目录
主要命令
CreateTimeSeriesData
FitPolynomial
GetPolynomialLayer
分组数据处理方法(GMDH)
PLOT
主要命令
采用分组数据处理方法(GMDH)对全球冰体积时间序列的建模和预测
fsz = size(A)返回一个行向量,其元素是A的相应维度的长度。例如,如果A是一个 3×4 矩阵,则size(A)返回向量[3 4]。如果
A是表或时间表,则size(A)返回由表中的行数和变量数组成的二元素行向量。
szdim = size(A,dim)返回维度dim的长度。还可以将dim指定为正整数向量,以一次查询多个维度长度。例如,size(A,[2 3])以 1×2 行向量szdim形式返回A的第二个维度和第三个维度的长度。
p = randperm(n)返回行向量,其中包含从 1 到n没有重复元素的整数随机排列。
p = randperm(n,k)返回行向量,其中包含在 1 到n之间随机选择的k个唯一整数。
round
Y = round(X)将X的每个元素四舍五入为最近的整数。在对等情况下,即有元素的小数部分恰为0.5时,round函数会偏离零四舍五入到具有更大幅值的整数。
Y = round(X,N)四舍五入到N位数:
N > 0:舍入到小数点右侧的第N位数。
N = 0:四舍五入到最接近的整数。
N < 0:舍入到小数点左侧的第N位数。which - 定位函数和文件
此 MATLAB 函数 显示 item 的完整路径。isempty - 确定数组是否为空
此 MATLAB 函数 返回逻辑值 1 (true),否则返回逻辑值 0 (false)。空数组、表或时间表有
至少一个长度为 0 的维度,如 0×0 或 0×5。plotregression - 绘制线性回归图
%导入冰川体积数据
data = load('global_ice_volume');
x = data.x;
Delays = [1 2 3 4 5];
[Inputs, Targets] = CreateTimeSeriesData(x,Delays);
nData = size(Inputs,2);
% Perm = randperm(nData);
Perm = 1:nData;
% Train Data
pTrain = 0.7;
nTrainData = round(pTrain*nData);
TrainInd = Perm(1:nTrainData);
TrainInputs = Inputs(:,TrainInd);
TrainTargets = Targets(:,TrainInd);
% Test Data
pTest = 1 - pTrain;
nTestData = nData - nTrainData;
TestInd = Perm(nTrainData+1:end);
TestInputs = Inputs(:,TestInd);
TestTargets = Targets(:,TestInd);
%% Create and Train GMDH Network
params.MaxLayerNeurons = 25; % Maximum Number of Neurons in a Layer
params.MaxLayers = 5; % Maximum Number of Layers
params.alpha = 0; % Selection Pressure
params.pTrain = 0.7; % Train Ratio
gmdh = GMDH(params, TrainInputs, TrainTargets);
%% Evaluate GMDH Network
Outputs = ApplyGMDH(gmdh, Inputs);
TrainOutputs = Outputs(:,TrainInd);
TestOutputs = Outputs(:,TestInd);
%% Show Results
figure;
PlotResults(TrainTargets, TrainOutputs, 'Train Data');
figure;
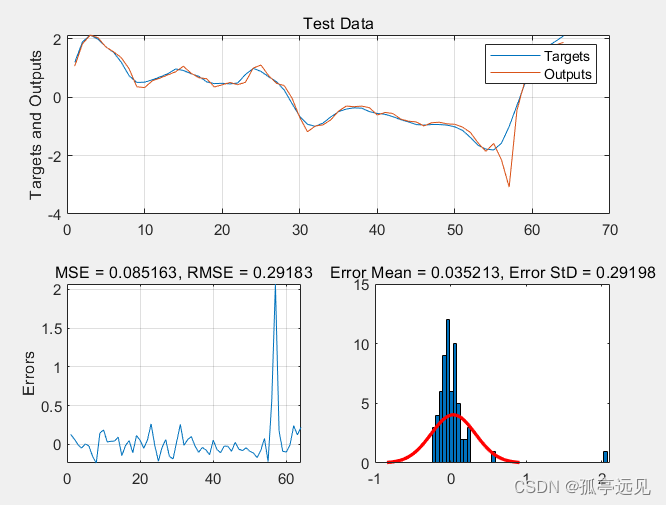
PlotResults(TestTargets, TestOutputs, 'Test Data');
figure;
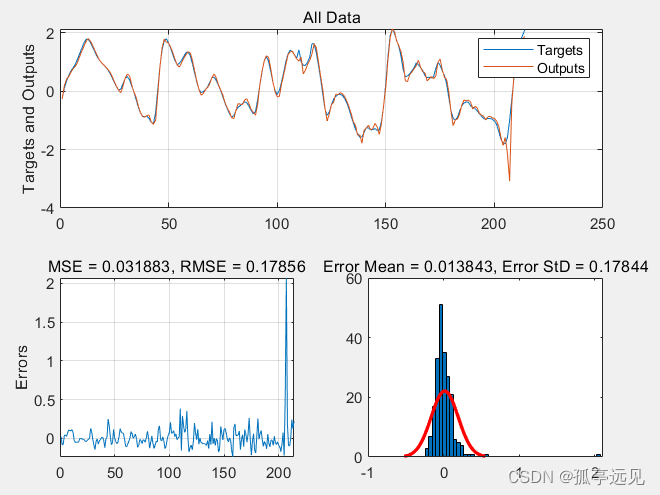
PlotResults(Targets, Outputs, 'All Data');
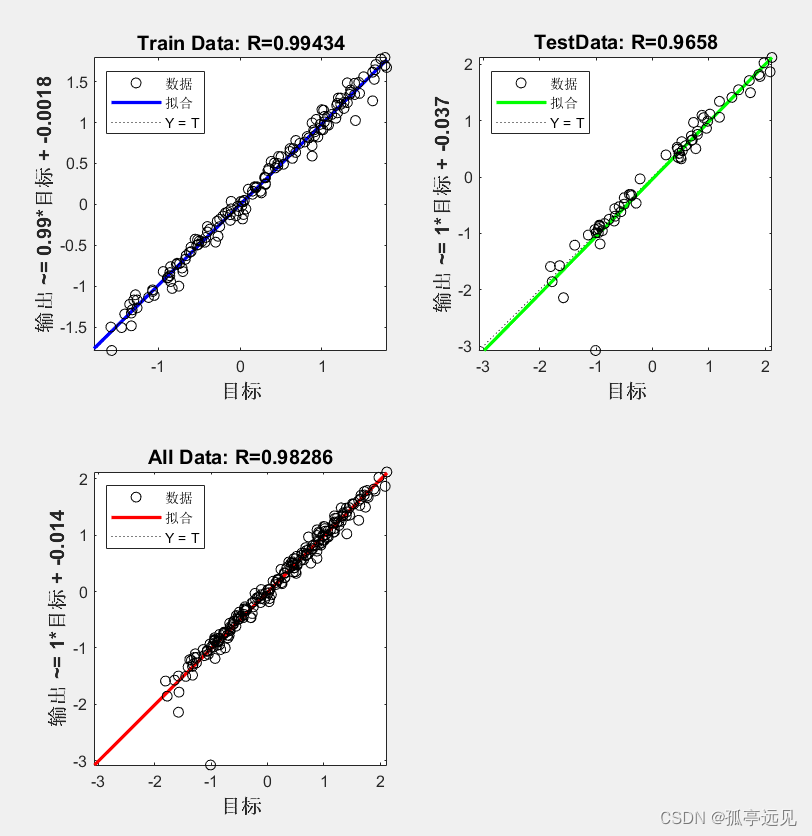
if ~isempty(which('plotregression'))
figure;
