目录
一. 归并排序的思想
1.归并排序的过程
2. 两种实现方式:
2.1 非递归实现方式
2.2递归实现方式
二. 归并排序的代码实现
1. 数组的辅助空间及初始化
2. 核心代码
2.1每个小组的基本设置
2.2小组内部的排序
三. 代码展示
四. 运行结果
五. 总结
一. 归并排序的思想
1.归并排序的过程
归并排序与之前学习的基于交换、选择等排序的思想不一样,“归并”的含义是将两个或者两个以上的有序表合并成一个新的有序表。假定排序表含有n个记录,则可将其视为n个有序的子表,每个子表的长度为1,然后两两归并,得到n/2个长度为2或1的有序表;继续两两归并......如此重复,直到合成一个长度为n的有序表为止,这种排序方法称为2路归并。

2. 两种实现方式:
2.1 非递归实现方式
由于还可以直接设置变量的方式,直接实现排序(没有递归,这里可以类比树的先序遍历——递归和非递归两种实现方式),只不过这里就是将数组直接分成小块,然后排序,最后直接组合,没有递归排序那种向下分的过程。
2.2递归实现方式
这里的递归实现方式十分简单,类似于快速排序里面的分治思想,将一个数组序列分成一半然后再次调用自身函数,再将这个数组序列的一半再分为一半,直到达到临界条件,最后将这些分散的数字序列合并起来。
二. 归并排序的代码实现
1. 数组的辅助空间及初始化
tempRow:用来控制现在进行到哪个小组(1,2,3,4...)
tempGroups:小组的个数
tempNextRow,tempNextRow:当前使用的哪个辅助数组
tempGroupNumber:遍历循环tempGroups
tempFirstStart, tempSecondStart, tempSecondEnd:同一个小组内第一个序列应该开始的位置,第二个序列应该开始的位置,第二个序列结束的位置(由于第一个序列结束的位置是第二个序列开始位置减一,故不设置tempFirstStartEnd)
tempFirstIndex, tempSecondIndex:相当于遍历完同一个小组内的临时变量
tempNumCopied:控制复制到辅助空间的数
这一段代码基本上是初始化,接着构建辅助空间1,辅助空间2,将原本的数组序列复制到辅助空间1。
// Step 1. Allocate space.
int tempRow; // The current row
int tempGroups; // Number of groups
int tempActualRow; // Only 0 or 1
int tempNextRow = 0;
int tempGroupNumber;
int tempFirstStart, tempSecondStart, tempSecondEnd;
int tempFirstIndex, tempSecondIndex;
int tempNumCopied;
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
System.out.print(data[i]);
} // Of for i
System.out.println();
DataNode[][] tempMatrix = new DataNode[2][length];
// Step 2. Copy data.
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
tempMatrix[0][i] = data[i];
} // Of for i2. 核心代码
2.1每个小组的基本设置
这里首先引入tempSize控制数字序列的分组(1,2,4,8...);现在进行到第tempRow号组;tempActualRow,tempNextRow表示现在的辅助空间;接着计算小组的个数(在tempSize的情况下)
tempRow = -1;
for (int tempSize = 1; tempSize <= length; tempSize *= 2) {
// Reuse the space of the two rows.
tempRow++;
System.out.println("Current row = " + tempRow);
tempActualRow = tempRow % 2;
tempNextRow = (tempRow + 1) % 2;
tempGroups = length / (tempSize * 2);
if (length % (tempSize * 2) != 0) {
tempGroups++;
} // Of if
System.out.println("tempSize = " + tempSize + ", numGroups = " + tempGroups);
2.2小组内部的排序
tempGroupNumber记录现在排到第几号小组,tempFirstStart记录当前小组的第一个序列的开始位,tempSecondStart记录当前小组的第二个序列的开始位;这里判断tempSecondStart是否越界,若越界说明这个小组只有第一个数字序列,直接复制到辅助空间;tempSecondEnd记录同一个小组的结束位。
记录完成开始位置和结束位置,对同一个小组的数据进行排序,若第一个序列的tempFirstIndex位置数据≤第二个序列tempSecondIndex位置数据,复制tempFirstIndex位置数据到辅助空间,同样当tempFirstIndex位置数据>第二个序列tempSecondIndex位置数据,复制tempSecondIndex位置数据到辅助空间,直到一方计算完毕,将另一方的所有数据复制到辅助空间。
最终for (int tempSize = 1; tempSize <= length; tempSize *= 2) 循环结束,排序完成。
for (tempGroupNumber = 0; tempGroupNumber < tempGroups; tempGroupNumber++) {
tempFirstStart = tempGroupNumber * tempSize * 2;
tempSecondStart = tempGroupNumber * tempSize * 2 + tempSize;
if (tempSecondStart > length - 1) {
// Copy the first part.
