Spring 之 jwt,过滤器,拦截器,aop,监听器
- 一、jwt编写
- 1.1 pom
- 1.2 JwtUtils
- 1.3 注意
- 1.4 用法
- 二、过滤器
- 2.1 原理
- 2.2 使用场景
- 2.3 使用步骤
- 2.3.1 自定义过滤器类implements Filter
- 2.3.2 配置类
- 2.3.3 过滤器使用场景
- 2.4 问题
- 三、拦截器
- 3.1 特点
- 3.2 使用
- 3.2.1 拦截器实现方式
- 3.3.1 自定义拦截器
- 3.3.2 拦截器配置信息
- 3.4 使用场景
- 3.5 拦截器案例
- 3.5.1 preHandle方法获取所需参数
- 3.6 执行过程
- 3.7 HandlerMethod类
- 四、aop
- 4.1 区别
- 4.2 案例
- 五、自定义参数解析器
- 5.1 自定义注解
- 5.2 配置自定义参数构造器
- 5.3 自定义参数解析器类
- 六、监听器
- 6.1 自定义事件源
- 6.2 自定义事件监听器
- 6.3 发布事件
- 七、servlet对象
- 7.1 request获取参数
- 7.1.1 获取url上的参数
- 7.1.2 获取请求头参数
- 7.1.3 请求体参数
- 7.1.3.1 form表单key-value数据
- 7.1.3.1 form表单文件类型数据
- 7.1.4 获取cookie信息
- 7.1.5 修改request参数信息
- 7.2 response
- 7.2.1 常用方法
- 7.3 后端参数接收
- 7.3.1 url参数接收
- 7.3.2 请求头参数接收
- 7.3.3 请求体参数接收
- 7.3.3.1 正常类型数据接收
- 7.3.3.2 文件类型数据接收
- 7.3.4 获取cookie
- 7.3.5 自定义传参使用
- 7.4 设置
- 7.4.1 大文件上传设置
- 7.5 seesion和cookie
- 7.5.1 区别
- 7.5.2 测试
- 7.5.3 重要概念
- 八、spring mvc
- 8.1 spring mvc流程
- 8.1.1 过程
- 八、总结
- 8.1 总结
一、jwt编写
1.1 pom
- 第二个pom为了生成公私钥
<dependency>
<groupId>io.jsonwebtoken</groupId>
<artifactId>jjwt</artifactId>
<version>0.9.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>cn.hutool</groupId>
<artifactId>hutool-all</artifactId>
<version>5.1.0</version>
</dependency>
1.2 JwtUtils
package org.example.JWT;
import cn.hutool.core.io.FileUtil;
import io.jsonwebtoken.*;
import org.example.Entity.User;
import org.springframework.beans.BeanUtils;
import java.io.DataInputStream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.security.*;
import java.security.spec.PKCS8EncodedKeySpec;
import java.security.spec.X509EncodedKeySpec;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class JWTUtil {
public static String keyPath = "D:\\";
public static int Expire = 1000 * 1000;
public static <T> String getToken(String id, T t) throws Exception {
HashMap head = new HashMap<>();
//添加jwt头
head.put("alg", SignatureAlgorithm.RS256.getValue());//不使用签名算法
head.put("typ", "JWT");
//JWT体结构
HashMap body = new HashMap();
Field[] declaredFields = t.getClass().getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field: declaredFields){
field.setAccessible(true);
body.put(field.getName(), field.get(t));
System.out.println(field.getName() + " " + field.get(t));
}
//生成JWT
String jwt = Jwts.builder()
.setHeader(head)
.setClaims(body)
.setId(id)
//.setExpiration(new Date(System.currentTimeMillis() + Expire))
.signWith(SignatureAlgorithm.RS256,getPriKey())
.compact();
return jwt;
}
public static <T> Map<String, Object> parseToken(String jwt, T t) throws Exception {
try {
Jwt result = Jwts.parser().setSigningKey(getPubKey()).parse(jwt);
Header header = result.getHeader();
Claims body = (Claims) result.getBody();
System.out.println(body);
HashMap<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
String subject = (String)body.get("jti");
map.put("id",subject);
System.out.println(subject);
T o = (T) t.getClass().newInstance();
Field[] declaredFields = t.getClass().getDeclaredFields();
for(Field field: declaredFields){
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(o, body.get(field.getName()));
}
System.out.println(o);
map.put("obj",o);
return map;
}catch (Exception e){
e.getMessage();
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
return null;
}
}
public static void getKey(String password) throws NoSuchAlgorithmException {
KeyPairGenerator keyPairGenerator = KeyPairGenerator.getInstance("RSA");
