基础知识
链表是一种通过指针串联在一起的线性结构。在内存中不是连续分布的,分配机制取决于操作系统内存管理。
类型
三种类型:单链表、双链表、循环链表
单链表:每个节点由两部分组成,数据域和指针域(存放指向下一个节点的指针),最后一个节点的指针域指向NULL。
双链表:每个节点有两个指针域( prec 和 next ),分别指向上一个和下一个节点,可以向前查询,也可以向后查询。
循环链表:首尾相连,可以解决约瑟夫环问题。
链表的c++定义
//单链表
struct ListNode {
int val;
ListNode *next;
//构造函数
ListNode (int x): val(x), next(nullptr) {}
};
重写构造函数,可以直接给 val 赋值:
ListNode *head = new ListNode(5);
使用默认函数不能直接赋值:
ListNode *head = new ListNode();
head->val = 5;
指针的简单知识
如下:ListNode* p = new ListNode()
不管是ListNode* p 还是ListNode *p,它的类型都是ListNode *,p是变量名,用来存储ListNode类型数据的地址。
C语言重点——指针篇(一篇让你完全搞懂指针) - 知乎 (zhihu.com)
移除元素
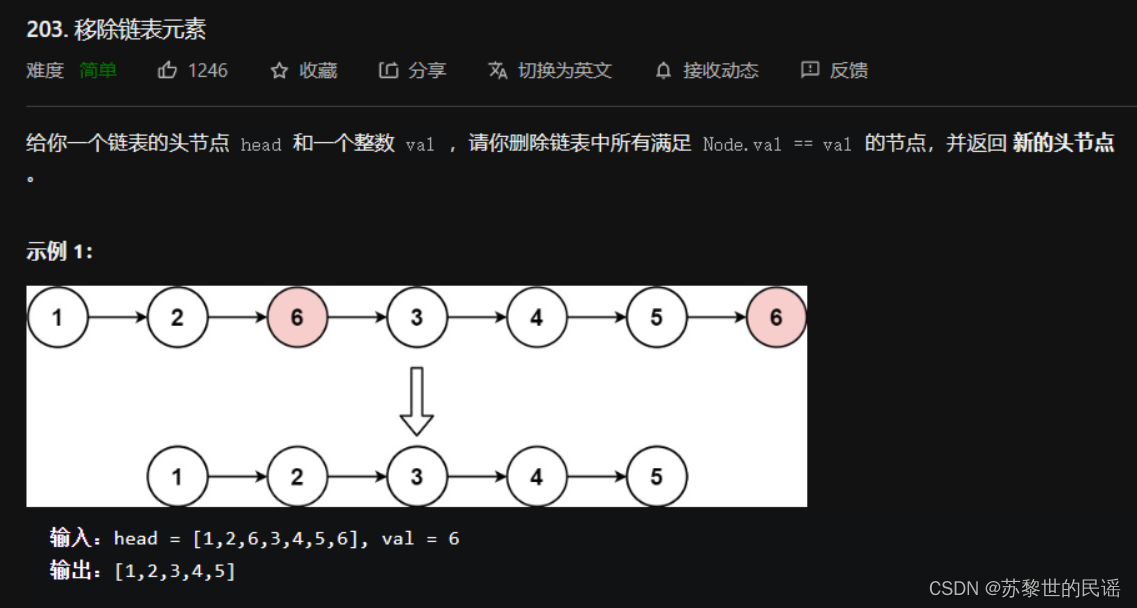
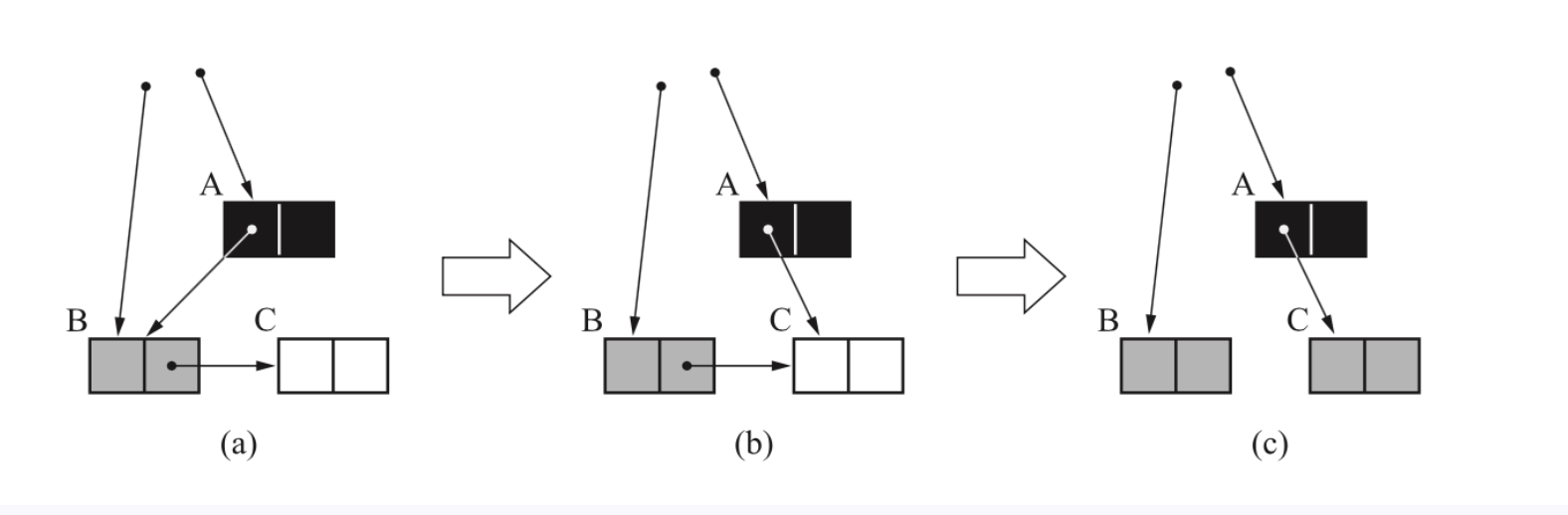
移除元素有两种方法:用/不用虚拟头节点
不用虚拟头节点
删除头节点的情况要单独讨论
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* removeElements(ListNode* head, int val) {
//删除头节点
while (head != NULL && head -> val == val) {
ListNode* tmp = head;
head = head -> next;
delete tmp;
}
//删除非头节点
ListNode* cur = head;
while (cur != NULL && cur -> next != NULL) {
if (cur -> next -> val == val) { //找到该元素
ListNode* tmp = cur -> next;
cur -> next = cur -> next -> next;
delete tmp;
} else { //没找到,继续找
cur = cur -> next;
}
}
return head;
}
};
用虚拟头节点
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* removeElements(ListNode* head, int val) {
ListNode* dummyNode = new ListNode(0); //创建
dummyNode -> next = head;
ListNode* cur = dummyNode;
while (cur -> next != NULL) {
if (cur -> next -> val == val) {
ListNode* tmp = cur -> next;
cur -> next = cur -> next -> next;
delete tmp;
} else {
cur = cur -> next;
}
}
head = dummyNode -> next;
delete dummyNode;
return head;
}
};
