【算法1-6】二分查找与二分答案
P1024[NOIP2001 提高组] 一元三次方程求解
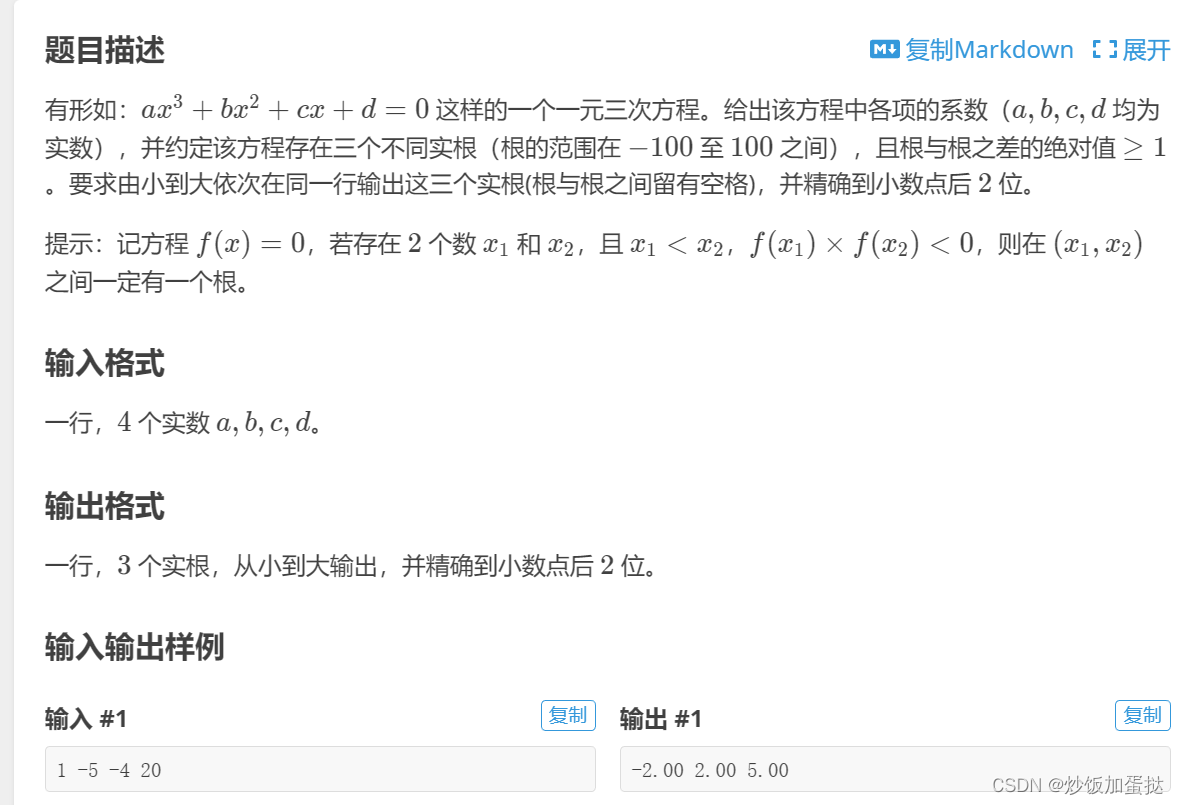
思路:题目说明根与根之差的绝对值>=1,且x1<x2&&f(x1)*f(x2)<0则其中存在解,于是联想到枚举,再用二分答案法控制精度
总结:二分对于精度的控制可以记录一下
扩展:盛金公式求解一元三次函数,记住公式模板即可,推导太过麻烦了,
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#pragma GCC optimize(2)
#pragma GCC optimize(3)
#pragma GCC optimize(fast)
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<map>
#include<set>
#include<queue>
#include<cstring>
#include<math.h>
#include<map>
#include<vector>
#include<stack>
#define ms(x,y) memset(x,y,sizeof x);
#define YES cout<<"YES"<<'\n';
#define NO cout<<"NO"<<'\n';
#define endl cout<<'\n';
typedef long long ll;
const ll maxn=2e5+10,inf = 1e18 ;
const ll mod = 1e9 + 7;
using namespace std;
double a, b, c, d;
double check(double x) {
return a * x * x * x + b * x * x + c * x + d;
}
void solve(){
cin >> a >> b >> c >> d;
double x1, x2,l,r,m;
int count = 0;
for (double i = -100; i <= 100; i++) {
l = i;
r = i + 1;
x1 = check(l);
x2 = check(r);
if (x1 == 0) {
printf("%.2lf ", l); //不考虑左端点,防止重复计算
count++;
}
if (x1 * x2 < 0) { //区间内有根。
while (r - l >= 0.001) { //二分控制精度。
m = (l + r) / 2;
if (check(m) * check(r) <= 0)
l = m;
else
r = m;
}
printf("%.2lf ", r);
//输出右端点。
count++;
}
if (count >= 3) {
break;
}
}
}
signed main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
int t=1;
//cin >> t;
while (t--) {
solve();
}
}
盛金公式:
#pragma GCC optimize(2)
#pragma GCC optimize(3)
#pragma GCC optimize(fast)
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<map>
#include<set>
#include<queue>
#include<cstring>
#include<math.h>
#include<map>
#include<vector>
#include<stack>
#define ms(x,y) memset(x,y,sizeof x);
#define YES cout<<"YES"<<'\n';
#define NO cout<<"NO"<<'\n';
#define endl cout<<'\n';
typedef long long ll;
const ll maxn=2e5+10,inf = 1e18 ;
const ll mod = 1e9 + 7;
using namespace std;
int a[maxn];
vector<double>X123;
void ShengJin(double a, double b, double c, double d){
double A = b * b - 3 * a * c;
double B = b * c - 9 * a * d;
double C = c * c - 3 * b * d;
double f = B * B - 4 * A * C;
double i_value;
double Y1, Y2;
if (fabs(A) < 1e-6 && fabs(B) < 1e-6)//公式1
{
X123.push_back(-b / (3 * a));
X123.push_back(-b / (3 * a));
X123.push_back(-b / (3 * a));
}
else if (fabs(f) < 1e-6) //公式3
{
double K = B / A;
X123.push_back(-b / a + K);
X123.push_back(-K / 2);
X123.push_back(-K / 2);
}
else if (f > 1e-6) //公式2
{
Y1 = A * b + 3 * a * (-B + sqrt(f)) / 2;
Y2 = A * b + 3 * a * (-B - sqrt(f)) / 2;
double Y1_value = (Y1 / fabs(Y1)) * pow((double)fabs(Y1), 1.0 / 3);
double Y2_value = (Y2 / fabs(Y2)) * pow((double)fabs(Y2), 1.0 / 3);
X123.push_back((-b - Y1_value - Y2_value) / (3 * a));//虚根我不要
//虚根还是看看吧,如果虚根的i小于0.1,则判定为方程的一根吧。。。
i_value = sqrt(3.0) / 2 * (Y1_value - Y2_value) / (3 * a);
if (fabs(i_value) < 1e-1)
{
X123.push_back((-b + 0.5 * (Y1_value + Y2_value)) / (3 * a));
}
}
else if (f < -1e-6) //公式4
{