SecureRandom secureRandom = new SecureRandom(password.getBytes());
keyPairGenerator.initialize(1024, secureRandom);
KeyPair keyPair = keyPairGenerator.genKeyPair();
byte[] publicKeyBytes = keyPair.getPublic().getEncoded();
byte[] privateKeyBytes = keyPair.getPrivate().getEncoded();
FileUtil.writeBytes(publicKeyBytes, keyPath +"pub.key");
FileUtil.writeBytes(privateKeyBytes, keyPath +"pri.key");
}
//获取私钥
public static PrivateKey getPriKey() throws Exception{
InputStream resourceAsStream =
new FileInputStream(keyPath +"pri.key");
DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(resourceAsStream);
byte[] keyBytes = new byte[resourceAsStream.available()];
dis.readFully(keyBytes);
PKCS8EncodedKeySpec spec = new PKCS8EncodedKeySpec(keyBytes);
KeyFactory kf = KeyFactory.getInstance("RSA");
return kf.generatePrivate(spec);
}
//获取公钥
public static PublicKey getPubKey() throws Exception{
InputStream resourceAsStream =
new FileInputStream(keyPath + "pub.key");
DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(resourceAsStream);
byte[] keyBytes = new byte[resourceAsStream.available()];
dis.readFully(keyBytes);
X509EncodedKeySpec spec = new X509EncodedKeySpec(keyBytes);
KeyFactory kf = KeyFactory.getInstance("RSA");
return kf.generatePublic(spec);
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
User user = new User();
user.setAge(12);
user.setId(1);
user.setUserName("jack");
String token = getToken("123", user);
User user1 = new User();
Map<String, Object> map = parseToken(token, new User());
User obj = (User)map.get("obj");
System.out.println(map.get("sub"));
System.out.println(obj);
}
}
1.3 注意
- jwt过期会返回null
- 设置jwt过期时间,参数是到期的时间点
- jwt本质上就是将用户的个人信息加密,将加密后的信息通过cookie形式传递。
.setExpiration(new Date(System.currentTimeMillis() + Expire))
1.4 用法
- getKey(“123456”);生成公私钥文件
- getToken(String key,T t):传入对象实例,获得token
- parseToken(String jwt, T t):传入jwt token,得到map,第一个是id,第二个是对象t。
二、过滤器
参考: 拦截器与过滤器详解,使用方式与注意事项,使用场景以及区别与联系
2.1 原理
依赖于servlet容器。在实现上基于函数回调
2.2 使用场景
统一设置编码
过滤敏感字符
登录校验
URL级别的访问权限控制
数据压缩
Filter可以拦截所有请求,包括静态资源
2.3 使用步骤
2.3.1 自定义过滤器类implements Filter
package org.example.Basic;
import javax.servlet.*;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
public class myFilter2 implements Filter {
@Override
public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException {
System.out.println("过滤器2初始化");
}
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException {
System.out.println("过滤器2前执行");
HttpServletRequest request1 = (HttpServletRequest) request;
System.out.println(request1.getRequestURI());
System.out.println(request1.getRequestURL());
chain.doFilter(request,response);
System.out.println("过滤器2后执行");
}
@Override
public void destroy() {
System.out.println("过滤器2毁灭");
}
}
2.3.2 配置类
- 注册过滤器对象,并设置过滤器顺序。
package org.example.Basic;
import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.FilterRegistrationBean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class MyFilterConfiguration {
@Bean
public FilterRegistrationBean filterRegistrationBean1(){
//创建一个注册过滤器对象
FilterRegistrationBean registrationBean = new FilterRegistrationBean();
//设置自定义过滤器
registrationBean.setFilter(new myFilter1());
//设置过滤拦截匹配规则,/*是匹配所有
// registrationBean.addUrlPatterns("/*");
//只拦截testController下面的接口
registrationBean.addUrlPatterns("/cache/*");
//存在多个过滤器时,设置执行顺序,值越大,执行顺序越靠后
