.append(y1)
tmp_box.append(x2)
tmp_box.append(y2)
tmp_box.append(box[-1])
merge_bbox.append(tmp_box)
return merge_bbox
def get_random_data_with_Mosaic(self, annotation_line, input_shape, max_boxes=100, hue=.1, sat=1.5, val=1.5):
h, w = input_shape
min_offset_x = self.rand(0.25, 0.75)
min_offset_y = self.rand(0.25, 0.75)
nws = [ int(w * self.rand(0.4, 1)), int(w * self.rand(0.4, 1)), int(w * self.rand(0.4, 1)), int(w * self.rand(0.4, 1))]
nhs = [ int(h * self.rand(0.4, 1)), int(h * self.rand(0.4, 1)), int(h * self.rand(0.4, 1)), int(h * self.rand(0.4, 1))]
place_x = [int(w*min_offset_x) - nws[0], int(w*min_offset_x) - nws[1], int(w*min_offset_x), int(w*min_offset_x)]
place_y = [int(h*min_offset_y) - nhs[0], int(h*min_offset_y), int(h*min_offset_y), int(h*min_offset_y) - nhs[3]]
image_datas = []
box_datas = []
index = 0
for line in annotation_line:
# 每一行进行分割
line_content = line.split()
# 打开图片
image = Image.open(line_content[0])
image = cvtColor(image)
# 图片的大小
iw, ih = image.size
# 保存框的位置
box = np.array([np.array(list(map(int,box.split(',')))) for box in line_content[1:]])
# 是否翻转图片
flip = self.rand()<.5
if flip and len(box)>0:
image = image.transpose(Image.FLIP_LEFT_RIGHT)
box[:, [0,2]] = iw - box[:, [2,0]]
nw = nws[index]
nh = nhs[index]
image = image.resize((nw,nh), Image.BICUBIC)
# 将图片进行放置,分别对应四张分割图片的位置
dx = place_x[index]
dy = place_y[index]
new_image = Image.new('RGB', (w,h), (128,128,128))
new_image.paste(image, (dx, dy))
image_data = np.array(new_image)
index = index + 1
box_data = []
# 对box进行重新处理
if len(box)>0:
np.random.shuffle(box)
box[:, [0,2]] = box[:, [0,2]]*nw/iw + dx
box[:, [1,3]] = box[:, [1,3]]*nh/ih + dy
box[:, 0:2][box[:, 0:2]<0] = 0
box[:, 2][box[:, 2]>w] = w
box[:, 3][box[:, 3]>h] = h
box_w = box[:, 2] - box[:, 0]
box_h = box[:, 3] - box[:, 1]
box = box[np.logical_and(box_w>1, box_h>1)]
box_data = np.zeros((len(box),5))
box_data[:len(box)] = box
image_datas.append(image_data)
box_datas.append(box_data)
# 将图片分割,放在一起
cutx = int(w * min_offset_x)
cuty = int(h * min_offset_y)
new_image = np.zeros([h, w, 3])
new_image[:cuty, :cutx, :] = image_datas[0][:cuty, :cutx, :]
new_image[cuty:, :cutx, :] = image_datas[1][cuty:, :cutx, :]
new_image[cuty:, cutx:, :] = image_datas[2][cuty:, cutx:, :]
new_image[:cuty, cutx:, :] = image_datas[3][:cuty, cutx:, :]
# 进行色域变换
hue = self.rand(-hue, hue)
sat = self.rand(1, sat) if self.rand()<.5 else 1/self.rand(1, sat)
val = self.rand(1, val) if self.rand()<.5 else 1/self.rand(1, val)
x = cv2.cvtColor(np.array(new_image/255,np.float32), cv2.COLOR_RGB2HSV)
x[..., 0] += hue*360
x[..., 0][x[..., 0]>1] -= 1
x[..., 0][x[..., 0]<0] += 1
x[..., 1] *= sat
x[..., 2] *= val
x[x[:, :, 0]>360, 0] = 360
x[:, :, 1:][x[:, :, 1:]>1] = 1
x[x<0] = 0
new_image = cv2.cvtColor(x, cv2.COLOR_HSV2RGB)*255
# 对框进行进一步的处理
new_boxes = self.merge_bboxes(box_datas, cutx, cuty)
return new_image, new_boxes

new_onehot_labels = onehot_labels * (1 - label_smoothing) + label_smoothing / num_classes
当label_smoothing的值为0.01得时候,公式变成如下所示:
new_onehot_labels = y * (1 - 0.01) + 0.01 / num_classes

#---------------------------------------------------#
# 平滑标签
#---------------------------------------------------#
def smooth_labels(y_true, label_smoothing,num_classes):
return y_true * (1.0 - label_smoothing) + label_smoothing / num_classes
def box_ciou(self, b1, b2):
"""
输入为:
----------
b1: tensor, shape=(batch, feat_w, feat_h, anchor_num, 4), xywh
b2: tensor, shape=(batch, feat_w, feat_h, anchor_num, 4), xywh
返回为:
-------
ciou: tensor, shape=(batch, feat_w, feat_h, anchor_num, 1)
"""
#----------------------------------------------------#
# 求出预测框左上角右下角
#----------------------------------------------------#
b1_xy = b1[..., :2]
b1_wh = b1[..., 2:4]
b1_wh_half = b1_wh/2.
