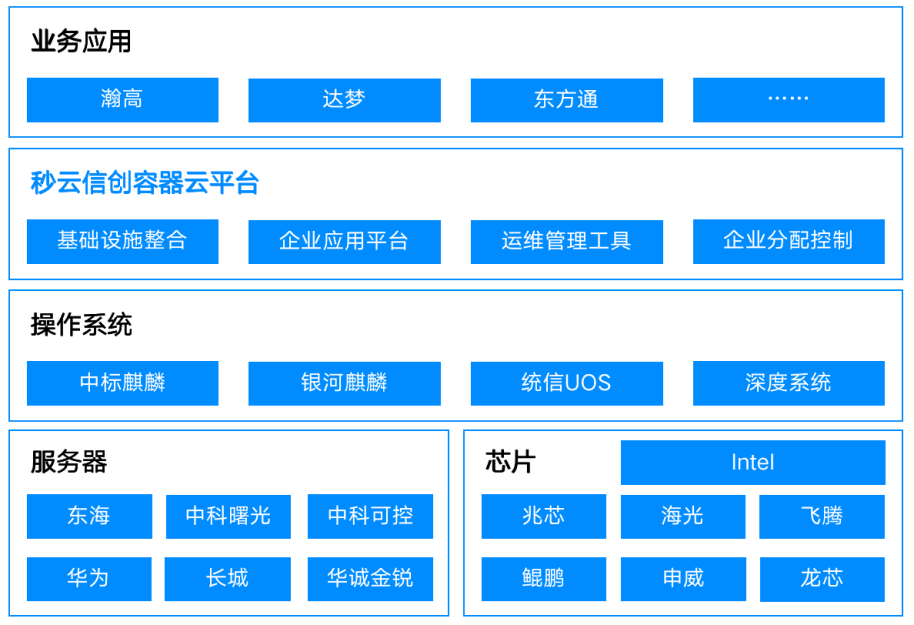
说明
- 本文基于 kafka 2.7 编写。
- @author JellyfishMIX - github / blog.jellyfishmix.com
- LICENSE GPL-2.0
java NIO 组件
几个 java NIO 的组件。
- Buffer: 缓冲区。这是一个接口,kafka 用它的 ByteBuffer 实现类,配合 SocketChannel 实现读写操作。读的时候,调用 channel#read(buffer) 把 SocketChannel 的数据读到 ByteBuffer 内。写的时候,调用 channel.write(buffer) 把 Buffer 中的数据写到 SocketChannel 内。
- SocketChannel: 网络连接通道, byte 数据的读写都发生在这个通道上,包括从通道中读出数据, 将数据写入通道。
- SelectionKey: 选择键。每个 SocketChannel 向 Selector 注册标识时,都会创建一个 SelectionKey。SelectionKey 里可以定义 Selector 监听 SocketChannel 的事件,包括连接、读、写事件(SelectionKey#OP_CONNECT, OP_READ, OP_WRITE)。
- Selector: 选择器,用来监听注册的 SelectionKey 关注的事件。
本文涉及 java NIO 相关内容, 推荐先阅读 ByteBuffer 相关内容。
kafka 对 java NIO 组件的封装
- Selector(Kafka 自己的 Selector 类): 对 NIO 中 Selector 的封装。
- TransportLayer: 对 NIO 中 SocketChannel 的封装。TransportLayer 是一个接口, 实现类有 PlaintextTransportLayer 和 SslTransportLayer,其中,PlaintextTransportLayer 是明文传输的实现,SslTransportLayer 是 SSL 加密传输的实现。本文只涉及 PlaintextTransportLayer。
- NetworkReceive: 对 NIO 中读 Buffer 的封装,用来缓存接收的数据。
- NetworkSend: 对 NIO 中写 Buffer 的封装,用来缓存发送的数据。
- KafkaChannel: 把 TransportLayer, NetworkReceive 和 NetworkSend 又做了一次封装,隐藏了底层组件的细节。
- Kafka 对 NIO 中的 SelectionKey 没有封装,直接使用。
kafka 封装的 NIO 组件关系
- Selector 监听到客户端的读写事件后,会获取绑定在 SelectionKey 上的 KafkaChannel。
- KafkaChannel 会调用 TransportLayer 进行读写操作, TransportLayer 会调用 SocketChannel 进行读写操作, 完成数据的发送。数据的接收流程类似。
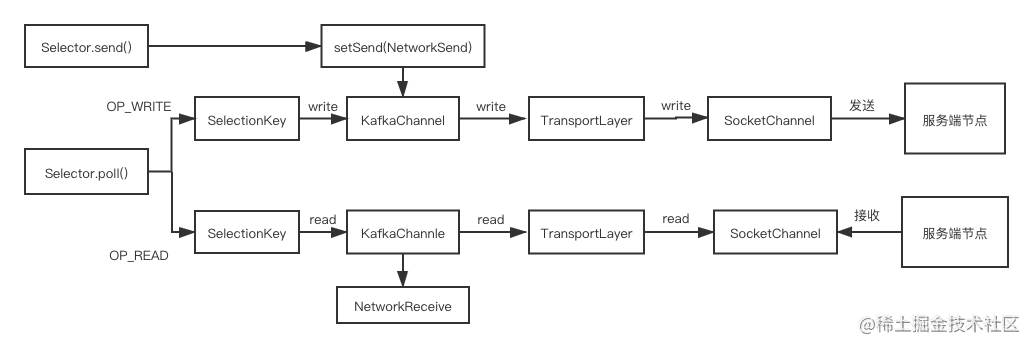
TransportLayer
TransportLayer 是对 NIO 中 SocketChannel 的封装。它的实现类有 2 个:
- PlaintextTransportLayer, 明文传输的实现。
- SslTransportLayer 类, SSL 加密传输的实现。
本文只涉及 PlaintextTransportLayer。
PlaintextTransportLayer
PlaintextTransportLayer#finishConnect 方法 – 完成网络连接
org.apache.kafka.common.network.PlaintextTransportLayer#finishConnect
- 调用 SocketChannel#finishConnect 方法,返回连接是否已经建立。
- 如果连接已经建立,则取消对连接事件的监听,增加对读事件的监听。
@Override
public boolean finishConnect() throws IOException {
// 调用 SocketChannel#finishConnect 方法,返回连接是否已经建立
boolean connected = socketChannel.finishConnect();
// 如果连接已经建立,则取消对连接事件的监听,增加对读事件的监听
if (connected)
key.interestOps(key.interestOps() & ~SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT | SelectionKey.OP_READ);
