(一)设计Conv2dBatchLeaky
1、了解LeakyReLU激活函数
LeakyReLU 激活层,创建一个可调用对象以计算输入 x 的 LeakReLU 。其中,x为输入的 Tensor

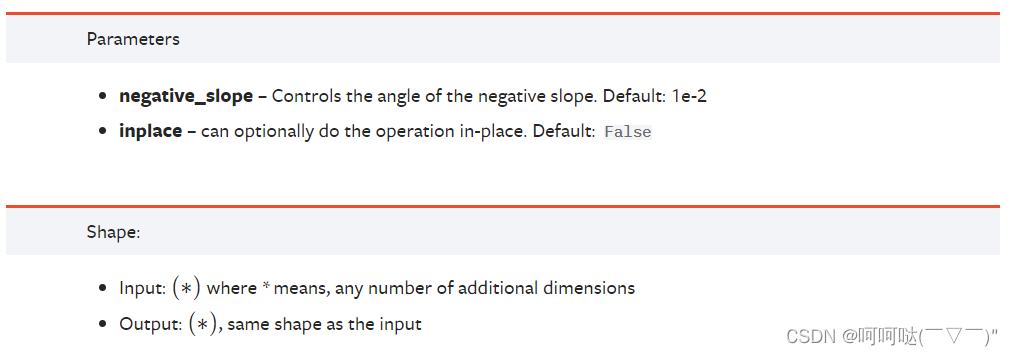
感觉和飞桨的api有点相同,可以对照参考理解:

LeakyReLU激活函数的图像

Examples:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
m = nn.LeakyReLU(0.1)
input = torch.randn(2)
output = m(input)
print(input)
print(output)演示效果:

2、了解isinstance内置函数
'''
isinstance函数:是Python中的一个内置函数,用来判断一个函数是否是一个已知的类型,类似 type()。
isinstance()与type()的区别:
例如在继承上的区别:
1、isinstance() 会认为子类是一种父类类型,考虑继承关系。
2、type() 不会认为子类是一种父类类型,不考虑继承关系。
'''
a = 2
print(isinstance(a,int) ) # 结果返回 True
print(isinstance(a,str)) # 结果返回 False
print(isinstance(a,(str,int,list)) ) # 是元组中的一个,结果返回 True
print("=======================================")
class Parent:
pass
class Son(Parent):
pass
print(isinstance(Parent(), Parent)) # returns True
print(type(Parent()) == Parent ) # returns True
print(isinstance(Son(), Parent)) # returns True
print(type(Son()) == Parent) # returns False
3、了解self.padding = int(kernel_size/2)
推荐文章:
CNN中卷积层的计算细节:CNN中卷积层的计算细节 - 知乎前几天在看CS231n中的CNN经典模型讲解时,花了一些时间才搞清楚卷积层输入输出的尺寸关系到底是什么样的,现总结如下。(可以参照我画的题图理解卷积层的运算) 卷积层尺寸的计算原理输入矩阵格式:四个维度,依次…
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/29119239
卷积神经网络:卷积神经网络2-padding_卷积padding计算公式_安好1997的博客-CSDN博客什么是padding? padding就是填充、覆盖的意思,也就是过滤器。padding的选择? 我们通常选择3x3的过滤器,但是如果你阅读大量文献,你也会发现也有许多5x5、7x7的过滤器。不难发现,这里都是奇数类型的过滤器。如果你阅读许多相关文献,你也会发现绝大多数都选择的是奇数过滤器,这也符合计算机视觉的惯例。之所以选择奇数,一方面有便于确定过滤器当前所在的位置(只有一个中心点),另外也不止是这个原因。当然,也可以选择偶数过滤器,可能也会有很...
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_37031892/article/details/109141826?spm=1001.2014.3001.5502pytorch中padding=kernel_size//2:
pytorch中padding=kernel_size//2_padding=2_gggoogle1020的博客-CSDN博客pytorch中padding=kernel_size//2到底是实现神魔形式的padding?padding=(kernel_size-1)/2若kernel_size是7*7,5*5,3*3,1*1常见的则padding是 3,2 ,1 ,0nn.Conv2d的padding是在卷积之前补0,如果愿意的话,可以通过使用torch.nn.Functional.pad来补非0的内容。四周都补!如果pad输入是一个tuple的话,则第一个参数表示上,下底的padding,第2个参数表示宽..
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_36249824/article/details/107005949
笔记抄录归纳:



4、torch.nn.Sequential(*args)
顺序容器。模块将按照它们在构造函数中传递的顺序添加到它中。或者,可以传入一个包含模块的OrderedDict。Sequential的forward()方法接受任何输入并将其转发到它包含的第一个模块。然后,它将输出按顺序“链接”到每个后续模块的输入,最后返回最后一个模块的输出。
Sequential通过手动调用模块序列提供的价值是,它允许将整个容器视为单个模块,这样在Sequential上执行转换就可以应用于它存储的每个模块(每个模块都是Sequential的注册子模块)。
Sequential和torch.nn.ModuleList的区别是什么?模块列表顾名思义就是一个用于存储模块的列表!另一方面,sequence中的层以级联方式连接。
# Using Sequential to create a small model. When `model` is run,
# input will first be passed to `Conv2d(1,20,5)`. The output of
# `Conv2d(1,20,5)` will be used as the input to the first
# `ReLU`; the output of the first `ReLU` will become the input
# for `Conv2d(20,64,5)`. Finally, the output of
# `Conv2d(20,64,5)` will be used as input to the second `ReLU`
model = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(1,20,5),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(20,64,5),
nn.ReLU()
)
# Using Sequential with OrderedDict. This is functionally the
# same as the above code
model = nn.Sequential(OrderedDict([
('conv1', nn.Conv2d(1,20,5)),
('relu1', nn.ReLU()),
('conv2', nn.Conv2d(20,64,5)),
('relu2', nn.ReLU())
]))使用Sequential创建一个小模型。当' model '运行时,输入将首先传递给' Conv2d(1,20,5) '。' Conv2d(1,20,5) '的输出将被用作第一个的输入“ReLU”;第一个“ReLU”的输出将成为“Conv2d(20,64,5)”的输入。最后,' Conv2d(20,64,5) '的输出将用作第二个' ReLU '的输入。
model = nn.Sequential( nn.Conv2d(1,20,5), nn.ReLU(), nn.Conv2d(20,64,5), nn.ReLU() )使用Sequential和OrderedDict。这在功能上与上面的代码相同
model = nn.Sequential(OrderedDict([ ('conv1', nn.Conv2d(1,20,5)), ('relu1', nn.ReLU()), ('conv2', nn.Conv2d(20,64,5)), ('relu2', nn.ReLU()) ]))
5、 torch.nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride=1, padding=0, dilation=1, groups=1, bias=True, padding_mode='zeros', device=None, dtype=None)