b1_mins = b1_xy - b1_wh_half
b1_maxes = b1_xy + b1_wh_half
#----------------------------------------------------#
# 求出真实框左上角右下角
#----------------------------------------------------#
b2_xy = b2[..., :2]
b2_wh = b2[..., 2:4]
b2_wh_half = b2_wh/2.
b2_mins = b2_xy - b2_wh_half
b2_maxes = b2_xy + b2_wh_half
#----------------------------------------------------#
# 求真实框和预测框所有的iou
#----------------------------------------------------#
intersect_mins = torch.max(b1_mins, b2_mins)
intersect_maxes = torch.min(b1_maxes, b2_maxes)
intersect_wh = torch.max(intersect_maxes - intersect_mins, torch.zeros_like(intersect_maxes))
intersect_area = intersect_wh[..., 0] * intersect_wh[..., 1]
b1_area = b1_wh[..., 0] * b1_wh[..., 1]
b2_area = b2_wh[..., 0] * b2_wh[..., 1]
union_area = b1_area + b2_area - intersect_area
iou = intersect_area / torch.clamp(union_area,min = 1e-6)
#----------------------------------------------------#
# 计算中心的差距
#----------------------------------------------------#
center_distance = torch.sum(torch.pow((b1_xy - b2_xy), 2), axis=-1)
#----------------------------------------------------#
# 找到包裹两个框的最小框的左上角和右下角
#----------------------------------------------------#
enclose_mins = torch.min(b1_mins, b2_mins)
enclose_maxes = torch.max(b1_maxes, b2_maxes)
enclose_wh = torch.max(enclose_maxes - enclose_mins, torch.zeros_like(intersect_maxes))
#----------------------------------------------------#
# 计算对角线距离
#----------------------------------------------------#
enclose_diagonal = torch.sum(torch.pow(enclose_wh,2), axis=-1)
ciou = iou - 1.0 * (center_distance) / torch.clamp(enclose_diagonal,min = 1e-6)
v = (4 / (math.pi ** 2)) * torch.pow((torch.atan(b1_wh[..., 0] / torch.clamp(b1_wh[..., 1],min = 1e-6)) - torch.atan(b2_wh[..., 0] / torch.clamp(b2_wh[..., 1], min = 1e-6))), 2)
alpha = v / torch.clamp((1.0 - iou + v), min=1e-6)
ciou = ciou - alpha * v
return ciou
2、loss组成

import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import math
import numpy as np
class YOLOLoss(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, anchors, num_classes, input_shape, cuda, anchors_mask = [[6,7,8], [3,4,5], [0,1,2]], label_smoothing = 0):
super(YOLOLoss, self).__init__()
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
# 13x13的特征层对应的anchor是[142, 110],[192, 243],[459, 401]
# 26x26的特征层对应的anchor是[36, 75],[76, 55],[72, 146]
# 52x52的特征层对应的anchor是[12, 16],[19, 36],[40, 28]
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
self.anchors = anchors
self.num_classes = num_classes
self.bbox_attrs = 5 + num_classes
self.input_shape = input_shape
self.anchors_mask = anchors_mask
self.label_smoothing = label_smoothing
self.ignore_threshold = 0.7
self.cuda = cuda
def clip_by_tensor(self, t, t_min, t_max):
t = t.float()
result = (t >= t_min).float() * t + (t < t_min).float() * t_min
result = (result <= t_max).float() * result + (result > t_max).float() * t_max
return result
def MSELoss(self, pred, target):
return torch.pow(pred - target, 2)
def BCELoss(self, pred, target):
epsilon = 1e-7
pred = self.clip_by_tensor(pred, epsilon, 1.0 - epsilon)
output = - target * torch.log(pred) - (1.0 - target) * torch.log(1.0 - pred)
return output
def box_ciou(self, b1, b2):
"""
输入为:
----------
b1: tensor, shape=(batch, feat_w, feat_h, anchor_num, 4), xywh
b2: tensor, shape=(batch, feat_w, feat_h, anchor_num, 4), xywh
返回为:
-------
ciou: tensor, shape=(batch, feat_w, feat_h, anchor_num, 1)
"""
#----------------------------------------------------#
# 求出预测框左上角右下角
#----------------------------------------------------#
b1_xy = b1[..., :2]
b1_wh = b1[..., 2:4]
b1_wh_half = b1_wh/2.