return connected;
}
PlaintextTransportLayer#read 方法 – 读取数据
org.apache.kafka.common.network.PlaintextTransportLayer#read(java.nio.ByteBuffer)
把 SocketChannel 中的数据读取到 ByteBuffer 中。
@Override
public int read(ByteBuffer dst) throws IOException {
// 把 SocketChannel 中的数据读取到 ByteBuffer 中
return socketChannel.read(dst);
}
PlaintextTransportLayer#write – 写入数据
org.apache.kafka.common.network.PlaintextTransportLayer#write(java.nio.ByteBuffer)
把 ByteBuffer 中的数据写入到 SocketChannel 中。
@Override
public int write(ByteBuffer src) throws IOException {
// 把 ByteBuffer 中的数据写入到 SocketChannel 中
return socketChannel.write(src);
}
NetworkReceive
- java NIO 一次读写不一定读写完数据,这样需要判断读写是否完成,没有读写完的数据需要继续执行读写操作。
- 这样的操作较为繁琐,对调用方不友好。于是 kafka 把 ByteBuffer 进行了封装,用于读的 Buffer 封装成 NetworkReceive, 用于写的 Buffer 封装成 NetworkSend。
NetworkReceive 的属性
/**
* channelId
*/
private final String source;
/**
* size 是固定大小的 4 byte ByteBuffer, kafka 传输数据时, 约定把要传输数据的长度放在最开头 4 byte, size 只用来接收这 4 byte 的长度信息
*/
private final ByteBuffer size;
/**
* 能接收的最大消息
*/
private final int maxSize;
/**
* 内存池
*/
private final MemoryPool memoryPool;
/**
* 记录真正数据内容长度信息大小
*/
private int requestedBufferSize = -1;
/**
* buffer 用来承载真正的数据内容, 即 4 byte 长度数据后的内容
*/
private ByteBuffer buffer;
NetworkReceive#readFrom 方法 – 把 channel 中的数据读到 ByteBuffer 中
org.apache.kafka.common.network.NetworkReceive#readFrom
- 注意 size 的作用, size 是固定大小的 4 byte ByteBuffer, kafka 传输数据时, 约定把要传输数据的长度放在最开头 4 byte, size 只用来接收这 4 byte 的长度信息。
- 判断 size 是否有剩余空间, 有剩余空间则从 channel 中读取数据至 size 中。
- 如果从 channel 中读取数据后, size 没有剩余空间了, 说明长度信息读取完了(因为长度信息总共只占 4 byte, 读取后刚好把 size 占满)。
- 前 4 个 byte 存放了数据的长度, 以 int 类型获取。
- 针对本次通过 channel 传输数据的长度做校验。
- 从 channel 中读取真正的数据内容, 即 4 byte 长度数据后的内容, buffer 用来承载真正的数据内容。
- 给 buffer 分配 size 中记录的长度信息大小的内存空间。
- 把 channel 中的数据读到 buffer 中。维护读取的字节大小数。
/**
* 把 channel 中的数据读到 ByteBuffer 中
*/
public long readFrom(ScatteringByteChannel channel) throws IOException {
// 维护读取的字节大小数
int read = 0;
// 注意 size 的作用, size 是固定大小的 4 byte ByteBuffer, kafka 传输数据时, 约定把要传输数据的长度放在最开头 4 byte, size 只用来接收这 4 byte 的长度信息
// 判断 size 是否有剩余空间, 有剩余空间则从 channel 中读取数据至 size 中