查看飞桨的Conv2d函数解释,可以参考理解:
Examples:
# With square kernels and equal stride
m = nn.Conv2d(16, 33, 3, stride=2)
# non-square kernels and unequal stride and with padding
m = nn.Conv2d(16, 33, (3, 5), stride=(2, 1), padding=(4, 2))
# non-square kernels and unequal stride and with padding and dilation
m = nn.Conv2d(16, 33, (3, 5), stride=(2, 1), padding=(4, 2), dilation=(3, 1))
input = torch.randn(20, 16, 50, 100)
output = m(input)6、torch.nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True, device=None, dtype=None)
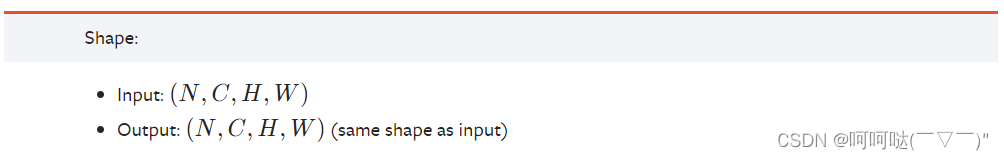
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
# With Learnable Parameters
m = nn.BatchNorm2d(100)
# Without Learnable Parameters
m = nn.BatchNorm2d(100, affine=False)
input = torch.randn(20, 100, 35, 45)
output = m(input)
print(output)7、设计Conv2dBatchLeaky(用自定义layer充当积木)
思考:实际操作中我们往往更想要设计一些自定义的layer,怎么办呢?
此时若我们需要用nn.Conv2d,BatchNorm2d,又要LeakyReLU等公用积木搭网络,我们可以直接设计一个layer,叫做Conv2dBatchLeaky(),一块积木顶三块
'''
in_channels:输入通道
out_channels:输出通道
kernel_size:核的大小
stride:步长
leaky_slop:默认设置为0.1
'''
class Conv2dBatchLeaky(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride, leaky_slope=0.1):
super(Conv2dBatchLeaky, self).__init__()
self.in_channels = in_channels
self.out_channels = out_channels
self.kernel_size = kernel_size
self.stride = stride
if isinstance(kernel_size, (list, tuple)):
self.padding = [int(ii/2) for ii in kernel_size]
if flag_yolo_structure:
print('------------------->>>> Conv2dBatchLeaky isinstance')
else:
self.padding = int(kernel_size/2)
self.leaky_slope = leaky_slope
