Java >>和>>>的区别
| 或: 有1得1, 全0得0
int temp = a|c;
System.out.println(Integer.toBinaryString(a));
System.out.println(Integer.toBinaryString(c));
System.out.println(Integer.toBinaryString(temp));
/**
* 结果输出
*
* 01
* 11
* 11
*
*/
& 与 : 全1 得1, 有0得0
int temp = a&c;
System.out.println("a : "+Integer.toBinaryString(a));
System.out.println("c : "+ Integer.toBinaryString(c));
System.out.println("temp : "+ Integer.toBinaryString(temp));
/**
* 结果输出
*
* a : 1
* c : 11
* temp : 1
*
*/
^ 异或 : 相同得0,不同得1
int temp = a|c;
System.out.println(Integer.toBinaryString(a));
System.out.println(Integer.toBinaryString(c));
System.out.println(Integer.toBinaryString(temp));
/**
* 结果输出
* 01
* 11
* 10
*
*/
Java >>和>>>的区别
java 中>>是带符号的位移,将所有的二进制数据全部向右移动指定位数(但是符号位不动,实际是补位,正数补0,负数补1)
>>:带符号右移。正数右移高位补0,负数右移高位补1。比如:
4>>1,结果为2;
-4>>1,结果为-2.
>>>:无符号右移。无论正数还是负数,高位通通补0.
对于正数而言,>>和>>>没有区别。
对于负数而言,-2>>>1,结果是2147483647(Integer.MAX_VALUE)
-1>>>1,结果是2147483647(Integer.MAX_VALUE)
如果要判断两个数符号是否相同时,可以这么干:
return ((a >> 31) ^ (b >> 31)) ==0;
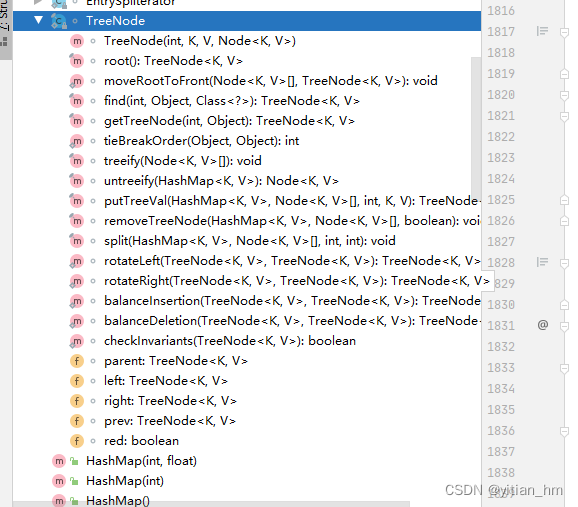
Map
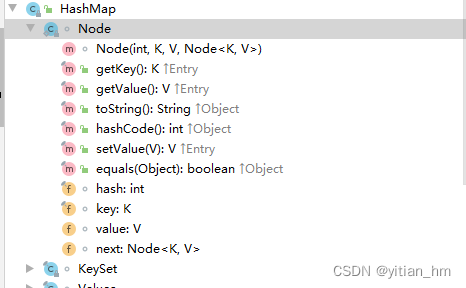
Node 的数据结构 (node链表 —> next是指针)
static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
final int hash;
final K key;
V value;
Node<K,V> next;
Node(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) {
this.hash = hash;
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
public final K getKey() { return key; }
public final V getValue() { return value; }
public final String toString() { return key + "=" + value; }
public final int hashCode() {
return Objects.hashCode(key) ^ Objects.hashCode(value); //异或
}
public final V setValue(V newValue) {
V oldValue = value;
value = newValue;
return oldValue; // 返回之前得值
}
public final boolean equals(Object o) {
if (o == this)
return true;
if (o instanceof Map.Entry) {
Map.Entry<?,?> e = (Map.Entry<?,?>)o;
if (Objects.equals(key, e.getKey()) &&
Objects.equals(value, e.getValue()))
return true;
}
return false;
}
}