高并发下缓存失效问题-穿透、雪崩、击穿
- 1.缓存穿透
- 2.缓存雪崩
- 3.缓存穿透
- 4.加锁
- 4.1 本地锁
- 4.2 Redis分布锁
- 4.3 RedLock 分布式锁-Redisson
- **4.3.1 整合Redisson实现分布式锁**
- 4.3.2 分布式锁
- 1)分布式锁 - - 可重入锁
- 2)分布式锁 - - 公平锁
- 3)分布式锁 - - 读写锁
- 4)分布式锁 - - 信号量Semaphore
- 4)分布式锁 - - 闭锁
- 4.4 缓存与数据库保持一致
- 4.5 SpringCache简化缓存
- 4.5.1 整合SpringCache
- 4.5.2 使用SpringCache
1.缓存穿透
说明:以不存在的数据攻击,数据库压力增加导致崩溃
风险:利用不存在数据攻击,数据库瞬时压力增大,导致崩溃
解决:设置不存在数据为 null 值 与 短暂过期时间
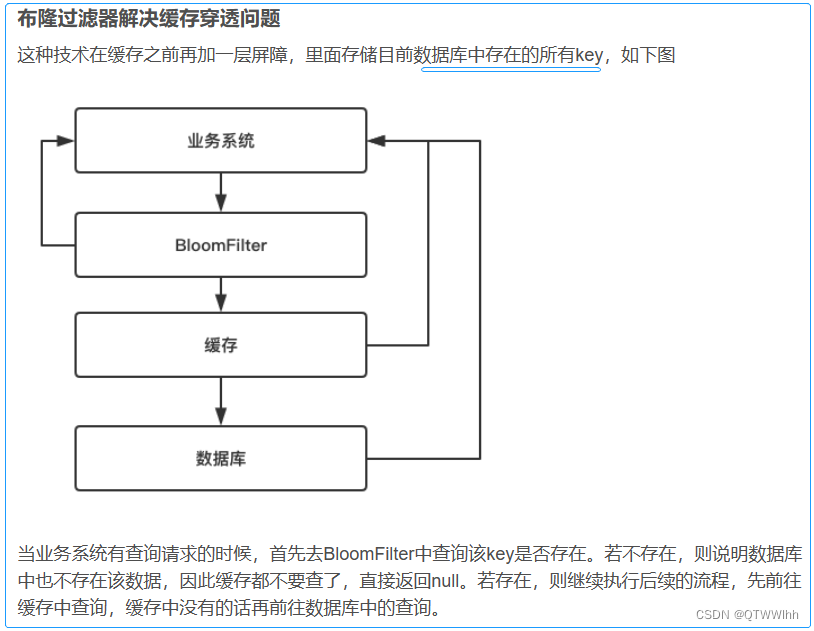
布隆过滤器
布隆过滤器 👇
本质二进制向量 和 一系列随机映射函数,布隆过滤器可以用于检索一个元素是否在一个集合中。
优点:空间效率和查询时间都比一般的算法要好的多
缺点:有一定的误识别率和删除困难
判断的结果:如果判断不存在则肯定不存在,判断存在不一定是存在
原理:值 --------(经过多个哈希函数处理)---→ 得多个索引值 【哈希碰撞:不同元素相同比特位】
实例: Google 著名的 Guava 库所提供布隆过滤器(Bloom Filter)
使用案例:
redission布隆过滤器解决缓存穿透问题,定时刷新bloomFilter中的数据
2.缓存雪崩
说明:设置缓存key采用了相同的过期时间,导致缓存同一时刻失效,DB压力瞬时增加,导致数据库崩溃
解决:原有失效基础增加随机值,例如1-5分钟,降低过期时间重复率
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("catalogJson",catalogJson,1, TimeUnit.DAYS); //1天
布谷鸟过滤器??