# Layer
# LeakyReLU : y = max(0, x) + leaky_slope*min(0,x)
self.layers = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(self.in_channels, self.out_channels, self.kernel_size, self.stride, self.padding, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(self.out_channels),
nn.LeakyReLU(self.leaky_slope, inplace=True)
)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.layers(x)
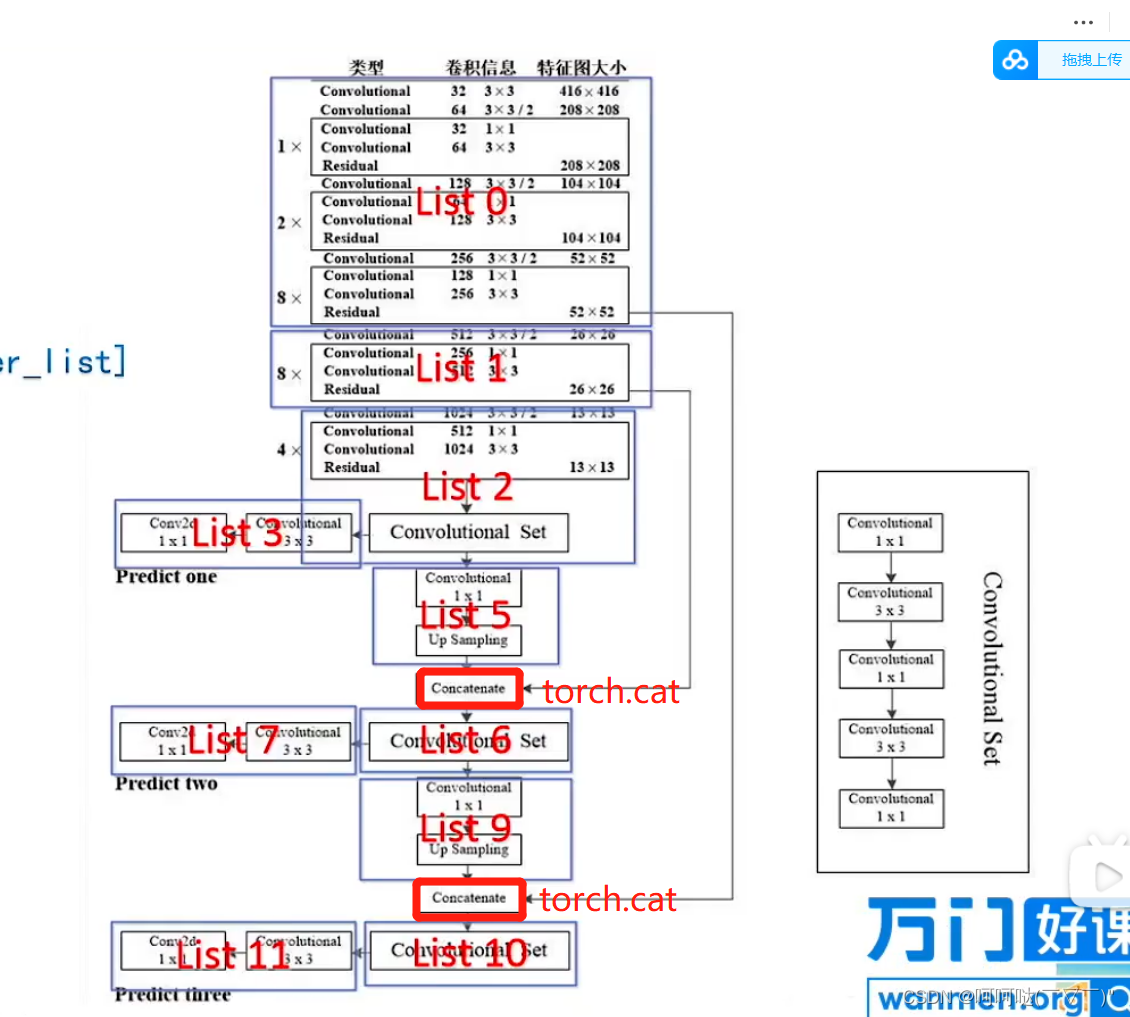
return x(二)设计ResBlockSum实现List0"黑色框框"结构(通俗讲,不知道怎么准确描述,哈哈哈~)
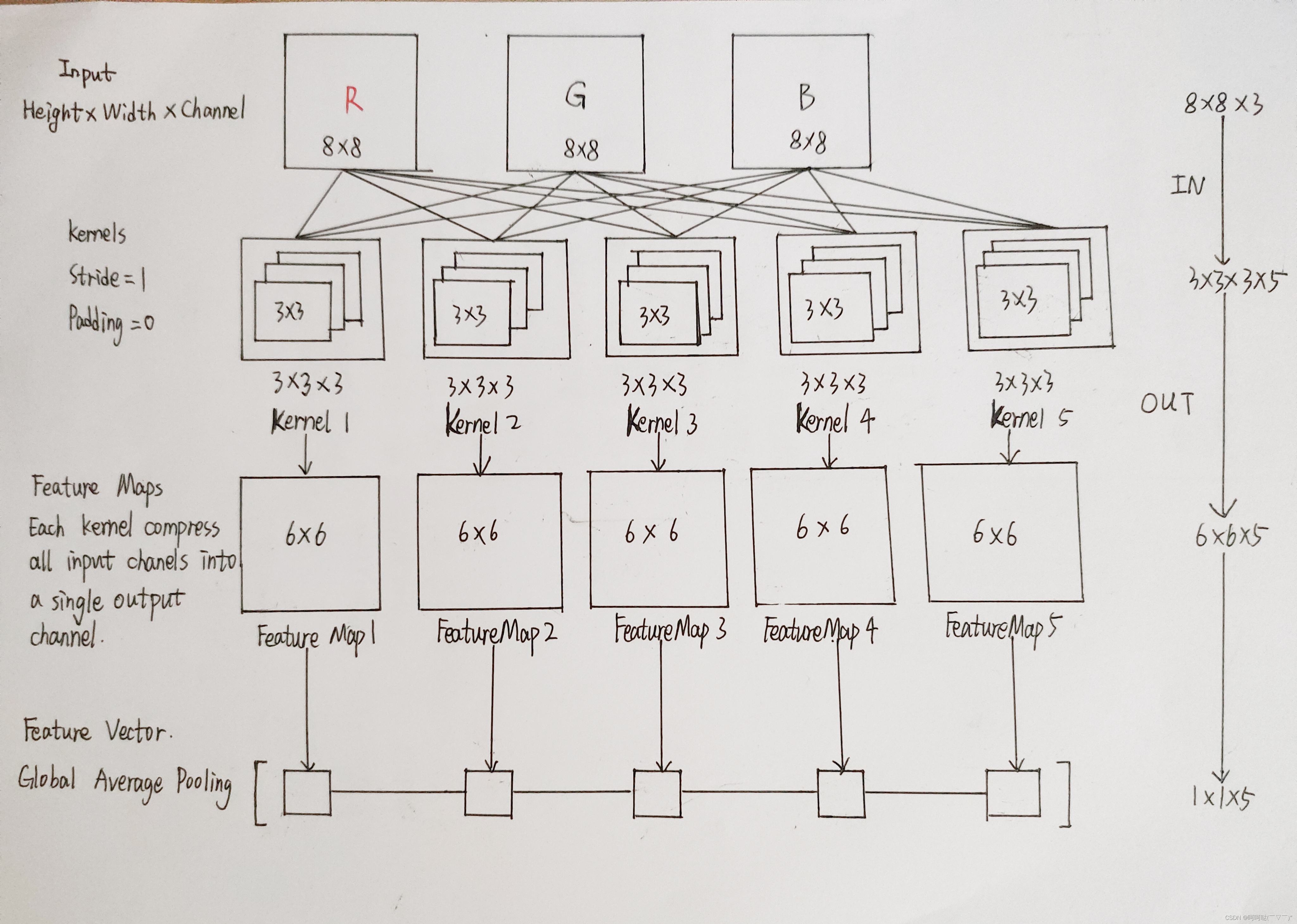
比如说我们要设计list0,可以发现图中的三个黑色的框框是一样的结构,都是两个Convolutional+一个Residual,其中第一个Convolutional的卷积信息为 32 1x1,第二个Convolutional的卷积信息为64 3x3;
观察list0,我们可以发现三个黑色框框除了是一样的结构,而且多次使用,所以我们可以考虑封装一个函数来实现复用。为此设计出了这个函数:ResBlockSum
class ResBlockSum(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, nchannels):
super().__init__()
self.block = nn.Sequential(
Conv2dBatchLeaky(nchannels, int(nchannels/2), 1, 1),
Conv2dBatchLeaky(int(nchannels/2), nchannels, 3, 1)
)
def forward(self, x):
return x + self.block(x)核心实现:
self.block = nn.Sequential( Conv2dBatchLeaky(nchannels, int(nchannels/2), 1, 1), Conv2dBatchLeaky(int(nchannels/2), nchannels, 3, 1) )
当传入nchannels=64,调用1次ResBlockSum(64),即
self.block = nn.Sequential(
Conv2dBatchLeaky(64, 32, 1, 1),
Conv2dBatchLeaky(32, 64, 3, 1)
)
即可实现该结构
当传入nchannels=128,调用2次ResBlockSum(128),即
self.block = nn.Sequential(
Conv2dBatchLeaky(128, 64, 1, 1),
Conv2dBatchLeaky(64, 128, 3, 1)
)即可实现该结构
当传入nchannels=256,调用8次ResBlockSum(256),即
self.block = nn.Sequential(
Conv2dBatchLeaky(256, 128, 1, 1),
Conv2dBatchLeaky(128, 256, 3, 1)
)即可实现该结构
(三)设计HeadBody,实现List2、List6、List10中的ConvolutionalSet
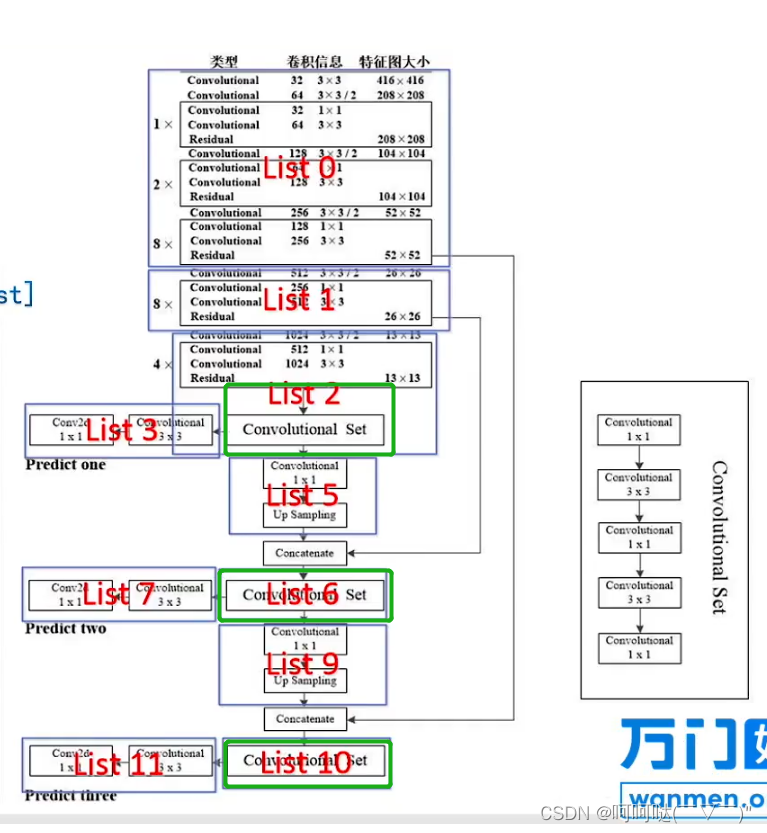

