二叉树的层序遍历
层序遍历:逐层地,从左到右访问所有节点
广度优先
文章目录
- 二叉树的层序遍历
- 102. 二叉树的层序遍历 - 力扣(LeetCode)
- 107. 二叉树的层序遍历 II - 力扣(LeetCode)
- 199. 二叉树的右视图 - 力扣(LeetCode)
- 429. N 叉树的层序遍历 - 力扣(LeetCode)
- 515. 在每个树行中找最大值 - 力扣(LeetCode)
- 104. 二叉树的最大深度 - 力扣(LeetCode)
- 111. 二叉树的最小深度 - 力扣(LeetCode)
- 总结
- 扩展
102. 二叉树的层序遍历 - 力扣(LeetCode)

代码及思路分析
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number[][]}
*/
var levelOrder = function(root) {
// res存储结果 queue队列里面存储每层节点
let res = [], queue = []
queue.push(root)
if(root === null) return res
// 遍历当前层的所有节点
while(queue.length!== 0) {
// 记录当前层级节点数
let length = queue.length
// 存放每一层的节点
let curLeverl = []
for(let i = 0; i < length; i++) {
// 弹出队列的节点,也就是当层的节点 从左到右
let node = queue.shift
// 弹出一个,并且把他的子节点压入队列,为了下一次的遍历
curLeverl.push(node.val)
// 存放当前层下一层的节点
node.left && queue.push(node.left)
node.right && queue.push(node.right)
}
// 把每一层的结果放到结果数组
res.push(curLeverl)
}
};
107. 二叉树的层序遍历 II - 力扣(LeetCode)
自底向上的层序遍历
思路:把上面一题的结果res数组反转一下就可以了,我们这里把当层的结果curLevel插入数组头部即可(上一题是push压入尾部)
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=107 lang=javascript
*
* [107] 二叉树的层序遍历 II
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number[][]}
*/
var levelOrderBottom = function(root) {
let res = [], queue = []
// 第一排根先入队
queue.push(root)
if(root === null) return res
while(queue.length != 0) {
// 记录当层级节点数
let len = queue.length
// 存放每一层节点
let curLevel = []
for(let i = 0; i < len; i++) {
// 弹出队里首位并且把当前节点的val压入到存放节点的数组
let node = queue.shift()
curLevel.push(node.val)
// 当前层下一层的节点入队
node.left && queue.push(node.left)
node.right && queue.push(node.right)
}
// 从数组前头插入值,避免最后反转数组,减少运算时间
res.unshift(curLevel);
}
return res
};
// @lc code=end
199. 二叉树的右视图 - 力扣(LeetCode)
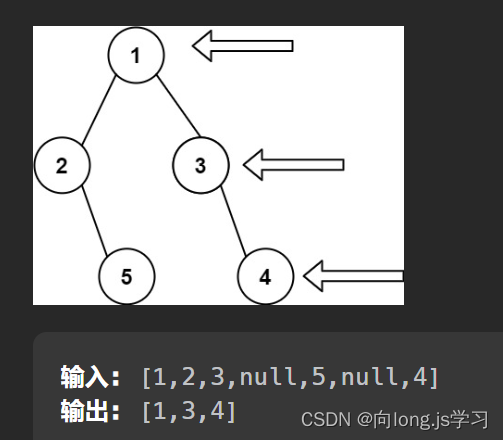
层序遍历的时候,判断是否遍历到单层的最后面的元素,如果是,就放进result数组中,随后返回result就可以了。
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=199 lang=javascript
*
* [199] 二叉树的右视图
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number[]}
*/
var rightSideView = function(root) {
//二叉树右视图 只需要把每一层最后一个节点存储到res数组
let res = [], queue = [];
queue.push(root);
while(queue.length && root!==null) {
// 记录当前层级节点个数
let length = queue.length;
while(length--) {
let node = queue.shift();
// length长度为0的时候表明到了层级最后一个节点
if(!length) {
res.push(node.val);
}
node.left && queue.push(node.left);
node.right && queue.push(node.right);
}
}
return res;
};
// @lc code=end
429. N 叉树的层序遍历 - 力扣(LeetCode)
思路:
这道题依旧是模板题,只不过一个节点有多个孩子了
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=429 lang=javascript
*
* [429] N 叉树的层序遍历
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* // Definition for a Node.