if (size.hasRemaining()) {
int bytesRead = channel.read(size);
if (bytesRead < 0)
throw new EOFException();
// 维护读取的字节大小数
read += bytesRead;
// 如果从 channel 中读取数据后, size 没有剩余空间了, 说明长度信息读取完了(因为长度信息总共只占 4 byte, 读取后刚好把 size 占满)
if (!size.hasRemaining()) {
// ByteBuffer#position 置 0, 从头开始读取
size.rewind();
// 前 4 个 byte 存放了数据的长度, 以 int 类型获取
int receiveSize = size.getInt();
// 针对本次通过 channel 传输数据的长度做校验
if (receiveSize < 0)
throw new InvalidReceiveException("Invalid receive (size = " + receiveSize + ")");
if (maxSize != UNLIMITED && receiveSize > maxSize)
throw new InvalidReceiveException("Invalid receive (size = " + receiveSize + " larger than " + maxSize + ")");
requestedBufferSize = receiveSize; //may be 0 for some payloads (SASL)
if (receiveSize == 0) {
buffer = EMPTY_BUFFER;
}
}
}
// 下面要从 channel 中读取真正的数据内容, 即 4 byte 长度数据后的内容, buffer 用来承载真正的数据内容
// 给 buffer 分配 size 中记录的长度信息大小的内存空间
if (buffer == null && requestedBufferSize != -1) { //we know the size we want but havent been able to allocate it yet
buffer = memoryPool.tryAllocate(requestedBufferSize);
if (buffer == null)
log.trace("Broker low on memory - could not allocate buffer of size {} for source {}", requestedBufferSize, source);
}
// 把 channel 中的数据读到 buffer 中
if (buffer != null) {
int bytesRead = channel.read(buffer);
if (bytesRead < 0)
throw new EOFException();
// 维护读取的字节大小数
read += bytesRead;
}
return read;
}
NetworkSend
层次关系
NetworkSend extends ByteBufferSend, ByteBufferSend implements Send
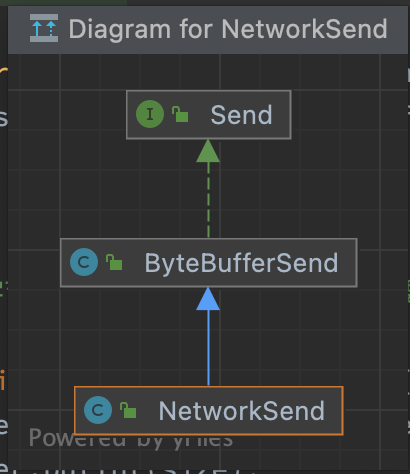
ByteBufferSend#writeTo 方法 – 把 ByteBuffer 中的数据写入 SocketChannel
org.apache.kafka.common.network.ByteBufferSend#writeTo
- 把 ByteBuffer 中的数据写入 SocketChannel, 返回写入的字节数。
- 维护还剩多少字节没有写进 SocketChannel。
/**
* 把 ByteBuffer 中的数据写入 SocketChannel
*/
@Override
public long writeTo(GatheringByteChannel channel) throws IOException {
// 把 ByteBuffer 中的数据写入 SocketChannel, 返回写入的字节数
long written = channel.write(buffers);
if (written < 0)
throw new EOFException("Wrote negative bytes to channel. This shouldn't happen.");
// 维护还剩多少字节没有写进 SocketChannel
remaining -= written;
pending = TransportLayers.hasPendingWrites(channel);
