函数默认参数
在C++中,函数的形参列表中的形参是可以有默认值的。
语法:返回值类型 函数名 (参数=默认值){}
问:C语言可以在函数的形参赋默认值吗?
答:
在C语言中,函数的形参不能直接为其提供默认值。C语言不支持像C++那样在函数的声明或定义中为形参提供默认值的语法。
在C语言中,如果你想实现类似于默认参数的功能,有以下两种常见的方法:
- 函数重载:在C中,可以通过编写多个具有不同参数的函数来模拟C++中的函数重载。这样,在调用函数时可以根据需要选择不同的函数,并通过函数的参数个数或类型来匹配相应的函数。例如:
void foo(int x) {
// ...
}
void fooWithDefault(int x, int y) {
// ...
}
// 调用时可以选择不同的函数
foo(10);
fooWithDefault(10, 20);
- 使用指针或结构体实现类似的功能:可以通过使用指针或结构体作为形参,并在函数内部进行检查和处理来模拟默认参数的功能。例如:
void foo(int x, int* y) {
int defaultVal = 42;
if (y == NULL) {
y = &defaultVal;
}
// 使用y参数的值进行操作
// ...
}
// 调用时可以选择传递第二个参数或不传
int main() {
int customVal = 20;
foo(10, &customVal); // y = &customVal
foo(10, NULL); // y = &defaultVal
}
需要注意的是,在C语言中,这些方法都不是直接为形参提供默认值的解决方案,而是通过其他手段实现了类似的功能。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int func(int a,int b=20,int c=30)
{
return a + b + c;
}
int main()
{
cout << func(10) << endl;
return 0;
}
如果传了数据,就用自己的数据,如果没有,就用默认值。
注意事项
1、如果某个位置已经有了默认参数,那么从这个位置往后,从左到右都必须有默认值
2、如果函数的声明有默认参数,函数实现就不能有默认参数(声明和实现只能有一个有默认参数)
函数占位参数
C++中函数的形参列表里可以有占位参数,用来做占位,调用函数时必须填补该位置
语法:返回值类型 函数名 (函数类型){}
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int func(int a, int)
{
return a;
}
int main()
{
cout << func(10,10) << endl;
return 0;
}
占位参数可以有默认参数
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int func(int a, int=10)
{
return a;
}
int main()
{
cout << func(10) << endl;
return 0;
}
☆函数重载
函数重载概述
作用:函数名可以相同,提高复用性
函数重载满足条件:
1、同一个作用域下
2、函数名称相同
3、函数参数类型不同或者个数不同或者顺序不同
注意:函数的返回值不可以作为函数重载的条件。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void func()
{
cout << "func的调用" << endl;
}
void func(long a)
{
cout << "func(double a)的调用" << endl;
}
void func(int a)
{
cout << "func(int a)的调用" << endl;
}
void func(int a,long b)
{
cout << "func(int a,long b)的调用" << endl;
}
void func(long b, int a)
{
cout << "func(int a,long b)的调用" << endl;
}
int main()
{
long c = 10;
func(c,10);
return 0;
}
函数重载的注意事项
1、引用作为重载条件
2、函数重载碰到函数默认参数
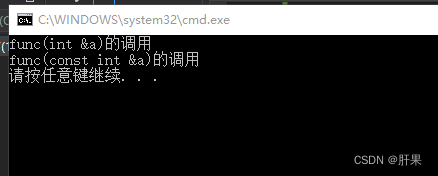
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void func(int &a)
{
cout << "func(int &a)的调用" << endl;
}
void func(const int &a)
{
cout << "func(const int &a)的调用" << endl;
}
int main()
{
int a = 10;
func(a);
func(10);
return 0;
}
错误示范:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void func2(int a)
{
cout << "func(int a)的调用" << endl;
}
void func2(int a,int b=10)
{
cout << "func(int a,int b)的调用" << endl;
}
int main()
{
func2(10);
return 0;
}