plotregression(TrainTargets, TrainOutputs, 'Train Data', ...
TestTargets, TestOutputs, 'TestData', ...
Targets, Outputs, 'All Data');
end
CreateTimeSeriesData
function [X, Y] = CreateTimeSeriesData(x, Delays)
T = size(x,2);
MaxDelay = max(Delays);
Range = MaxDelay+1:T;
X= [];
for d = Delays
X=[X; x(:,Range-d)];
end
Y = x(:,Range);
endFitPolynomial
function p = FitPolynomial(x1, Y1, x2, Y2, vars)
X1 = CreateRegressorsMatrix(x1);
c = Y1*pinv(X1);
Y1hat = c*X1;
e1 = Y1- Y1hat;
MSE1 = mean(e1.^2);
RMSE1 = sqrt(MSE1); %方差和均方差
f = @(x) c*CreateRegressorsMatrix(x);
Y2hat = f(x2);
e2 = Y2- Y2hat;
MSE2 = mean(e2.^2);
RMSE2 = sqrt(MSE2);
p.vars = vars;
p.c = c;
p.f = f;
p.Y1hat = Y1hat;
p.MSE1 = MSE1;
p.RMSE1 = RMSE1;
p.Y2hat = Y2hat;
p.MSE2 = MSE2;
p.RMSE2 = RMSE2;
end
function X = CreateRegressorsMatrix(x)
X = [ones(1,size(x,2))
x(1,:)
x(2,:)
x(1,:).^2
x(2,:).^2
x(1,:).*x(2,:)];
endGetPolynomialLayer
repmat 重复数组副本
B = repmat(A,n)返回一个数组,该数组在其行维度和列维度包含A的n个副本。A为矩阵时,B大小为size(A)*n。
B = repmat(A,r1,...,rN)指定一个标量列表r1,..,rN,这些标量用于描述A的副本在每个维度中如何排列。当A具有N维时,B的大小为size(A).*[r1...rN]。例如:repmat([1 2; 3 4],2,3)返回一个 4×6 的矩阵。
B = repmat(A,r)使用行向量r指定重复方案。例如,repmat(A,[2 3])与repmat(A,2,3)返回相同的结果。sort 对数组元素进行排列
B = sort(A)按升序对A的元素进行排序。
B = sort(A,dim)返回A沿维度dim的排序元素。
B = sort(___,direction)使用上述任何语法返回按direction指定的顺序显示的A的有序元素。'ascend'表示升序(默认值),'descend'表示降序。
B = sort(___,Name,Value)指定用于排序的其他参数。例如,sort(A,'ComparisonMethod','abs')按模对A的元素进行排序。
[B,I] = sort(___)还会为上述任意语法返回一个索引向量的集合。I的大小与A的大小相同,它描述了A的元素沿已排序的维度在B中的排列情况。例如,如果A是一个向量,则B = A(I)。
function L = GetPolynomialLayer(X1, Y1, X2, Y2)
n = size(X1,1);
N = n*(n-1)/2;
template = FitPolynomial(rand(2,3),rand(1,3),rand(2,3),rand(1,3),[]);
L = repmat(template, N, 1);
k = 0;
for i=1:n-1
for j=i+1:n
k = k+1;
L(k) = FitPolynomial(X1([i j],:), Y1, X2([i j],:), Y2, [i j]);
end
end
[~, SortOrder] = sort([L.RMSE2]);
L = L(SortOrder);
end分组数据处理方法(GMDH)
reshape - 重构数组
此 MATLAB 函数 使用大小向量 sz 重构 A 以定义 size(B)。例如,reshape(A,[2,3]) 将
A 重构为一个 2×3 矩阵。sz 必须至少包含 2 个元素,prod(sz) 必须与 numel(A) 相同。
function gmdh = GMDH(params, X, Y)