return written;
}
NetworkSend#sizeBuffer 方法 – 分配 4 个字节的 sizeBuffer
org.apache.kafka.common.network.NetworkSend#sizeBuffer
分配 4 个字节的 sizeBuffer, 用来存储要发送的数据长度
/**
* 分配 4 个字节的 sizeBuffer, 用来存储要发送的数据长度
*/
private static ByteBuffer sizeBuffer(int size) {
ByteBuffer sizeBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(4);
sizeBuffer.putInt(size);
sizeBuffer.rewind();
return sizeBuffer;
}
KafkaChannel
org.apache.kafka.common.network.KafkaChannel
KafkaChannel#setSend 方法-- 正式发送请求前设置 NetworkSend
org.apache.kafka.common.network.KafkaChannel#setSend
正式发送请求前设置 NetworkSend(用于发送的 byteBuffer), 并让 SelectionKey 关注写事件。
/**
* 正式发送请求前设置 NetworkSend(用于发送的 byteBuffer), 并让 SelectionKey 关注写事件
*/
public void setSend(Send send) {
if (this.send != null)
throw new IllegalStateException("Attempt to begin a send operation with prior send operation still in progress, connection id is " + id);
this.send = send;
// SelectionKey 关注写事件
this.transportLayer.addInterestOps(SelectionKey.OP_WRITE);
}
KafkaChannel#write – 发送数据
org.apache.kafka.common.network.KafkaChannel#write
把 NetworkSend 中的数据写入 SocketChannel。
/**
* 把 NetworkSend 中的数据发送出去
*/
public long write() throws IOException {
if (send == null)
return 0;
midWrite = true;
// 把 NetworkSend 中的数据写入 SocketChannel
return send.writeTo(transportLayer);
}
KafkaChannel#read 方法 – 读取数据
org.apache.kafka.common.network.KafkaChannel#read
- 把 SocketChannel 中的数据读取到 NetworkReceive 中。
- 判断是否读完的条件是 NetworkReceive 里的 size 和 buffer 是否用完, 因为 NetworkReceive 的 size 和 buffer 两个 byteBuffer 的大小,正好是 SocketChannel 中接收到数据的大小。
/**
* 把 SocketChannel 中的数据读取到 NetworkReceive 中
*/
public long read() throws IOException {
if (receive == null) {
receive = new NetworkReceive(maxReceiveSize, id, memoryPool);
}
// 把 SocketChannel 中的数据读取到 NetworkReceive 中, 返回读取信息的字节数
long bytesReceived = receive(this.receive);
// 判断是否读完的条件是 NetworkReceive 里的 size 和 buffer 是否用完, 因为 NetworkReceive 的 size 和 buffer 两个 byteBuffer 的大小,正好是 SocketChannel 中接收到数据的大小
if (this.receive.requiredMemoryAmountKnown() && !this.receive.memoryAllocated() && isInMutableState()) {
//pool must be out of memory, mute ourselves.