for (int i = tempFirstStart; i < length; i++) {
tempMatrix[tempNextRow][i] = tempMatrix[tempActualRow][i];
} // Of for i
continue;
} // Of if
tempSecondEnd = tempGroupNumber * tempSize * 2 + tempSize * 2 - 1;
if (tempSecondEnd > length - 1) {
tempSecondEnd = length - 1;
} // Of if
System.out
.println("Trying to merge [" + tempFirstStart + ", " + (tempSecondStart - 1)
+ "] with [" + tempSecondStart + ", " + tempSecondEnd + "]");
tempFirstIndex = tempFirstStart;
tempSecondIndex = tempSecondStart;
tempNumCopied = 0;
while ((tempFirstIndex <= tempSecondStart - 1)
&& (tempSecondIndex <= tempSecondEnd)) {
if (tempMatrix[tempActualRow][tempFirstIndex].key <= tempMatrix[tempActualRow][tempSecondIndex].key) {
tempMatrix[tempNextRow][tempFirstStart
+ tempNumCopied] = tempMatrix[tempActualRow][tempFirstIndex];
tempFirstIndex++;
System.out.println("copying " + tempMatrix[tempActualRow][tempFirstIndex]);
} else {
tempMatrix[tempNextRow][tempFirstStart
+ tempNumCopied] = tempMatrix[tempActualRow][tempSecondIndex];
System.out.println("copying " + tempMatrix[tempActualRow][tempSecondIndex]);
tempSecondIndex++;
} // Of if
tempNumCopied++;
} // Of while
while (tempFirstIndex <= tempSecondStart - 1) {
tempMatrix[tempNextRow][tempFirstStart
+ tempNumCopied] = tempMatrix[tempActualRow][tempFirstIndex];
tempFirstIndex++;
tempNumCopied++;
} // Of while
while (tempSecondIndex <= tempSecondEnd) {
tempMatrix[tempNextRow][tempFirstStart
+ tempNumCopied] = tempMatrix[tempActualRow][tempSecondIndex];
tempSecondIndex++;
tempNumCopied++;
} // Of while
} // Of for groupNumber三. 代码展示
主类:
package Day_49;
public class demo1 {
/**
*********************
* The entrance of the program.
*
* @param args Not used now.
*********************
*/
public static void main(String args[]) {
// System.out.println("\r\n-------sequentialSearchTest-------");
int []paraKeyArray;
paraKeyArray=new int[]{11,2,3};
String[] paraContentArray = new String[]{"121","21","324"};
// System.out.println(paraKeyArray.length);
DataArray test=new DataArray(paraKeyArray,paraContentArray);
// test.insertionSort();
// System.out.println("Result\r\n" + test);
test.mergeSortTest();
}// Of main
}调用类:
package Day_49;
/**
* Data array for searching and sorting algorithms.
*
* @author Fan Min minfanphd@163.com.
*/
public class DataArray {
/**
* An inner class for data nodes. The text book usually use an int value to
* represent the data. I would like to use a key-value pair instead.
*/
class DataNode {
/**
* The key.
*/
int key;
/**
* The data content.
*/
String content;
/**
*********************
* The first constructor.
*********************
*/
DataNode(int paraKey, String paraContent) {
key = paraKey;
content = paraContent;
}// Of the first constructor
/**
*********************
* Overrides the method claimed in Object, the superclass of any class.
*********************
*/
public String toString() {
return "(" + key + ", " + content + ") ";
}// Of toString
}// Of class DataNode
/**
* The data array.
*/
DataNode[] data;
/**
* The length of the data array.
*/
int length;
/**
*********************
* The first constructor.
*
* @param paraKeyArray The array of the keys.
* @param paraContentArray The array of contents.
*********************
*/
public DataArray(int[] paraKeyArray, String[] paraContentArray) {
length = paraKeyArray.length;
data = new DataNode[length];
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
data[i] = new DataNode(paraKeyArray[i], paraContentArray[i]);
} // Of for i
}// Of the first constructor
/**
*********************
* Overrides the method claimed in Object, the superclass of any class.
*********************
*/
public String toString() {
String resultString = "I am a data array with " + length + " items.\r\n";
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
resultString += data[i] + " ";
} // Of for i
return resultString;
}// Of toString
/**
*********************
* Sequential search. Attention: It is assume that the index 0 is NOT used.
*
* @param paraKey The given key.
* @return The content of the key.
*********************
*/
public String sequentialSearch(int paraKey) {
data[0].key = paraKey;
int i;
// Note that we do not judge i >= 0 since data[0].key = paraKey.
// In this way the runtime is saved about 1/2.
// This for statement is equivalent to
//for (i = length - 1; data[i].key != paraKey; i--);
for (i = length - 1; data[i].key != paraKey; i--) {
;
}//Of for i
return data[i].content;
}// Of sequentialSearch
/**
*********************
* Test the method.
