文章目录
- 一、 缓存技术介绍
- 1. 缓存技术简介
- 2. JSR107核心接口
- 3. JSR107 图示
- 3. SpringBoot缓存抽象
- 4. 缓存常用注解和接口
- 一、 缓存技术实战
- 1. @Cacheable注解
- 2. 缓存的工作原理
- 4. @Cacheable注解的工作流程
一、 缓存技术介绍
1. 缓存技术简介
缓存技术主要分为两大类缓存可分为2大类:
- 本地缓存:速度快、效率高,但分布式环境下容易出现数据不一致的问题、且缓存的数据量一般不能太大,常见的比如guava、ehcache、caffeine
- 分布式缓存:速度比本地缓存慢,常用于多个服务、应用之间的数据共享,常见的比如redis、memcached
Spring Boot提供了对多种本地缓存技术的支持,例如Caffeine、Ehcache、Guava等。本地缓存技术常用于提高应用程序的性能,避免频繁地访问数据库或其他外部资源,同时也可以降低系统的负载。JSR是Java Specification Requests 的缩写 ,Java规范请求,故名思议提交Java规范, JSR-107呢就是关于如何使用缓存的规范,是java提供的一个接口规范,类似于JDBC规范,没有具体的实现,具体的实现就是reds等这些缓存。
2. JSR107核心接口
Java Caching(JSR-107)定义了5个核心接口,分别是CachingProvider、CacheManager、Cache、Entry和Expiry。
- CachingProvider(缓存提供者):创建、配置、获取、管理和控制多个CacheManager
- CacheManager(缓存管理器):创建、配置、获取、管理和控制多个唯一命名的Cache,Cache存在于CacheManager的上下文中。一个CacheManager仅对应一个CachingProvider
- Cache(缓存):是由CacheManager管理的,CacheManager管理Cache的生命周期,Cache存在于CacheManager的上下文中,是一个类似map的数据结构,并临时存储以key为索引的值。一个Cache仅被一个CacheManager所拥有
- Entry(缓存键值对):是一个存储在Cache中的key-value对
- Expiry(缓存时效):每一个存储在Cache中的条目都有一个定义的有效期。一旦超过这个时间,条目就自动过期,过期后,条目将不可以访问、更新和删除操作。缓存有效期可以通过ExpiryPolicy设置
3. JSR107 图示
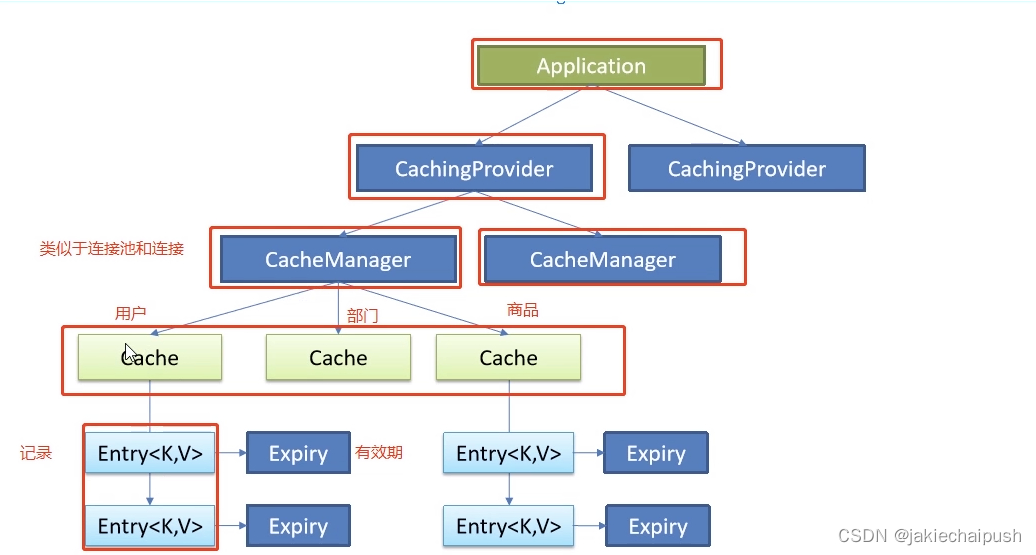
一个应用里面可以有多个缓存提供者(CachingProvider),一个缓存提供者可以获取到多个缓存管理器(CacheManager),一个缓存管理器管理着不同的缓存(Cache),缓存中是一个个的缓存键值对(Entry),每个entry都有一个有效期(Expiry)。缓存管理器和缓存之间的关系有点类似于数据库中连接池和连接的关系。
使用JSR107需要导入依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.cache</groupId>
<artifactId>cache-api</artifactId>
</dependency>
3. SpringBoot缓存抽象
Spring从3.1开始定义了org.springframework.cache.Cache和org.springframework.cache.CacheManager接口来统一不同的缓存技术,并支持使用JCache(JSR-107)注解来简化缓存开发
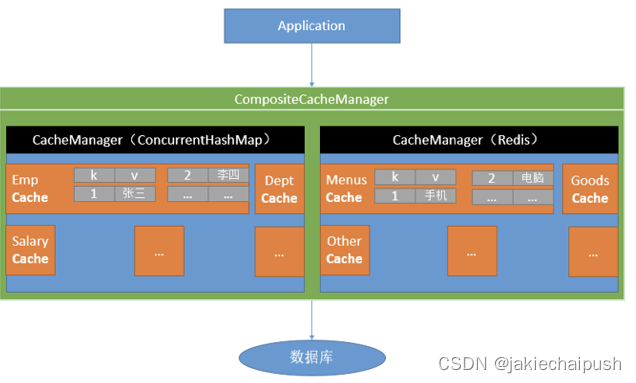
- Cache接口为缓存的组件规范定义,包含缓存的各种操作集合。
- Cache接口下Spring提供了各种xxxCache的实现,如RedisCache、EhCacheCache等。
- 每次调用需要缓存功能的方法时,Spring会检查指定参数的目标方法是否已经被调用过,如果已经被调用过就直接从缓存中获取方法调用后的结果;如果没有调用过就调用方法并缓存结果后返回给用户,下次调用直接从缓存中获取。
- 使用Spring缓存抽象的时候我们需要关注:
- 确定方法需要被缓存以及它们的缓存策略。
- 从缓存中读取数据之前需要缓存存储的数据
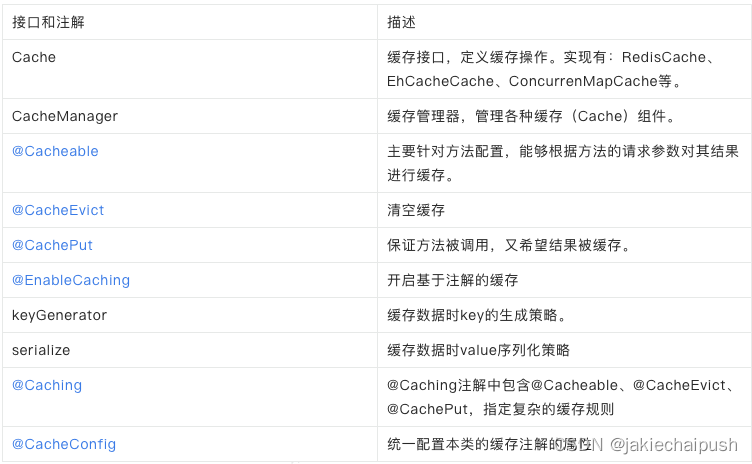
4. 缓存常用注解和接口
一、 缓存技术实战
1. @Cacheable注解
- 将方法运行的结果进行缓存,以后再要相同的数据,直接从缓存中获取,不需要再调用方法。
- CacheManager管理多个Cache组件,对缓存真正的CRUD操作在Cache组件中,每一个缓存组件都有自己唯一的名称。
- 属性:
■ value/cacheNames:指定缓存组件的名称
■ key:缓存数据使用的key,默认是方法参数的值(如果传入的参数是1,那么值就是1对应的返回的返回值。),支持SPEL表达式。
■ keyGenerator:key的生成器,可以自己指定key的生成器的组件id。key和keyGenerator只能二选一。
■ cacheManager:指定缓存管理器。
■ cacheResolver:指定缓存解析器。
■ condition:指定符合条件的情况下才缓存。支持SPEL表达式。
■ unless:否定缓存。当unless指定的条件为true,方法的返回值就不会返回;可以获取到结果进行判断。
■ sync:是否同步,默认值是false,即异步,在多线程环境中需要设置为true,避免缓存击穿的问题。 - 实战