mute();
}
return bytesReceived;
}
Selector
Selector#connect – 建立连接
org.apache.kafka.common.network.Selector#connect
- 验证。
- 创建并配置 SocketChannel。
- 包括配置非阻塞模式, 设置长连接, 设置 SO_SNDBUF 和 SO_RCVBUF 的大小。SO_SNDBUF、SO_RCVBUF 表示发送和接收数据缓存的大小。
- 建立一个连接,由于是非阻塞建立连接,方法会直接返回,不一定连接建立完毕。后面会通过 Selector#finishConnect 方法, 连接并确认是否连接成功。
- 将上面创建的 SocketChannel 注册到 nioSelector 上,关注 OP_CONNECT 事件。
@Override
public void connect(String id, InetSocketAddress address, int sendBufferSize, int receiveBufferSize) throws IOException {
// 验证
ensureNotRegistered(id);
// 创建 SocketChannel
SocketChannel socketChannel = SocketChannel.open();
SelectionKey key = null;
try {
// 配置 SocketChannel
configureSocketChannel(socketChannel, sendBufferSize, receiveBufferSize);
// 建立一个连接,由于是非阻塞建立连接,方法会直接返回,不一定连接建立完毕
// 后面会通过 Selector#finishConnect 方法, 连接并确认是否连接成功
boolean connected = doConnect(socketChannel, address);
// 将上面创建的 SocketChannel 注册到 nioSelector 上,关注 OP_CONNECT 事件
key = registerChannel(id, socketChannel, SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT);
// 如果已经连接成功了,则取消对OP_CONNECT的监听
if (connected) {
// OP_CONNECT won't trigger for immediately connected channels
log.debug("Immediately connected to node {}", id);
immediatelyConnectedKeys.add(key);
key.interestOps(0);
}
} catch (IOException | RuntimeException e) {
if (key != null)
immediatelyConnectedKeys.remove(key);
channels.remove(id);
socketChannel.close();
throw e;
}
}
Selector#send – 将 Send 设置到 KafkaChannel 中
org.apache.kafka.common.network.Selector#send
- 获取 channelId 作为 connectionId, 获取连接。
- 把 send 放入 KafkaChannel 里,并让 SelectionKey 关注写事件。
/**
* 将 Send 设置到 KafkaChannel 的 send 字段中,并让 SelectionKey 关注写事件
*/
public void send(Send send) {
// 获取 channelId 作为 connectionId
String connectionId = send.destination();
// 获取连接
KafkaChannel channel = openOrClosingChannelOrFail(connectionId);
// 如果连接是关闭的,就把 connectionId 放到 closingChannels 集合里
if (closingChannels.containsKey(connectionId)) {
// ensure notification via `disconnected`, leave channel in the state in which closing was triggered
this.failedSends.add(connectionId);
} else {
try {
// 把 send 放入 KafkaChannel 里,并让 SelectionKey 关注写事件
channel.setSend(send);
} catch (Exception e) {
// update the state for consistency, the channel will be discarded after `close`
// 异常处理
channel.state(ChannelState.FAILED_SEND);
// ensure notification via `disconnected` when `failedSends` are processed in the next poll
this.failedSends.add(connectionId);
close(channel, CloseMode.DISCARD_NO_NOTIFY);
if (!(e instanceof CancelledKeyException)) {
log.error("Unexpected exception during send, closing connection {} and rethrowing exception {}",