registrationBean.setOrder(1);
//返回这个注册过滤器对象
return registrationBean;
}
@Bean
public FilterRegistrationBean filterRegistrationBean2(){
//创建一个注册过滤器对象
FilterRegistrationBean registrationBean1 = new FilterRegistrationBean();
//设置自定义过滤器
registrationBean1.setFilter(new myFilter2());
//设置过滤拦截匹配规则,/*是匹配所有
// registrationBean.addUrlPatterns("/*");
//只拦截testController下面的接口
registrationBean1.addUrlPatterns("/cache/*");
//存在多个过滤器时,设置执行顺序,值越大,执行顺序越靠后
registrationBean1.setOrder(2);
//返回这个注册过滤器对象
return registrationBean1;
}
}
2.3.3 过滤器使用场景
- 过滤参数,参数校验
- 生成日志等等
2.4 问题
- 过滤器的路径如果设置为/*可能会执行2次,有一次会访问/favicon.ico,设置访问路径即可解决。
三、拦截器
3.1 特点
- 拦截器依赖于SpringMvc的,需要导入Mvc的依赖
preHandle() 在目标请求完成之前执行。有返回值Boolean类型,true:表示放行 postHandle()
在目标请求之完成后执行。 afterCompletion() 在整个请求完成之后【modelAndView已被渲染执行】。
-
拦截器只能拦截action请求,不包括静态资源(有待验证)
-
基于java反射机制实现
-
拦截器可以获取IOC容器中的各个bean,而过滤器就不行,这点很重要,在拦截器里注入一个service,可以调用业务逻辑。
3.2 使用
3.2.1 拦截器实现方式
- AOP切面方式实现
- 使用Spring的拦截器相关接口来自定义拦截器
3.3.1 自定义拦截器
3.3.2 拦截器配置信息
package org.example.Intecepter;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.CorsRegistry;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.InterceptorRegistration;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.InterceptorRegistry;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurer;
@Configuration
public class MyInterceptorConfiguration implements WebMvcConfigurer {
/**
* 重写addCorsMappings()解决跨域问题
* 配置:允许http请求进行跨域访问
*
* @param registry
* @Author 有梦想的肥宅
*/
// @Override
// public void addCorsMappings(CorsRegistry registry) {
// registry.addMapping("/**")//指哪些接口URL需要增加跨域设置
// .allowedOrigins("*")//指的是前端哪些域名被允许跨域
// .allowCredentials(true)//需要带cookie等凭证时,设置为true,就会把cookie的相关信息带上
// .allowedMethods("GET", "HEAD", "POST", "PUT", "DELETE", "OPTIONS")//指的是允许哪些方法
// .maxAge(3600);//cookie的失效时间,单位为秒(s),若设置为-1,则关闭浏览器就失效
// }
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
//注册Interceptor拦截器(Interceptor这个类是我们自己写的拦截器类)
InterceptorRegistration registration = registry.addInterceptor(new MyIntercrptor());
//addPathPatterns()方法添加需要拦截的路径
registration.addPathPatterns("/**"); //所有路径都被拦截
//excludePathPatterns()方法添加不拦截的路径
registration.excludePathPatterns( //添加不拦截路径
"/demo/loginPage", //登录页面的地址【不拦截】
"/**/*.html", //html静态资源
"/**/*.js", //js静态资源
"/**/*.css" //css静态资源
);
}
}
3.4 使用场景
- 配置跨域
- 登录校验
3.5 拦截器案例
3.5.1 preHandle方法获取所需参数
- 执行方法名称
- 是否有某个注解
- 方法所需参数名称
package org.example.Intecepter;
import lombok.Data;
import org.checkerframework.checker.units.qual.A;
import org.springframework.core.MethodParameter;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.method.HandlerMethod;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerInterceptor;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpSession;
import java.lang.invoke.MethodHandle;
@Data
public class MyIntercrptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
//return true才进行下一步操作
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
System.out.println("使用拦截器1进行操作");
HandlerMethod hand = (HandlerMethod)handler;
//执行的方法名称
System.out.println(hand.getMethod().getName());
//获取执行的参数信息
MethodParameter[] methodParameters = hand.getMethodParameters();
for(MethodParameter methodParameter : methodParameters){
System.out.println(methodParameter.getParameter().getName());
System.out.println(methodParameter.getParameter().getType());
}
//判断类上有没有某个注解
