学完C语言之后,我就去阅读《C Primer Plus》这本经典的C语言书籍,对每一章的编程练习题都做了相关的解答,仅仅代表着我个人的解答思路,如有错误,请各位大佬帮忙点出!
由于使用的是命令行参数常用于linux系统或者vscode,但此代码是运行于vs2022的,测试截图就不弄了。
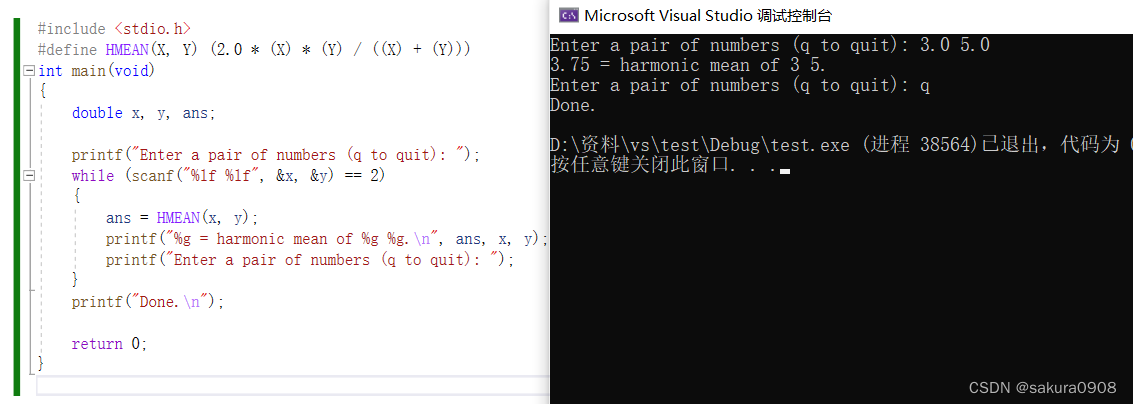
2.两数的调和平均数这样计算:先得到两数的倒数,然后计算两个倒数 的平均值,最后取计算结果的倒数。使用#define指令定义一个宏“函数”,执 行该运算。编写一个简单的程序测试该宏。
#include <stdio.h>
#define HMEAN(X, Y) (2.0 * (X) * (Y) / ((X) + (Y)))
int main(void)
{
double x, y, ans;
printf("Enter a pair of numbers (q to quit): ");
while (scanf("%lf %lf", &x, &y) == 2)
{
ans = HMEAN(x, y);
printf("%g = harmonic mean of %g %g.\n", ans, x, y);
printf("Enter a pair of numbers (q to quit): ");
}
printf("Done.\n");
return 0;
}
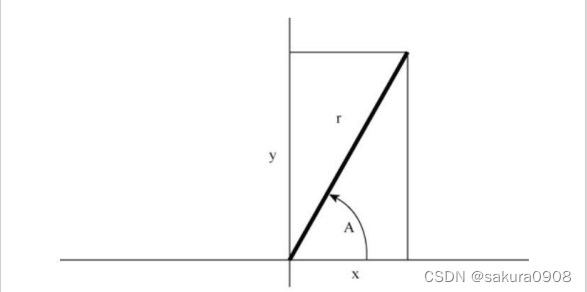
3.极坐标用向量的模(即向量的长度)和向量相对x轴逆时针旋转的角 度来描述该向量。直角坐标用向量的x轴和y轴的坐标来描述该向量(见图 16.3)。编写一个程序,读取向量的模和角度(单位:度),然后显示x轴 和y轴的坐标。相关方程如下:
x = r*cos A y = r*sin A
需要一个函数来完成转换,该函数接受一个包含极坐标的结构,并返回 一个包含直角坐标的结构(或返回指向该结构的指针)。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
#define PI 3.1415926
typedef struct
{
double length;
double angle;
} polar;
typedef struct
{
double x;
double y;
} rect;
rect polar_to_rect(const polar* temp)
{
rect res;
static const double rad = PI / 180.0;
double ang = rad * temp->angle;
res.x = temp->length * cos(ang);
res.y = temp->length * sin(ang);
return res;
}
int main(void)
{
polar input;
rect answer;
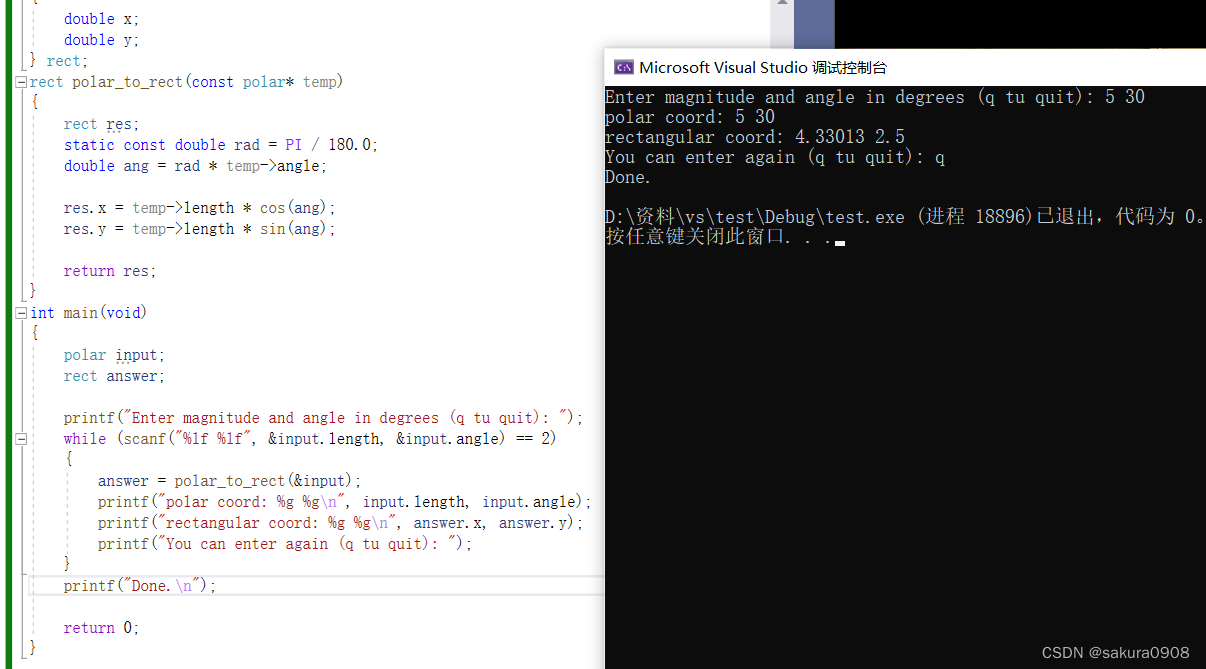
printf("Enter magnitude and angle in degrees (q tu quit): ");
while (scanf("%lf %lf", &input.length, &input.angle) == 2)
{