3.缓存穿透
说明:热点数据,某key在大量请求时正好失效,请求到DB,增大数据库压力
解决:加锁,大量并发一个人查,其他人等待,查到以后释放锁,其他人再拿锁,先查缓存,有数据就不用去db
4.加锁
1.空结果缓存、解决缓存穿透
2.设置过期时间(加随机数),缓存雪崩
3.加锁,缓存击穿
4.1 本地锁
本地锁 synchronized (this){}、JUC(Lock),适用在单例 ,在分布式下,想锁住所有,需要分布式锁
JUC: java.util.concurrent.locks
代码案例
public Map<String, List<Catalog2Vo>> getCatalogJsonFromDBWithLocalLock() {
synchronized(this){
//1.拿到锁,再从缓存获取一次
String catalogJson = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("catalogJson");
if(!StringUtil.isEmpty(catalogJson)) {
Map<String, List<Catalog2Vo>> result = JSON.parseObject(catalogJson,new TypeReference<Map<String, List<Catalog2Vo>>>(){});
return result;
}
//2.缓存没有,走数据库
Map<String, List<Catalog2Vo>> parentCid = getDataFromDB();
//3.放入缓存
catalogJson = JSON.toJSONString(parentCid);
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("catalogJson",catalogJson,1, TimeUnit.DAYS); //1天
return parentCid;
}
}
4.2 Redis分布锁
此方式并不推荐,已有成熟的框架,可运用在分布式里面
官方文档:http://www.redis.cn/commands/set.html
视频:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1np4y1C7Yf?p=158
问题:设置锁,删除锁,保证原子性
解决:设置过期时间
-->删除锁时,因锁过期,可能删除别人的锁
-->使用uuid,uuid后,key可能过期,删除别人锁
-->推荐 Lua脚本操作
/**
* 方式二 redis锁 适用在分布式
* 原子加锁 原子解锁
* setIfAbsent key存在返回1 key不存在返回0
*
* 风险:可能业务执行期间锁过期了
* 解决:1.可以设置长些,一个请求时间达不到的时间,
* 2.业务期间给锁设置自动续期
*
* @return
*/
public Map<String, List<Catalog2Vo>> getCatalogJsonFromDBWithRedisLock() {
String uuid = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
Boolean lock = redisTemplate.opsForValue().setIfAbsent("lock", uuid,300,TimeUnit.SECONDS); //300s
if(lock){
System.out.println("获取分布式锁成功...");
Map<String, List<Catalog2Vo>> dataFromDB;
/*
// 对比后删除,可能获取完,key过期,删除了其他线程的锁,所以操作需要保证原子性,可采用lua脚本
String lock1 = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("lock");
if(uuid.equals(lock1)) { //可能在对比时key过期,删除了别的线程的key
//删除锁
redisTemplate.delete("lock");
}
*/
try {
dataFromDB = getDataFromDB();
}finally {
//删除锁,原子操作,lua脚本,成功返回 1 失败 0
String script = "if redis.call('get',KEYS[1]) == ARGV[1]\n" +
"then\n" +
" return redis.call('del',KEYS[1])\n" +
"else\n" +
" return 0\n" +
"end";
redisTemplate.execute(new DefaultRedisScript<>(script,Long.class),Arrays.asList("lock"),uuid);
}
return dataFromDB;
} else {
System.out.println("获取分布式锁失败...等待重试");
try{
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (Exception e){
}
return getCatalogJsonFromDBWithRedisLock();
}
}
4.3 RedLock 分布式锁-Redisson
Redisson是一个在redis的基础上实现的java驻内存的数据网格
官方链接:https://redis.io/docs/manual/patterns/distributed-locks/
Redisson: https://github.com/redisson/redisson
文档:https://github.com/redisson/redisson/wiki/1.-概述
https://github.com/redisson/redisson/wiki/8.-分布式锁和同步器