b1_mins = b1_xy - b1_wh_half
b1_maxes = b1_xy + b1_wh_half
#----------------------------------------------------#
# 求出真实框左上角右下角
#----------------------------------------------------#
b2_xy = b2[..., :2]
b2_wh = b2[..., 2:4]
b2_wh_half = b2_wh/2.
b2_mins = b2_xy - b2_wh_half
b2_maxes = b2_xy + b2_wh_half
#----------------------------------------------------#
# 求真实框和预测框所有的iou
#----------------------------------------------------#
intersect_mins = torch.max(b1_mins, b2_mins)
intersect_maxes = torch.min(b1_maxes, b2_maxes)
intersect_wh = torch.max(intersect_maxes - intersect_mins, torch.zeros_like(intersect_maxes))
intersect_area = intersect_wh[..., 0] * intersect_wh[..., 1]
b1_area = b1_wh[..., 0] * b1_wh[..., 1]
b2_area = b2_wh[..., 0] * b2_wh[..., 1]
union_area = b1_area + b2_area - intersect_area
iou = intersect_area / torch.clamp(union_area,min = 1e-6)
#----------------------------------------------------#
# 计算中心的差距
#----------------------------------------------------#
center_distance = torch.sum(torch.pow((b1_xy - b2_xy), 2), axis=-1)
#----------------------------------------------------#
# 找到包裹两个框的最小框的左上角和右下角
#----------------------------------------------------#
enclose_mins = torch.min(b1_mins, b2_mins)
enclose_maxes = torch.max(b1_maxes, b2_maxes)
enclose_wh = torch.max(enclose_maxes - enclose_mins, torch.zeros_like(intersect_maxes))
#----------------------------------------------------#
# 计算对角线距离
#----------------------------------------------------#
enclose_diagonal = torch.sum(torch.pow(enclose_wh,2), axis=-1)
ciou = iou - 1.0 * (center_distance) / torch.clamp(enclose_diagonal,min = 1e-6)
v = (4 / (math.pi ** 2)) * torch.pow((torch.atan(b1_wh[..., 0] / torch.clamp(b1_wh[..., 1],min = 1e-6)) - torch.atan(b2_wh[..., 0] / torch.clamp(b2_wh[..., 1], min = 1e-6))), 2)
alpha = v / torch.clamp((1.0 - iou + v), min=1e-6)
ciou = ciou - alpha * v
return ciou
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 平滑标签
#---------------------------------------------------#
def smooth_labels(self, y_true, label_smoothing, num_classes):
return y_true * (1.0 - label_smoothing) + label_smoothing / num_classes
def forward(self, l, input, targets=None):
#----------------------------------------------------#
# l 代表使用的是第几个有效特征层
# input的shape为 bs, 3*(5+num_classes), 13, 13
# bs, 3*(5+num_classes), 26, 26
# bs, 3*(5+num_classes), 52, 52
# targets 真实框的标签情况 [batch_size, num_gt, 5]
#----------------------------------------------------#
#--------------------------------#
# 获得图片数量,特征层的高和宽
#--------------------------------#
bs = input.size(0)
in_h = input.size(2)
in_w = input.size(3)
#-----------------------------------------------------------------------#
# 计算步长
# 每一个特征点对应原来的图片上多少个像素点
#
# 如果特征层为13x13的话,一个特征点就对应原来的图片上的32个像素点
# 如果特征层为26x26的话,一个特征点就对应原来的图片上的16个像素点
# 如果特征层为52x52的话,一个特征点就对应原来的图片上的8个像素点
# stride_h = stride_w = 32、16、8
#-----------------------------------------------------------------------#
stride_h = self.input_shape[0] / in_h
stride_w = self.input_shape[1] / in_w
#-------------------------------------------------#
# 此时获得的scaled_anchors大小是相对于特征层的
#-------------------------------------------------#
scaled_anchors = [(a_w / stride_w, a_h / stride_h) for a_w, a_h in self.anchors]
#-----------------------------------------------#
# 输入的input一共有三个,他们的shape分别是
# bs, 3 * (5+num_classes), 13, 13 => bs, 3, 5 + num_classes, 13, 13 => batch_size, 3, 13, 13, 5 + num_classes
# batch_size, 3, 13, 13, 5 + num_classes
# batch_size, 3, 26, 26, 5 + num_classes
# batch_size, 3, 52, 52, 5 + num_classes
#-----------------------------------------------#