GetMapping annotation = hand.getBeanType().getAnnotation(GetMapping.class);
boolean annotation1 = hand.getBeanType().isAnnotationPresent(GetMapping.class);
//获取方法的注解,判断方法上有没该注解
GetMapping annotation2 = hand.getMethod().getAnnotation(GetMapping.class);
boolean annotationPresent = hand.getMethod().isAnnotationPresent(GetMapping.class);
System.out.println(annotation1 + " " + annotationPresent);
return true;
}
@Override
public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception {
// HandlerMethod handler1 = (HandlerMethod) handler;
// System.out.println(handler1.getReturnType().getMember().getName());
// String viewName = modelAndView.getViewName();
// System.out.println(viewName);
}
@Override
public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception {
}
}
3.6 执行过程
如果在preHandle()阶段就有某个拦截器校验不通过,会从上一个拦截器开始执行afterCompletion()进行返回
3.7 HandlerMethod类
spring mvc的HandlerMethod简介四、aop
4.1 区别
Java AOP篇过滤器,拦截器拦截的是URL。AOP拦截的是类的元数据(包、类、方法名、参数等)。
过滤器并没有定义业务用于执行逻辑前、后等,仅仅是请求到达就执行。
拦截器有三个方法,相对于过滤器更加细致,有被拦截逻辑执行前、后等。
AOP针对具体的代码,能够实现更加复杂的业务逻辑。
三者功能类似,但各有优势,从过滤器 -> 拦截器 -> 切面,拦截规则越来越细致。
执行顺序依次是过滤器、拦截器、切面。
4.2 案例
- 自定义注解
package org.example.AOP;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
public @interface MyAnn {
String value() default "";
}
- aop案例
package org.example.AOP;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.aspectj.lang.reflect.MethodSignature;
import org.example.Event.OptLogDTO;
import org.example.Event.SysLogEvent;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationEvent;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.RequestContextHolder;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.ServletRequestAttributes;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
@Component
@Aspect
public class MyAop {
@Autowired
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
private static final ThreadLocal<OptLogDTO> THREAD_LOCAL = new ThreadLocal<>();
/***
* 定义controller切入点拦截规则,拦截SysLog注解的方法
*/
@Pointcut("@annotation(MyAnn)")
public void myAnnTest() {
}
@Before(value = "myAnnTest()")
public void doBefore(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
//得到连接点执行的方法对象
MethodSignature signature= (MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature();
Method method = signature.getMethod();
//得到方法上的注解
MyAnn annotation = method.getAnnotation(MyAnn.class);
if (annotation!=null){
//获取注解属性的value值
String value = annotation.value();
System.out.println("自定义注解的值" + " " + value);
}
}
@Around(value = "myAnnTest()")
public Object doAround(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
//HttpServletRequest request = ((ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes()).getRequest();
HttpServletResponse response = ((ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes()).getResponse();
// 类名
String className = joinPoint.getTarget().getClass().getName();
System.out.println(className);
//获取执行的方法名
MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature();
String methodName = signature.getMethod().getName();
System.out.println(methodName);
//方法的返回类型
String name = signature.getReturnType().getName();
System.out.println(name);
//获取方法的参数,这里的参数可能包含有文件
Object[] args1 = joinPoint.getArgs();
for (int i = 0; i < args1.length; i++) {
System.out.println(args1.toString());
}
Object proceed = joinPoint.proceed();
if(proceed instanceof String){
System.out.println(proceed.toString());
}