double T = (2 * A * b - 3 * a * B) / (2 * A * sqrt(A));
double S = acos(T);
X123.push_back((-b - 2 * sqrt(A) * cos(S / 3)) / (3 * a));
X123.push_back((-b + sqrt(A) * (cos(S / 3) + sqrt(3.0) * sin(S / 3))) / (3 * a));
X123.push_back((-b + sqrt(A) * (cos(S / 3) - sqrt(3.0) * sin(S / 3))) / (3 * a));
}
}
void solve(){
double a, b, c, d;
cin >> a >> b >> c >> d;
ShengJin(a, b, c, d);
sort(X123.begin(), X123.end());
for (auto i : X123) {
printf("%.2lf ", i);
}
}
signed main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
int t=1;
//in >> t;
while (t--) {
solve();
}
}
P1182 数列分段 Section II

思路:关键字眼最大值的最小化联想二分,直接二分最大值,l应取数组最大值,r应取数组和,
总结:这道题启发挺大,总结出二分的套路,最大值的最小化,最小值的最大化一般联想到二分,在范围内直接二分(最大值,最小值)
同时二分板子的l,r一定要写清楚,不然要调好久,并且二分的l,r并不是简单的l=0或1,r=无穷,应该考虑极端情况设想就像这题
此类问题check()函数的判定一般根据给定的划分个数
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<map>
#include<set>
#include<queue>
#include<cstring>
#include<math.h>
#include<map>
#include<vector>
#include<stack>
#define ms(x,y) memset(x,y,sizeof x);
#define YES cout<<"YES"<<'\n';
#define NO cout<<"NO"<<'\n';
#define endl cout<<'\n';
#define int long long
typedef long long ll;
const ll maxn=2e5+10,inf = 1e18 ;
const ll mod = 1e9 + 7;
using namespace std;
int a[maxn];
int n, m;
bool check(int x) {
ll sum = 0;
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (sum + a[i] <= x) {
sum += a[i];
}
else {
cnt++;
sum = a[i];
}
}
return cnt >= m;
}
void solve(){
cin >> n >> m;
int l=0,r=0;
for (int i = 1; i <=n; i++) {
cin >> a[i];
l = max(l, a[i]);
r += a[i];
}
while (l <= r) { //二分板子
int mid=(l + r) / 2;
if (check(mid)) {
l = mid+1 ;
}
else {
r = mid - 1;
}
}
cout << l << '\n';
}
signed main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
int t=1;
//cin >> t;
while (t--) {
solve();
}
}
扩展:最小值的最大化(二分)
POJ2456
题意:英文题写下题意:有n个牛栏,m头牛,然牛住进牛栏,使住牛的相邻牛栏最小间隔最大
思路:根据上题,直接二分(最小值),范围l=0(同住一个栏),r=(数组最大值-最小值)
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<map>
#include<set>
#include<queue>
#include<cstring>
#include<math.h>
#include<map>
#include<vector>
#include<stack>
#define ms(x,y) memset(x,y,sizeof x);
#define YES cout<<"YES"<<'\n';
#define NO cout<<"NO"<<'\n';
#define endl cout<<'\n';
typedef long long ll;
const ll maxn=2e5+10,inf = 1e18 ;
const ll mod = 1e9 + 7;
using namespace std;
int a[maxn];
int n, m;
bool check(int x) {
int pre = 1;
int cnt = 1;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
if ((a[i] - a[pre])>=x) {
cnt++;
pre = i;
if (cnt >= m)
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
void solve(){
int l = 0, r = 0;
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> a[i];
}
sort(a + 1, a + 1 + n); //使之具有单调性
r = a[n] - a[1];
while (l < r) {
int mid = (l+r+1) >> 1;
if (check(mid)) {
l = mid;
}
else {
r = mid-1;
}
}
cout << l << '\n';
}
signed main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
int t=1;
//cin >> t;
while (t--) {
solve();
}
}
扩展:
P3853[TJOI2007]路标设置
