目录
28. 找出字符串中第一个匹配项的下标 Find-the-index-of-the-first-occurrence-in-a-string 🌟🌟
29. 两数相除 Divide Two Integers 🌟🌟
30. 串联所有单词的子串 Substring-with-concatenation-of-all-words 🌟🌟🌟
🌟 每日一练刷题专栏 🌟
Rust每日一练 专栏
Golang每日一练 专栏
Python每日一练 专栏
C/C++每日一练 专栏
Java每日一练 专栏
28. 找出字符串中第一个匹配项的下标 Find-the-index-of-the-first-occurrence-in-a-string
给你两个字符串 haystack 和 needle ,请你在 haystack 字符串中找出 needle 字符串出现的第一个位置(下标从 0 开始)。如果不存在,则返回 -1 。
说明:实现 strStr() 函数。对于本题而言,当 needle 是空字符串时我们应当返回 0 。这与 C 语言的 strStr() 以及 Java 的 indexOf() 定义相符。
当 needle 是空字符串时,我们应当返回什么值呢?这是一个在面试中很好的问题。
示例 1:
输入:haystack = "hello", needle = "ll" 输出:2
示例 2:
输入:haystack = "aaaaa", needle = "bba" 输出:-1
提示:
1 <= haystack.length, needle.length <= 10^4haystack和needle仅由小写英文字符组成
代码1:
fn str_str(haystack: String, needle: String) -> i32 {
let n = haystack.len();
let m = needle.len();
if m == 0 {
return 0;
}
if n < m {
return -1;
}
for i in 0..=n-m {
if haystack[i..i+m] == needle {
return i as i32;
}
}
return -1;
}
fn main() {
let haystack = "hello".to_string();
let needle = "ll".to_string();
println!("{}", str_str(haystack, needle));
let haystack = "aaaaa".to_string();
let needle = "bba".to_string();
println!("{}", str_str(haystack, needle));
}
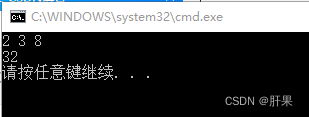
输出:
2
-1
代码2:
fn str_str(haystack: String, needle: String) -> i32 {
let mut i = 0_usize;
loop {
let mut j = 0_usize;
loop {
if j == needle.len() {
return i as i32;
}
if i + j == haystack.len() {
return -1;
}
if needle.as_bytes()[j] != haystack.as_bytes()[i+j] {
break;
}
j += 1;
}
i += 1;
}
}
fn main() {
let haystack = "hello".to_string();
let needle = "ll".to_string();
println!("{}", str_str(haystack, needle));
let haystack = "aaaaa".to_string();
let needle = "bba".to_string();
println!("{}", str_str(haystack, needle));
}
另: Rust语言有现成的字符串方法 haystack.find(&needle)
fn main() {
let haystack = "hello".to_string();
let needle = "ll".to_string();
println!("{:?}", haystack.find(&needle));
let haystack = "aaaaa".to_string();
let needle = "bba".to_string();
println!("{:?}", haystack.find(&needle));
}29. 两数相除 Divide Two Integers
给定两个整数,被除数 dividend 和除数 divisor。将两数相除,要求不使用乘法、除法和 mod 运算符。
返回被除数 dividend 除以除数 divisor 得到的商。
整数除法的结果应当截去(truncate)其小数部分,例如:truncate(8.345) = 8 以及 truncate(-2.7335) = -2
示例 1:
输入: dividend = 10, divisor = 3 输出: 3 解释: 10/3 = truncate(3.33333..) = truncate(3) = 3
示例 2:
输入: dividend = 7, divisor = -3 输出: -2 解释: 7/-3 = truncate(-2.33333..) = -2
提示:
- 被除数和除数均为 32 位有符号整数。
- 除数不为 0。
- 假设我们的环境只能存储 32 位有符号整数,其数值范围是 [−2^31, 2^31 − 1]。本题中,如果除法结果溢出,则返回 2^31 − 1。
代码:
pub fn divide(dividend: i32, divisor: i32) -> i32 {
// 处理特殊情况
if dividend == std::i32::MIN && divisor == -1 {
return std::i32::MAX;
}
if divisor == 1 {
return dividend;
}
if divisor == -1 {
return -dividend;
}
// 处理符号
let mut res = 0;
let mut sign = 1;
if (dividend > 0 && divisor < 0) || (dividend < 0 && divisor > 0) {
sign = -1;
}
let mut a = abs(dividend);
let b = abs(divisor);
// 计算商
while a >= b {
let (mut temp, mut tb) = (1, b);
while a >= (tb << 1) {
tb <<= 1;
temp <<= 1;
}
res += temp;
a -= tb;
}
res * sign
}
fn abs(x: i32) -> i32 {
if x < 0 {
-x
} else {
x
}
}
fn main() {
println!("{}", divide(10, 3));
println!("{}", divide(7, -3));
}
输出:
3
-2
30. 串联所有单词的子串 Substring-with-concatenation-of-all-words
给定一个字符串 s 和一些 长度相同 的单词 words 。找出 s 中恰好可以由 words 中所有单词串联形成的子串的起始位置。