connectionId, e);
throw e;
}
}
}
}
Selector#write 方法 – 调用 KafkaChannel 执行写操作
org.apache.kafka.common.network.Selector#write
- 获取 KafkaChannel 对应的 nodeId。
- 把 NetworkSend 中的数据发送出去。
- 如果发送完成,则返回 send,并取消 SelectionKey 对写事件的关注。
/**
* 调用 KafkaChannel 执行写操作
*/
// package-private for testing
void write(KafkaChannel channel) throws IOException {
// 获取 KafkaChannel 对应的 nodeId
String nodeId = channel.id();
// 把 NetworkSend 中的数据发送出去
long bytesSent = channel.write();
// 如果发送完成,则返回 send,并取消 SelectionKey 对写事件的关注
Send send = channel.maybeCompleteSend();
// We may complete the send with bytesSent < 1 if `TransportLayer.hasPendingWrites` was true and `channel.write()`
// caused the pending writes to be written to the socket channel buffer
if (bytesSent > 0 || send != null) {
long currentTimeMs = time.milliseconds();
if (bytesSent > 0)
this.sensors.recordBytesSent(nodeId, bytesSent, currentTimeMs);
if (send != null) {
this.completedSends.add(send);
this.sensors.recordCompletedSend(nodeId, send.size(), currentTimeMs);
}
}
}
Selector#attemptWrite 方法 – 尝试调用 KafkaChannel 执行写操作
org.apache.kafka.common.network.Selector#attemptWrite
尝试调用 KafkaChannel 执行写操作,需满足如下条件:
- send 不为空。
- KafkaChannel 连接正常。
- SelectionKey 是可写状态。
- 客户端验证没有开启。
/**
* 尝试调用 KafkaChannel 执行写操作
*/
private void attemptWrite(SelectionKey key, KafkaChannel channel, long nowNanos) throws IOException {
/*
* 1. send 不为空
* 2. KafkaChannel 连接正常
* 3. SelectionKey 是可写状态
* 4. 客户端验证没有开启
*/
if (channel.hasSend()
&& channel.ready()
&& key.isWritable()
&& !channel.maybeBeginClientReauthentication(() -> nowNanos)) {
write(channel);
}
}
Selector#attemptRead 方法 – 尝试调用 kafkaChannel 执行读操作
org.apache.kafka.common.network.Selector#attemptRead
- 调用 kafkaChannel 执行读操作, 返回读取的字节数。
- 如果当前 NetworkReceive 读取满了(说明本次请求完整接收了),则将其置空,下次读操作时会创建新的 NetworkReceive 对象。
- 读完的 NetworkReceive 加入 completedReceives 队列中。
/**
* 尝试调用 kafkaChannel 执行读操作
*/
private void attemptRead(KafkaChannel channel) throws IOException {
String nodeId = channel.id();
// 调用 kafkaChannel 执行读操作, 返回读取的字节数
long bytesReceived = channel.read();
if (bytesReceived != 0) {
long currentTimeMs = time.milliseconds();
sensors.recordBytesReceived(nodeId, bytesReceived, currentTimeMs);
madeReadProgressLastPoll = true;
// 如果当前 NetworkReceive 读取满了(说明本次请求完整接收了),则将其置空,下次读操作时会创建新的 NetworkReceive 对象
NetworkReceive receive = channel.maybeCompleteReceive();
if (receive != null) {
// 读完的 NetworkReceive 加入 completedReceives 队列中
addToCompletedReceives(channel, receive, currentTimeMs);
}
}
if (channel.isMuted()) {
outOfMemory = true; //channel has muted itself due to memory pressure.