思路:关键字相邻路标的最大距离的最小值,直接二分最小值,套板子,check的判定在距离内本就有两个路标,若有余数说明需要y/x向下取整的路标数,但没余数则多出一个
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<map>
#include<set>
#include<queue>
#include<cstring>
#include<math.h>
#include<map>
#include<vector>
#include<stack>
#define ms(x,y) memset(x,y,sizeof x);
#define YES cout<<"YES"<<'\n';
#define NO cout<<"NO"<<'\n';
#define endl cout<<'\n';
typedef long long ll;
const ll maxn=2e5+10,inf = 1e18 ;
const ll mod = 1e9 + 7;
using namespace std;
int a[maxn];
int L, n, k;
bool check(int x) {
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
int y = a[i] - a[i - 1];
if (y > x) {
cnt += (y)/x;
if (y % x == 0) {
cnt--;
}
}
}
return cnt <= k;
}
void solve(){
cin >> L >> n >> k;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> a[i];
}
int l = 1, r = L;
while (l <= r) {
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if (check(mid)) {
r = mid-1;
}
else {
l = mid +1;
}
}
cout << l << '\n';
}
signed main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
int t=1;
//cin >> t;
while (t--) {
solve();
}
}【算法2-1】前缀和、差分与离散化(上)
AcWing 802. 区间和

思路:对于操作的位置x,和查询的位置l,r值域大,个数较少,于是离散化,
之后二分映射找到离散化后的操作位置+c,前缀和处理,对于询问也同样二分映射找到离散化后的询问位置查询,
对于查询有点像离线操作,这道题在ACW
总结:在数据值域很大,但个数较少的时候,可以使用离散化,如果使用map会爆内存,
离散化的本质还是映射,将值域间隔大的点映射到间隔数组,无论是对查询,还是操作都会节省时间和空间要求,这道题感觉很典型
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<map>
#include<set>
#include<queue>
#include<cstring>
#include<math.h>
#include<map>
#include<vector>
#include<stack>
#define ms(x,y) memset(x,y,sizeof x);
#define YES cout<<"YES"<<'\n';
#define NO cout<<"NO"<<'\n';
#define endl cout<<'\n';
typedef long long ll;
const ll maxn=2e5+10,inf = 1e18 ;
const ll mod = 1e9 + 7;
using namespace std;
int a[maxn];
int Hash[maxn<<1];
int s[maxn];
int sum[maxn];
vector<pair<int, int>>v; //操作
vector<pair<int, int>>v1; //询问
void solve(){
int n,m;
cin >> n>>m;
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
int x, c;
cin >> x >> c;
v.push_back({ x,c }); //操作离线
Hash[++cnt] = x; //离散
}
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
int l, r;
cin >> l >> r;
v1.push_back({ l,r }); //查询离线
Hash[++cnt] = l;
Hash[++cnt] = r;
}
sort(Hash + 1, Hash + 1 + cnt);
auto k = unique(Hash, Hash + 1 + cnt);
for (auto x : v) { //执行操作
int y = lower_bound(Hash + 1, Hash + 1 + cnt, x.first) - Hash; //找到离散化后的操作位置
a[y] += x.second;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= cnt; i++) {
a[i] += a[i - 1];
}
for (auto x : v1) {
int l= lower_bound(Hash + 1, Hash + 1 + cnt, x.first) - Hash;
int r = lower_bound(Hash + 1, Hash + 1 + cnt, x.second) - Hash;
cout << a[r] - a[l - 1] << '\n';
}
}
signed main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
int t=1;
//cin >> t;
while (t--) {
solve();
}
}
扩展:P1496 火烧赤壁
思路:同样是数据值域很大,但个数较少,于是离散化,在离散化后的数组操作,同上,一定注意左开右闭,像我没注意到调了好久
总结:离散化的套路很明显,数据值域很大,但个数较少,把原数组操作转化到离散数组的操作,映射即可
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<map>
#include<set>
#include<queue>