answer = polar_to_rect(&input);
printf("polar coord: %g %g\n", input.length, input.angle);
printf("rectangular coord: %g %g\n", answer.x, answer.y);
printf("You can enter again (q tu quit): ");
}
printf("Done.\n");
return 0;
}
4.ANSI库这样描述clock()函数的特性:
#include <time.h>
clock_t clock (void);
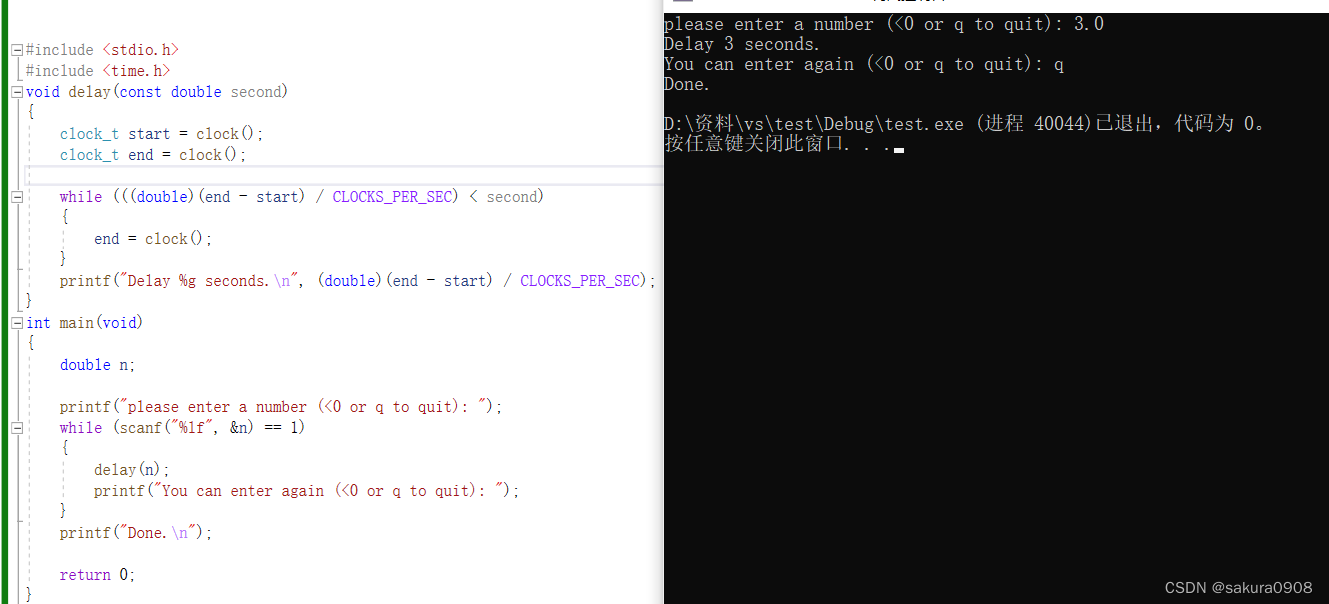
这里,clock_t是定义在time.h中的类型。该函数返回处理器时间,其单 位取决于实现(如果处理器时间不可用或无法表示,该函数将返回-1)。然 而,CLOCKS_PER_SEC(也定义在time.h中)是每秒处理器时间单位的数 量。因此,两个 clock()返回值的差值除以 CLOCKS_PER_SEC得到两次调用 之间经过的秒数。在进行除法运算之前,把值的类型强制转换成double类 型,可以将时间精确到小数点以后。编写一个函数,接受一个double类型的 参数表示时间延迟数,然后在这段时间运行一个循环。编写一个简单的程序 测试该函数。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <time.h>
void delay(const double second)
{
clock_t start = clock();
clock_t end = clock();
while (((double)(end - start) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC) < second)
{
end = clock();
}
printf("Delay %g seconds.\n", (double)(end - start) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC);
}
int main(void)
{
double n;
printf("please enter a number (<0 or q to quit): ");
while (scanf("%lf", &n) == 1)
{
delay(n);
printf("You can enter again (<0 or q to quit): ");
}
printf("Done.\n");
return 0;
}
5.编写一个函数接受这些参数:内含int类型元素的数组名、数组的大小 和一个代表选取次数的值。该函数从数组中随机选择指定数量的元素,并打 印它们。每个元素只能选择一次(模拟抽奖数字或挑选陪审团成员)。另 外,如果你的实现有time()(第12章讨论过)或类似的函数,可在srand()中 使用这个函数的输出来初始化随机数生成器rand()。编写一个简单的程序测 试该函数。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#define LEN 30
#define PICK 6
void random_pick(int ar[],int picks)
