前言
现在绝大多数java项目都上了Springboot框架, 因此深入理解Springboot框架的运行原理,能帮助我们更好的在Springboot框架下进行业务开发,同时能学习框架中优秀的设计思想, 本文主要是通过对Springboot源码的分析, 来理解整个springboot项目的启动流程. 因为Springboot不同版本的源码有差异, 因此特别声明, 本文是基于2.2.10.RELEASE版本进行的原理分析.
1. 导入依赖
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.2.10.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
1.1 Springboot项目在spring官网已经作为顶级项目存在, 官网描述非常清楚,如果只是想搭建一个springboot项目, 只需要导入spring-boot-starter-parent, 如果是做web开发, 则还需导入spring-boot-starter-web, 本文只分析Springboot的启动流程,因此只需要导入spring-boot-starter-parent
2. 创建启动类
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringbootApplication{
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringbootApplication.class, args);
}
}
2.1 一个Springboot项目只需要在启动类上加@SpringBootApplicatio注解就可以, 可能很多人会有疑问,为什么加入了这个注解,就是一个springboot项目了,回答这个问题之前,我们首先要知道什么是一个Springboot项目, 接下来我会从源码角度为大家深入分析.
3. springboot启动流程图
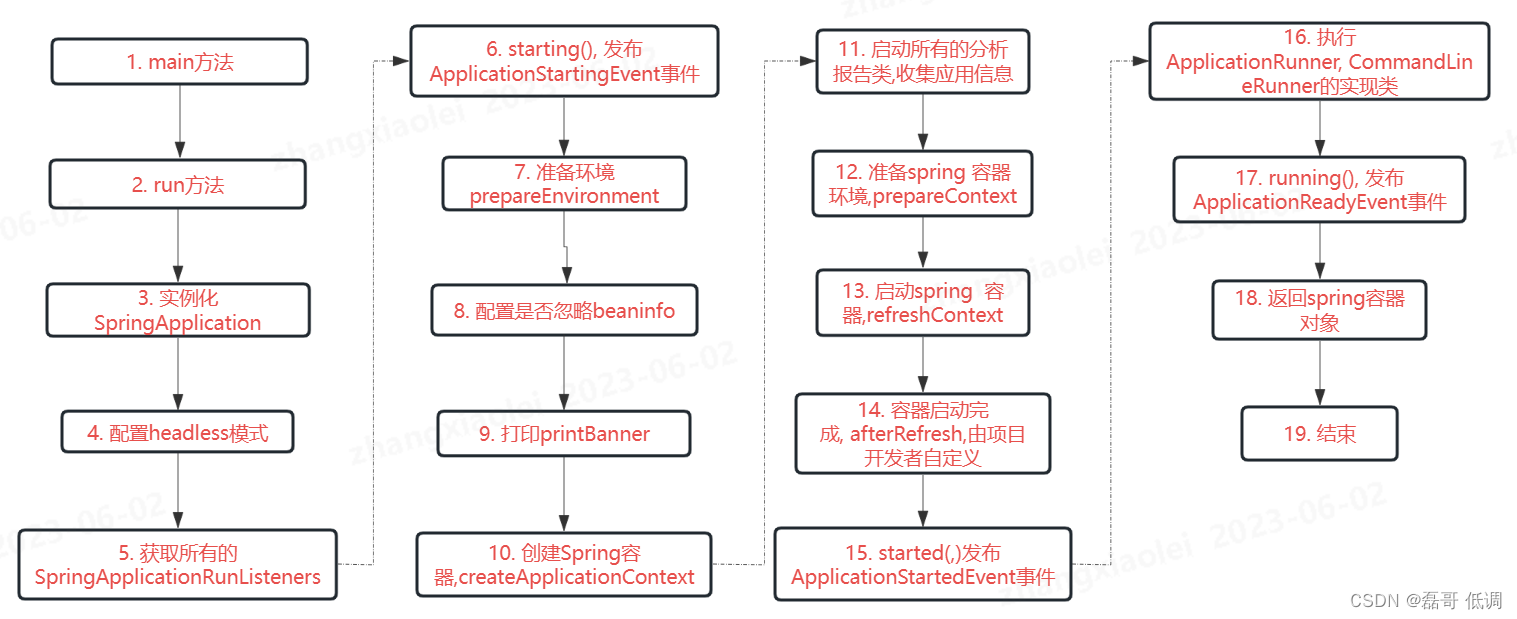
3.1 以上是整个Springboot的run方法的执行流程, 这只是一个总体流程图, 接下里对每一步我将通过源码深入分析.