#include<cstring>
#include<math.h>
#include<map>
#include<vector>
#include<stack>
#define ms(x,y) memset(x,y,sizeof x);
#define YES cout<<"YES"<<'\n';
#define NO cout<<"NO"<<'\n';
#define endl cout<<'\n';
#define int long long
typedef long long ll;
const ll maxn = 2e5 + 10, inf = 1e18;
const ll mod = 1e9 + 7;
using namespace std;
int Hash[maxn << 1];
vector<pair<int, int>>v; //操作
int flag[maxn];
void solve() {
int n;
cin >> n;
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
int l, r;
cin >> l >> r;
v.push_back({ l,r }); //操作离线
Hash[++cnt] = l;
Hash[++cnt] = r;
}
cnt++;
sort(Hash + 1, Hash + 1 + cnt);
for (auto x : v) { //执行操作
int l = lower_bound(Hash + 1, Hash + 1 + cnt, x.first) - Hash; //找到离散化后的操作位置
int r = lower_bound(Hash + 1, Hash + 1 + cnt, x.second) - Hash;
for (int i = l; i <= r-1; i++) { //左闭右开
flag[i]++;
}
}
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= cnt; i++) {
if (flag[i]) {
ans += Hash[i + 1] - Hash[i];
}
}
cout << ans << '\n';
}
signed main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
int t = 1;
//cin >> t;
while (t--) {
solve();
}
}
P1955[NOI2015] 程序自动分析

思路:同样注意到i,j值域很大,但个数较小,离散化,判定满不满足条件,可以并查集判定,这道题还是挺简单的
总结:通过前几个题目可以发现,把原数组操作转化到离散数组的操作,操作是离线的
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<map>
#include<set>
#include<queue>
#include<cstring>
#include<math.h>
#include<map>
#include<vector>
#include<stack>
#define ms(x,y) memset(x,y,sizeof x);
#define YES cout<<"YES"<<'\n';
#define NO cout<<"NO"<<'\n';
#define endl cout<<'\n';
typedef long long ll;
const ll maxn=2e6+10,inf = 1e18 ;
const ll mod = 1e9 + 7;
using namespace std;
int t, n, f[maxn], Hash[maxn];
struct node {
int x, y, e;
}a[maxn];
bool cmp(node a, node b) {
return a.e > b.e;
}
int find(int x) {
return f[x] == x ? x : f[x] = find(f[x]);
} //并查集
void solve(){
int cnt = 0;
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> a[i].x >> a[i].y >> a[i].e;
Hash[++cnt] = a[i].x;
Hash[++cnt] = a[i].y;
}
sort(Hash, Hash + cnt);//排序
int len = unique(Hash, Hash + cnt) - Hash-1; //去重
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
a[i].x = lower_bound(Hash, Hash + len, a[i].x) - Hash;
a[i].y = lower_bound(Hash, Hash + len, a[i].y) - Hash;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= len; ++i) {
f[i] = i;
}
sort(a + 1, a + n + 1, cmp); //按e排序
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
int r1 = find(a[i].x);
int r2 = find(a[i].y);
if (a[i].e) {
f[r1] = r2;
}
else if (r1 == r2) {
NO;
return;
}
}
YES;
}
int main() {
cin >> t;
while (t--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}这周任务安排
除cf,牛客重现赛补题,坚持对以前的算法,数据结构进行横向刷题,这周为【算法2-1】前缀和、差分与离散化(上),【算法2-3】分治与倍增
总结
通过对以前的算法进行巩固,发现了许多套路,像二分的最大值的最小化,最小值的最大化,离散的数据值域很大,但个数较少,这都是以前没有发现的,还有对题目的总结,扩展也很重要,做题的时候切忌浮躁,一定好好好琢磨背后考察的知识点,另外就是与师傅的沟通不够









![[数字图像处理]第五章 图像复原与重建](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/37d56fb609e5463fb0f3c8e72972f97e.png)