注意子串要与 words 中的单词完全匹配,中间不能有其他字符 ,但不需要考虑 words 中单词串联的顺序。
示例 1:
输入:s = "barfoothefoobarman", words = ["foo","bar"] 输出:[0,9] 解释: 从索引 0 和 9 开始的子串分别是 "barfoo" 和 "foobar" 。 输出的顺序不重要, [9,0] 也是有效答案。
示例 2:
输入:s = "wordgoodgoodgoodbestword", words = ["word","good","best","word"] 输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:s = "barfoofoobarthefoobarman", words = ["bar","foo","the"] 输出:[6,9,12]
提示:
1 <= s.length <= 10^4s由小写英文字母组成1 <= words.length <= 50001 <= words[i].length <= 30words[i]由小写英文字母组成
代码1: 暴力枚举
pub fn find_substring(s: String, words: Vec<String>) -> Vec<i32> {
let n = s.len();
let m = words.len();
if n == 0 || m == 0 {
return Vec::new();
}
let word_len = words[0].len();
let mut ans = Vec::new();
for i in 0..=n - m * word_len {
let mut j = 0;
let mut used = vec![false; m];
while j < m {
let word = &s[i + j * word_len..i + j * word_len + word_len];
let mut k = 0;
while k < m {
if !used[k] && word == &words[k] {
used[k] = true;
break;
}
k += 1;
}
if k == m {
break;
}
j += 1;
}
if j == m {
ans.push(i as i32);
}
}
ans
}
fn main() {
let s = String::from("barfoothefoobarman");
let words = vec![String::from("foo"), String::from("bar")];
println!("{:?}", find_substring(s, words));
let s = String::from("wordgoodgoodgoodbestword");
let words = vec![
String::from("word"),
String::from("good"),
String::from("best"),
String::from("word"),
];
println!("{:?}", find_substring(s, words));
let s = String::from("barfoofoobarthefoobarman");
let words = vec![String::from("bar"), String::from("foo"), String::from("the")];
println!("{:?}", find_substring(s, words));
}输出:
[0, 9]
[]
[6, 9, 12]
代码2: 滑动窗口
use std::collections::HashMap;
pub fn find_substring(s: String, words: Vec<String>) -> Vec<i32> {
let n = s.len();
let m = words.len();
if n == 0 || m == 0 {
return vec![];
}
let word_len = words[0].len();
let mut cnt = HashMap::new();
for word in words {
*cnt.entry(word).or_insert(0) += 1;
}
let mut ans = Vec::new();
for i in 0..word_len {
let mut left = i;
let mut right = i;
let mut window = HashMap::new();
while right + word_len <= n {
let word = &s[right..right + word_len];
right += word_len;
if *cnt.get(word).unwrap_or(&0) == 0 {
left = right;
window.clear();
} else {
*window.entry(word.to_string()).or_insert(0) += 1;
while *window.get(word).unwrap_or(&0) > *cnt.get(word).unwrap_or(&0) {
let d_word = &s[left..left + word_len];
left += word_len;
*window.entry(d_word.to_string()).or_insert(0) -= 1;
}
if right - left == word_len * m {
ans.push(left as i32);
}
}
}
}
ans
}
fn main() {
let s = String::from("barfoothefoobarman");
let words = vec![String::from("foo"), String::from("bar")];
println!("{:?}", find_substring(s, words));
let s = String::from("wordgoodgoodgoodbestword");
let words = vec![
String::from("word"),
String::from("good"),
String::from("best"),
String::from("word"),
];
println!("{:?}", find_substring(s, words));
let s = String::from("barfoofoobarthefoobarman");
let words = vec![String::from("bar"), String::from("foo"), String::from("the")];
println!("{:?}", find_substring(s, words));
}
代码3:滑动窗口
use std::collections::HashMap;
pub fn find_substring(s: String, words: Vec<String>) -> Vec<i32> {
let n = s.len();
let m = words.len();
if n == 0 || m == 0 {
return vec![];
}
let word_len = words[0].len();