prediction = input.view(bs, len(self.anchors_mask[l]), self.bbox_attrs, in_h, in_w).permute(0, 1, 3, 4, 2).contiguous()
#-----------------------------------------------#
# 先验框的中心位置的调整参数
#-----------------------------------------------#
x = torch.sigmoid(prediction[..., 0])
y = torch.sigmoid(prediction[..., 1])
#-----------------------------------------------#
# 先验框的宽高调整参数
#-----------------------------------------------#
w = prediction[..., 2]
h = prediction[..., 3]
#-----------------------------------------------#
# 获得置信度,是否有物体
#-----------------------------------------------#
conf = torch.sigmoid(prediction[..., 4])
#-----------------------------------------------#
# 种类置信度
#-----------------------------------------------#
pred_cls = torch.sigmoid(prediction[..., 5:])
#-----------------------------------------------#
# 获得网络应该有的预测结果
#-----------------------------------------------#
y_true, noobj_mask, box_loss_scale = self.get_target(l, targets, scaled_anchors, in_h, in_w)
#---------------------------------------------------------------#
# 将预测结果进行解码,判断预测结果和真实值的重合程度
# 如果重合程度过大则忽略,因为这些特征点属于预测比较准确的特征点
# 作为负样本不合适
#----------------------------------------------------------------#
noobj_mask, pred_boxes = self.get_ignore(l, x, y, h, w, targets, scaled_anchors, in_h, in_w, noobj_mask)
if self.cuda:
y_true = y_true.cuda()
noobj_mask = noobj_mask.cuda()
box_loss_scale = box_loss_scale.cuda()
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
# reshape_y_true[...,2:3]和reshape_y_true[...,3:4]
# 表示真实框的宽高,二者均在0-1之间
# 真实框越大,比重越小,小框的比重更大。
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
box_loss_scale = 2 - box_loss_scale
#---------------------------------------------------------------#
# 计算预测结果和真实结果的CIOU
#----------------------------------------------------------------#
ciou = (1 - self.box_ciou(pred_boxes[y_true[..., 4] == 1], y_true[..., :4][y_true[..., 4] == 1])) * box_loss_scale[y_true[..., 4] == 1]
loss_loc = torch.sum(ciou)
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
# 计算置信度的loss
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
loss_conf = torch.sum(self.BCELoss(conf, y_true[..., 4]) * y_true[..., 4]) + \
torch.sum(self.BCELoss(conf, y_true[..., 4]) * noobj_mask)
loss_cls = torch.sum(self.BCELoss(pred_cls[y_true[..., 4] == 1], self.smooth_labels(y_true[..., 5:][y_true[..., 4] == 1], self.label_smoothing, self.num_classes)))
loss = loss_loc + loss_conf + loss_cls
num_pos = torch.sum(y_true[..., 4])
num_pos = torch.max(num_pos, torch.ones_like(num_pos))
return loss, num_pos
def calculate_iou(self, _box_a, _box_b):
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
# 计算真实框的左上角和右下角
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
b1_x1, b1_x2 = _box_a[:, 0] - _box_a[:, 2] / 2, _box_a[:, 0] + _box_a[:, 2] / 2
b1_y1, b1_y2 = _box_a[:, 1] - _box_a[:, 3] / 2, _box_a[:, 1] + _box_a[:, 3] / 2
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
# 计算先验框获得的预测框的左上角和右下角
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
b2_x1, b2_x2 = _box_b[:, 0] - _box_b[:, 2] / 2, _box_b[:, 0] + _box_b[:, 2] / 2
b2_y1, b2_y2 = _box_b[:, 1] - _box_b[:, 3] / 2, _box_b[:, 1] + _box_b[:, 3] / 2
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
# 将真实框和预测框都转化成左上角右下角的形式
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
box_a = torch.zeros_like(_box_a)
box_b = torch.zeros_like(_box_b)
box_a[:, 0], box_a[:, 1], box_a[:, 2], box_a[:, 3] = b1_x1, b1_y1, b1_x2, b1_y2
box_b[:, 0], box_b[:, 1], box_b[:, 2], box_b[:, 3] = b2_x1, b2_y1, b2_x2, b2_y2
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
# A为真实框的数量,B为先验框的数量
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
A = box_a.size(0)
B = box_b.size(0)