class HeadBody(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels):
super(HeadBody, self).__init__()
self.layer = nn.Sequential(
Conv2dBatchLeaky(in_channels, out_channels, 1, 1),
Conv2dBatchLeaky(out_channels, out_channels*2, 3, 1),
Conv2dBatchLeaky(out_channels*2, out_channels, 1, 1),
Conv2dBatchLeaky(out_channels, out_channels*2, 3, 1),
Conv2dBatchLeaky(out_channels*2, out_channels, 1, 1)
)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.layer(x)
return x(四)实现上采样Upsample,需要实现两次Upsample

推荐文章:
interpolate-API文档-PaddlePaddle深度学习平台调整一个 batch 中图片的大小。 输入为 4-D Tensor 时形状为(num_batches, channels, in_h, in_w)或者(num_batches, in_h, in_w,
https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/documentation/docs/zh/api/paddle/nn/functional/interpolate_cn.html
torch.nn.functional.interpolate(input, size=None, scale_factor=None, mode='nearest', align_corners=None, recompute_scale_factor=None)torch.nn.functional.interpolate — PyTorch 1.10 documentation
https://pytorch.org/docs/1.10/generated/torch.nn.functional.interpolate.html?highlight=f%20interpolate#torch.nn.functional.interpolate
了解torch的上采样Upsample的api:
import torch import torch.nn as nn # output_shape = [64, 48] # up = nn.Upsample(scale_factor=2, mode='bilinear', align_corners=True) up = nn.Upsample(scale_factor=2) input = torch.rand(32, 17, 32, 24) output = up(input) print(output.shape)
import torch import torch.nn.functional as F input = torch.rand(32, 17, 32, 24) output = F.interpolate(input,scale_factor=2) print(output.shape)
class Upsample(nn.Module):
# Custom Upsample layer (nn.Upsample gives deprecated warning message)
def __init__(self, scale_factor=1, mode='nearest'):
super(Upsample, self).__init__()
self.scale_factor = scale_factor
self.mode = mode
def forward(self, x):
return F.interpolate(x, scale_factor=self.scale_factor, mode=self.mode)(五)实现YOLOLayer,得到物体的anchor和num_classes
# default anchors=[(10,13), (16,30), (33,23), (30,61), (62,45), (59,119), (116,90), (156,198), (373,326)]
class YOLOLayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, anchors, nC):
super(YOLOLayer, self).__init__()
self.anchors = torch.FloatTensor(anchors)
self.nA = len(anchors) # number of anchors (3)
self.nC = nC # number of classes
self.img_size = 0
if flag_yolo_structure:
print('init YOLOLayer ------ >>> ')
print('anchors : ',self.anchors)
print('nA : ',self.nA)
print('nC : ',self.nC)
print('img_size : ',self.img_size)
def forward(self, p, img_size, var=None):# p : feature map
bs, nG = p.shape[0], p.shape[-1] # batch_size , grid
if flag_yolo_structure:
print('bs, nG --->>> ',bs, nG)
if self.img_size != img_size:
create_grids(self, img_size, nG, p.device)
# p.view(bs, 255, 13, 13) -- > (bs, 3, 13, 13, 85) # (bs, anchors, grid, grid, xywh + confidence + classes)
p = p.view(bs, self.nA, self.nC + 5, nG, nG).permute(0, 1, 3, 4, 2).contiguous() # prediction
if self.training:
return p
else: # inference
io = p.clone() # inference output
io[..., 0:2] = torch.sigmoid(io[..., 0:2]) + self.grid_xy # xy
io[..., 2:4] = torch.exp(io[..., 2:4]) * self.anchor_wh # wh yolo method
io[..., 4:] = torch.sigmoid(io[..., 4:]) # p_conf, p_cls
io[..., :4] *= self.stride
if self.nC == 1:
io[..., 5] = 1 # single-class model
# flatten prediction, reshape from [bs, nA, nG, nG, nC] to [bs, nA * nG * nG, nC]
return io.view(bs, -1, 5 + self.nC), p
def create_grids(self, img_size, nG, device='cpu'):
# self.nA : len(anchors) # number of anchors (3)
# self.nC : nC # number of classes
# nG : feature map grid 13*13 26*26 52*52
self.img_size = img_size
self.stride = img_size / nG
if flag_yolo_structure:
print('create_grids stride : ',self.stride)
# build xy offsets
grid_x = torch.arange(nG).repeat((nG, 1)).view((1, 1, nG, nG)).float()
grid_y = grid_x.permute(0, 1, 3, 2)
self.grid_xy = torch.stack((grid_x, grid_y), 4).to(device)
if flag_yolo_structure:
print('grid_x : ',grid_x.size(),grid_x)
print('grid_y : ',grid_y.size(),grid_y)
print('grid_xy : ',self.grid_xy.size(),self.grid_xy)
# build wh gains
self.anchor_vec = self.anchors.to(device) / self.stride # 基于 stride 的归一化
# print('self.anchor_vecself.anchor_vecself.anchor_vec:',self.anchor_vec)
self.anchor_wh = self.anchor_vec.view(1, self.nA, 1, 1, 2).to(device)
self.nG = torch.FloatTensor([nG]).to(device)
def get_yolo_layer_index(module_list):
yolo_layer_index = []
for index, l in enumerate(module_list):
try:
a = l[0].img_size and l[0].nG # only yolo layer need img_size and nG
yolo_layer_index.append(index)
except:
pass
assert len(yolo_layer_index) > 0, "can not find yolo layer"
return yolo_layer_index>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>
>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>得到大物体的anchor和num_classes>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>
>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>
【一】实现List0
推荐文章:
Pytorch 快速搭建网络搭积木方法:Pytorch 快速搭建网络搭积木方法_w55100的博客-CSDN博客前言研究lightnet源代码时,看到这种技巧,惊为天人,于是单独摘出来。感谢作者EAVISE,lightnet传送门。一、 使用OrderedDict([ ])import torchimport torch.nn as nnfrom collections import OrderedDictlayer_list = [ # Seque...
https://blog.csdn.net/w55100/article/details/89083776
1、了解OrderedDict(参考上文,运行结果如下)
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from collections import OrderedDict
layer_list = [
# Sequence 1 :
OrderedDict([
('1_conv2d', nn.Conv2d(32, 64, 1, 1)),
('2_Relu', nn.ReLU(inplace=True)),
]),
# Sequence 2 :
OrderedDict([
('3_conv2d', nn.Conv2d((4 * 64) + 1024, 1024, 3, 1)),
('4_bn', nn.BatchNorm2d(1024, 20, 1, 1, 0)),
]),
]
sequence_list = [nn.Sequential(layer_dict) for layer_dict in layer_list]
print(sequence_list)
>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>准备就绪,开始实现List0的结构搭建>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>