* function Node(val,children) {
* this.val = val;
* this.children = children;
* };
*/
/**
* @param {Node|null} root
* @return {number[][]}
*/
var levelOrder = function(root) {
//每一层可能有2个以上,所以不再使用node.left node.right
let res = [], queue = [];
queue.push(root);
while(queue.length && root!==null) {
//记录每一层节点个数还是和二叉树一致
let length = queue.length;
//存放每层节点 也和二叉树一致
let curLevel = [];
while(length--) {
let node = queue.shift();
curLevel.push(node.val);
//这里不再是 ndoe.left node.right 而是循坏node.children
for(let item of node.children){
item && queue.push(item);
}
}
res.push(curLevel);
}
return res;
};
// @lc code=end
515. 在每个树行中找最大值 - 力扣(LeetCode)
思路:
层序遍历,取每一层的最大值
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=515 lang=javascript
*
* [515] 在每个树行中找最大值
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number[]}
*/
var largestValues = function(root) {
//使用层序遍历
let res = [], queue = [];
queue.push(root);
while(root !== null && queue.length) {
//设置max初始值就是队列的第一个元素
let max = queue[0].val;
let length = queue.length;
while(length--) {
let node = queue.shift();
max = max > node.val ? max : node.val;
node.left && queue.push(node.left);
node.right && queue.push(node.right);
}
//把每一层的最大值放到res数组
res.push(max);
}
return res;
};
// @lc code=end
104. 二叉树的最大深度 - 力扣(LeetCode)
思路:
使用迭代法的话,使用层序遍历是最为合适的,因为最大的深度就是二叉树的层数,和层序遍历的方式极其吻合。
在二叉树中,一层一层的来遍历二叉树,记录一下遍历的层数就是二叉树的深度,如图所示:
![[图片]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/626df1143e7e4c2887bfd547dfc7464c.png)
所以这道题的迭代法就是一道模板题,可以使用二叉树层序遍历的模板来解决的。
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=104 lang=javascript
*
* [104] 二叉树的最大深度
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number}
*/
var maxDepth = function(root) {
// 最大的深度就是二叉树的层数
if (root === null) return 0;
let queue = [root];
let height = 0;
while (queue.length) {
let n = queue.length;
height++;
for (let i=0; i<n; i++) {
let node = queue.shift();
node.left && queue.push(node.left);
node.right && queue.push(node.right);
}
}
return height;
};
// @lc code=end
111. 二叉树的最小深度 - 力扣(LeetCode)
相对于 104.二叉树的最大深度 ,本题还也可以使用层序遍历的方式来解决,思路是一样的。
需要注意的是,只有当左右孩子都为空的时候,才说明遍历的最低点了。如果其中一个孩子为空则不是最低点
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=111 lang=javascript
*
* [111] 二叉树的最小深度
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number}
*/
var minDepth = function(root) {
if (root === null) return 0;
let queue = [root];
let depth = 0;
while (queue.length) {
let n = queue.length;
depth++;
for (let i=0; i<n; i++) {
let node = queue.shift();
// 如果左右节点都是null(在遇见的第一个leaf节点上),则该节点深度最小
if (node.left === null && node.right === null) {
return depth;
}
node.left && queue.push(node.left);;
node.right && queue.push(node.right);
}
}
return depth;
};
// @lc code=end
总结
二叉树的层序遍历,就是图论中的广度优先搜索在二叉树中的应用,需要借助队列来实现(此时又发现队列的一个应用了)。
扩展
在二叉树中,广度优先搜索的应用主要包括以下几个方面:
- 层次遍历:广度优先搜索可以实现对二叉树的层次遍历。从二叉树的根节点开始,先将根节点放入队列中,然后对队列中的节点进行出队操作,依次输出节点的值,并将其左右子节点放入队列中,直到队列为空。
- 查找最短路径:在二叉树中,广度优先搜索可以用于查找根节点到某个节点的最短路径。首先将根节点放入队列中,然后对队列中的节点进行出队操作,依次遍历节点的左右子节点,如果找到目标节点,则直接返回路径长度;否则,将子节点加入队列中,继续遍历,直到队列为空。
- 找到某一层节点:可以使用广度优先搜索来找到二叉树中的某一层节点。首先将根节点放入队列中,然后对队列中的节点进行出队操作,记录当前节点所在的层数,如果层数等于目标层,则将节点加入结果列表中;否则,将子节点加入队列中,继续遍历,直到队列为空。
- 判断是否为完全二叉树:广度优先搜索还可以用于判断二叉树是否为完全二叉树。首先将根节点放入队列中,然后对队列中的节点进行出队操作,依次遍历节点的左右子节点,如果当前节点只有右子节点没有左子节点,或者当前节点已经出现了只有左子节点没有右子节点的节点,则说明这不是一颗完全二叉树,直接返回false;否则,将子节点加入队列中,继续遍历,直到队列为空。如果成功遍历完所有节点,则说明这是一颗完全二叉树,返回true。
广度搜索