System.out.println(response.getStatus());
return proceed;
}
}
package org.example.Service.controller.Aop.OptAop;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiOperation;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.aspectj.lang.reflect.MethodSignature;
import org.example.Demo.util.JwtUtils;
import org.example.Demo.util.LoginInfo;
import org.example.Service.Util.DateUtil;
import org.example.Service.entity.PdAuthUser;
import org.example.Service.entity.PdCommonOptLog;
import org.example.Service.service.PdAuthUserService;
import org.example.Service.service.PdCommonLoginLogService;
import org.example.Service.service.impl.PdCommonOptLogServiceImpl;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.AnnotationUtils;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.RequestContextHolder;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.ServletRequestAttributes;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.lang.annotation.Annotation;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.Map;
@Component
@Aspect
public class OptLogAspect {
@Autowired
PdCommonOptLogServiceImpl pdCommonOptLogService;
@Autowired
PdAuthUserService pdAuthUserService;
@Pointcut("@annotation(org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping)")
public void getOpt(){
}
@Pointcut("@annotation(org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PutMapping)")
public void putOpt(){
}
@Pointcut("@annotation(org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping)")
public void postOpt(){
}
@Pointcut("@annotation(org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.DeleteMapping)")
public void DelOpt(){
}
@Around(value = "getOpt()||putOpt()||postOpt()||DelOpt()")
public Object doAround(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
LocalDateTime nowStart = LocalDateTime.now();
String start = DateUtil.getNowDateStr(nowStart);
Long startInstant = DateUtil.getNowInstant(nowStart);
Object proceed = joinPoint.proceed();
HttpServletRequest request = ((ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes()).getRequest();
HttpServletResponse response = ((ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes()).getResponse();
if(request.getRequestURL().toString().contains("login")){
return proceed;
}
LocalDateTime nowEnd = LocalDateTime.now();
String end = DateUtil.getNowDateStr(nowEnd);
Long endInstant = DateUtil.getNowInstant(nowEnd);
String token = request.getHeader("token");
LoginInfo memberIdByJwtToken = JwtUtils.getMemberIdByJwtToken(token);
if(memberIdByJwtToken == null){
return proceed;
}
String account = memberIdByJwtToken.getAccount();
System.out.println(account);
PdAuthUser user = pdAuthUserService.getByAccout(account);
PdCommonOptLog pdCommonOptLog = new PdCommonOptLog();
pdCommonOptLog.setRequestIp(request.getRemoteHost());
pdCommonOptLog.setUserName(user.getNamed());
pdCommonOptLog.setType("OPT");
pdCommonOptLog.setRequestUri(request.getRequestURI());
Map<String, String[]> parameterMap = request.getParameterMap();
StringBuilder param = new StringBuilder();
parameterMap.forEach((k,v) -> {
param.append(k).append(":").append(v).append(",");
});
pdCommonOptLog.setParams(new String(param));
pdCommonOptLog.setStartTime(nowStart);
pdCommonOptLog.setFinishTime(nowEnd);
pdCommonOptLog.setConsumingTime(endInstant - startInstant);
pdCommonOptLog.setUa(request.getHeader("User-Agent"));