# list 0
layer_list.append(OrderedDict([
('0_stage1_conv', Conv2dBatchLeaky(3, 32, 3, 1, 1)), # 416 x 416 x 32 # Convolutional
("0_stage2_conv", Conv2dBatchLeaky(32, 64, 3, 2)), # 208 x 208 x 64 # Convolutional
("0_stage2_ressum1", ResBlockSum(64)), # Convolutional*2 + Resiudal
("0_stage3_conv", Conv2dBatchLeaky(64, 128, 3, 2)), # 104 x 104 128 # Convolutional
("0_stage3_ressum1", ResBlockSum(128)),
("0_stage3_ressum2", ResBlockSum(128)), # (Convolutional*2 + Resiudal)**2
("0_stage4_conv", Conv2dBatchLeaky(128, 256, 3, 2)), # 52 x 52 x 256 # Convolutional
("0_stage4_ressum1", ResBlockSum(256)),
("0_stage4_ressum2", ResBlockSum(256)),
("0_stage4_ressum3", ResBlockSum(256)),
("0_stage4_ressum4", ResBlockSum(256)),
("0_stage4_ressum5", ResBlockSum(256)),
("0_stage4_ressum6", ResBlockSum(256)),
("0_stage4_ressum7", ResBlockSum(256)),
("0_stage4_ressum8", ResBlockSum(256)), # 52 x 52 x 256 output_feature_0 (Convolutional*2 + Resiudal)**8
]))【二】实现List1
>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>准备就绪,开始实现List1的结构搭建>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>

# list 1
layer_list.append(OrderedDict([
("1_stage5_conv", Conv2dBatchLeaky(256, 512, 3, 2)), # 26 x 26 x 512 # Convolutional
("1_stage5_ressum1", ResBlockSum(512)),
("1_stage5_ressum2", ResBlockSum(512)),
("1_stage5_ressum3", ResBlockSum(512)),
("1_stage5_ressum4", ResBlockSum(512)),
("1_stage5_ressum5", ResBlockSum(512)),
("1_stage5_ressum6", ResBlockSum(512)),
("1_stage5_ressum7", ResBlockSum(512)),
("1_stage5_ressum8", ResBlockSum(512)), # 26 x 26 x 512 output_feature_1 # (Convolutional*2 + Resiudal)**8
]))【三】实现List2
>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>准备就绪,开始实现List2的结构搭建>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>

# list 2
layer_list.append(OrderedDict([
("2_stage6_conv", Conv2dBatchLeaky(512, 1024, 3, 2)), # 13 x 13 x 1024 # Convolutional
("2_stage6_ressum1", ResBlockSum(1024)),
("2_stage6_ressum2", ResBlockSum(1024)),
("2_stage6_ressum3", ResBlockSum(1024)),
("2_stage6_ressum4", ResBlockSum(1024)), # 13 x 13 x 1024 output_feature_2 # (Convolutional*2 + Resiudal)**4
("2_headbody1", HeadBody(in_channels=1024, out_channels=512)), # 13 x 13 x 512 # Convalutional Set = Conv2dBatchLeaky * 5
]))【四】实现List3
>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>准备就绪,开始实现List3的结构搭建>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>

# list 3
layer_list.append(OrderedDict([
("3_conv_1", Conv2dBatchLeaky(in_channels=512, out_channels=1024, kernel_size=3, stride=1)),
("3_conv_2", nn.Conv2d(in_channels=1024, out_channels=len(anchor_mask1) * (num_classes + 5), kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=True)),
])) # predict one【五】实现List4,得到大物体的anchor和num_classes
# list 4
layer_list.append(OrderedDict([
("4_yolo", YOLOLayer([anchors[i] for i in anchor_mask1], num_classes))
])) # 3*((x, y, w, h, confidence) + classes )>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>
>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>得到中物体的anchor和num_classes>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>
>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>
【一】实现List5

# list 5
layer_list.append(OrderedDict([
("5_conv", Conv2dBatchLeaky(512, 256, 1, 1)),
("5_upsample", Upsample(scale_factor=2)),
]))【二】实现List6

# list 6
layer_list.append(OrderedDict([
("6_head_body2", HeadBody(in_channels=768, out_channels=256)) # Convalutional Set = Conv2dBatchLeaky * 5
]))【三】实现List7

# list 7
layer_list.append(OrderedDict([
("7_conv_1", Conv2dBatchLeaky(in_channels=256, out_channels=512, kernel_size=3, stride=1)),
("7_conv_2", nn.Conv2d(in_channels=512, out_channels=len(anchor_mask2) * (num_classes + 5), kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=True)),
])) # predict two【四】实现List8,得到中物体的anchor和num_classes
# list 8
layer_list.append(OrderedDict([
("8_yolo", YOLOLayer([anchors[i] for i in anchor_mask2], num_classes))
])) # 3*((x, y, w, h, confidence) + classes )>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>
>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>得到小物体的anchor和num_classes>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>
>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>
【一】实现List9

# list 9
layer_list.append(OrderedDict([
("9_conv", Conv2dBatchLeaky(256, 128, 1, 1)),
("9_upsample", Upsample(scale_factor=2)),
]))【二】实现List10

# list 10
layer_list.append(OrderedDict([
("10_head_body3", HeadBody(in_channels=384, out_channels=128)) # Convalutional Set = Conv2dBatchLeaky * 5
]))【三】实现List11