{
int count = 0;
int i, br[LEN];
memcpy(br, ar, LEN * sizeof(int));
srand((unsigned int)time(0));
printf("Pick %d numbers:\n", picks);
while (picks > 0)
{
i = rand() % LEN;
if (0 == br[i])
{
continue;
}
else
{
printf("%-8d", br[i]);
br[i] = 0;
--picks;
}
if (++count % 10 == 0)
{
putchar('\n');
}
}
printf("\n");
}
int main(void)
{
int i, ch;
int choices[LEN];
for (i = 0; i < LEN; i++)
{
choices[i] = i + 1;
}
do
{
random_pick(choices, PICK);
printf("Can you do again (y/n)? ");
ch = getchar();
while (getchar() != '\n')
continue;
} while ('y' == ch || 'Y' == ch);
printf("Done.\n");
return 0;
}
6.修改程序清单16.17,使用struct names元素(在程序清单16.17后面的 讨论中定义过),而不是double类型的数组。使用较少的元素,并用选定的 名字显式初始化数组。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#define LEN 40
#define SLEN 5
struct names
{
char first[LEN];
char last[LEN];
};
int comp(const void* p1, const void* p2)
{
const struct names* ps1 = (const struct names*)p1;
const struct names* ps2 = (const struct names*)p2;
if (strcmp(ps1->last, ps2->last) != 0)
{
return 0;
}
else
{
return strcmp(ps1->first, ps2->first);
}
}
void show_names(const struct names* begin, int n)
{
const struct names* end = begin + n;
while (begin < end)
{
printf("%s %s\n", begin->first, begin->last);
++begin;
}
return;
}
int main(void)
{
struct names staff[SLEN] ={{"Francy, card"},{"Coffee, cancy"},
{"Stephen, lory"},{"Jack, rosery"},{"Black, clover"}};
printf("Random list:\n");
show_names(staff, SLEN);