*********************
*/
public static void sequentialSearchTest() {
int[] tempUnsortedKeys = { -1, 5, 3, 6, 10, 7, 1, 9 };
String[] tempContents = { "null", "if", "then", "else", "switch", "case", "for", "while" };
DataArray tempDataArray = new DataArray(tempUnsortedKeys, tempContents);
System.out.println(tempDataArray);
System.out.println("Search result of 10 is: " + tempDataArray.sequentialSearch(10));
System.out.println("Search result of 5 is: " + tempDataArray.sequentialSearch(5));
System.out.println("Search result of 4 is: " + tempDataArray.sequentialSearch(4));
}// Of sequentialSearchTest
/**
*********************
* Binary search. Attention: It is assume that keys are sorted in ascending
* order.
*
* @param paraKey The given key.
* @return The content of the key.
*********************
*/
public String binarySearch(int paraKey) {
int tempLeft = 0;
int tempRight = length - 1;
int tempMiddle = (tempLeft + tempRight) / 2;
while (tempLeft <= tempRight) {
tempMiddle = (tempLeft + tempRight) / 2;
if (data[tempMiddle].key == paraKey) {
return data[tempMiddle].content;
} else if (data[tempMiddle].key <= paraKey) {
tempLeft = tempMiddle + 1;
} else {
tempRight = tempMiddle - 1;
}
} // Of while
// Not found.
return "null";
}// Of binarySearch
/**
*********************
* Test the method.
*********************
*/
public static void binarySearchTest() {
int[] tempSortedKeys = { 1, 3, 5, 6, 7, 9, 10 };
String[] tempContents = { "if", "then", "else", "switch", "case", "for", "while" };
DataArray tempDataArray = new DataArray(tempSortedKeys, tempContents);
System.out.println(tempDataArray);
System.out.println("Search result of 10 is: " + tempDataArray.binarySearch(10));
System.out.println("Search result of 5 is: " + tempDataArray.binarySearch(5));
System.out.println("Search result of 4 is: " + tempDataArray.binarySearch(4));
}// Of binarySearchTest
/**
*********************
* The entrance of the program.
*
* @param args Not used now.
*********************
*/
public static void main(String args[]) {
System.out.println("\r\n-------sequentialSearchTest-------");
sequentialSearchTest();
System.out.println("\r\n-------binarySearchTest-------");
binarySearchTest();
}// Of main
//-------------------------------------------
/**
*********************
* Merge sort. Results are stored in the member variable data.
*********************
*/
public void mergeSort() {
// Step 1. Allocate space.
int tempRow; // The current row
int tempGroups; // Number of groups
int tempActualRow; // Only 0 or 1
int tempNextRow = 0;
int tempGroupNumber;
int tempFirstStart, tempSecondStart, tempSecondEnd;
int tempFirstIndex, tempSecondIndex;
int tempNumCopied;
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
System.out.print(data[i]);
} // Of for i
System.out.println();
DataNode[][] tempMatrix = new DataNode[2][length];
// Step 2. Copy data.
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
tempMatrix[0][i] = data[i];
} // Of for i
// Step 3. Merge. log n rounds
tempRow = -1;
for (int tempSize = 1; tempSize <= length; tempSize *= 2) {
// Reuse the space of the two rows.
tempRow++;
System.out.println("Current row = " + tempRow);
tempActualRow = tempRow % 2;
tempNextRow = (tempRow + 1) % 2;
tempGroups = length / (tempSize * 2);
if (length % (tempSize * 2) != 0) {
tempGroups++;
} // Of if
System.out.println("tempSize = " + tempSize + ", numGroups = " + tempGroups);
for (tempGroupNumber = 0; tempGroupNumber < tempGroups; tempGroupNumber++) {
tempFirstStart = tempGroupNumber * tempSize * 2;
tempSecondStart = tempGroupNumber * tempSize * 2 + tempSize;
if (tempSecondStart > length - 1) {
// Copy the first part.