在启动类上使用@EnableCaching注解开启缓存
package com.sunxiaping.springboot;
import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.EnableCaching;
@SpringBootApplication
@MapperScan(basePackages = "com.sunxiaping.springboot.mapper")
@EnableCaching
public class SpringbootApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringbootApplication.class, args);
}
}
使用@Cacheable注解方法返回的结果缓存:
package com.sunxiaping.springboot.service.impl;
import com.sunxiaping.springboot.domain.Employee;
import com.sunxiaping.springboot.mapper.EmployeeMapper;
import com.sunxiaping.springboot.service.EmployeeService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.Cacheable;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import java.util.Optional;
/**
* @author 许威威
* @version 1.0
*/
@Service
@Transactional
public class EmployeeServiceImpl implements EmployeeService {
@Autowired
private EmployeeMapper employeeMapper;
/**
* @Cacheable注解: 将方法的运行结果进行缓存,以后再要相同的数据,直接从缓存中获取,不需要再调用方法
* CacheManager管理多个Cache组件,对缓存的真正CRUD操作在Cache组件中,每一个缓存组件都有自己唯一的名称
* @Cacheable注解的属性:
* value/cacheNames:指定缓存组件的名称
* key:缓存数据使用的key,默认是方法参数的值(如果传入的参数是1,那么值就是1对应的返回的返回值。),支持SPEL表达式。
* keyGenerator:key的生成器,可以自己指定key的生成器的组件id。key和keyGenerator二选一。
* cacheManager:指定缓存管理器。
* cacheResolver:指定缓存解析器。
* condition:指定符合条件的情况下才缓存。支持SPEL表达式。
* unless:否定缓存。当unless指定的条件为true,方法的返回值就不会返回。
* sync:是否同步,默认值是false,即异步,在多线程环境中需要设置为true,避免缓存击穿的问题。
*/
@Cacheable(cacheNames = "emp", key = "#id")
@Override
public Employee findEmpById(Integer id) {
return Optional.ofNullable(employeeMapper.findEmpById(id)).orElse(new Employee());
}
}
2. 缓存的工作原理
- 缓存的自动配置类源码
@AutoConfiguration(after = { CouchbaseDataAutoConfiguration.class, HazelcastAutoConfiguration.class,
HibernateJpaAutoConfiguration.class, RedisAutoConfiguration.class })
@ConditionalOnClass(CacheManager.class)
@ConditionalOnBean(CacheAspectSupport.class)
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = CacheManager.class, name = "cacheResolver")
@EnableConfigurationProperties(CacheProperties.class)
//这个注解给可以知道其向Spring容器中导入了一些组件
@Import({ CacheConfigurationImportSelector.class, CacheManagerEntityManagerFactoryDependsOnPostProcessor.class })
public class CacheAutoConfiguration {
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public CacheManagerCustomizers cacheManagerCustomizers(ObjectProvider<CacheManagerCustomizer<?>> customizers) {
return new CacheManagerCustomizers(customizers.orderedStream().collect(Collectors.toList()));