4.3.1 整合Redisson实现分布式锁
1)引入依赖
* <dependency>
* <groupId>org.redisson</groupId>
* <artifactId>redisson</artifactId>
* <version>3.21.1</version>
* </dependency>
2)配置 Redisson
import org.redisson.Redisson;
import org.redisson.api.RedissonClient;
import org.redisson.config.Config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* redisson 配置类
*/
@Configuration
public class MyRedissonConfig {
/**
* 所有对 Redisson 的使用,都通过 RedissonClient对象
* destroyMethod: 销毁方法,服务停止会调用
* @return
* @throws IOException
*/
@Bean(destroyMethod="shutdown")
public RedissonClient redisson() throws IOException {
// 1.创建配置
Config config = new Config();
config.useSingleServer().setAddress("redis://192.168.13.128:6379").setPassword("123456"); //单节点模式,设置了密码的需要设置Password
//2. 根据config创建RedissonClient示例
RedissonClient redissonClient = Redisson.create(config);
return redissonClient;
}
}
3)使用-参考文档
文档:https://github.com/redisson/redisson/wiki/1.-概述
https://github.com/redisson/redisson/wiki/8.-分布式锁和同步器
4.3.2 分布式锁
1)分布式锁 - - 可重入锁
A { B{ } }
若A加锁,执行方法A,A调用了B,B可以拿A的锁过来用,然后执行完,A直接释放锁
/**
* 可重入锁
* https://github.com/redisson/redisson/wiki/8.-distributed-locks-and-synchronizers
* 加锁-未指定时间
* 0) 占锁成功,启动定时任务 (重新设置过期时间), this.internalLockLeaseTime / 3L,默认30s 即10S续一次,续到30s
* 1) 锁自动续期,如果业务超长,运行期间自动给锁续上新的30s(看门狗机制),不用担心业务时间长,锁自动过期被删掉
* 2) 加锁的业务只要运行完成,就不会给当前时间续期,默认30S后删除锁
* 3) 解锁 假设解锁代码没有真运行、redisson不会出现死锁
*
* 加锁-指定时间
* 1) 时间到了不会自动续期,所以时间要大于业务运行时间
* 2) lock.lock(30, TimeUnit.SECONDS); 推荐使用,设置指定时间,去掉了续期业务
* @return
*/
@ResponseBody
@GetMapping("/helloLock")
public String helloLock(){
//1.获取锁,名字一样就是一把锁
RLock lock = redissonClient.getLock("my-lock");
//2.加锁
// lock.lock(); //阻塞式等待,默认加的锁是30s lockWatchdogTimeout 看门狗
// boolean res = lock.tryLock(100, 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS); //尝试等待100s h还没有拿到锁就放弃
lock.lock(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS); //设置10s过期时间 时间到了 不会 自动续期 所以时间要大于业务运行时间
try{
System.out.println("加锁成功,执行业务..."+Thread.currentThread().getId());
Thread.sleep(30000);
}catch(Exception e){
}finally{
System.out.println("释放锁..."+Thread.currentThread().getId());
lock.unlock();
}
return "hello";
}
2)分布式锁 - - 公平锁
公平锁:根据请求的顺序分发锁,
RLock fairlock = redissonClient.geFairLock("my-lock");
fairlock.lock();
3)分布式锁 - - 读写锁
/**
* 读写锁
* 保证一定能读到最新数据,修改期间,写锁是一个排他锁(互斥锁 独享锁)。读锁是一个共享锁
*
* 写锁没释放,读写必须等待
* 读 + 读 相当于无锁,并发读,同时加锁成功
* 读 + 写 有读锁,写等待
* 写 + 读 等待写锁释放
* 写 + 写 阻塞方式
*
* 有写就需要等
*/
@GetMapping("/write")
@ResponseBody
public String write(){
RReadWriteLock rwLock = redissonClient.getReadWriteLock("rw-lock");
String s = "";
RLock wLock = rwLock.writeLock();