# list 11
layer_list.append(OrderedDict([
("11_conv_1", Conv2dBatchLeaky(in_channels=128, out_channels=256, kernel_size=3, stride=1)),
("11_conv_2", nn.Conv2d(in_channels=256, out_channels=len(anchor_mask3) * (num_classes + 5), kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=True)),
])) # predict three【四】实现List12,得到小物体的anchor和num_classes
# list 12
layer_list.append(OrderedDict([
("12_yolo", YOLOLayer([anchors[i] for i in anchor_mask3], num_classes))
])) # 3*((x, y, w, h, confidence) + classes )>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>
>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>整合List1-List12>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>
>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>
nn.ModuleList类似于pytho中的list类型,只是将一系列层装入列表,并没有实现forward()方法,因此也不会有网络模型产生的副作用
# nn.ModuleList类似于pytho中的list类型,只是将一系列层装入列表,并没有实现forward()方法,因此也不会有网络模型产生的副作用
self.module_list = nn.ModuleList([nn.Sequential(i) for i in layer_list])
self.yolo_layer_index = get_yolo_layer_index(self.module_list)
if flag_yolo_structure:
print('yolo_layer : ',len(layer_list),'\n')
print(self.module_list[4])
print(self.module_list[8])
print(self.module_list[12])实现yolov3的forward()函数,将module_list中的list结构像搭积木一样搭建出该网络模型
def forward(self, x):
img_size = x.shape[-1]
if flag_yolo_structure:
print('forward img_size : ',img_size,x.shape)
output = []
x = self.module_list[0](x)
x_route1 = x
x = self.module_list[1](x)
x_route2 = x
x = self.module_list[2](x)
yolo_head = self.module_list[3](x)
if flag_yolo_structure:
print('mask1 yolo_head : ',yolo_head.size())
yolo_head_out_13x13 = self.module_list[4][0](yolo_head, img_size)
output.append(yolo_head_out_13x13)
x = self.module_list[5](x)
x = torch.cat([x, x_route2], 1)
x = self.module_list[6](x)
yolo_head = self.module_list[7](x)
if flag_yolo_structure:
print('mask2 yolo_head : ',yolo_head.size())
yolo_head_out_26x26 = self.module_list[8][0](yolo_head, img_size)
output.append(yolo_head_out_26x26)
x = self.module_list[9](x)
x = torch.cat([x, x_route1], 1)
x = self.module_list[10](x)
yolo_head = self.module_list[11](x)
if flag_yolo_structure:
print('mask3 yolo_head : ',yolo_head.size())
yolo_head_out_52x52 = self.module_list[12][0](yolo_head, img_size)
output.append(yolo_head_out_52x52)
if self.training:
return output
else:
io, p = list(zip(*output)) # inference output, training output
return torch.cat(io, 1), p完整代码
import os
import numpy as np
from collections import OrderedDict
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch.nn as nn
flag_yolo_structure = False # True 查看 相关的网络 log
'''
in_channels:输入通道
out_channels:输出通道
kernel_size:核的大小
stride:步长
leaky_slop:默认设置为0.1
'''
class Conv2dBatchLeaky(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride, leaky_slope=0.1):
super(Conv2dBatchLeaky, self).__init__()
self.in_channels = in_channels
self.out_channels = out_channels
self.kernel_size = kernel_size
self.stride = stride
if isinstance(kernel_size, (list, tuple)):
self.padding = [int(ii/2) for ii in kernel_size]
if flag_yolo_structure:
print('------------------->>>> Conv2dBatchLeaky isinstance')
else:
self.padding = int(kernel_size/2)
self.leaky_slope = leaky_slope
# Layer
# LeakyReLU : y = max(0, x) + leaky_slope*min(0,x)
self.layers = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(self.in_channels, self.out_channels, self.kernel_size, self.stride, self.padding, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(self.out_channels),
nn.LeakyReLU(self.leaky_slope, inplace=True)
)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.layers(x)
return x
class ResBlockSum(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, nchannels):
super().__init__()
self.block = nn.Sequential(
Conv2dBatchLeaky(nchannels, int(nchannels/2), 1, 1),
Conv2dBatchLeaky(int(nchannels/2), nchannels, 3, 1)
)
def forward(self, x):
return x + self.block(x)
class HeadBody(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels):
super(HeadBody, self).__init__()
self.layer = nn.Sequential(
Conv2dBatchLeaky(in_channels, out_channels, 1, 1),
Conv2dBatchLeaky(out_channels, out_channels*2, 3, 1),
Conv2dBatchLeaky(out_channels*2, out_channels, 1, 1),
Conv2dBatchLeaky(out_channels, out_channels*2, 3, 1),
Conv2dBatchLeaky(out_channels*2, out_channels, 1, 1)
)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.layer(x)
return x
class Upsample(nn.Module):
# Custom Upsample layer (nn.Upsample gives deprecated warning message)
def __init__(self, scale_factor=1, mode='nearest'):
super(Upsample, self).__init__()
self.scale_factor = scale_factor
self.mode = mode
def forward(self, x):
return F.interpolate(x, scale_factor=self.scale_factor, mode=self.mode)
# default anchors=[(10,13), (16,30), (33,23), (30,61), (62,45), (59,119), (116,90), (156,198), (373,326)]
class YOLOLayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, anchors, nC):
super(YOLOLayer, self).__init__()
self.anchors = torch.FloatTensor(anchors)
self.nA = len(anchors) # number of anchors (3)
self.nC = nC # number of classes
self.img_size = 0
if flag_yolo_structure:
print('init YOLOLayer ------ >>> ')
print('anchors : ',self.anchors)
print('nA : ',self.nA)
print('nC : ',self.nC)
print('img_size : ',self.img_size)