let mut cnt = HashMap::new();
for word in &words {
*cnt.entry(word.to_string()).or_insert(0) += 1;
}
let mut ans = Vec::new();
for i in 0..word_len {
let mut left = i;
let mut right = i;
let mut window = HashMap::new();
let mut count = 0;
while right + word_len <= n {
let word = &s[right..right + word_len];
right += word_len;
if cnt.get(word).cloned().unwrap_or(0) == 0 {
left = right;
window.clear();
count = 0;
} else {
*window.entry(word.to_string()).or_insert(0) += 1;
count += 1;
while window.get(word).cloned().unwrap_or(0) > cnt.get(word).cloned().unwrap_or(0) {
let d_word = &s[left..left + word_len];
left += word_len;
*window.entry(d_word.to_string()).or_insert(0) -= 1;
count -= 1;
}
if count == m {
ans.push(left as i32);
}
}
}
}
ans
}
fn main() {
let s = String::from("barfoothefoobarman");
let words = vec![String::from("foo"), String::from("bar")];
println!("{:?}", find_substring(s, words));
let s = String::from("wordgoodgoodgoodbestword");
let words = vec![
String::from("word"),
String::from("good"),
String::from("best"),
String::from("word"),
];
println!("{:?}", find_substring(s, words));
let s = String::from("barfoofoobarthefoobarman");
let words = vec![String::from("bar"), String::from("foo"), String::from("the")];
println!("{:?}", find_substring(s, words));
}
代码4: 滑动窗口
use std::collections::HashMap;
pub fn find_substring(s: String, words: Vec<String>) -> Vec<i32> {
let n = s.len();
let m = words.len();
if n == 0 || m == 0 {
return vec![];
}
let word_len = words[0].len();
let mut cnt = HashMap::new();
for word in &words {
*cnt.entry(word.to_string()).or_insert(0) += 1;
}
let mut ans = Vec::new();
for i in 0..word_len {
let mut left = i;
let mut right = i;
let mut window = HashMap::new();
let mut count = 0;
while right + word_len <= n {
let word = &s[right..right + word_len];
right += word_len;
if cnt.get(word).cloned().unwrap_or(0) == 0 {
left = right;
window.clear();
count = 0;
} else {
*window.entry(word.to_string()).or_insert(0) += 1;
count += 1;
while window.get(word).cloned().unwrap_or(0) > cnt.get(word).cloned().unwrap_or(0) {
let d_word = &s[left..left + word_len];
left += word_len;
*window.entry(d_word.to_string()).or_insert(0) -= 1;
count -= 1;
}
if count == m {
ans.push(left as i32);
}
}
if right - left == word_len * (m + 1) {
let d_word = &s[left..left + word_len];
left += word_len;
*window.entry(d_word.to_string()).or_insert(0) -= 1;
count -= 1;
}
}
}
ans
}
fn main() {
let s = String::from("barfoothefoobarman");
let words = vec![String::from("foo"), String::from("bar")];
println!("{:?}", find_substring(s, words));
let s = String::from("wordgoodgoodgoodbestword");
let words = vec![
String::from("word"),
String::from("good"),
String::from("best"),
String::from("word"),
];
println!("{:?}", find_substring(s, words));
let s = String::from("barfoofoobarthefoobarman");
let words = vec![String::from("bar"), String::from("foo"), String::from("the")];
println!("{:?}", find_substring(s, words));
}
🌟 每日一练刷题专栏 🌟
✨ 持续,努力奋斗做强刷题搬运工!
👍 点赞,你的认可是我坚持的动力!
🌟 收藏,你的青睐是我努力的方向!
✎ 评论,你的意见是我进步的财富!
☸ 主页:https://hannyang.blog.csdn.net/
|
| Rust每日一练 专栏(2023.5.16~)更新中... |
|
| Golang每日一练 专栏(2023.3.11~)更新中... |
|
| Python每日一练 专栏(2023.2.18~2023.5.18)暂停更 |
|
| C/C++每日一练 专栏(2023.2.18~2023.5.18)暂停更 |
|
| Java每日一练 专栏(2023.3.11~2023.5.18)暂停更 |