qsort(staff, SLEN, sizeof(struct names), comp);
printf("\nSorted list:\n");
show_names(staff, SLEN);
return 0;
}
7.下面是使用变参函数的一个程序段:
#include
#include
#include
void show_array(const double ar[], int n);
double * new_d_array(int n, ...);
int main() {
double * p1;
double * p2;
p1 = new_d_array(5, 1.2, 2.3, 3.4, 4.5, 5.6);
p2 = new_d_array(4, 100.0, 20.00, 8.08, -1890.0);
show_array(p1, 5);
show_array(p2, 4);
free(p1);
free(p2);
return 0; }
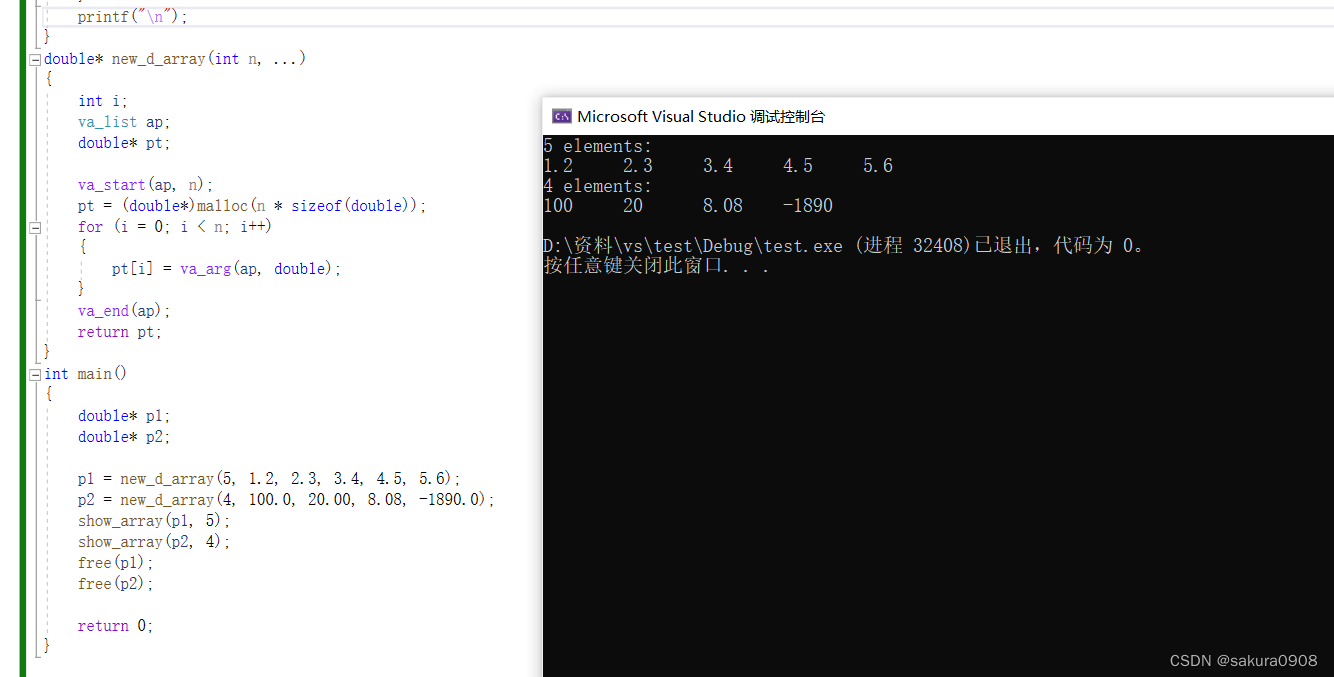
new_d_array()函数接受一个int类型的参数和double类型的参数。该函数 返回一个指针,指向由malloc()分配的内存块。int类型的参数指定了动态数 组中的元素个数,double类型的值用于初始化元素(第1个值赋给第1个元 素,以此类推)。编写show_array()和new_d_array()函数的代码,完成这个 程序。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdarg.h>
void show_array(const double ar[], int n)
{
int i;
printf("%d elements:\n", n);
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
printf("%-8g", ar[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
double* new_d_array(int n, ...)
{
int i;
va_list ap;
double* pt;
va_start(ap, n);
pt = (double*)malloc(n * sizeof(double));
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
pt[i] = va_arg(ap, double);
}
va_end(ap);
return pt;
}
int main()
{
double* p1;
double* p2;
p1 = new_d_array(5, 1.2, 2.3, 3.4, 4.5, 5.6);
p2 = new_d_array(4, 100.0, 20.00, 8.08, -1890.0);
show_array(p1, 5);
show_array(p2, 4);
free(p1);
free(p2);
return 0;
}
![[SpringBoot]创建聚合项目](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/0d387290d69340128ef1df004aeb2f76.png)