wLock.lock();
try{
s = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
Thread.sleep(15000);
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("writeValue",s);
}catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
wLock.unlock();
}
return s;
}
@ResponseBody
@GetMapping("/read")
public String read(){
String s = "";
RReadWriteLock rwLock = redissonClient.getReadWriteLock("rw-lock");
RLock rLock = rwLock.readLock();
rLock.lock();
try {
s = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("writeValue");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
rLock.unlock();
}
return s;
}
4)分布式锁 - - 信号量Semaphore
/**
* 假设 车库停车 3个车位
* 信号量 Semaphore
*
* 停车,占位
*/
@GetMapping("/park")
@ResponseBody
public String park() throws InterruptedException {
RSemaphore park = redissonClient.getSemaphore("park");
park.trySetPermits(3);
// park.acquire(); // 阻塞式,获取一个信号量 ,未获取到则等待
boolean b = park.tryAcquire();// 未获取到信号量直接返回,不等待
if (b) {
//执行业务
} else{
//直接响应
}
return "ok";
}
/**
* 释放车位
*/
@GetMapping("/parkGo")
@ResponseBody
public String parkGo() throws InterruptedException {
RSemaphore park = redissonClient.getSemaphore("park");
park.release(); //释放车位
return "ok";
}
4)分布式锁 - - 闭锁
可以运用场景 其他并发业务执行完成,再执行接下来的业务
/**
* 闭锁
*
* 相当于等 5个班人全走了 再关门
*/
@GetMapping("/lockDoor")
@ResponseBody
public String lockDoor() throws InterruptedException {
RCountDownLatch door = redissonClient.getCountDownLatch("door");
door.trySetCount(5); // 等5个班都走后再锁门
door.await(); //等待闭锁都完成
return "放假了...";
}
/**
* 一个班走
*/
@GetMapping("/gogo/{id}")
@ResponseBody
public String gogo(@PathVariable("id") Long id) {
RCountDownLatch door = redissonClient.getCountDownLatch("door");
door.countDown(); //相当于计数减1
return id + "斑人都走了";
}
4.4 缓存与数据库保持一致
* 缓存一致性问题,设计到两个模式
*
* 1)双写模式:写完数据库,继续写缓存,会产生脏数据
* -- 线程1写数据库准备写缓存,线程2接着写数据和缓存,然后线程1写缓存,此时缓存里最终数据不是线程2的,存了线程1出现脏数据
*
* 2)失效模式:写完数据库,删除缓存 ,产生脏数据
* -- 线程1写数据库准备删缓存,线程2获取到未删的缓存接着写数据,然后线程1执行删缓存,线程2此时的缓存并没有线程1最新数据
*
* 解决缓存不一致问题
*
* 1)数据都有过期时间-数据过期触发主动更新
*
* 2)使用分布式读写锁
*
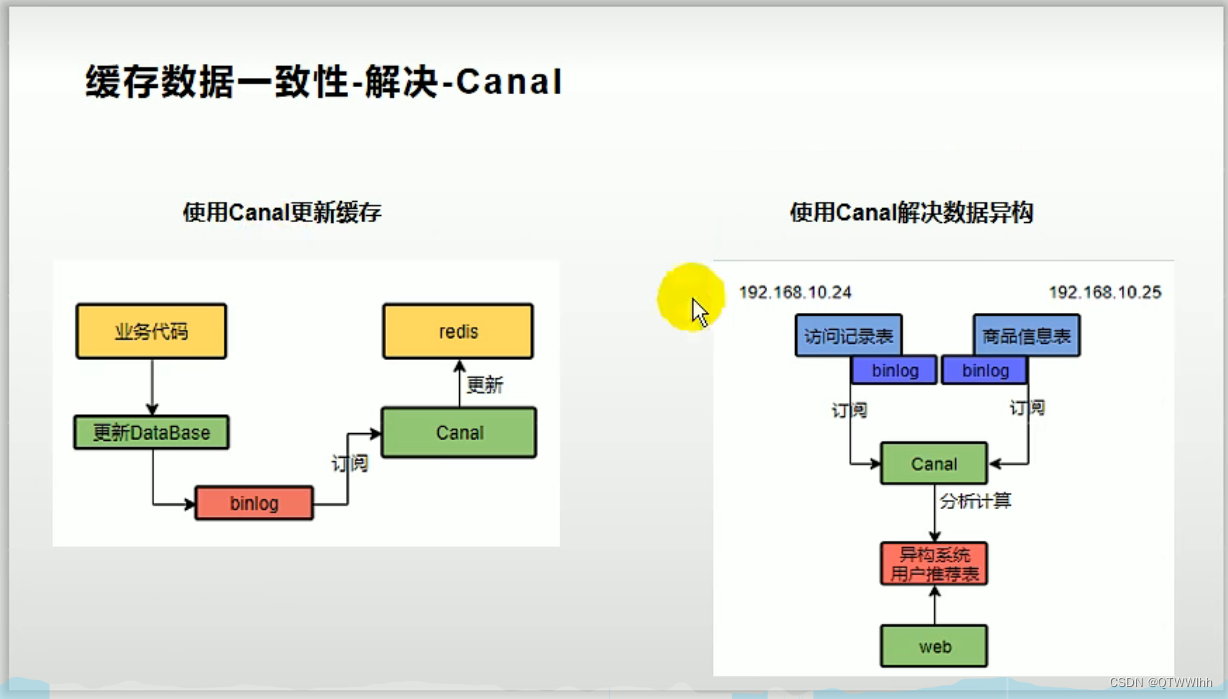
* 3)Canal 阿里开源的中间件,缺点增加了中间件,额外增加自定义功能
* 使用Canal 更新缓存、解决数据异构
* 【Canal 模拟数据库(假设是mysql)的从服务器,mysql里面的变化,开启binlog日志,它会自动同步过来】
* 【
* 缺点:加入Canal,相当于增加了中间件,需要开发自定义功能
* 好处:开发一次,后面就不用再重复更新缓存操作操作,并且可以解决数据异构
* 】
*
* 经常修改,或者实时性要求高的,可直接读数据库

4.5 SpringCache简化缓存
4.5.1 整合SpringCache
1)引入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- 使用缓存场景 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cache</artifactId>
</dependency>
2)配置
* 1)分析自动配置了哪些
* CacheAutoConfiguration 会导入 RedisCacheConfiguration
*
* CacheAutoConfiguration 里面 CacheProperties : xml可配置属性的封装