MaxLayerNeurons = params.MaxLayerNeurons;
MaxLayers = params.MaxLayers;
alpha = params.alpha;
nData = size(X,2);
% Shuffle Data对数据进行随机排列
Permutation = randperm(nData);
X = X(:,Permutation);
Y = Y(:,Permutation);
% Divide Data
pTrainData = params.pTrain;
nTrainData = round(pTrainData*nData);
X1 = X(:,1:nTrainData);
Y1 = Y(:,1:nTrainData);
pTestData = 1-pTrainData;
nTestData = nData - nTrainData;
X2 = X(:,nTrainData+1:end);
Y2 = Y(:,nTrainData+1:end);
Layers = cell(MaxLayers, 1);
Z1 = X1;
Z2 = X2;
for l = 1:MaxLayers
L = GetPolynomialLayer(Z1, Y1, Z2, Y2);
ec = alpha*L(1).RMSE2 + (1-alpha)*L(end).RMSE2;
ec = max(ec, L(1).RMSE2);
L = L([L.RMSE2] <= ec);
if numel(L) > MaxLayerNeurons
L = L(1:MaxLayerNeurons);
end
if l==MaxLayers && numel(L)>1
L = L(1);
end
Layers{l} = L;
Z1 = reshape([L.Y1hat],nTrainData,[])';
Z2 = reshape([L.Y2hat],nTestData,[])';
disp(['Layer ' num2str(l) ': Neurons = ' num2str(numel(L)) ', Min Error = ' num2str(L(1).RMSE2)]);
if numel(L)==1
break;
end
end
Layers = Layers(1:l);
gmdh.Layers = Layers;
endPLOT
%
% Copyright (c) 2015, Yarpiz (www.yarpiz.com)
% All rights reserved. Please read the "license.txt" for license terms.
%
% Project Code: YPML120
% Project Title: Time-Series Prediction using GMDH
% Publisher: Yarpiz (www.yarpiz.com)
%
% Developer: S. Mostapha Kalami Heris (Member of Yarpiz Team)
%
% Contact Info: sm.kalami@gmail.com, info@yarpiz.com
%
function PlotResults(Targets, Outputs, Title)
Errors = Targets - Outputs;
MSE = mean(Errors.^2);
RMSE = sqrt(MSE);
ErrorMean = mean(Errors);
ErrorStd = std(Errors);
subplot(2,2,[1 2]);
plot(Targets);
hold on;
plot(Outputs);
legend('Targets','Outputs');
ylabel('Targets and Outputs');
grid on;
title(Title);
subplot(2,2,3);
plot(Errors);
title(['MSE = ' num2str(MSE) ', RMSE = ' num2str(RMSE)]);
ylabel('Errors');
grid on;
subplot(2,2,4);
histfit(Errors, 50);
title(['Error Mean = ' num2str(ErrorMean) ', Error StD = ' num2str(ErrorStd)]);
end



![[NOIP2003 提高组] 加分二叉树](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/a2ecbc64b8394652a5963604458c3ac5.png)