} else {
madeReadProgressLastPoll = true;
}
}
Selector#poll 方法 – 获取监听的网络 IO 事件并处理
org.apache.kafka.common.network.Selector#poll
- 将上一次 poll 方法的结果全部清除掉。
- nioSelector 线程 selectNow 非阻塞或 select 阻塞地获取 IO 事件。
- 监听到 IO 事件, 或立即连接的集合不为空,或有数据在缓存中,则进行处理。
- 获取有 IO 事件的 SelectionKey 集合。
- 调用处理有 IO 事件的 SelectionKey。
- 处理立即连接的 SelectionKey。
@Override
public void poll(long timeout) throws IOException {
if (timeout < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("timeout should be >= 0");
boolean madeReadProgressLastCall = madeReadProgressLastPoll;
// 将上一次 poll 方法的结果全部清除掉
clear();
boolean dataInBuffers = !keysWithBufferedRead.isEmpty();
if (!immediatelyConnectedKeys.isEmpty() || (madeReadProgressLastCall && dataInBuffers))
timeout = 0;
if (!memoryPool.isOutOfMemory() && outOfMemory) {
//we have recovered from memory pressure. unmute any channel not explicitly muted for other reasons
log.trace("Broker no longer low on memory - unmuting incoming sockets");
for (KafkaChannel channel : channels.values()) {
if (channel.isInMutableState() && !explicitlyMutedChannels.contains(channel)) {
channel.maybeUnmute();
}
}
outOfMemory = false;
}
/* check ready keys */
long startSelect = time.nanoseconds();
// nioSelector 线程 selectNow 非阻塞或 select 阻塞地获取 IO 事件
int numReadyKeys = select(timeout);
long endSelect = time.nanoseconds();
this.sensors.selectTime.record(endSelect - startSelect, time.milliseconds());
// 监听到 IO 事件, 或立即连接的集合不为空,或有数据在缓存中
if (numReadyKeys > 0 || !immediatelyConnectedKeys.isEmpty() || dataInBuffers) {
// 获取有 IO 事件的 SelectionKey 集合
Set<SelectionKey> readyKeys = this.nioSelector.selectedKeys();
// Poll from channels that have buffered data (but nothing more from the underlying socket)
if (dataInBuffers) {
keysWithBufferedRead.removeAll(readyKeys); //so no channel gets polled twice
Set<SelectionKey> toPoll = keysWithBufferedRead;
keysWithBufferedRead = new HashSet<>(); //poll() calls will repopulate if needed
pollSelectionKeys(toPoll, false, endSelect);
}
// Poll from channels where the underlying socket has more data
// 处理有 IO 事件的 SelectionKey
pollSelectionKeys(readyKeys, false, endSelect);
// Clear all selected keys so that they are included in the ready count for the next select
readyKeys.clear();
// 处理立即连接的 SelectionKey
pollSelectionKeys(immediatelyConnectedKeys, true, endSelect);
immediatelyConnectedKeys.clear();
} else {
madeReadProgressLastPoll = true; //no work is also "progress"
}
long endIo = time.nanoseconds();
this.sensors.ioTime.record(endIo - endSelect, time.milliseconds());
// Close channels that were delayed and are now ready to be closed
completeDelayedChannelClose(endIo);
// we use the time at the end of select to ensure that we don't close any connections that
// have just been processed in pollSelectionKeys
maybeCloseOldestConnection(endSelect);
}
Selector#pollSelectionKeys 方法 – 处理监听到的 IO 事件
org.apache.kafka.common.network.Selector#pollSelectionKeys
具体处理监听到的 IO 事件,包括连接事件, 读事件和写事件,处理立即完成的连接。
- 遍历有 IO 事件的 SelectionKey。
- 判断连接是否建立好了, 如果连接已经建立,则取消对连接事件的监听,增加对读事件的监听。
- 连接尚未建立, 跳过当前 SelectionKey。
- 维护 KafkaChannel 的状态。
- 处理读事件()和写事件。
void pollSelectionKeys(Set<SelectionKey> selectionKeys,
boolean isImmediatelyConnected,
long currentTimeNanos) {
// 遍历有 IO 事件的 SelectionKey
for (SelectionKey key : determineHandlingOrder(selectionKeys)) {
KafkaChannel channel = channel(key);
long channelStartTimeNanos = recordTimePerConnection ? time.nanoseconds() : 0;