4. 实例化SpringAppliaciton
4.1 实例化SpringAppliaciton的核心是实例化了两种类型的class, 一个是ApplicationContextInitializer.class, 另一个是 ApplicationListener.class
setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class));
setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
4.2 getSpringFactoriesInstances该方法的核心是实例化所有依赖下META-INF/spring.factories文件里ApplicationContextInitializer和ApplicationListener类型, 并放入initializers和listeners属性中
//将META-INF/spring.factories目录下对应类型的全类名加入到set集合中
Set<String> names = new LinkedHashSet<>
(SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(type, classLoader));
//通过反射实例化
List<T> instances = createSpringFactoriesInstances(type, parameterTypes, classLoader, args, names);
4.3 SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames方法就是去加载META-INF/spring.factories, 请对这个方法有些印象, 因为这个方法在Springboot自动装配的时候也会调用.
public static List<String> loadFactoryNames(Class<?> factoryType, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
//对应类型的全类名,这里是org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer和org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener
String factoryTypeName = factoryType.getName();
//通过key筛选对应的value集合
return (List)loadSpringFactories(classLoader).getOrDefault(factoryTypeName, Collections.emptyList());
}
private static Map<String, List<String>> loadSpringFactories(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
//这个集合在web项目的源码中经常出现,它和普通的map区别在于一个key可以对应多个value
MultiValueMap<String, String> result = (MultiValueMap)cache.get(classLoader);
if (result != null) {
return result;
} else {
try {
//核心是加载所有类路径下META-INF/spring.factories文件
Enumeration<URL> urls = classLoader != null ? classLoader.getResources("META-INF/spring.factories") : ClassLoader.getSystemResources("META-INF/spring.factories");
LinkedMultiValueMap result = new LinkedMultiValueMap();
while(urls.hasMoreElements()) {
URL url = (URL)urls.nextElement();
UrlResource resource = new UrlResource(url);
Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource);
Iterator var6 = properties.entrySet().iterator();
while(var6.hasNext()) {
Entry<?, ?> entry = (Entry)var6.next();
String factoryTypeName = ((String)entry.getKey()).trim();
String[] var9 = StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray((String)entry.getValue());
int var10 = var9.length;
for(int var11 = 0; var11 < var10; ++var11) {
String factoryImplementationName = var9[var11];
result.add(factoryTypeName, factoryImplementationName.trim());
}
}
}
cache.put(classLoader, result);
return result;
} catch (IOException var13) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to load factories from location [META-INF/spring.factories]", var13);
}
}
}
4.4 createSpringFactoriesInstances是通过反射实例化所有的对象
private <T> List<T> createSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type, Class<?>[] parameterTypes,
ClassLoader classLoader, Object[] args, Set<String> names) {
List<T> instances = new ArrayList<>(names.size());
for (String name : names) {
try {
Class<?> instanceClass = ClassUtils.forName(name, classLoader);
Assert.isAssignable(type, instanceClass);
Constructor<?> constructor = instanceClass.getDeclaredConstructor(parameterTypes);
T instance = (T) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(constructor, args);
instances.add(instance);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Cannot instantiate " + type + " : " + name, ex);
}
}
return instances;
}
4.5 因为是加载所有类路径下的spring.factories文件, 因此会加载spring-boot-starter-parent依赖的所有模块的spring.factories文件, 默认是加载8个initializer对象和12个listener对象.
5. 配置headless模式
5.1 headless模式springboot是默认开启的,通过System.setProperty(“java.awt.headless”,”true”)设置, 因为对于服务端而言,可能缺少显示屏、键盘或者鼠标等设备.
private void configureHeadlessProperty() {
System.setProperty(SYSTEM_PROPERTY_JAVA_AWT_HEADLESS,
System.getProperty(SYSTEM_PROPERTY_JAVA_AWT_HEADLESS, Boolean.toString(this.headless)));
}
6. 获取所有的SpringApplicationRunListeners
6.1 同样是加载META-INF/spring.factories文件下所有的SpringApplicationRunListener类型的全类名,通过反射实例化.
因为我们只导入了spring-boot-starter-parent包,在子模块spring-boot下的META-INF/spring.factories文件中只有一个EventPublishingRunListener实现了SpringApplicationRunListener,因此只实例化一个SpringApplicationRunListener类型
# Run Listeners
org.springframework.boot.SpringApplicationRunListener=\
org.springframework.boot.context.event.EventPublishingRunListener