pdCommonOptLog.setCreateUser(user.getId());
// 类名
Class<?> aClass = joinPoint.getTarget().getClass();
String className = aClass.getName();
System.out.println(className);
//获取执行的方法名
MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature();
Method method = signature.getMethod();
//获取注解
//Annotation[] annotations = method.getAnnotations();
//获取指定注解
ApiOperation annotation = method.getAnnotation(ApiOperation.class);
//方法的返回类型
// String name = signature.getReturnType().getName();
// System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(response.getStatus());
pdCommonOptLog.setDescription1(annotation.value());
pdCommonOptLog.setClassPath(aClass.getName());
//方法名称
pdCommonOptLog.setActionMethod(signature.getName());
//请求类型
pdCommonOptLog.setHttpMethod(request.getMethod());
//获取方法的参数,这里的参数可能包含有文件
Object[] args1 = joinPoint.getArgs();
String string = "";
System.out.println("返回值的返回类型" + response.getContentType());
if(!(response == null) && !(response.getContentType() == null) && !(request.getContentType() == "") && !request.getContentType().contains("multipart/form-data")){
string = JSONObject.toJSONString(args1);
}
pdCommonOptLog.setResult(string);
pdCommonOptLog.setExDesc(null);
pdCommonOptLogService.save(pdCommonOptLog);
return proceed;
}
}
五、自定义参数解析器
5.1 自定义注解
@Target({ElementType.PARAMETER})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface CurrentUser {
}
5.2 配置自定义参数构造器
package org.example.Args;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.method.support.HandlerMethodArgumentResolver;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurer;
import java.util.List;
@Configuration
public class ArgumentResolverConfiguration implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Override
//注册自定义参数解析器
public void addArgumentResolvers(List<HandlerMethodArgumentResolver> resolvers) {
resolvers.add(new CurrentUserMethodArgumentResolver());
}
}
5.3 自定义参数解析器类
package org.example.Args;
import org.springframework.core.MethodParameter;
import org.springframework.web.bind.support.WebDataBinderFactory;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.NativeWebRequest;
import org.springframework.web.method.support.HandlerMethodArgumentResolver;
import org.springframework.web.method.support.ModelAndViewContainer;
public class CurrentUserMethodArgumentResolver implements HandlerMethodArgumentResolver {
public CurrentUserMethodArgumentResolver() {
System.out.println("CurrentUserMethodArgumentResolver自定义参数解析器初始化...");
}
//判断自定义注解 注解的参数是否正确
@Override
public boolean supportsParameter(MethodParameter parameter) {
//如果Controller的方法参数类型为User同时还加入了CurrentUser注解,则返回true
if (parameter.getParameterType().equals(User.class) &&
parameter.hasParameterAnnotation(CurrentUser.class)) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
//当supportsParameter方法返回true时执行此方法
@Override
public Object resolveArgument(MethodParameter parameter,
ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer,
NativeWebRequest webRequest,
WebDataBinderFactory binderFactory) throws Exception {
System.out.println("参数解析器...");
//此处直接模拟了一个User对象,实际项目中可能需要从请求头中获取登录用户的令牌然后进行解析,
//最终封装成User对象返回即可,这样在Controller的方法形参就可以直接引用到User对象了
User user = new User("jack","admin");
return user;
}
}
六、监听器
Spring监听器
6.1 自定义事件源
public class SysLogEvent extends ApplicationEvent {
public SysLogEvent(OptLogDTO optLogDTO) {
super(optLogDTO);
}
}
6.2 自定义事件监听器