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
# 计算交的面积
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
max_xy = torch.min(box_a[:, 2:].unsqueeze(1).expand(A, B, 2), box_b[:, 2:].unsqueeze(0).expand(A, B, 2))
min_xy = torch.max(box_a[:, :2].unsqueeze(1).expand(A, B, 2), box_b[:, :2].unsqueeze(0).expand(A, B, 2))
inter = torch.clamp((max_xy - min_xy), min=0)
inter = inter[:, :, 0] * inter[:, :, 1]
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
# 计算预测框和真实框各自的面积
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
area_a = ((box_a[:, 2]-box_a[:, 0]) * (box_a[:, 3]-box_a[:, 1])).unsqueeze(1).expand_as(inter) # [A,B]
area_b = ((box_b[:, 2]-box_b[:, 0]) * (box_b[:, 3]-box_b[:, 1])).unsqueeze(0).expand_as(inter) # [A,B]
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
# 求IOU
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
union = area_a + area_b - inter
return inter / union # [A,B]
def get_target(self, l, targets, anchors, in_h, in_w):
#-----------------------------------------------------#
# 计算一共有多少张图片
#-----------------------------------------------------#
bs = len(targets)
#-----------------------------------------------------#
# 用于选取哪些先验框不包含物体
#-----------------------------------------------------#
noobj_mask = torch.ones(bs, len(self.anchors_mask[l]), in_h, in_w, requires_grad = False)
#-----------------------------------------------------#
# 让网络更加去关注小目标
#-----------------------------------------------------#
box_loss_scale = torch.zeros(bs, len(self.anchors_mask[l]), in_h, in_w, requires_grad = False)
#-----------------------------------------------------#
# batch_size, 3, 13, 13, 5 + num_classes
#-----------------------------------------------------#
y_true = torch.zeros(bs, len(self.anchors_mask[l]), in_h, in_w, self.bbox_attrs, requires_grad = False)
for b in range(bs):
if len(targets[b])==0:
continue
batch_target = torch.zeros_like(targets[b])
#-------------------------------------------------------#
# 计算出正样本在特征层上的中心点
#-------------------------------------------------------#
batch_target[:, [0,2]] = targets[b][:, [0,2]] * in_w
batch_target[:, [1,3]] = targets[b][:, [1,3]] * in_h
batch_target[:, 4] = targets[b][:, 4]
batch_target = batch_target.cpu()
#-------------------------------------------------------#
# 将真实框转换一个形式
# num_true_box, 4
#-------------------------------------------------------#
gt_box = torch.FloatTensor(torch.cat((torch.zeros((batch_target.size(0), 2)), batch_target[:, 2:4]), 1))
#-------------------------------------------------------#
# 将先验框转换一个形式
# 9, 4
#-------------------------------------------------------#
anchor_shapes = torch.FloatTensor(torch.cat((torch.zeros((len(anchors), 2)), torch.FloatTensor(anchors)), 1))
#-------------------------------------------------------#
# 计算交并比
# self.calculate_iou(gt_box, anchor_shapes) = [num_true_box, 9]每一个真实框和9个先验框的重合情况
# best_ns:
# [每个真实框最大的重合度max_iou, 每一个真实框最重合的先验框的序号]
#-------------------------------------------------------#
best_ns = torch.argmax(self.calculate_iou(gt_box, anchor_shapes), dim=-1)
for t, best_n in enumerate(best_ns):
if best_n not in self.anchors_mask[l]:
continue
#----------------------------------------#
# 判断这个先验框是当前特征点的哪一个先验框
#----------------------------------------#
k = self.anchors_mask[l].index(best_n)
#----------------------------------------#
# 获得真实框属于哪个网格点
#----------------------------------------#
i = torch.floor(batch_target[t, 0]).long()
j = torch.floor(batch_target[t, 1]).long()
#----------------------------------------#
# 取出真实框的种类
#----------------------------------------#
c = batch_target[t, 4].long()
#----------------------------------------#