for (int i = tempFirstStart; i < length; i++) {
tempMatrix[tempNextRow][i] = tempMatrix[tempActualRow][i];
} // Of for i
continue;
} // Of if
tempSecondEnd = tempGroupNumber * tempSize * 2 + tempSize * 2 - 1;
if (tempSecondEnd > length - 1) {
tempSecondEnd = length - 1;
} // Of if
System.out.println("Trying to merge [" + tempFirstStart + ", " + (tempSecondStart - 1)
+ "] with [" + tempSecondStart + ", " + tempSecondEnd + "]");
tempFirstIndex = tempFirstStart;
tempSecondIndex = tempSecondStart;
tempNumCopied = 0;
while ((tempFirstIndex <= tempSecondStart - 1)
&& (tempSecondIndex <= tempSecondEnd)) {
if (tempMatrix[tempActualRow][tempFirstIndex].key <= tempMatrix[tempActualRow][tempSecondIndex].key) {
tempMatrix[tempNextRow][tempFirstStart
+ tempNumCopied] = tempMatrix[tempActualRow][tempFirstIndex];
tempFirstIndex++;
System.out.println("copying " + tempMatrix[tempActualRow][tempFirstIndex]);
} else {
tempMatrix[tempNextRow][tempFirstStart
+ tempNumCopied] = tempMatrix[tempActualRow][tempSecondIndex];
System.out.println("copying " + tempMatrix[tempActualRow][tempSecondIndex]);
tempSecondIndex++;
} // Of if
tempNumCopied++;
} // Of while
while (tempFirstIndex <= tempSecondStart - 1) {
tempMatrix[tempNextRow][tempFirstStart
+ tempNumCopied] = tempMatrix[tempActualRow][tempFirstIndex];
tempFirstIndex++;
tempNumCopied++;
} // Of while
while (tempSecondIndex <= tempSecondEnd) {
tempMatrix[tempNextRow][tempFirstStart
+ tempNumCopied] = tempMatrix[tempActualRow][tempSecondIndex];
tempSecondIndex++;
tempNumCopied++;
} // Of while
} // Of for groupNumber
System.out.println("Round " + tempRow);
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
System.out.print(tempMatrix[tempNextRow][i] + " ");
} // Of for j
System.out.println();
} // Of for tempStepSize
data = tempMatrix[tempNextRow];
}// Of mergeSort
/**
*********************
* Test the method.
*********************
*/
public static void mergeSortTest() {
int[] tempUnsortedKeys = { 5, 3, 6, 10, 7, 1, 9 };
String[] tempContents = { "if", "then", "else", "switch", "case", "for", "while" };
DataArray tempDataArray = new DataArray(tempUnsortedKeys, tempContents);
System.out.println(tempDataArray);
tempDataArray.mergeSort();
System.out.println(tempDataArray);
}// Of mergeSortTest
}// Of class DataArray
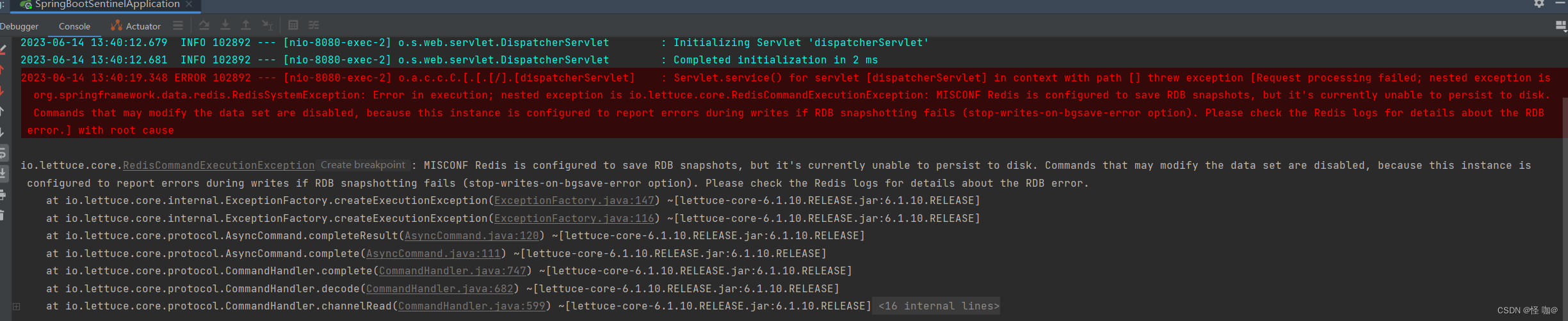
四. 运行结果

五. 总结
这部分代码变量相当多,虽然多,但是必须弄懂每个变量指代的含义,至于一个变量的含义首先可以根据闵来师变量的名字来理解,其次归并排序的过程一定要理解;只有这两者同时具备才是看懂这部分代码的第一步(这里举个例子tempSize这个变量是在每次循环乘2,那么总共它就循环logn次,这不就是归并的分治深度吗?所以我才将tempSize理解为归并循环的次数)。其次这里的代码不像递归排序的代码,递归排序的代码很简单,就几行,它没有许多的变量,只是反复调用自身即可。
总而言之,这部分代码我个人的看法是①首先把归并排序思想过程要理解到位,②用人脑模拟计算机运行代码的过程,③闵老师的代码名字要好好理解。这样这部分代码就可以解决了。




![[AI语音克隆] 5秒内克隆您的声音并生成任意语音内容](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/6ba6098992f54511a193d114d7083c6d.png)