设计链表
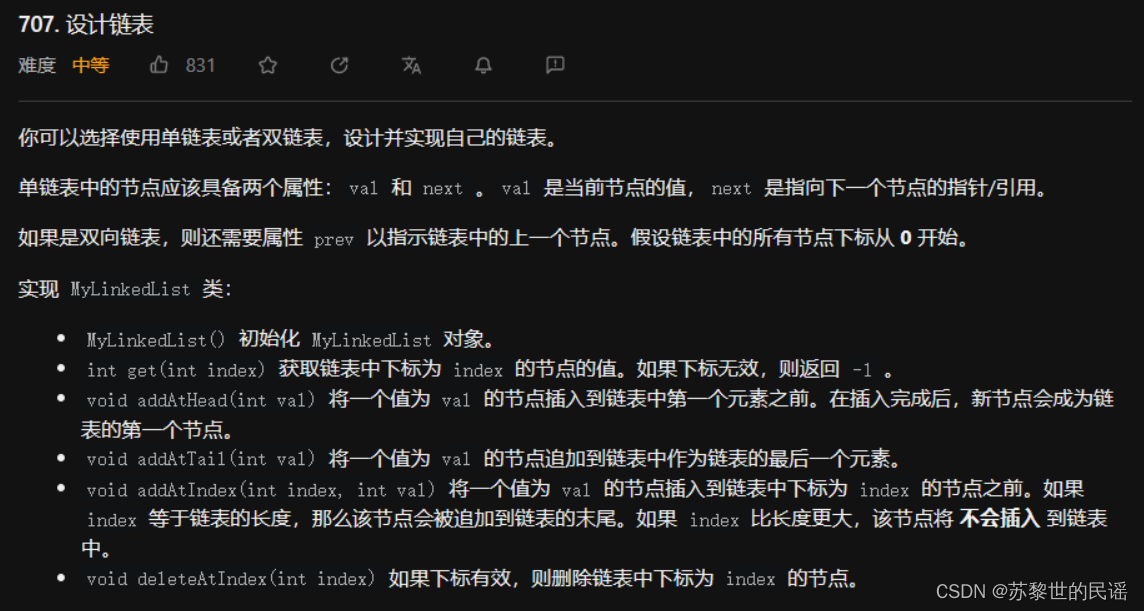
这题真难,但真的顶。
自己写出来一堆错,看着题解改了好久
class MyLinkedList {
public:
// 定义结构体
struct LinkedNode {
int val;
LinkedNode* next;
LinkedNode(int val): val(val), next(nullptr) {}
};
// 初始化链表
MyLinkedList() {
_size = 0;
_dummyHead = new LinkedNode(0);
}
// 根据索引获取元素
int get(int index) {
// 若值不合理,返回-1
if (index > (_size - 1) || index < 0) {
return -1;
}
LinkedNode* cur = _dummyHead->next;
while (index--) {
cur = cur->next;
}
return cur->val;
}
// 在头部添加新节点
void addAtHead(int val) {
LinkedNode* newNode = new LinkedNode(val);
newNode->next = _dummyHead->next;
_dummyHead->next = newNode;
_size++;
}
// 在尾部添加新节点
void addAtTail(int val) {
LinkedNode* newNode = new LinkedNode(val);
LinkedNode* cur = _dummyHead;
while (cur->next != NULL) {
cur = cur->next;
}
cur->next = newNode;
_size++;
}
// 在Index前插入新节点
void addAtIndex(int index, int val) {
if (index > _size) { // 若等于size,就插入size-1,就是尾部。若小于0,就插入头部
return; // 不作处理
}
LinkedNode* newNode = new LinkedNode(val);
LinkedNode* cur = _dummyHead;
while (index--) {
cur = cur->next;
}
newNode->next = cur->next;
cur->next = newNode;
_size++;
}
// 删除Index的节点
void deleteAtIndex(int index) {
if (index >= _size || index < 0) {
return;
}
LinkedNode* cur = _dummyHead;
while (index--) {
cur = cur->next;
}
// 要删的是下一个节点
LinkedNode* tmp = cur->next;
cur->next = cur->next->next;
delete tmp;
_size--;
}
void printLinkedList() {
LinkedNode* cur = _dummyHead;
while (cur->next != NULL) {
cout << cur->next->val << " ";
cur = cur->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
private:
int _size;
LinkedNode* _dummyHead;
};
反转链表
两种方法:双指针法、递归法