}
@Bean
public CacheManagerValidator cacheAutoConfigurationValidator(CacheProperties cacheProperties,
ObjectProvider<CacheManager> cacheManager) {
return new CacheManagerValidator(cacheProperties, cacheManager);
}
@ConditionalOnClass(LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean.class)
@ConditionalOnBean(AbstractEntityManagerFactoryBean.class)
static class CacheManagerEntityManagerFactoryDependsOnPostProcessor
extends EntityManagerFactoryDependsOnPostProcessor {
CacheManagerEntityManagerFactoryDependsOnPostProcessor() {
super("cacheManager");
}
}
通过CacheAutoConfiguration上面的@Import注解,可以知道其向Spring容器中导入了一些组件,dubug后的缓存配置类如下所示
- SimpleCacheConfiguration给容器中添加了ConcurrentMapCacheManager组件
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(CacheManager.class)
@Conditional(CacheCondition.class)
class SimpleCacheConfiguration {
//给容器中添加了ConcurrentMapCacheManager组件
@Bean
ConcurrentMapCacheManager cacheManager(CacheProperties cacheProperties,
CacheManagerCustomizers cacheManagerCustomizers) {
ConcurrentMapCacheManager cacheManager = new ConcurrentMapCacheManager();
List<String> cacheNames = cacheProperties.getCacheNames();
if (!cacheNames.isEmpty()) {
cacheManager.setCacheNames(cacheNames);
}
return cacheManagerCustomizers.customize(cacheManager);
}
}
- ConcurrentMapCacheManager的部分源码如下:可以获取和创建ConcurrentMapCache类型的缓存组件,并把数据保存在ConcurrentMap中
public class ConcurrentMapCacheManager implements CacheManager, BeanClassLoaderAware {
//重写CacheManager的getCache方法
@Override
@Nullable
public Cache getCache(String name) {
//根据传入的name从CacheManager中获取Cache对象
Cache cache = this.cacheMap.get(name);
//如果cache不存在
if (cache == null && this.dynamic) {
//加锁
synchronized (this.cacheMap) {
//再获取一次
cache = this.cacheMap.get(name);
//如果依然不遵从
if (cache == null) {
//创建一个新的ConcurrentMapCache并返回
cache = createConcurrentMapCache(name);
//将上面创建的ConcurrentMapCache作为value放入到CacheManager中,key就是传入的name
this.cacheMap.put(name, cache);
}
}
}
return cache;
}
}
4. @Cacheable注解的工作流程
- 方法运行之前,先去查询Cache(缓存组件),按照cacheNames(指定的缓存名称,可以在配置文件中指定)从CacheManager中获取相应的缓存组件。
- 第一次获取缓存,如果没有对应的Cache组件,会自动创建Cache组件(默认为ConcurrentMapCache),然后将其保存到ConcurrentMapCacheManager中的cacheMap中,key是cacheNames,value是ConcurrentMapCache。
- 根据指定的key,即@Cacheable注解中属性key对应的值(默认是方法传入的实际参数值),去Cache中查找缓存的内容。
- key是按照某种策略自自动生成的,默认是使用keyGenerator(SimpleKeyGenerator)生成的。
- 如果没有参数,key=new SimpleKey()。
- 如果有一个参数,key=参数值。
- 如果有多个参数,key就是new SimipleKey(params)。
- 没有查到缓存就调用目标方法。
- 将目标方法返回的结果,放入到缓存。