boolean sendFailed = false;
String nodeId = channel.id();
// register all per-connection metrics at once
sensors.maybeRegisterConnectionMetrics(nodeId);
if (idleExpiryManager != null)
idleExpiryManager.update(nodeId, currentTimeNanos);
try {
/* complete any connections that have finished their handshake (either normally or immediately) */
// 判断连接是否建立好了, 如果连接已经建立,则取消对连接事件的监听,增加对读事件的监听
if (isImmediatelyConnected || key.isConnectable()) {
if (channel.finishConnect()) {
this.connected.add(nodeId);
this.sensors.connectionCreated.record();
SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
log.debug("Created socket with SO_RCVBUF = {}, SO_SNDBUF = {}, SO_TIMEOUT = {} to node {}",
socketChannel.socket().getReceiveBufferSize(),
socketChannel.socket().getSendBufferSize(),
socketChannel.socket().getSoTimeout(),
nodeId);
} else {
// 连接尚未建立, 跳过当前 SelectionKey
continue;
}
}
/* if channel is not ready finish prepare */
if (channel.isConnected() && !channel.ready()) {
channel.prepare();
if (channel.ready()) {
long readyTimeMs = time.milliseconds();
boolean isReauthentication = channel.successfulAuthentications() > 1;
if (isReauthentication) {
sensors.successfulReauthentication.record(1.0, readyTimeMs);
if (channel.reauthenticationLatencyMs() == null)
log.warn(
"Should never happen: re-authentication latency for a re-authenticated channel was null; continuing...");
else
sensors.reauthenticationLatency
.record(channel.reauthenticationLatencyMs().doubleValue(), readyTimeMs);
} else {
sensors.successfulAuthentication.record(1.0, readyTimeMs);
if (!channel.connectedClientSupportsReauthentication())
sensors.successfulAuthenticationNoReauth.record(1.0, readyTimeMs);
}
log.debug("Successfully {}authenticated with {}", isReauthentication ?
"re-" : "", channel.socketDescription());
}
}
// 维护 KafkaChannel 的状态
if (channel.ready() && channel.state() == ChannelState.NOT_CONNECTED)
channel.state(ChannelState.READY);
Optional<NetworkReceive> responseReceivedDuringReauthentication = channel.pollResponseReceivedDuringReauthentication();
responseReceivedDuringReauthentication.ifPresent(receive -> {
long currentTimeMs = time.milliseconds();
addToCompletedReceives(channel, receive, currentTimeMs);
});
//if channel is ready and has bytes to read from socket or buffer, and has no
//previous completed receive then read from it
if (channel.ready() && (key.isReadable() || channel.hasBytesBuffered()) && !hasCompletedReceive(channel)
&& !explicitlyMutedChannels.contains(channel)) {
// 处理读事件
attemptRead(channel);
}
if (channel.hasBytesBuffered()) {
keysWithBufferedRead.add(key);
}
/* if channel is ready write to any sockets that have space in their buffer and for which we have data */
long nowNanos = channelStartTimeNanos != 0 ? channelStartTimeNanos : currentTimeNanos;
try {
// 处理写事件
attemptWrite(key, channel, nowNanos);
} catch (Exception e) {
sendFailed = true;
throw e;
}
/* cancel any defunct sockets */
if (!key.isValid())
close(channel, CloseMode.GRACEFUL);
} catch (Exception e) {
// ...
} finally {
maybeRecordTimePerConnection(channel, channelStartTimeNanos);
}
}
}




![[游戏开发][Unity]Assetbundle下载篇(7)获取运行时(边玩边下)下载列表](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/077f21f4021814ff9c8600be308bc768.png)
![[STJson]一个.Net开源json解析库](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/d3d5e2bcf81f47e6a5579a6eb1237a11.png#pic_center)