双指针法
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* pre = NULL; // 指向前一个结点
ListNode* tmp; // 指向下一个结点
ListNode* cur = head;
while (cur) {
tmp = cur->next; // 保存下一个结点
cur->next = pre; // 反转
// 循环
pre = cur;
cur = tmp;
}
return pre;
}
};
递归法
与双指针完全相同的逻辑,只是写法不同
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverse(ListNode* pre, ListNode* cur) {
if (cur == NULL) return pre;
ListNode* tmp = cur->next;
cur->next = pre;
return reverse(cur, tmp); // 这里就是循环
}
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
return reverse(NULL, head); // 初始化赋值
}
};
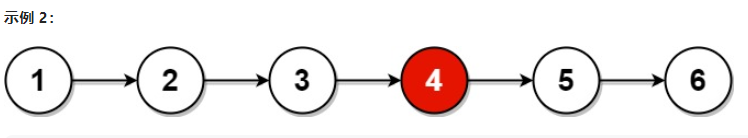
删除倒数第n个节点
用一种非常美妙的双指针法,根本想不到
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* removeNthFromEnd(ListNode* head, int n) {
ListNode* dummyHead = new ListNode(0);
dummyHead->next = head;
ListNode* fast = dummyHead;
ListNode* slow = dummyHead;
// fast先走
while (n-- && fast != NULL) {
fast = fast->next;
}
// fast再走一步,因为要指向前一个结点,好删
fast = fast->next;
// fast和slow一起走
while (fast != NULL) {
fast = fast->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
ListNode* tmp = slow->next;
slow->next = slow->next->next;
delete tmp;
return dummyHead->next;
}
};
环形链表
双指针法
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *detectCycle(ListNode *head) {
ListNode* fast = head;
ListNode* slow = head;
while (fast != NULL && fast->next != NULL) {
// fast走两步,slow走一步
fast = fast->next->next;
slow = slow->next;
// 二者相遇
if (fast == slow) {
ListNode* index1 = fast;
ListNode* index2 = head;
while (index1 != index2) {
index1 = index1->next;
index2 = index2->next;
}
return index1; // 有环的情况
}
}
return NULL; // 无环的情况
}
};