# noobj_mask代表无目标的特征点
#----------------------------------------#
noobj_mask[b, k, j, i] = 0
#----------------------------------------#
# tx、ty代表中心调整参数的真实值
#----------------------------------------#
y_true[b, k, j, i, 0] = batch_target[t, 0]
y_true[b, k, j, i, 1] = batch_target[t, 1]
y_true[b, k, j, i, 2] = batch_target[t, 2]
y_true[b, k, j, i, 3] = batch_target[t, 3]
y_true[b, k, j, i, 4] = 1
y_true[b, k, j, i, c + 5] = 1
#----------------------------------------#
# 用于获得xywh的比例
# 大目标loss权重小,小目标loss权重大
#----------------------------------------#
box_loss_scale[b, k, j, i] = batch_target[t, 2] * batch_target[t, 3] / in_w / in_h
return y_true, noobj_mask, box_loss_scale
def get_ignore(self, l, x, y, h, w, targets, scaled_anchors, in_h, in_w, noobj_mask):
#-----------------------------------------------------#
# 计算一共有多少张图片
#-----------------------------------------------------#
bs = len(targets)
FloatTensor = torch.cuda.FloatTensor if x.is_cuda else torch.FloatTensor
LongTensor = torch.cuda.LongTensor if x.is_cuda else torch.LongTensor
#-----------------------------------------------------#
# 生成网格,先验框中心,网格左上角
#-----------------------------------------------------#
grid_x = torch.linspace(0, in_w - 1, in_w).repeat(in_h, 1).repeat(
int(bs * len(self.anchors_mask[l])), 1, 1).view(x.shape).type(FloatTensor)
grid_y = torch.linspace(0, in_h - 1, in_h).repeat(in_w, 1).t().repeat(
int(bs * len(self.anchors_mask[l])), 1, 1).view(y.shape).type(FloatTensor)
# 生成先验框的宽高
scaled_anchors_l = np.array(scaled_anchors)[self.anchors_mask[l]]
anchor_w = FloatTensor(scaled_anchors_l).index_select(1, LongTensor([0]))
anchor_h = FloatTensor(scaled_anchors_l).index_select(1, LongTensor([1]))
anchor_w = anchor_w.repeat(bs, 1).repeat(1, 1, in_h * in_w).view(w.shape)
anchor_h = anchor_h.repeat(bs, 1).repeat(1, 1, in_h * in_w).view(h.shape)
#-------------------------------------------------------#
# 计算调整后的先验框中心与宽高
#-------------------------------------------------------#
pred_boxes_x = torch.unsqueeze(x + grid_x, -1)
pred_boxes_y = torch.unsqueeze(y + grid_y, -1)
pred_boxes_w = torch.unsqueeze(torch.exp(w) * anchor_w, -1)
pred_boxes_h = torch.unsqueeze(torch.exp(h) * anchor_h, -1)
pred_boxes = torch.cat([pred_boxes_x, pred_boxes_y, pred_boxes_w, pred_boxes_h], dim = -1)
for b in range(bs):
#-------------------------------------------------------#
# 将预测结果转换一个形式
# pred_boxes_for_ignore num_anchors, 4
#-------------------------------------------------------#
pred_boxes_for_ignore = pred_boxes[b].view(-1, 4)
#-------------------------------------------------------#
# 计算真实框,并把真实框转换成相对于特征层的大小
# gt_box num_true_box, 4
#-------------------------------------------------------#
if len(targets[b]) > 0:
batch_target = torch.zeros_like(targets[b])
#-------------------------------------------------------#
# 计算出正样本在特征层上的中心点
#-------------------------------------------------------#
batch_target[:, [0,2]] = targets[b][:, [0,2]] * in_w
batch_target[:, [1,3]] = targets[b][:, [1,3]] * in_h
batch_target = batch_target[:, :4]
#-------------------------------------------------------#
# 计算交并比
# anch_ious num_true_box, num_anchors
#-------------------------------------------------------#
anch_ious = self.calculate_iou(batch_target, pred_boxes_for_ignore)
#-------------------------------------------------------#
# 每个先验框对应真实框的最大重合度
# anch_ious_max num_anchors
#-------------------------------------------------------#
anch_ious_max, _ = torch.max(anch_ious, dim = 0)
anch_ious_max = anch_ious_max.view(pred_boxes[b].size()[:3])
noobj_mask[b][anch_ious_max > self.ignore_threshold] = 0
return noobj_mask, pred_boxes
训练自己的YoloV4模型