- @EventListener(SysLogEvent.class)定义监听的类
@Component
public class SysLogListener {
@Async//异步处理
@EventListener(SysLogEvent.class)
public void saveSysLog(SysLogEvent event) {
OptLogDTO sysLog = (OptLogDTO) event.getSource();
long id = Thread.currentThread().getId();
System.out.println("监听到日志操作事件:" + sysLog + " 线程id:" + id);
//将日志信息保存到数据库...
}
}
6.3 发布事件
- 可在aop中监听事件
@Autowired
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
//构造事件对象
ApplicationEvent event = new SysLogEvent(logInfo);
//发布事件
applicationContext.publishEvent(event);
七、servlet对象
Servlet基础之HttpServletRequest详解
7.1 request获取参数
7.1.1 获取url上的参数
- getParameter(String name)
- getParameterMap()
http://localhost:9000/cache/hello?name=%22jack%22&&age=12
System.out.println("name参数" + request1.getParameter("name"));
System.out.println("param参数");
Map<String, String[]> parameterMap = request1.getParameterMap();
parameterMap.forEach((k,v)-> {System.out.println(k + " " + v[0]);});
7.1.2 获取请求头参数
- 请求头中会包含cookie信息,cookie : cookie=qwqdqdq; us=qweq
//获取请求头参数
String myHead = request1.getHeader("myHead");
System.out.println("请求头参数" + myHead);
Enumeration headerNames = request1.getHeaderNames();
// 使用循环遍历所有请求头,并通过getHeader()方法获取一个指定名称的头字段
while (headerNames.hasMoreElements()) {
String headerName = (String) headerNames.nextElement();
System.out.println((headerName + " : " + request1.getHeader(headerName)));
}
7.1.3 请求体参数
7.1.3.1 form表单key-value数据
- form-data,和获取url上的参数方式一致
HttpServletRequest request1 = (HttpServletRequest) request;
//获取请求体参数
System.out.println("----------------------------");
System.out.println(request1.getParameter("form2"));
String[] form1s = request1.getParameterValues("form1");
System.out.println(form1s[0]);
Map<String, String[]> parameterMap = request1.getParameterMap();
parameterMap.forEach((k,v)-> {System.out.println(k + " " + v[0]);});
7.1.3.1 form表单文件类型数据
HttpServletRequest req = (HttpServletRequest) request;
System.out.println(request.getContentType());
System.out.println(req.getCharacterEncoding());
Collection<Part> parts = req.getParts();
for (Part part:parts) {
//提交文件添加的名称
System.out.println("-----类型名称------->"+part.getName());
System.out.println("-----类型------->"+part.getContentType());
//文件的原名称
System.out.println("-----提交的类型名称------->"+part.getSubmittedFileName());
System.out.println("----流-------->"+part.getInputStream());
}
7.1.4 获取cookie信息
Cookie[] cookies = request1.getCookies();
for (int i = 0; i < cookies.length; i++) {
System.out.println(cookies[i].getName() + " " + cookies[i].getValue());
}
7.1.5 修改request参数信息
修改request的parameter的几种方式总结
- 自定义MyRequestWrapMapper对象
package org.example.Basic;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequestWrapper;
public class MyRequestWrapMapper extends HttpServletRequestWrapper {
/**
* Constructs a request object wrapping the given request.
*
* @param request The request to wrap
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the request is null
*/
public MyRequestWrapMapper(HttpServletRequest request) {
super(request);
}
@Override
public String getParameter(String name) {
String parameter = super.getParameter(name);
if(parameter != null){
parameter = parameter + "hahahah";
}
return parameter;
}
}
- 包装原对象即可,原对象是HttpServletRequest
new MyRequestWrapMapper(req)
7.2 response
Servlet之Response
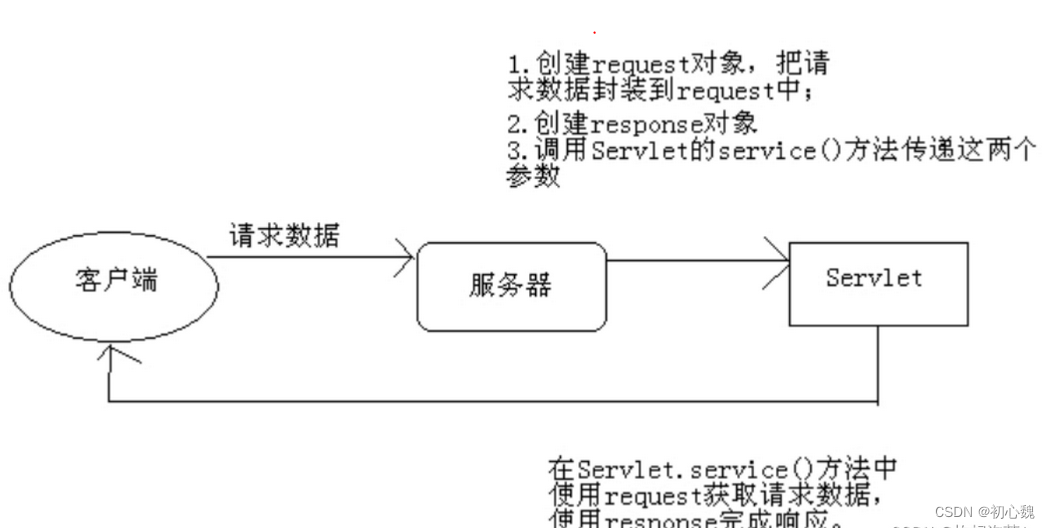
7.2.1 常用方法