* CacheConfigurations.getConfigurationClass(types[i]); :缓存配置类,得到每一种类型的缓存
* Class<?> configurationClass = (Class)MAPPINGS.get(cacheType); :MAPPINGS类型映射
* mappings.put(CacheType.REDIS, RedisCacheConfiguration.class);
* initialCacheNames : 初始化缓存 哪些缓存配置哪些规则
* RedisCacheConfiguration : redisCache缓存规则
* RedisCacheConfiguration.class => createConfiguration : 定义缓存规则
2) 配置使用redis作为缓存,yml文件需配置
spring:
redis:
host: 192.168.13.128
port: 6379
password: 123456
cache:
type: redis
redis:
time-to-live: 3600000 # ms单位
# key-prefix: CACHE_ # key 前缀用来区分
use-key-prefix: true # 是否使用前缀 true 使用 指定前缀就用指定的,没有就默认使用缓存名字作为前缀
cache-null-values: true # 是否缓存空值 防止缓存穿透
3)测试使用缓存
官方文档 - https://docs.spring.io/spring-framework/reference/integration/cache/annotations.html
4.5.2 使用SpringCache
SpringCache的使用:
1)开启缓存功能 @EnableCaching
2) 只需要使用注解就可以完成缓存操作
注解:
* @Cacheable: Triggers cache population. 触发数据保存到缓存的操作
*
* @CacheEvict: Triggers cache eviction. 触发数据从缓存删除的操作
*
* @CachePut: Updates the cache without interfering with the method execution.不影响方法执行更新缓存
*
* @Caching: Regroups multiple cache operations to be applied on a method. 组合以上多个操作
*
* @CacheConfig: Shares some common cache-related settings at class-level. 在类级别共享缓存相同配置
@Cacheable(value = "category", key = "#root.method.name",sync = true)
@Override
public List<CategoryEntity> getLevel1Category() {
或
@Cacheable(value = "category",key = "#root.methodName")
* 1.@Cacheable 但概念方法结果需缓存,若缓存中有,不用调用,如果缓存没有,调用方法将结果放入缓存
*
* 2.每个需要缓存的数据,都要指定放到哪个名字的缓存【缓存的分区(业务类型分)】
*
* 3.默认行为
* 1)如果缓存中有,方法不调用
* 2)key默认自动生成:缓存名::SimpleKey [] (这是自主生成的key值)
* 3)缓存的value的值,默认使用json序列化机制,序列化后数据存redis
* 4)默认ttl时间:-1
*
可以自定义的设置有:
可以自定义行为:
1)指定生成的缓存使用的key :key属性指定,接受一个SpEl,例如"#root.method.name"
spel:https://docs.spring.io/spring-framework/reference/integration/cache/annotations.html#cache-spel-context
2)指定缓存的数据的存活时间 :配置文件中ttl,"spring.cache.redis.time-to-live=3600000 # ms单位,一个小时"
3)数据保存为json格式:需要自定义缓存管理器
自定义配置类MyCacheConfig :
可以设置redis数据保存的格式
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.CacheProperties;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.EnableConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.EnableCaching;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheConfiguration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.RedisSerializationContext;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer;
/**
* 缓存配置
*/
@EnableConfigurationProperties(CacheProperties.class)
@Configuration
@EnableCaching
public class MyCacheConfig {
// @Autowired
// CacheProperties cacheProperties;
/**
* 1.GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer 兼容 RedisSerializer<String>继承类