def forward(self, p, img_size, var=None):# p : feature map
bs, nG = p.shape[0], p.shape[-1] # batch_size , grid
if flag_yolo_structure:
print('bs, nG --->>> ',bs, nG)
if self.img_size != img_size:
create_grids(self, img_size, nG, p.device)
# p.view(bs, 255, 13, 13) -- > (bs, 3, 13, 13, 85) # (bs, anchors, grid, grid, xywh + confidence + classes)
p = p.view(bs, self.nA, self.nC + 5, nG, nG).permute(0, 1, 3, 4, 2).contiguous() # prediction
if self.training:
return p
else: # inference
io = p.clone() # inference output
io[..., 0:2] = torch.sigmoid(io[..., 0:2]) + self.grid_xy # xy
io[..., 2:4] = torch.exp(io[..., 2:4]) * self.anchor_wh # wh yolo method
io[..., 4:] = torch.sigmoid(io[..., 4:]) # p_conf, p_cls
io[..., :4] *= self.stride
if self.nC == 1:
io[..., 5] = 1 # single-class model
# flatten prediction, reshape from [bs, nA, nG, nG, nC] to [bs, nA * nG * nG, nC]
return io.view(bs, -1, 5 + self.nC), p
def create_grids(self, img_size, nG, device='cpu'):
# self.nA : len(anchors) # number of anchors (3)
# self.nC : nC # number of classes
# nG : feature map grid 13*13 26*26 52*52
self.img_size = img_size
self.stride = img_size / nG
if flag_yolo_structure:
print('create_grids stride : ',self.stride)
# build xy offsets
grid_x = torch.arange(nG).repeat((nG, 1)).view((1, 1, nG, nG)).float()
grid_y = grid_x.permute(0, 1, 3, 2)
self.grid_xy = torch.stack((grid_x, grid_y), 4).to(device)
if flag_yolo_structure:
print('grid_x : ',grid_x.size(),grid_x)
print('grid_y : ',grid_y.size(),grid_y)
print('grid_xy : ',self.grid_xy.size(),self.grid_xy)
# build wh gains
self.anchor_vec = self.anchors.to(device) / self.stride # 基于 stride 的归一化
# print('self.anchor_vecself.anchor_vecself.anchor_vec:',self.anchor_vec)
self.anchor_wh = self.anchor_vec.view(1, self.nA, 1, 1, 2).to(device)
self.nG = torch.FloatTensor([nG]).to(device)
def get_yolo_layer_index(module_list):
yolo_layer_index = []
for index, l in enumerate(module_list):
try:
a = l[0].img_size and l[0].nG # only yolo layer need img_size and nG
yolo_layer_index.append(index)
except:
pass
assert len(yolo_layer_index) > 0, "can not find yolo layer"
return yolo_layer_index
class Yolov3(nn.Module):
'''
9个anchors,有小中大三个尺寸
小 (10,13), (16,30), (33,23),
中 (30,61), (62,45), (59,119),
大 (116,90), (156,198), (373,326)
为什么有小中大三个尺寸?
答:是因为得符合长宽比,因为有的物体会偏长形,也就是长比宽高;有的物体时宽比长高;有的物体是比较偏于正方形的,也就是长宽差距不大
yolov的作者,通过经验,统一出了常用的achors,长宽比例
有时候人脸是有角度变化的,随着不同的角度变化,的确是不可能正对人脸,也就是长宽基本一样的情况。
也就是它也会出现长比宽多,或者宽比长多,或者是长和宽的比例相差不大
'''
def __init__(self, num_classes=80, anchors=[(10,13), (16,30), (33,23), (30,61), (62,45), (59,119), (116,90), (156,198), (373,326)]):
super().__init__()
'''
anchor_mask1 : 大物体 anchor [6, 7, 8] --->anchors[6] anchors[7] anchors[8] ---> (116,90), (156,198), (373,326)
anchor_mask2 : 中物体 anchor [3, 4, 5] --->anchors[3] anchors[4] anchors[5] ---> (30,61), (62,45), (59,119)
anchor_mask3 : 小物体 anchor [0, 1, 2] --->anchors[0] anchors[1] anchors[2] ---> (10,13), (16,30), (33,23)
'''
anchor_mask1 = [i for i in range(2 * len(anchors) // 3, len(anchors), 1)] # [6, 7, 8]
anchor_mask2 = [i for i in range(len(anchors) // 3, 2 * len(anchors) // 3, 1)] # [3, 4, 5]
anchor_mask3 = [i for i in range(0, len(anchors) // 3, 1)] # [0, 1, 2]
if flag_yolo_structure:
print('anchor_mask1 : ',anchor_mask1) # 大物体 anchor
print('anchor_mask2 : ',anchor_mask2) # 中物体 anchor
print('anchor_mask3 : ',anchor_mask3) # 小物体 anchor
# Network
# OrderedDict 是 dict 的子类,其最大特征是,它可以“维护”添加 key-value 对的顺序
layer_list = []
'''
****** Conv2dBatchLeaky *****
op : Conv2d,BatchNorm2d,LeakyReLU
inputs : in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride, leaky_slope
'''
'''
****** ResBlockSum ******
op : Conv2dBatchLeaky * 2 + x
inputs : nchannels
'''
# list 0
layer_list.append(OrderedDict([
('0_stage1_conv', Conv2dBatchLeaky(3, 32, 3, 1, 1)), # 416 x 416 x 32 # Convolutional
("0_stage2_conv", Conv2dBatchLeaky(32, 64, 3, 2)), # 208 x 208 x 64 # Convolutional
("0_stage2_ressum1", ResBlockSum(64)), # Convolutional*2 + Resiudal
("0_stage3_conv", Conv2dBatchLeaky(64, 128, 3, 2)), # 104 x 104 128 # Convolutional
("0_stage3_ressum1", ResBlockSum(128)),
("0_stage3_ressum2", ResBlockSum(128)), # (Convolutional*2 + Resiudal)**2
("0_stage4_conv", Conv2dBatchLeaky(128, 256, 3, 2)), # 52 x 52 x 256 # Convolutional
("0_stage4_ressum1", ResBlockSum(256)),
("0_stage4_ressum2", ResBlockSum(256)),
("0_stage4_ressum3", ResBlockSum(256)),
("0_stage4_ressum4", ResBlockSum(256)),
("0_stage4_ressum5", ResBlockSum(256)),
("0_stage4_ressum6", ResBlockSum(256)),
("0_stage4_ressum7", ResBlockSum(256)),
("0_stage4_ressum8", ResBlockSum(256)), # 52 x 52 x 256 output_feature_0 (Convolutional*2 + Resiudal)**8
]))
# list 1
layer_list.append(OrderedDict([
("1_stage5_conv", Conv2dBatchLeaky(256, 512, 3, 2)), # 26 x 26 x 512 # Convolutional
("1_stage5_ressum1", ResBlockSum(512)),
("1_stage5_ressum2", ResBlockSum(512)),
("1_stage5_ressum3", ResBlockSum(512)),
("1_stage5_ressum4", ResBlockSum(512)),
("1_stage5_ressum5", ResBlockSum(512)),
("1_stage5_ressum6", ResBlockSum(512)),
("1_stage5_ressum7", ResBlockSum(512)),
("1_stage5_ressum8", ResBlockSum(512)), # 26 x 26 x 512 output_feature_1 # (Convolutional*2 + Resiudal)**8