- 过滤器前:只是新建了response对象,并赋予初值,经过controller后,才对其中的值进行了赋值。
Collection<String> headerNames1 = rsp.getHeaderNames();
headerNames1.forEach(s-> System.out.println(s + " " + rsp.getHeader(s)));
System.out.println(rsp.getStatus());
System.out.println(rsp.getCharacterEncoding());
7.3 后端参数接收
7.3.1 url参数接收
- @PathVariable url中带{}的参数
@GetMapping("/hello5/{id}")
public String hello5(@PathVariable("id")int id){
System.out.println(id);
return "hello";
}
- url上的参数:?name=“xx”
@GetMapping("/hello1")
public String hello(@RequestParam("name")String name, @RequestParam("head")String head){
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(head);
return "hello";
}
7.3.2 请求头参数接收
- @RequestHeader
@GetMapping("/hello2")
public String hello1(@RequestHeader("head")String head){
System.out.println(head);
return "hello";
}
7.3.3 请求体参数接收
7.3.3.1 正常类型数据接收
- @RequestParam
也是上面那个注解
7.3.3.2 文件类型数据接收
SpringBoot项目中使用MultipartFile来上传文件(包含多文件)
- @RequestParam
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String hello(@RequestParam("file") MultipartFile[] file,@RequestParam String body){
for (int i = 0; i < file.length; i++) {
MultipartFile multipartFile = file[i];
System.out.println(multipartFile.getOriginalFilename());
System.out.println(multipartFile.getName());
}
System.out.println(body);
return "hello";
}
7.3.4 获取cookie
- @CookieValue:获取cookie参数
@GetMapping("/hello1")
public String hello1(@CookieValue("name") String name ){
System.out.println(name);
return "hello";
}
7.3.5 自定义传参使用
- @RequestAttribute
@PostMapping("/hello6")
public String hello4(@RequestAttribute("num") String num){
System.out.println(num);
return "hello";
}
- request设置值
req.setAttribute("num",12);
7.4 设置
7.4.1 大文件上传设置
servlet:
multipart:
max-file-size: 100MB
max-request-size: 100MB
7.5 seesion和cookie
session和cookie的作用原理和区别
【JavaWeb】Cookie和Session
- session技术就是一种基于后端有别于数据库的临时存储技术
- session是基于cookie实现的,服务器存储每个会话的session信息,如何找到该session的信息呢?session通过cookie保存session的id信息来实现寻找同一个session对象。
7.5.1 区别
- cookie存在浏览器端的浏览器缓存中,session存在服务端,服务端的内存中。
- tomcat默认session的生命周期是20min,一旦session重新活跃,刷新生命周期。关闭浏览器,sessionID就会失效,但是服务器依然会存储session信息,session一般存放在服务器内存,如果服务器重启session则会清空。cookie也可以设置过期时间,但是关闭浏览器,cookie就失效。
- cookie不是很安全,容易被窃取,session存储到服务端,不容易被窃取。
7.5.2 测试
- response添加cookie
DateTimeFormatter formatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH-mm-ss");
String format = formatter.format(LocalDateTime.now());
String s = format.replaceAll(" ", "");
System.out.println("设置cookie的值为" + " " + s);
Cookie cookie = new Cookie("sessionID", s);
//20s
//cookie.setMaxAge(20*60);
//cookie.setPath("/*");
//response添加cookie
rsp.addCookie(cookie);
- 关闭浏览器,cookie失效
- 设置session
HttpServletRequest req = (HttpServletRequest) request;
HttpServletResponse rsp = (HttpServletResponse) response;
HttpSession session = req.getSession();
session.setAttribute("name","jack");
System.out.println(session.getId());
7.5.3 重要概念
- 会话:用户打开一个浏览器访问服务器,如果浏览器和服务器有一个关闭则会话结束,否则之间的所有操作都算一次会话。多个浏览器是多个会话。
八、spring mvc
8.1 spring mvc流程
SpringMVC工作流程(超级详细版)8.1.1 过程
- 用户发送请求,(调度服务器)dispatchServlet接收请求,转发请求到handermapping(处理器映射器),处理器映射器查找对应的handler,返回handler
- dispatchServlet请求执行handler,处理器适配器执行handler,返回Modelandview对象
- dispatchServlet请求解析Modelandview,viewresolver解析视图,返回view对象到dispatchServlet
- dispatchServlet返回view对象
八、总结
8.1 总结
- 过滤器对所有请求做增强,拦截器只对spring mvc的访问做增强
- 过滤器依赖servlet容器,拦截器依赖spring mvc
- 拦截器更强调对controller具体方法的前后做增强