* 2.配置文件没有用上
* 1)原来的配置文件绑定的配置类这样
* @ConfigurationProperties( prefix = "spring.cache" )
* public class CacheProperties {
* 2)如果要生效
* 1)@EnableConfigurationProperties(CacheProperties.class) 开启 读取属性配置类
* 2)@Autowired
* CacheProperties cacheProperties;
* 或者直接在方法上
* RedisCacheConfiguration redisCacheConfiguration(CacheProperties cacheProperties){
*/
@Bean
RedisCacheConfiguration redisCacheConfiguration(CacheProperties cacheProperties){
RedisCacheConfiguration config = RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig();
config = config.serializeKeysWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(new StringRedisSerializer()));
config = config.serializeValuesWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer()));
CacheProperties.Redis redisProperties = cacheProperties.getRedis();
//设置配置文件所有配置生效 - package org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache;
if (redisProperties.getTimeToLive() != null) {
config = config.entryTtl(redisProperties.getTimeToLive());
}
if (redisProperties.getKeyPrefix() != null) {
config = config.prefixKeysWith(redisProperties.getKeyPrefix());
}
if (!redisProperties.isCacheNullValues()) {
config = config.disableCachingNullValues();
}
if (!redisProperties.isUseKeyPrefix()) {
config = config.disableKeyPrefix();
}
return config;
}
}
多操作组合Caching例子:
/**
* 级联更新所有关联的数据
*
* CacheEvict: 失效模式,触发数据从缓存删除的操作,不能同时删除多个缓存 @CacheEvict(value = "category",key = "#root.method.name")
*
* 需求删除多个方法如下
* 1)@Caching: 同时进行多个缓存操作
* 2)@CacheEvict(value = "category", allEntries = true) 删除category分区下所有缓存
* 存储同一类型的数据,都可以指定成一个分区,分区名默认是缓存前缀,这样在redis结构里面会以属性结构显示 category::getLevel1Category
*/
// @CacheEvict(value = "category", allEntries = true)
@Caching(evict = {
@CacheEvict(value = "category",key = "'getLevel1Category'"),
@CacheEvict(value = "category",key = "'getCatalogJson'")
})
@Transactional
@Override
public void updateCascade(CategoryEntity category) {
this.updateById(category);
if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(category.getName())) {
categoryBrandRelationService.updateCategory(category.getCatId(),category.getName());
//TODO 其他冗余表字段更新
}
}
Spring-Cache 的不足
* 1)读模式
* 缓存穿透,查询一个null数据,解决:缓存空数据 cache-null-values
*
* *缓存击穿,大量并发进来同时查询一个正好过期的数据,解决:加锁 ?--默认无加锁/sync = true 加锁(解决击穿,不是分布式锁)
*
* 缓存雪崩,大量的key同时过期,解决:加随机时间,加过期时间 time-to-live: 3600000 # ms单位
* 2)写模式 (缓存与数据库数据一致)
* 1)读写加锁
*
* 2) 引入Canal,感知到MySQL的更新,去更新缓存
*
* 3) 读多写多,直接去数据库查询即可
* 总结:
* 常规数据(读多写少,即时性、一致性要求不高的数据),可使用spring-cache,设置过期时间
*
* 特殊数据,特殊设计
* 原理:
* CacheManager(RedisCacheManager) -> Cache(RedisCache) -> Cache负责缓存的读写