]))
'''
****** HeadBody ******
op : Conv2dBatchLeaky * 5
inputs : in_channels, out_channels
'''
# list 2
layer_list.append(OrderedDict([
("2_stage6_conv", Conv2dBatchLeaky(512, 1024, 3, 2)), # 13 x 13 x 1024 # Convolutional
("2_stage6_ressum1", ResBlockSum(1024)),
("2_stage6_ressum2", ResBlockSum(1024)),
("2_stage6_ressum3", ResBlockSum(1024)),
("2_stage6_ressum4", ResBlockSum(1024)), # 13 x 13 x 1024 output_feature_2 # (Convolutional*2 + Resiudal)**4
("2_headbody1", HeadBody(in_channels=1024, out_channels=512)), # 13 x 13 x 512 # Convalutional Set = Conv2dBatchLeaky * 5
]))
# list 3
layer_list.append(OrderedDict([
("3_conv_1", Conv2dBatchLeaky(in_channels=512, out_channels=1024, kernel_size=3, stride=1)),
("3_conv_2", nn.Conv2d(in_channels=1024, out_channels=len(anchor_mask1) * (num_classes + 5), kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=True)),
])) # predict one
# list 4
layer_list.append(OrderedDict([
("4_yolo", YOLOLayer([anchors[i] for i in anchor_mask1], num_classes))
])) # 3*((x, y, w, h, confidence) + classes )
# list 5
layer_list.append(OrderedDict([
("5_conv", Conv2dBatchLeaky(512, 256, 1, 1)),
("5_upsample", Upsample(scale_factor=2)),
]))
# list 6
layer_list.append(OrderedDict([
("6_head_body2", HeadBody(in_channels=768, out_channels=256)) # Convalutional Set = Conv2dBatchLeaky * 5
]))
# list 7
layer_list.append(OrderedDict([
("7_conv_1", Conv2dBatchLeaky(in_channels=256, out_channels=512, kernel_size=3, stride=1)),
("7_conv_2", nn.Conv2d(in_channels=512, out_channels=len(anchor_mask2) * (num_classes + 5), kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=True)),
])) # predict two
# list 8
layer_list.append(OrderedDict([
("8_yolo", YOLOLayer([anchors[i] for i in anchor_mask2], num_classes))
])) # 3*((x, y, w, h, confidence) + classes )
# list 9
layer_list.append(OrderedDict([
("9_conv", Conv2dBatchLeaky(256, 128, 1, 1)),
("9_upsample", Upsample(scale_factor=2)),
]))
# list 10
layer_list.append(OrderedDict([
("10_head_body3", HeadBody(in_channels=384, out_channels=128)) # Convalutional Set = Conv2dBatchLeaky * 5
]))
# list 11
layer_list.append(OrderedDict([
("11_conv_1", Conv2dBatchLeaky(in_channels=128, out_channels=256, kernel_size=3, stride=1)),
("11_conv_2", nn.Conv2d(in_channels=256, out_channels=len(anchor_mask3) * (num_classes + 5), kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=True)),
])) # predict three
# list 12
layer_list.append(OrderedDict([
("12_yolo", YOLOLayer([anchors[i] for i in anchor_mask3], num_classes))
])) # 3*((x, y, w, h, confidence) + classes )
# nn.ModuleList类似于pytho中的list类型,只是将一系列层装入列表,并没有实现forward()方法,因此也不会有网络模型产生的副作用
self.module_list = nn.ModuleList([nn.Sequential(i) for i in layer_list])
self.yolo_layer_index = get_yolo_layer_index(self.module_list)
if flag_yolo_structure:
print('yolo_layer : ',len(layer_list),'\n')
print(self.module_list[4])
print(self.module_list[8])
print(self.module_list[12])
# print('self.module_list -------->>> ',self.module_list)
# print('self.yolo_layer_index -------->>> ',self.yolo_layer_index)
def forward(self, x):
img_size = x.shape[-1]
if flag_yolo_structure:
print('forward img_size : ',img_size,x.shape)
output = []
x = self.module_list[0](x)
x_route1 = x
x = self.module_list[1](x)
x_route2 = x
x = self.module_list[2](x)
yolo_head = self.module_list[3](x)
if flag_yolo_structure:
print('mask1 yolo_head : ',yolo_head.size())
yolo_head_out_13x13 = self.module_list[4][0](yolo_head, img_size)
output.append(yolo_head_out_13x13)
x = self.module_list[5](x)
x = torch.cat([x, x_route2], 1)
x = self.module_list[6](x)
yolo_head = self.module_list[7](x)
if flag_yolo_structure:
print('mask2 yolo_head : ',yolo_head.size())
yolo_head_out_26x26 = self.module_list[8][0](yolo_head, img_size)
output.append(yolo_head_out_26x26)
x = self.module_list[9](x)
x = torch.cat([x, x_route1], 1)
x = self.module_list[10](x)
yolo_head = self.module_list[11](x)
if flag_yolo_structure:
print('mask3 yolo_head : ',yolo_head.size())
yolo_head_out_52x52 = self.module_list[12][0](yolo_head, img_size)
output.append(yolo_head_out_52x52)
if self.training:
return output
else:
io, p = list(zip(*output)) # inference output, training output
return torch.cat(io, 1), p
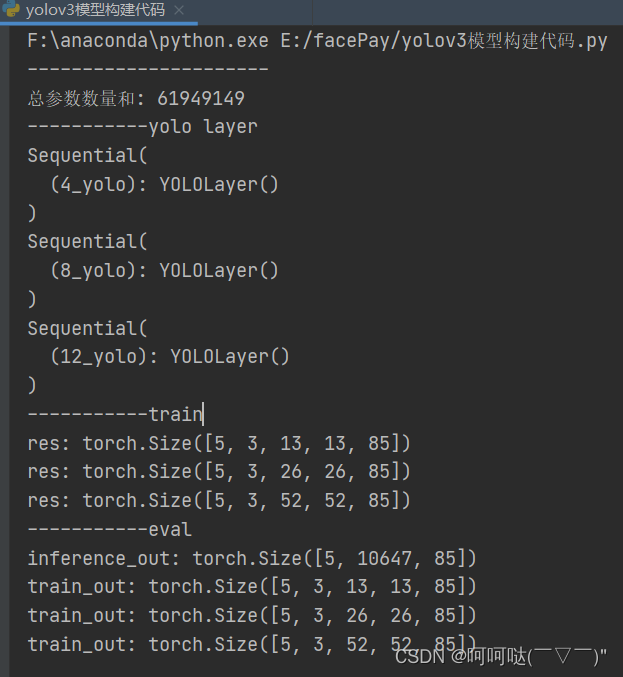
if __name__ == "__main__":
dummy_input = torch.Tensor(5, 3, 416, 416)
model = Yolov3(num_classes=80)
params = list(model.parameters())
k = 0
for i in params:
l = 1
for j in i.size():
l *= j
# print("该层的结构: {}, 参数和: {}".format(str(list(i.size())), str(l)))
k = k + l
print("----------------------")
print("总参数数量和: " + str(k))
print("-----------yolo layer")
for index in model.yolo_layer_index:
print(model.module_list[index])
print("-----------train")
model.train()
for res in model(dummy_input):
print("res:", np.shape(res))
print("-----------eval")
model.eval()
inference_out, train_out = model(dummy_input)
print("inference_out:", np.shape(inference_out))
for o in train_out:
print("train_out:", np.shape(o))
如果您喜欢我的分享,就点个赞👍+收藏,这也是我努力更新文章的动力!!!!!









![“AI Earth”人工智能创新挑战赛:助力精准气象和海洋预测Baseline[2]:数据探索性分析(温度风场可视化)、CNN+LSTM模型建模](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/d553c7dadca54bdb82a3a234befb74d8.png#pic_center)

